Abstract
1. The contribution of the sodium pump to the membrane potential of mouse pancreatic B-cells was studied with micro-electrodes.
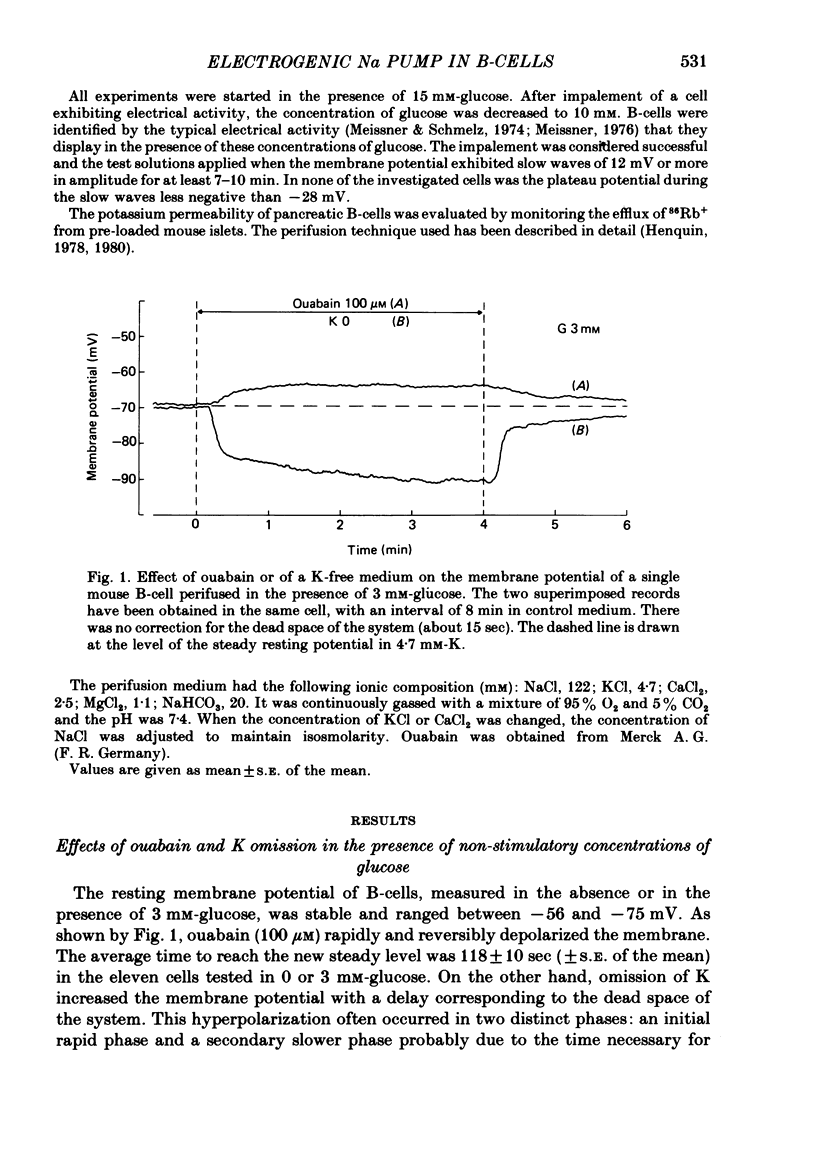
2. In 0 or 3 mM-glucose, ouabain rapidly (within 2 min) depolarized the B-cell membrane by an