Abstract
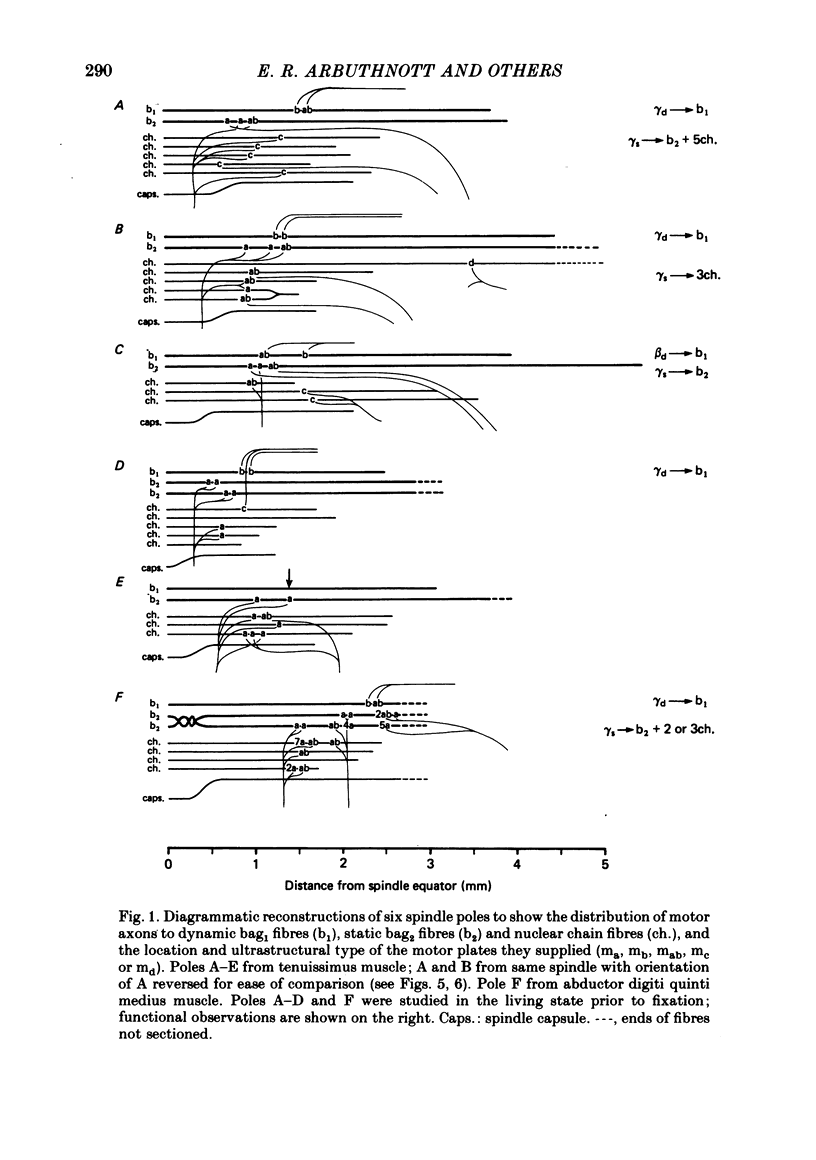
1. Six muscle spindle poles, five from experiments in which foci of sarcomere convergence had been observed during stimulation of fusimotor axons, were serially sectioned for light and electron microscopy. Every somatic motor terminal was studied in ultrathin sections at several levels.
2. In all six poles static γ axons, or presumed static γ axons, supplying the static bag2 fibre and/or chain fibres had no terminations on the dynamic bag1 fibre. In five poles, the dynamic bag1 fibre was selectively innervated by dynamic γ or β axons save in one case where a dynamic γ axon also innervated one chain fibre.
