Abstract
1. Properties of the Ca-activated K channel were studied in excised patches of surface membrane from cultured rat muscle cells using single channel recording techniques.
2. Increasing the concentration of calcium at the intracellular membrane surface [Ca]i, increased both the frequency and effective duration of channel openings. Ca at the extracellular membrane surface was not sufficient to activate the channels.
3. An approximate third power relationship (slope = 2·7) was observed between [Ca]i and the percentage of time the channels spent in the open state.
4. Both the frequency and effective duration of channel openings increased as the intracellular membrane surface was made more positive; the percentage of time spent in the open state increased e-fold for a 15 mV depolarization for low levels of activity.
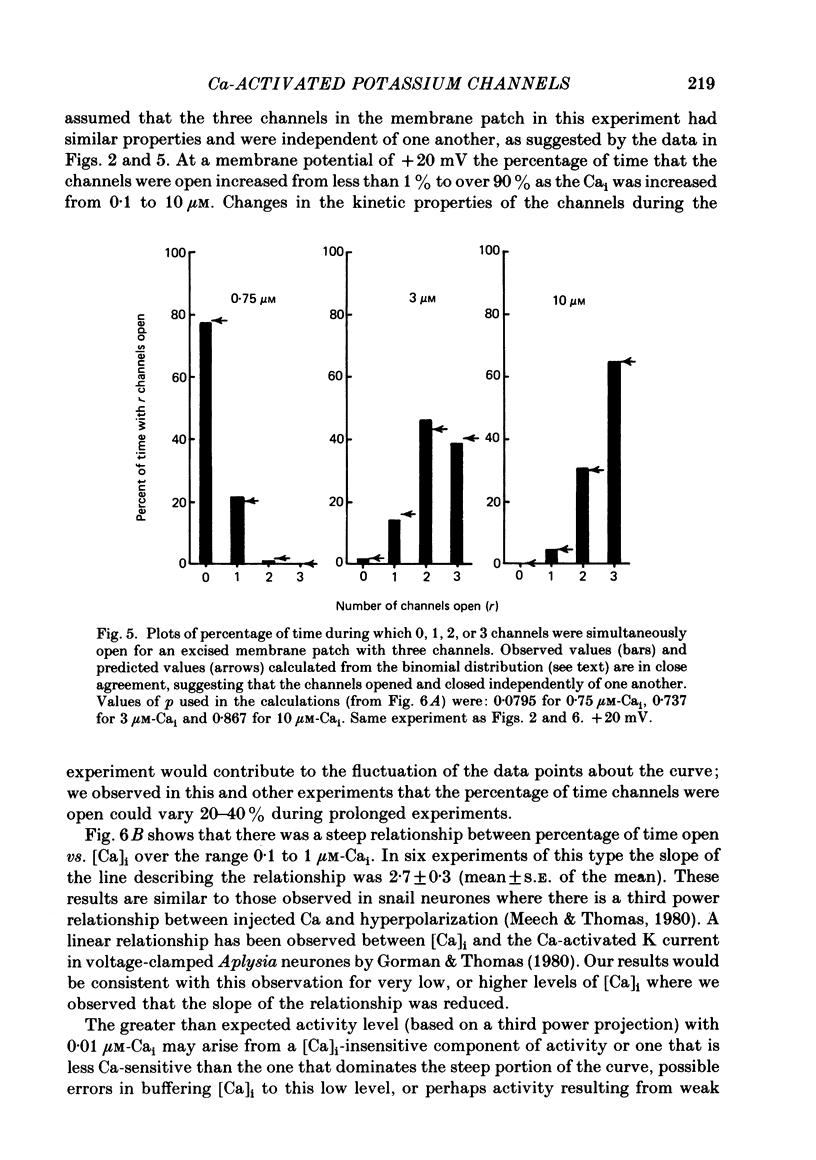
5. The percentage of time spent with 1, 2,...n channels open in membrane patches with n channels was described by the binomial distribution, suggesting that the channels opened and shut independently of one another.
6. Single channel conductance (144 mM-K on both sides of the membrane) was essentially independent of membrane potential (-50 to +50 mV) and [Ca]i (0·1 μM -1 mM), but did increase with temperature, from 100 pS at 1 °C to 300 pS at 37 °C.