average of 7 mV, whereas K omission hyperpolarized it markedly.
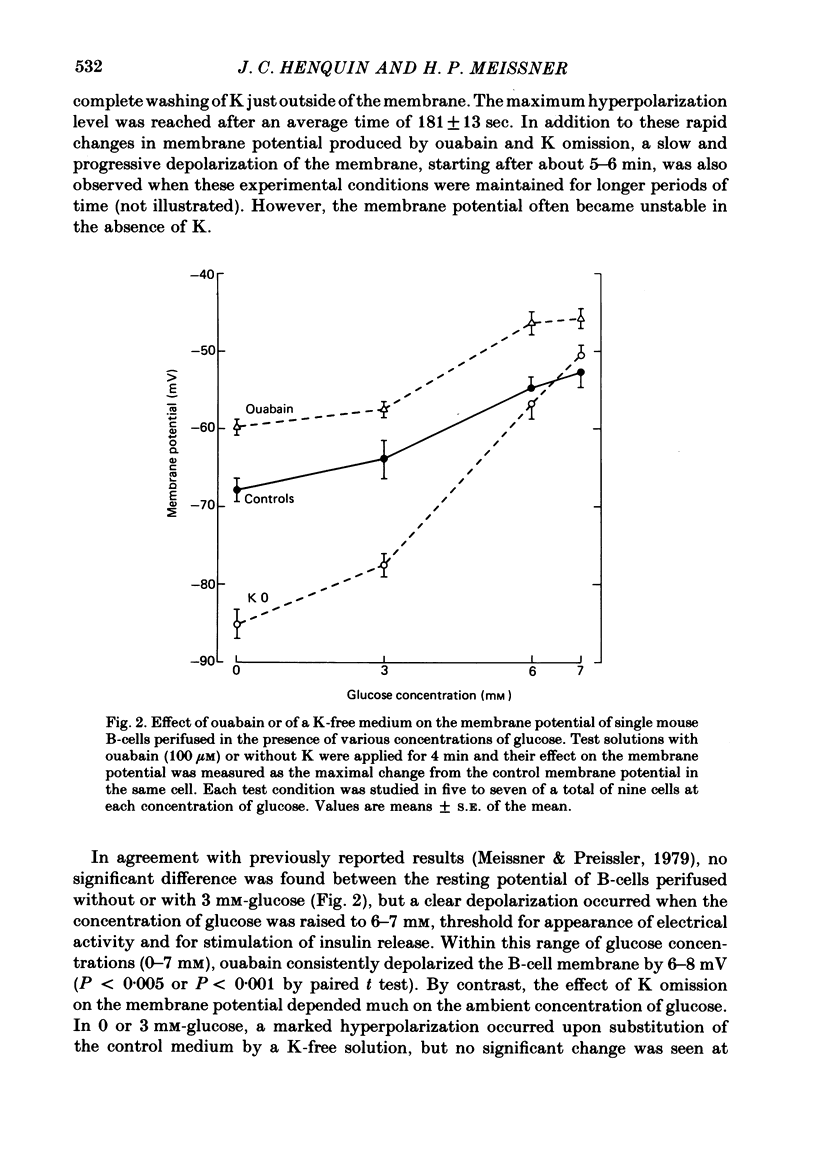
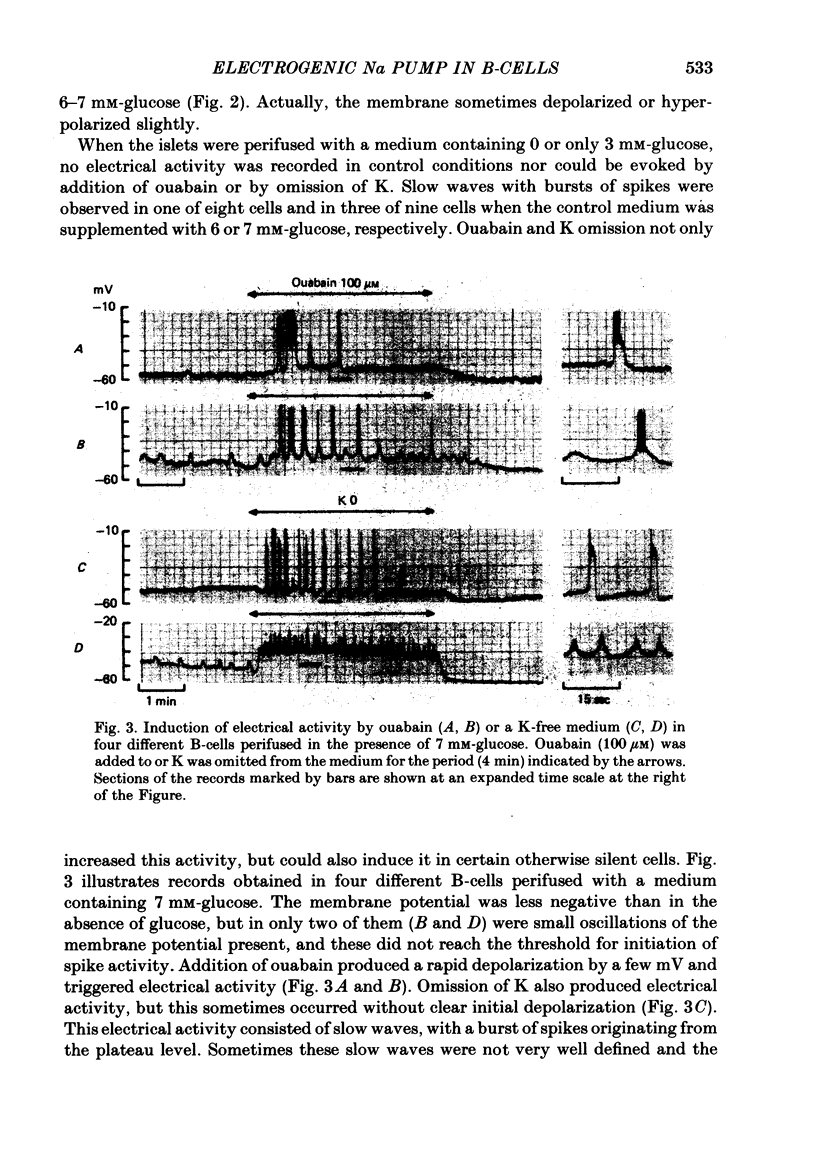
3. In 6 or 7 mM-glucose, ouabain still produced depolarization, but K omission had no consistent effect. Both induced electrical activity in certain cells.