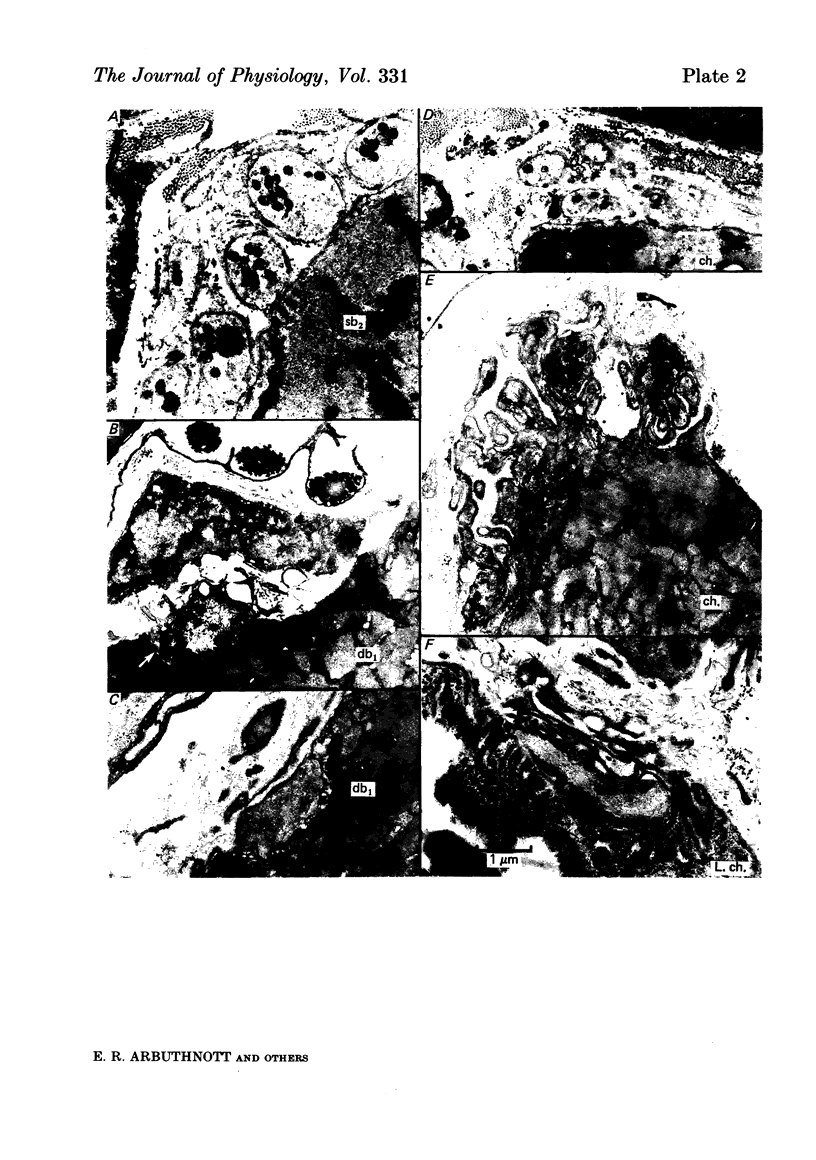
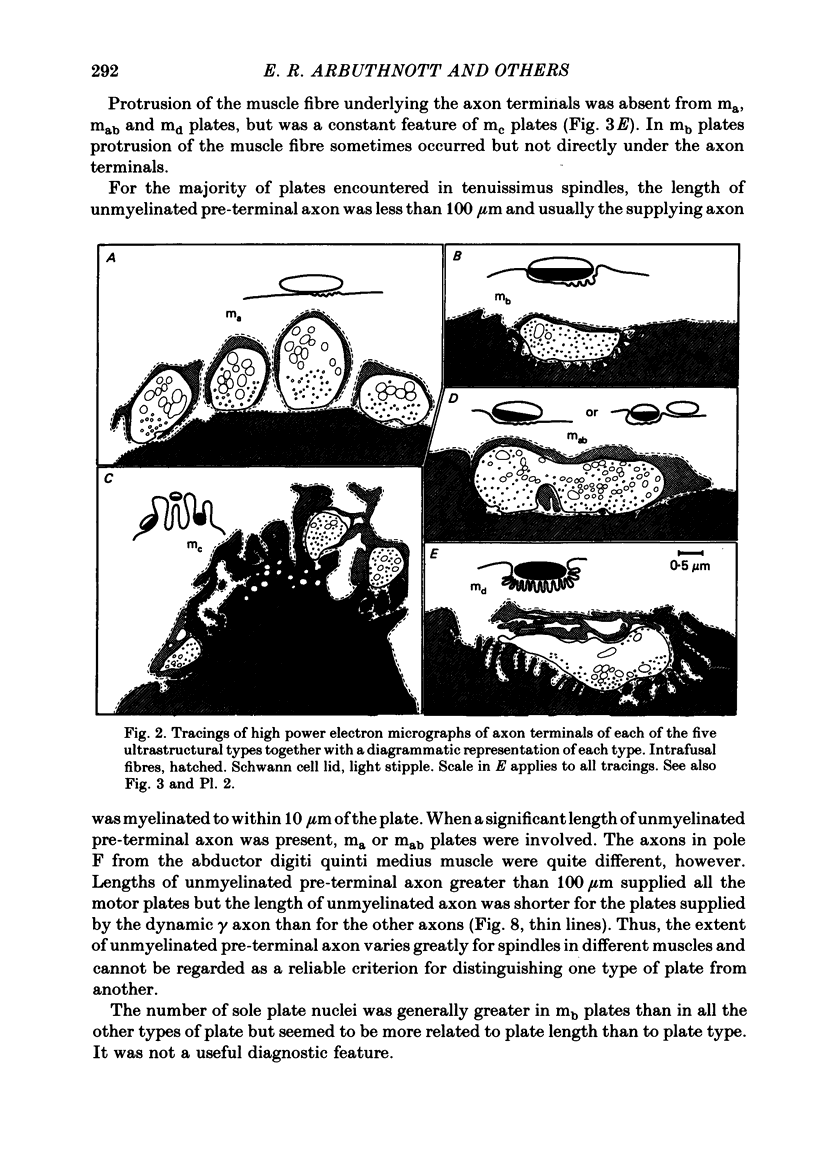
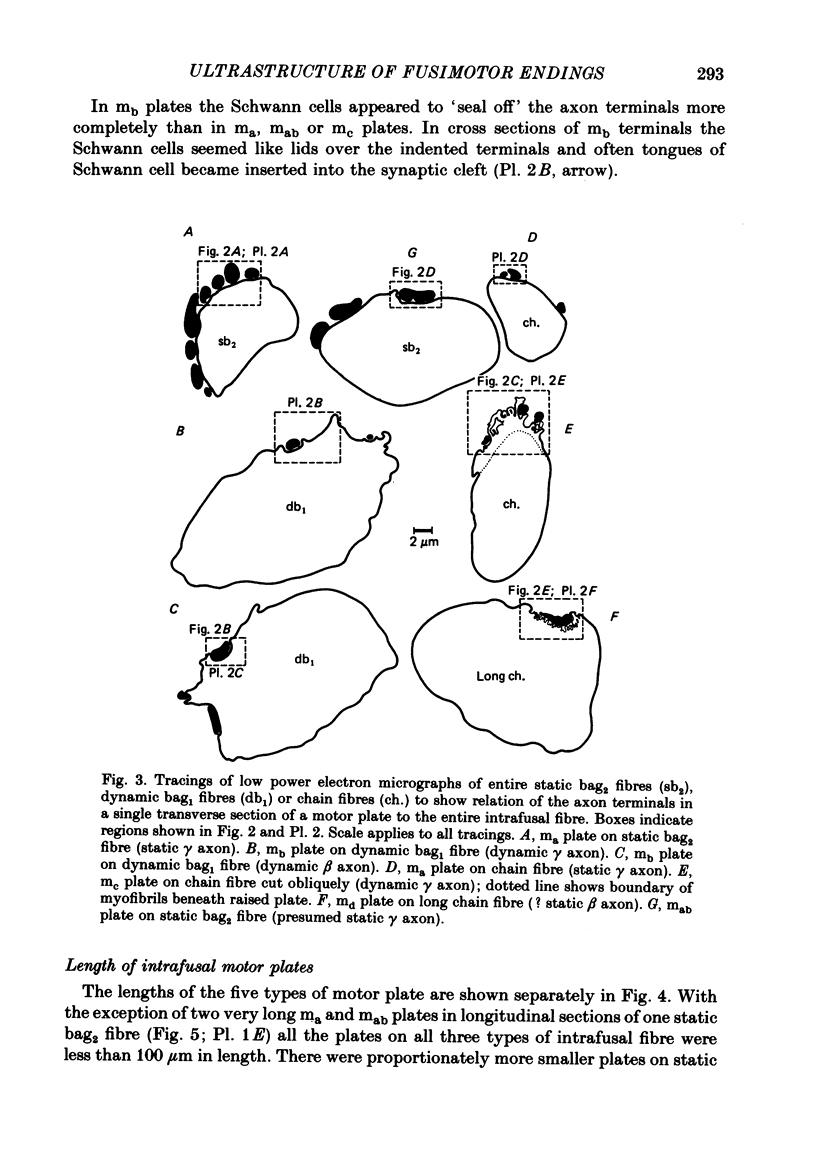
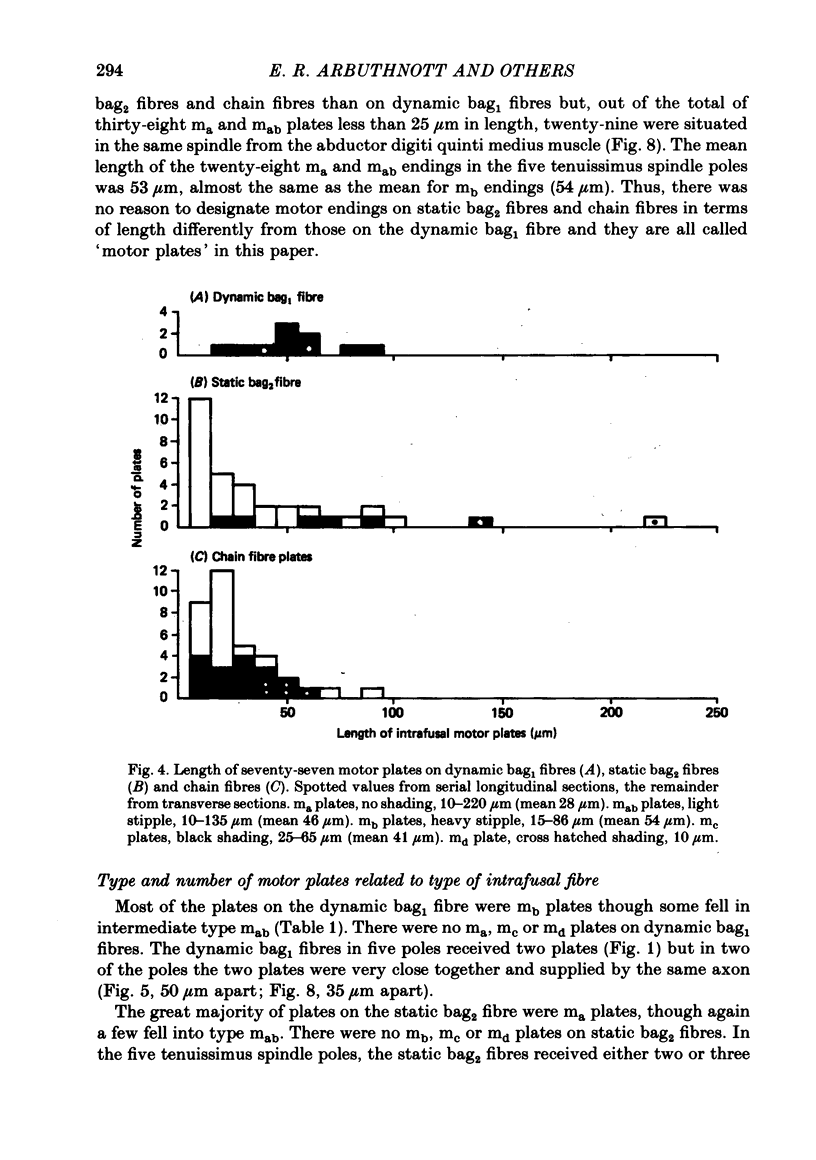
3. Seventy-seven motor endings were of four distinct ultrastructural types: `ma plates' lay superficially on the surface of static bag2 or chain fibres; `mb plates' were deeply indented into dynamic bag1 fibres; in `mc plates', found on chain fibres only, the muscle surface was thrown into projecting fingers between which the axon terminals were embedded; one type `md plate' was found, fully indented into a long chain fibre. A few plates of intermediate form (mab) were variants of ma and mb plates.
4. The muscle membrane beneath both ma and mb plates was smooth, or had a few wide, shallow folds; mc plates usually had wide, shallow subjunctional folds; numerous deep, narrow folds were characteristic of the md plate. The length of unmyelinated pre-terminal axon or the number of sole plate nuclei were not useful diagnostic features.
