Abstract
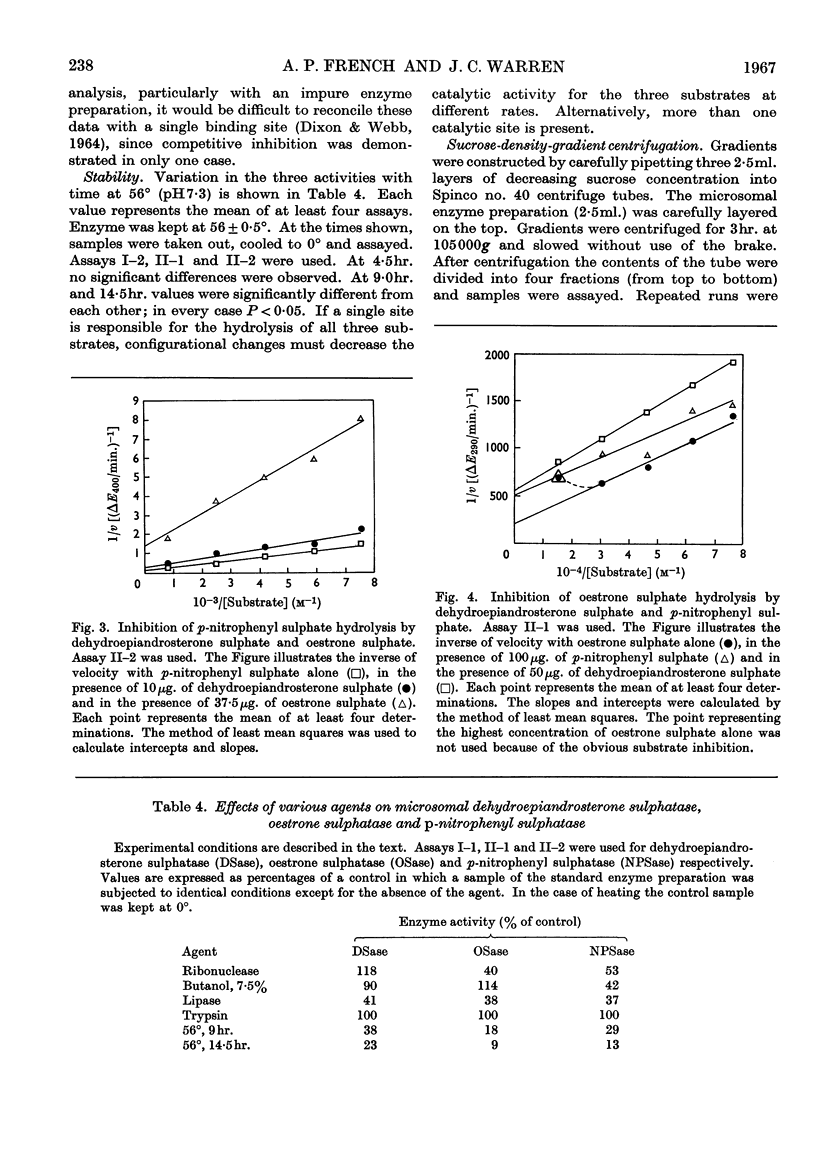
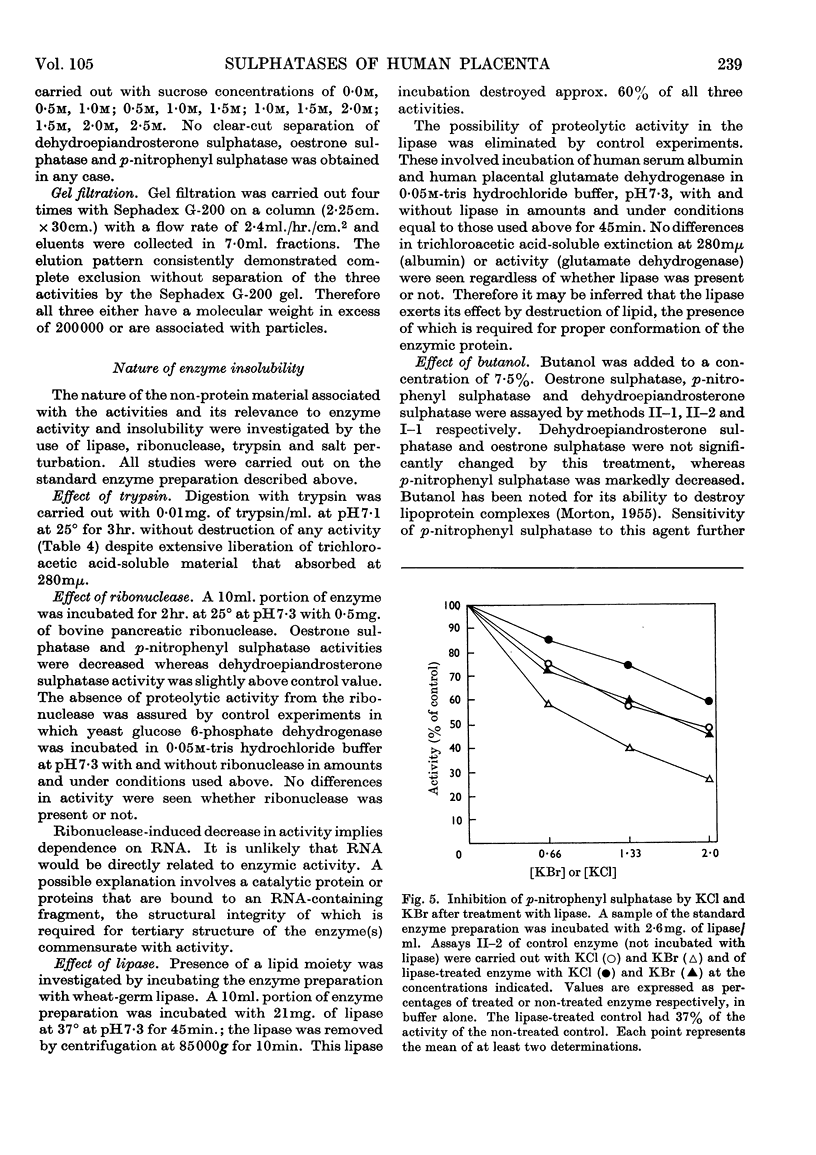
1. The properties of enzyme activities hydrolysing the sulphate esters of dehydroepiandrosterone, oestrone and p-nitrophenol are reported. The preparation studied was obtained from the microsomal fraction of human placenta by ultrasonic treatment and addition of Triton X-100. 2. The behaviour of the preparation during sedimentation at 105000g and attempts at purification indicated that the activities were particulate. Electron microscopy demonstrated the rupture of vesicular structures approx. 0·5μ in diameter concurrent with the release of activity. 3. The three activities were always associated throughout repeated attempts at separation by sucrose-density-gradient centrifugation and Sephadex-gel filtration. On the basis of kinetic studies, stability studies and treatment with butanol and ribonuclease it was concluded that a separate enzyme is responsible for each of the three activities. Widely varying plots of activity as a function of pH were consistent with this conclusion. 4. On the basis of sensitivity of the enzymes hydrolysing dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate and oestrone sulphate to ribonuclease and sensitivity of all three enzymes to lipase, it was concluded that the three enzymes are bound to a particle containing lipid and RNA. Enzymic activity is dependent on structural integrity of the particle. 5. A spectrophotometric method for the assay of oestrone sulphate hydrolysis is described. 6. Hydrolysis of nitrocatechol sulphate by human placenta under conditions described for arylsulphatases A and B is reported.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAULIEU E. E., DRAY F. CONVERSION OF H3-DEHYDROISOANDROSTERONE (3BETA-HYDROXY-DELTA5-ANDROSTEN-17-ONE) SULFATE TO H3-ESTROGENS IN NORMAL PREGNANT WOMEN. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Dec;23:1298–1301. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-12-1298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLTE E., MANCUSO S., ERIKSSON G., WIQVIST N., DICZFALUSY E. STUDIES ON THE AROMATISATION OF NEUTRAL STEROIDS IN PREGNANT WOMEN. I. AROMATISATION OF C-19 STEROIDS BY PLACENTAS PERFUSED IN SITU. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1964 Apr;45:535–559. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0450535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTEIN S., DORFMAN R. I. Determination of mammalian steroid sulfatase with 7 alpha-H3-3beta-hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1963 May;238:1656–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann E., Allmann D. W., Green D. E. The membrane systems of the mitochondrion. I. The S fraction of the outer membrane of beef heart mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jul;115(1):153–164. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(66)81051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner G., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Synthesis of microsomal membranes and their enzymic constituents in developing rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 12;20(2):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French A. P., Warren J. C. Steroid-3-beta-sulfatase in fetal and placental tissues. Steroids. 1965 Dec;6(6):865–869. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(65)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Person P., Felton J. H., Zipper H. Disruption of mitochondria and solubilization of cytochrome oxidase by NaOH and KOH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;105(2):393–396. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY A. B. The steroid sulphatase of Patella vulgata. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):41–50. doi: 10.1042/bj0620041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY A. B. The sulphatase of ox liver. I. The complex nature of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):12–15. doi: 10.1042/bj0530012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY A. B. The sulphatase of ox liver. VI. Steroid sulphatase. Biochem J. 1957 Aug;66(4):700–703. doi: 10.1042/bj0660700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN J. C., FRENCH A. P. DISTRIBUTION OF STEROID SULFATASE IN HUMAN TISSUES. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Feb;25:278–282. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-2-278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN J. C., TIMBERLAKE C. E. Steroid sulfatase in the human pacenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Nov;22:1148–1151. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-11-1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. C., Stowring L., Morales M. F. The effect of structure-disrupting ions on the activity of myosin and other enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]