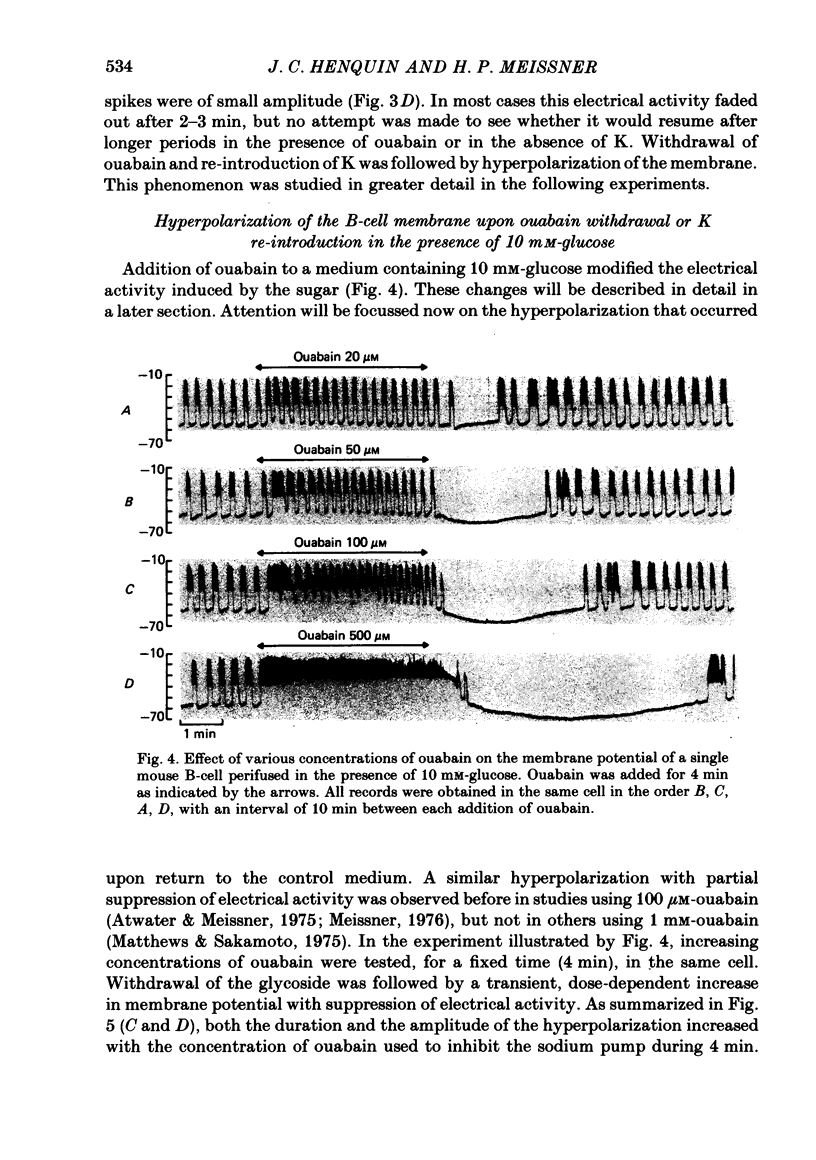
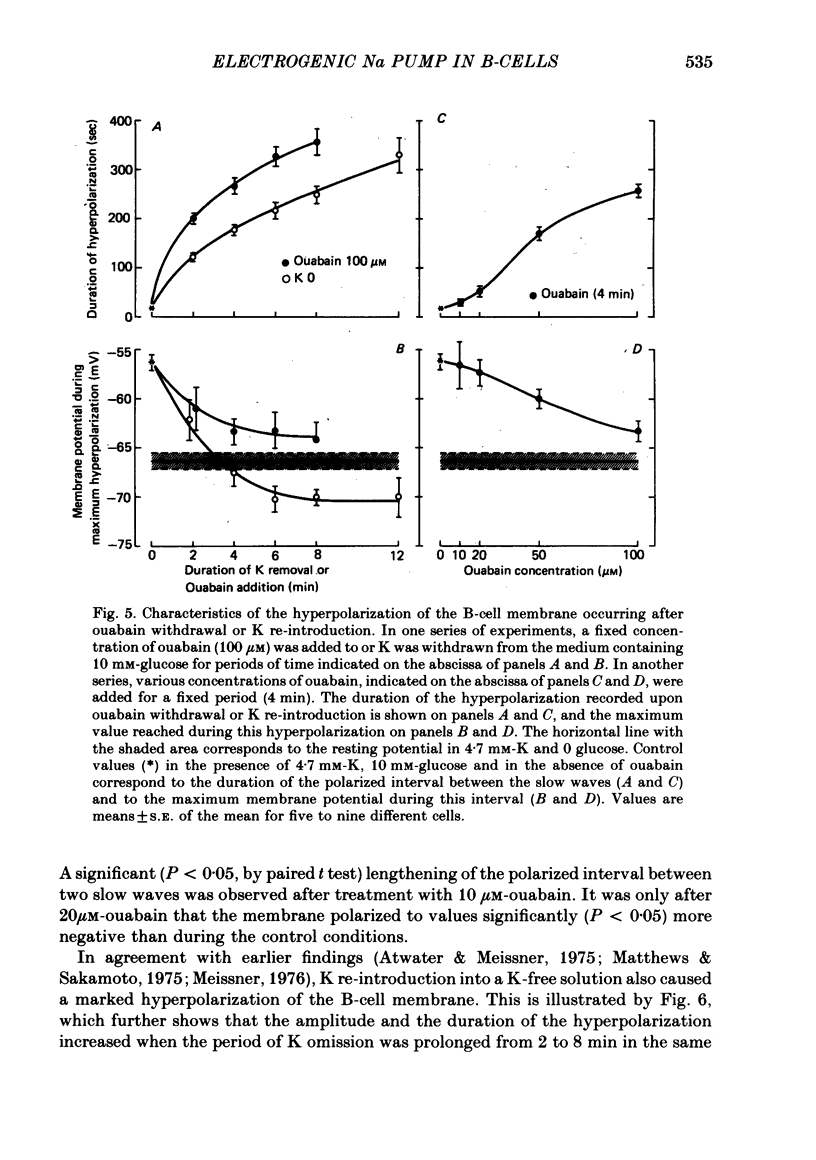
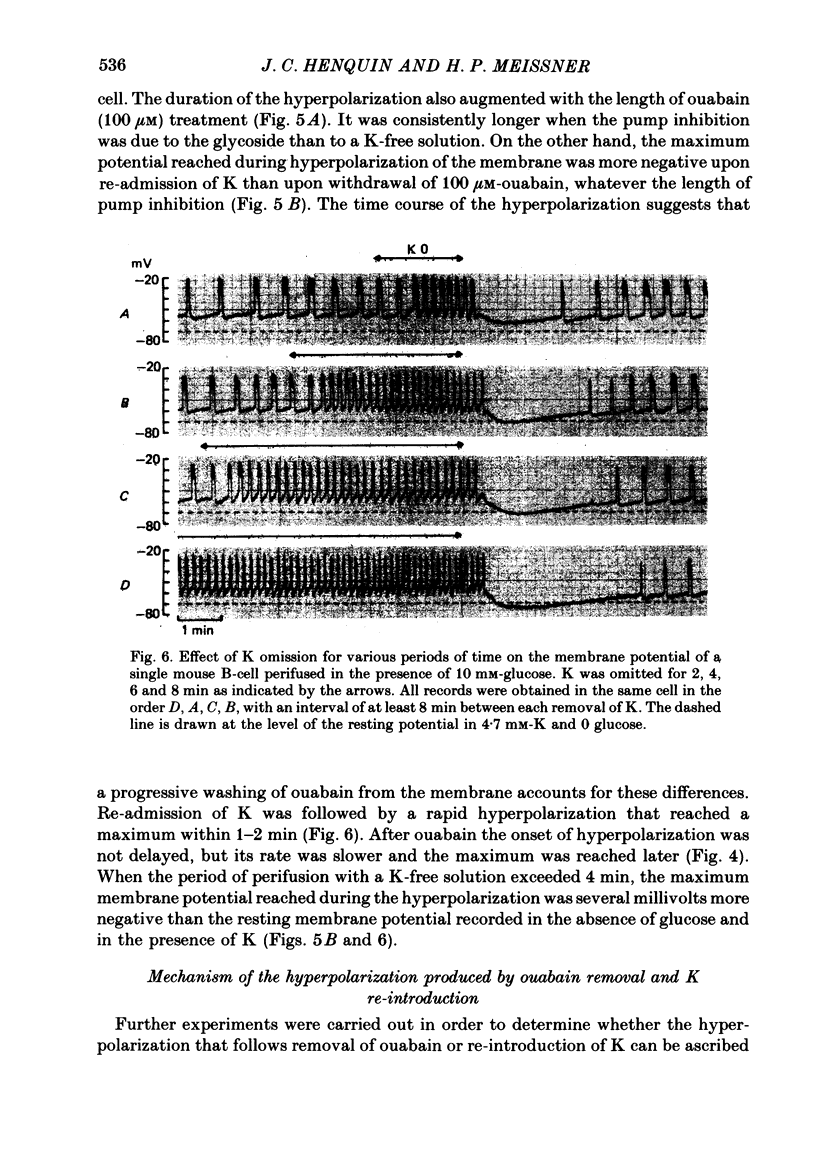
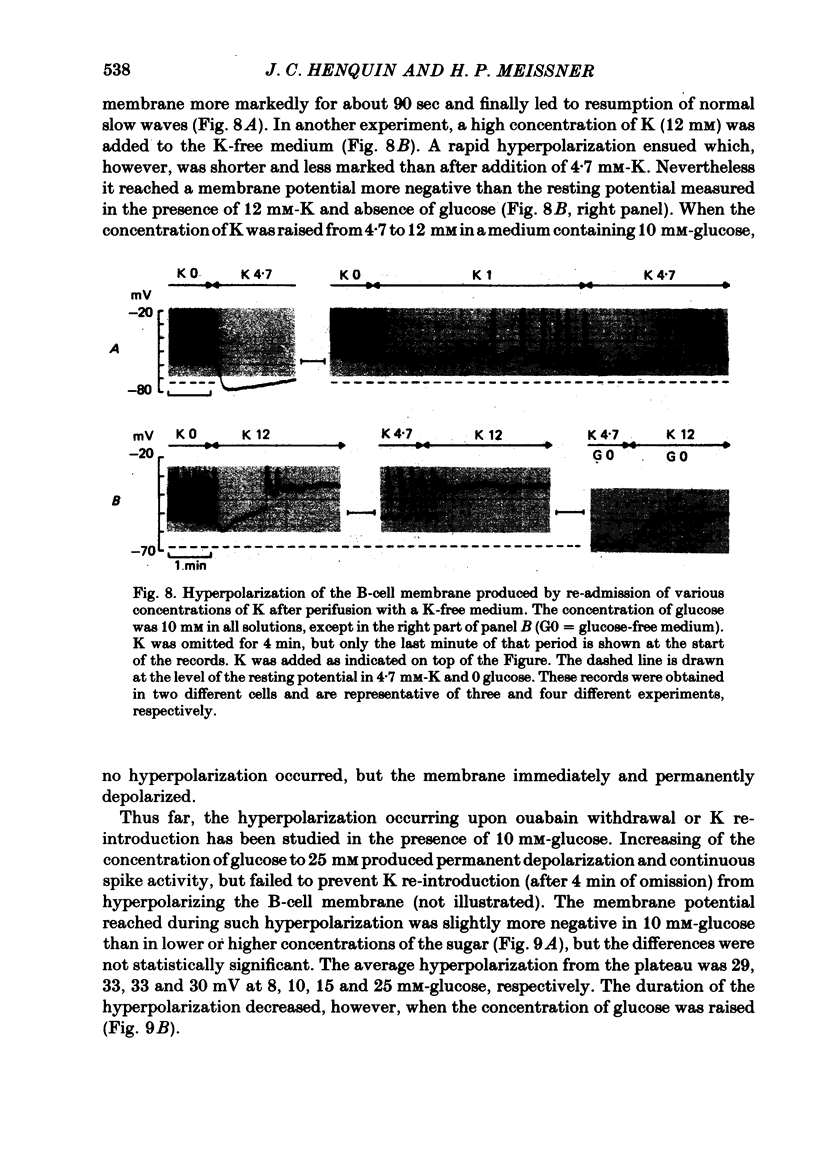
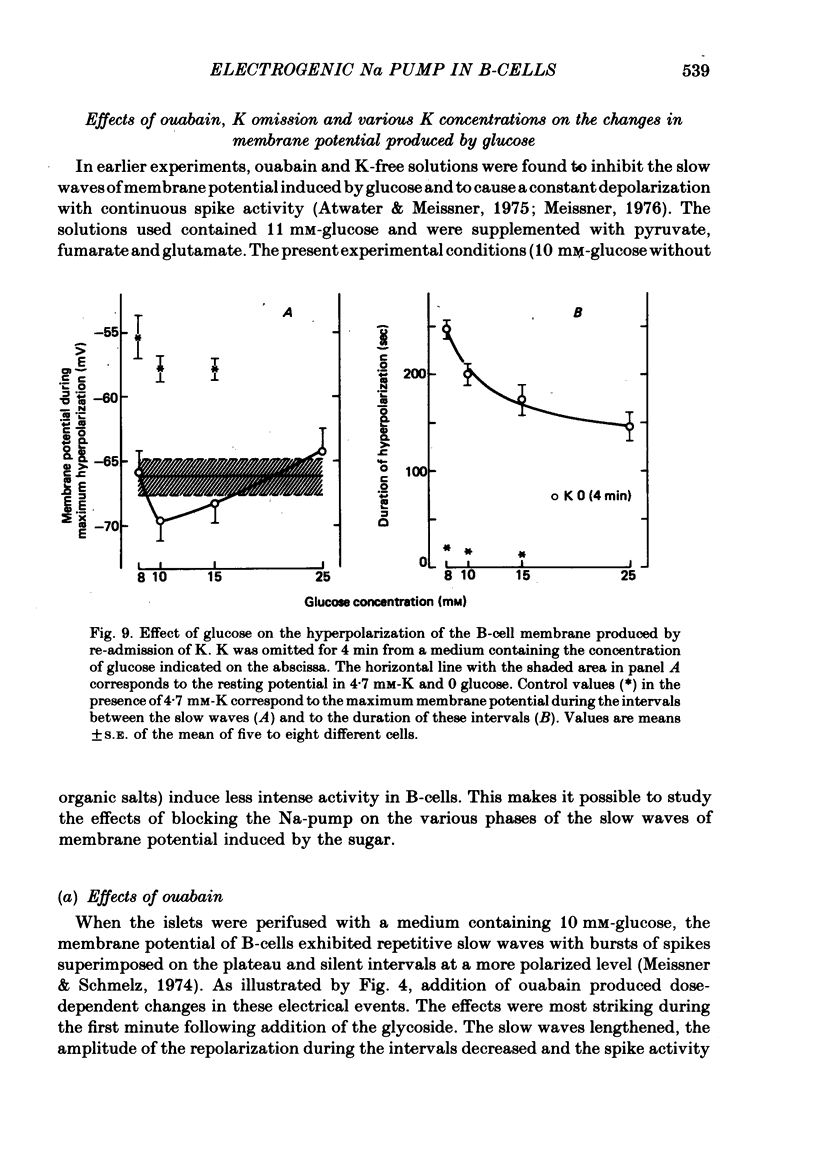
4. In 10 mM-glucose, withdrawal of ouabain