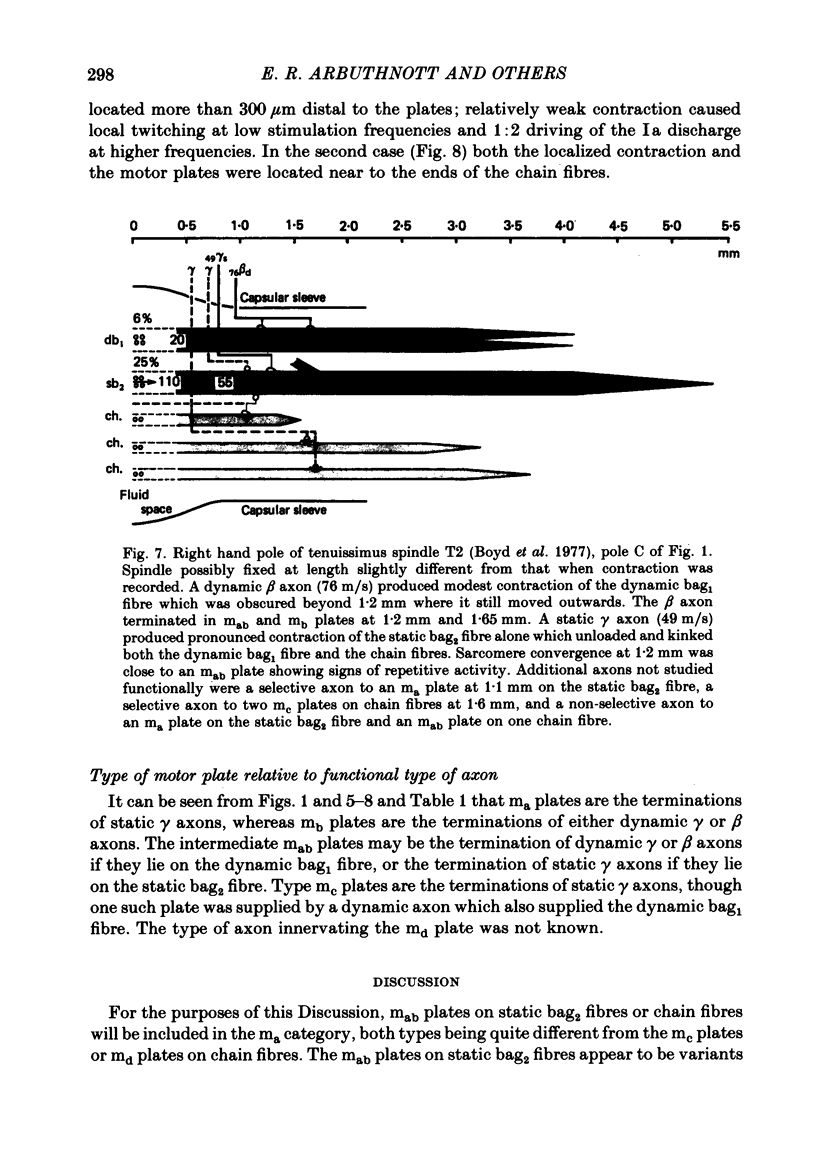
5. Obvious foci of sarcomere convergence in the capsular sleeve region of dynamic bag1 and static bag2 fibres coincided with the location of motor plates. Additional contraction foci were observed in the extracapsular region of dynamic bag1 fibres where there was no motor innervation; contraction occurs principally in the outer half of these fibres. No foci of contraction or motor plates were observed in the extracapsular region of static bag2 fibres; contraction in these fibres is typically mid-polar.
6. In some poles local contraction of chain fibres centred on the location of mc plates. In others, very localized contraction occurred distal to the sites of ma plates. Both ma and mc plates were never found on the same pole of a chain fibre.
7. Dynamic γ or β axons end in mb plates, probably equivalent to p2 plates. The concept of distinctly different p1 and p2 plates on dynamic bag1 fibres, supplied by dynamic β and γ axons, respectively, is not supported by ultrastructural evidence.
8. Some static γ axons end in multiple ma plates which correspond with `trail endings', or in single large ma plates, on static bag2 or chain fibres. The mc plates are the terminations of other static γ, or occasionally dynamic γ, axons on chain fibres. Static β axons probably end in md plates on long chain fibres which may correspond with p1 plates.
9. It is proposed that there are two types of static γ motoneurone, one terminating in ma plates and the other in mc plates, possibly directed preferentially towards static bag2 fibres and chain fibres, respectively.