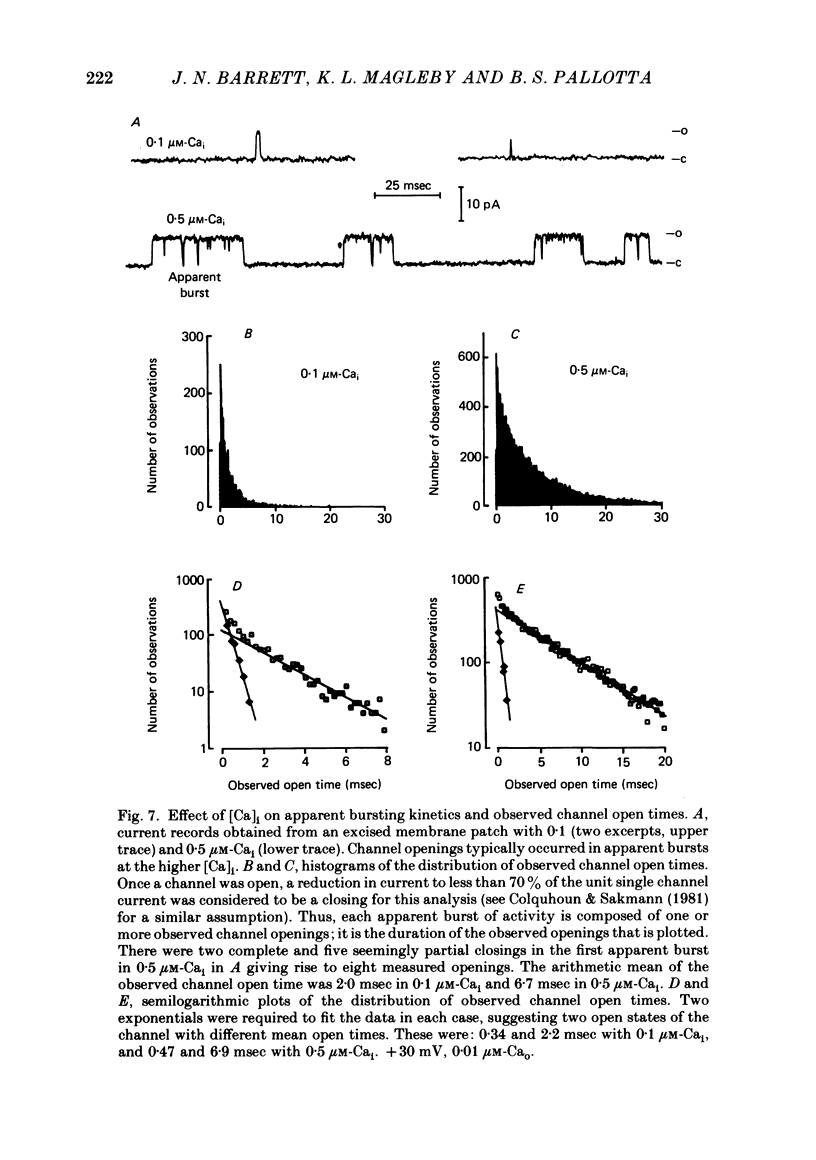
7. Channel activity occurred in apparent bursts, with the duration of the apparent bursts increasing with increasing [Ca]i.
8. Two exponentials were required to describe the distribution of observed channel open times, suggesting two different open channel states of apparently normal conductance. The observed mean channel open time of these states at +30 mV was 0·34 and 2·2 msec with 0·1 μM-Cai and was 0·47 and 6·9 msec with 0·5 μM-Cai.
9. The channel occasionally entered an apparent third open channel state with a single channel current amplitude about 40% the amplitude of the normally observed single channel currents. The reduced conductance state was immediately preceded and followed by a normal conducting state.
10. While the kinetics of the Ca-activated K channel appear complex, its large conductance and high Ca and voltage sensitivity suggest that it is uniquely suited to resist depolarizations of the cell membrane potential that are accompanied by increases in intracellular Ca.
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barret J. N. Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents, and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):737–774. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Barrett E. F., Dribin L. B. Calcium-dependent slow potassium conductance in rat skeletal myotubes. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90450-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):205–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fluctuations in the microsecond time range of the current through single acetylcholine receptor ion channels. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):464–466. doi: 10.1038/294464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., Neher E. Single channel recordings of K+ currents in squid axons. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):140–143. doi: 10.1038/285140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Stevens C. F. Voltage dependence of agonist effectiveness at the frog neuromuscular junction: resolution of a paradox. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):245–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Müller K. D., Peper K., Sterz R. The M. omohyoideus of the mouse as a convenient mammalian muscle preparation. A study of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by noise analysis and cooperativity. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Dec 28;367(2):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00585146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. Potassium activation associated with intraneuronal free calcium. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):437–439. doi: 10.1126/science.644308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Lass Y. A transition temperature for acetylcholine channel conductance in chick myoballs. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:527–536. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Potassium conductance and internal calcium accumulation in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:287–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gration K. A., Lambert J. J., Ramsey R., Usherwood P. N. Non-random openings and concentration-dependent lifetimes of glutamate-gated channels in muscle membrane. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):423–425. doi: 10.1038/291423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Multiple conductance states of single acetylcholine receptor channels in embryonic muscle cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):462–464. doi: 10.1038/294462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):349–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Properties of a facilitating calcium current in pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):319–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Patlak J. Single channel currents from excised patches of muscle membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6930–6934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Doroshenko P. A., Tsyndrenko A. Y. Calcium-dependent potassium conductance studied on internally dialysed nerve cells. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2187–2192. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca P. P., Miller C. A K+-selective, three-state channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum of frog leg muscle. J Membr Biol. 1981;61(1):31–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01870750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Neher E., Marty A. Single channel activity associated with the calcium dependent outward current in Helix pomatia. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Mar;389(3):293–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00584792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Thomas R. C. Effect of measured calcium chloride injections on the membrane potential and internal pH of snail neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:111–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. The calcium current and the activation of a slow potassium conductance in voltage-clamped mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:307–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B., Steinbach J. H. The extracellular patch clamp: a method for resolving currents through individual open channels in biological membranes. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Jul 18;375(2):219–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00584247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. J., Sachs F. Single ionic channels observed in tissue-cultured muscle. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):861–863. doi: 10.1038/282861a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. D. The determination of the stability constant for calcium-EGTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 18;451(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta B. S., Magleby K. L., Barrett J. N. Single channel recordings of Ca2+-activated K+ currents in rat muscle cell culture. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):471–474. doi: 10.1038/293471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Gration K. A., Usherwood P. N. Single glutamate-activated channels in locust muscle. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):643–645. doi: 10.1038/278643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Patlak J., Neher E. Single acetylcholine-activated channels show burst-kinetics in presence of desensitizing concentrations of agonist. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):71–73. doi: 10.1038/286071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