or K re-introduction caused a transient hyperpolarization with suppression of electrical activity. Duration and amplitude of the hyperpolarization increased with the time of pump blockade and with the concentration of ouabain.
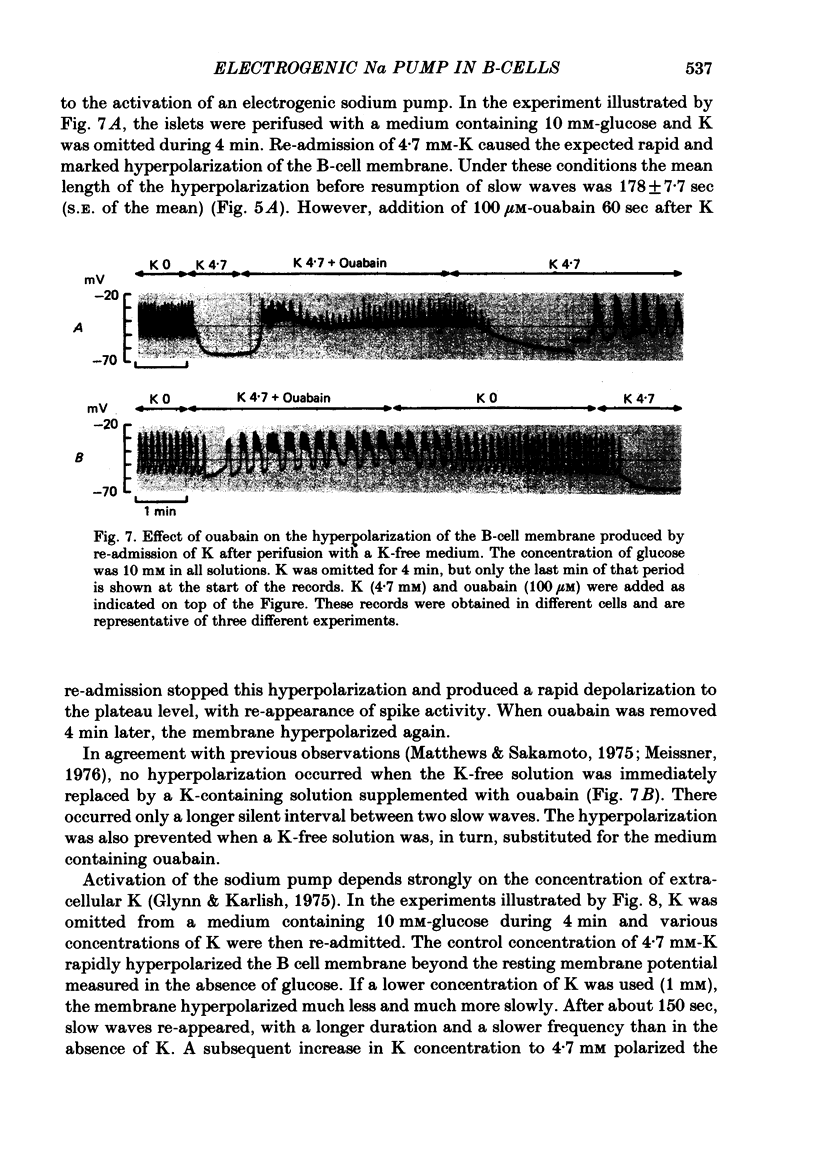
5. The hyperpolarization following K re-admission was abolished by ouabain and that following ouabain withdrawal was prevented by K omission. Re-admission of various K concentrations showed that the hyperpolarization was not due to depletion of K just outside of the membrane.