Full text
PDF





















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott E. R., Boyd I. A., Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N. Real and apparent gamma axon contraction sites in intrafusal fibres [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):25P–26P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott E. R. Routine collection of flat large-area sections for electron microscopy as applied to a detailed study of axon dimensions. J Microsc. 1974 Jul;101(Pt 2):219–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1974.tb03888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott E., Boyd I. A., Gladden M. H. Ultrastructural observations of a muscle spindle in the region of a contraction site of a dynamic gamma axon. Prog Brain Res. 1976;44:61–65. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60723-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W. A histological study of the motor innervation of the cat's muscle spindle. J Anat. 1981 Dec;133(Pt 4):571–591. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W., Barker D., Bessou P., Pagès B., Stacey M. J. Histological analysis of cat muscle spindles following direct observation of the effects of stimulating dynamic and static motor axons. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:605–619. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Banks R. W., Harker D. W., Milburn A., Stacey M. J. Studies of the histochemistry, ultrastructure, motor innervation, and regeneration of mammalian intrafusal muscle fibres. Prog Brain Res. 1976;44:67–88. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60724-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Bessou P., Jankowska E., Pagès B., Stacey M. J. Identification of intrafusal muscle fibres activated by single fusimotor axons and injected with fluorescent dye in cat tenuissimus spindles. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:149–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y. Distribution of fusimotor axons to intrafusal muscle fibres in cat tenuissimus spindles as determined by the glycogen-depletion method. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):49–69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y. Types of intra- and extrafusal muscle fibre innervated by dynamic skeleto-fusimotor axons in cat peroneus brevis and tenuissimus muscles, as determined by the glycogen-depletion method. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):713–726. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Proske U., Stacey M. J. Morphological identification and intrafusal distribution of the endings of static fusimotor axons in the cat. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):405–427. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Stacey M. J. Identifications of the intrafusal endings of skeletofusimotor axons in the cat. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 10;185(2):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Pagés B. Cinematographic analysis of contractile events produced in intrafusal muscle fibres by stimulation of static and dynamic fusimotor axons. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):397–427. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A., Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N., Ward J. Control of dynamic and static nuclear bag fibres and nuclear chain fibres by gamma and beta axons in isolated cat muscle spindels. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):133–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A., Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N., Ward J. Proceedings: "Static" and "dynamic" nuclear bag fibres in isolated cat muscle spindles. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):11P–12P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A., Gladden M. H., Ward J. The effect of contraction in the three types of intrafusal fibre in isolated cat muscle spindles on the Ia discharge during stretch [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:41P–41P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A. The response of fast and slow nuclear bag fibres and nuclear chain fibres in isolated cat muscle spindles to fusimotor stimulation, and the effect of intrafusal contraction on the sensory endings. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1976 Jul;61(3):203–254. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1976.sp002354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Butler R. G. An investigation into the site of termination of static gamma fibres within muscle spindles of the cat peroneus longus muscle. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):131–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Butler R. G. Studies on the site of termination of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres within muscle spindles of the tenuissimus muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):553–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L., Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, distribution of fibres and fatiguability of single motor units. Anterior tibial muscle of the rat. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):424–433. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Matthews P. B., Petit J. On the subdivision of static and dynamic fusimotor actions on the primary ending of the cat muscle spindle. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):827–861. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N. The activity of intrafusal muscle fibres during cortical stimulation in the cat [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):28P–29P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H. Structural features relative to the function of intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. Prog Brain Res. 1976;44:51–59. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60722-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jami L., Lan-Couton D., Malmgren K., Petit J. Histophysiological observations on fast skeleto-fusimotor axons. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 23;164:53–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. A study of motor nerve terminals on cat nuclear bag1 intrafusal muscle fibers using the ChE staining technique. Anat Rec. 1982 Mar;202(3):407–418. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092020313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Motor innervation of the cat muscle spindle studied by the cholinesterase technique. Histochemistry. 1980;67(3):291–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00692762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Motor nerve terminals of cat nuclear chain fibers studied by the cholinesterase technique. Neuroscience. 1980;5(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovalle W. K., Smith R. S. Histochemical identification of three types of intrafusal muscle fibers in the cat and monkey based on the myosin ATPase reaction. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1972 Mar;50(3):195–202. doi: 10.1139/y72-030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELENA J. DEVELOPMENT, DEGENERATION AND REGENERATION OF RECEPTOR ORGANS. Prog Brain Res. 1964;13:175–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelená J., Soukup T. Development of muscle spindles deprived of fusimotor innervation. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Nov 7;144(3):435–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00307586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelená J., Soukup T. The differentiation of intrafusal fibre types in rat muscle spindles after motor denervation. Cell Tissue Res. 1974;153(1):115–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00225450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]