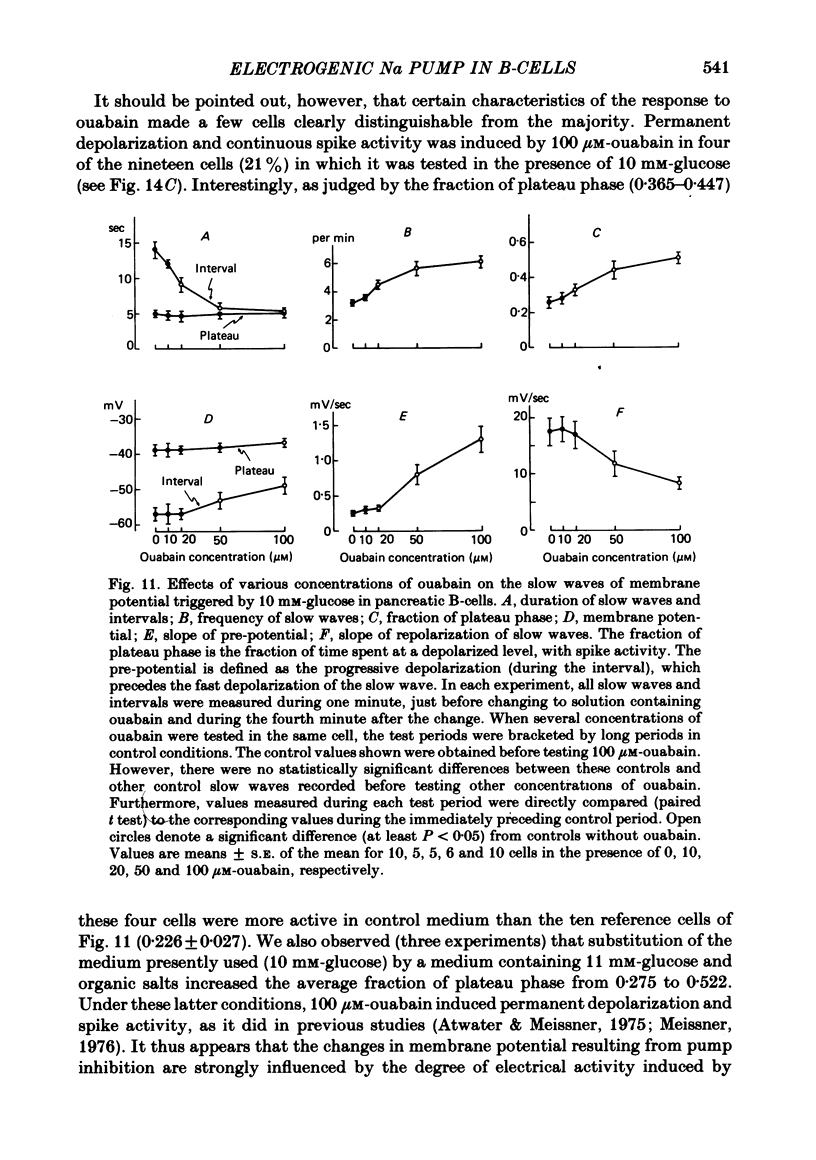
6. In 10 mM-glucose, the membrane potential of B-cells exhibited repetitive slow waves with bursts of spikes on the plateau. These electrical events were modified by ouabain in a dose-dependent manner. The frequency of the slow waves augmented markedly because of an increase in the slope of the pre-potential and a shortening of the intervals; the slope of their repolarization phase decreased, but their duration was not changed.
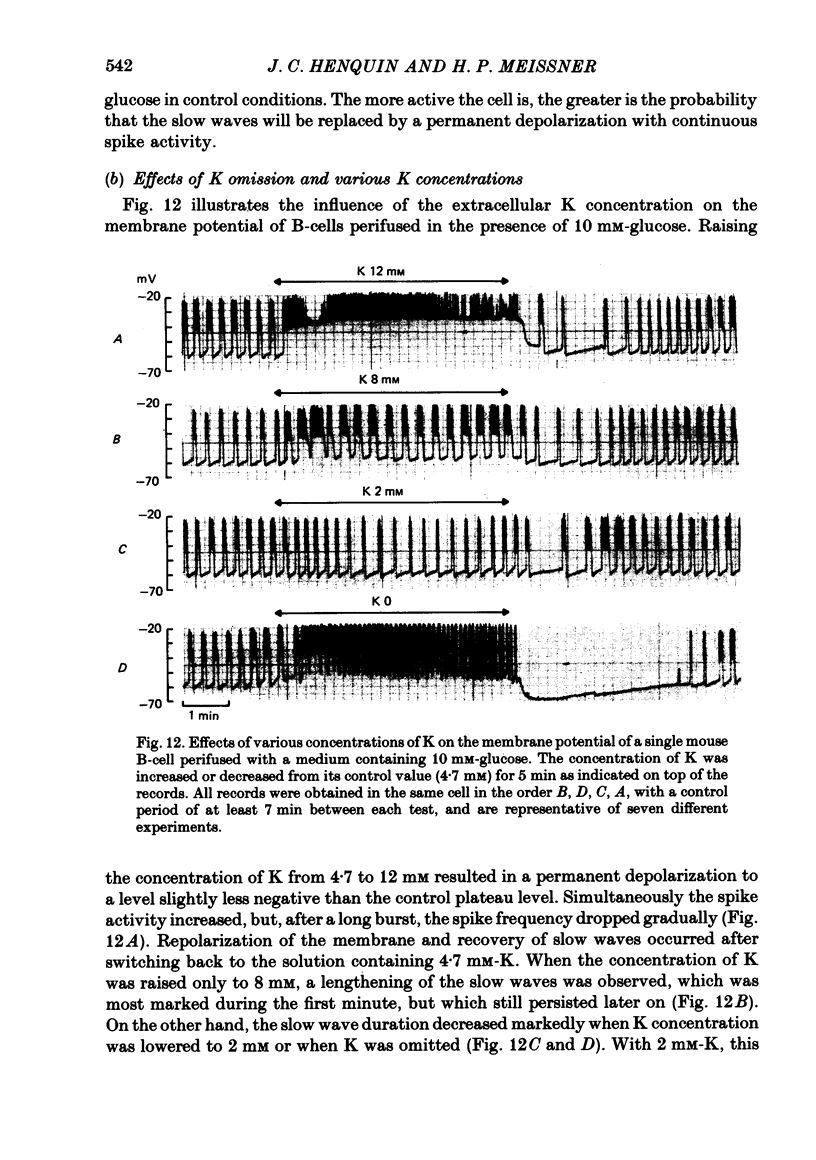
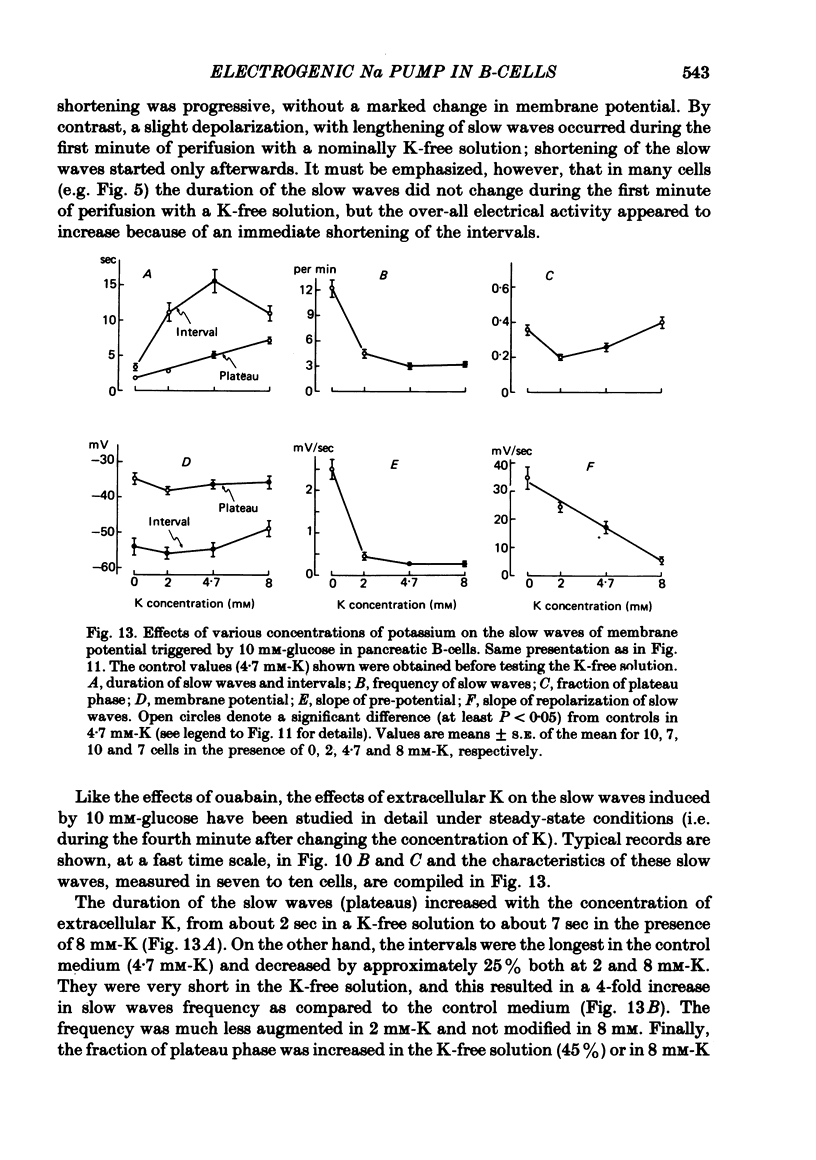
7. Omission of K increased the slope of the pre-potential and the frequency of the slow waves. It also accelerated their repolarization phase and reduced their duration, likely because of the increase in driving force for K efflux. Increasing K concentration to 8 mM slowed the repolarization phase and lengthened the slow waves without changing their frequency.
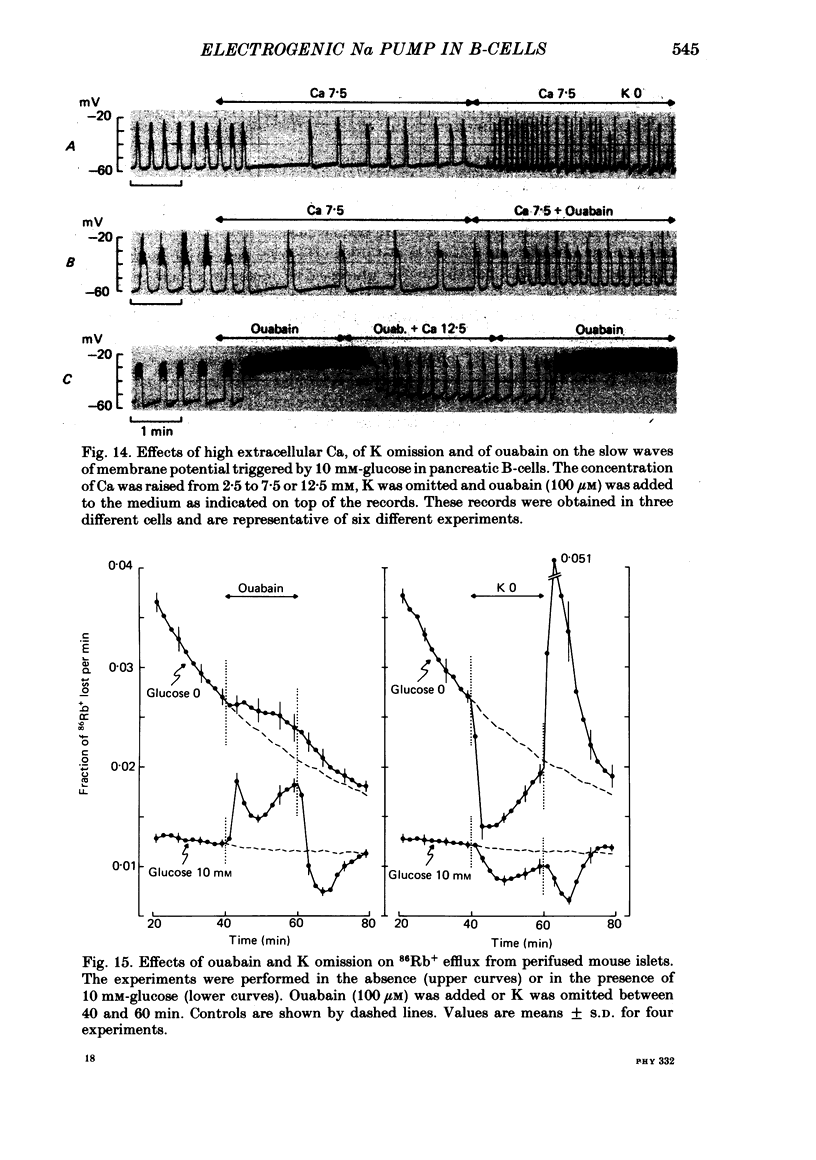
8. Even when K permeability of the B-cell membrane was increased by high extracellular Ca, ouabain and K omission augmented the frequency of the slow waves.
9. In 0 or 10 mM-glucose, ouabain increased 86Rb+ efflux from perifused islets, whereas K omission decreased it. In 10 mM-glucose, a marked decrease in 86Rb+ efflux accompanied ouabain withdrawal and K re-introduction. The hyperpolarization is thus not due to an increase in K permeability.
10. It is concluded that, in pancreatic B-cells, the sodium pump is truly electrogenic, contributes to the resting potential and modulates the slow waves of membrane potential induced by glucose. Rapid changes in insulin release occurring upon inhibition or activation of the sodium pump may thus be due to the changes in B-cell membrane potential.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Potassium permeability activated by intracellular calcium ion concentration in the pancreatic beta-cell. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:575–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Meissner H. P. Electrogenic sodium pump in beta-cells of islets of Langerhans. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):56P–58P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Cyclic changes in potential and resistance of the beta-cell membrane induced by glucose in islets of Langerhans from mouse. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:117–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J. Effects of membrane potential on sodium and potassium fluxes in squid axons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):406–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Porte D., Jr, Crill W. E. Voltage dependence of rhythmic plateau potentials of pancreatic islet cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):E290–E296. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.3.E290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formby B., Capito K., Hedeskov C. J. (Na+, K+)-activated ATPase in microsomes from mouse pancreatic islets. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Jan;96(1):143–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Cranefield P. F. Electrogenic sodium extrusion in cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Jun;73(6):819–837. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.6.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Niedergerke R., Ogden D. C. The dual nature of the membrane potential increase associated with the activity of the sodium/potassium exchange pump in skeletal muscle fibres. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Sep 19;198(1133):463–472. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagerman E., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effects of acetylcholine on ion fluxes and chlorotetracycline fluorescence in pancreatic islets. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:505–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The stoicheiometry of the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):217–235. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glitsch H. G. Characteristics of active Na transport in intact cardiac cells. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):H189–H199. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.2.H189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. The sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1975;37:13–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.37.030175.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Milner R. D. The role of sodium and potassium in insulin secretion from rabbit pancreas. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):725–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):271–273. doi: 10.1038/271271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Lambert A. E. Cationic environment and dynamics of insulin secretion. III. Effect of the absence of potassium. Diabetologia. 1974 Dec;10(6):789–794. doi: 10.1007/BF01219542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. Effects of amino acids on membrane potential and 86Rb+ fluxes in pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):E245–E252. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.3.E245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P., Preissler M. 9-Aminoacridine- and tetraethylammonium-induced reduction of the potassium permeability in pancreatic B-cells. Effects on insulin release and electrical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 1;587(4):579–592. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Metabolic control of potassium permeability in pancreatic islet cells. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):541–550. doi: 10.1042/bj1860541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Opposite effects of intracellular Ca2+ and glucose on K+ permeability of pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):66–68. doi: 10.1038/280066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Taylor K. W. Potassium ions and the secretion of insulin by islets of Langerhans incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(1):17–24. doi: 10.1042/bj1080017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawazu S., Boschero A. C., Delcroix C., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXVIII. Effect of glucose on Na+ fluxes in isolated islets. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Jul 18;375(2):197–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00584244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Nathans A., Steiner D. F. Preparation and characterization of plasma membrane-enriched fractions from rat pancreatic islets. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):606–623. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin S. R., Kasson B. G., Driessen J. F. Adenosine triphosphatases of rat pancreatic islets: comparison with those of rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):692–701. doi: 10.1172/JCI109177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J., NODA K. THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM-FREE SOLUTIONS ON THE MEMBRANE POTENTIAL OF FROG MUSCLE FIBERS. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Sep;47:117–132. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Boschero A. C., Kawazu S., Hutton J. C. The stimulus secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXVII. Effect of glucose on K+ fluxes in isolated islets. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Mar 20;373(3):237–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00580830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattews E. K., Sakamoto Y. Pancreatic islet cells: electrogenic and electrodiffusional control of membrane potential. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):439–457. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P. Electrical characteristics of the beta-cells in pancreatic islets. J Physiol (Paris) 1976 Nov;72(6):757–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Henquin J. C., Preissler M. Potassium dependence of the membrane potential of pancreatic B-cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 1;94(1):87–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80912-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Preissler M. Glucose-induced changes of the membrane potential of pancreatic B-cells: their significance for the regulation of insulin release. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;119:97–107. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9110-8_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Preissler M. Ionic mechanisms of the glucose-induced membrane potential changes in B-cells. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:91–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Schmelz H. Membrane potential of beta-cells in pancreatic islets. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(3):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00586918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Cyclic variation of K+ conductance in pancreatic beta-cells: Ca2+ and voltage dependence. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):C137–C146. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.237.3.C137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Transport of rubidium and sodium in pancreatic islets. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):505–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers G., Devis G., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XL. Effect of K+ deprivation upon insulin release by the perfused rat pancreas. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Jun;385(3):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00647460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarvin J. T., Pace C. S. Glucose-induced electrical activity in the pancreatic beta-cell: effect of veratridine. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):C127–C134. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.240.3.C127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Electrogenic sodium pump in nerve and muscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):563–594. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]