Abstract
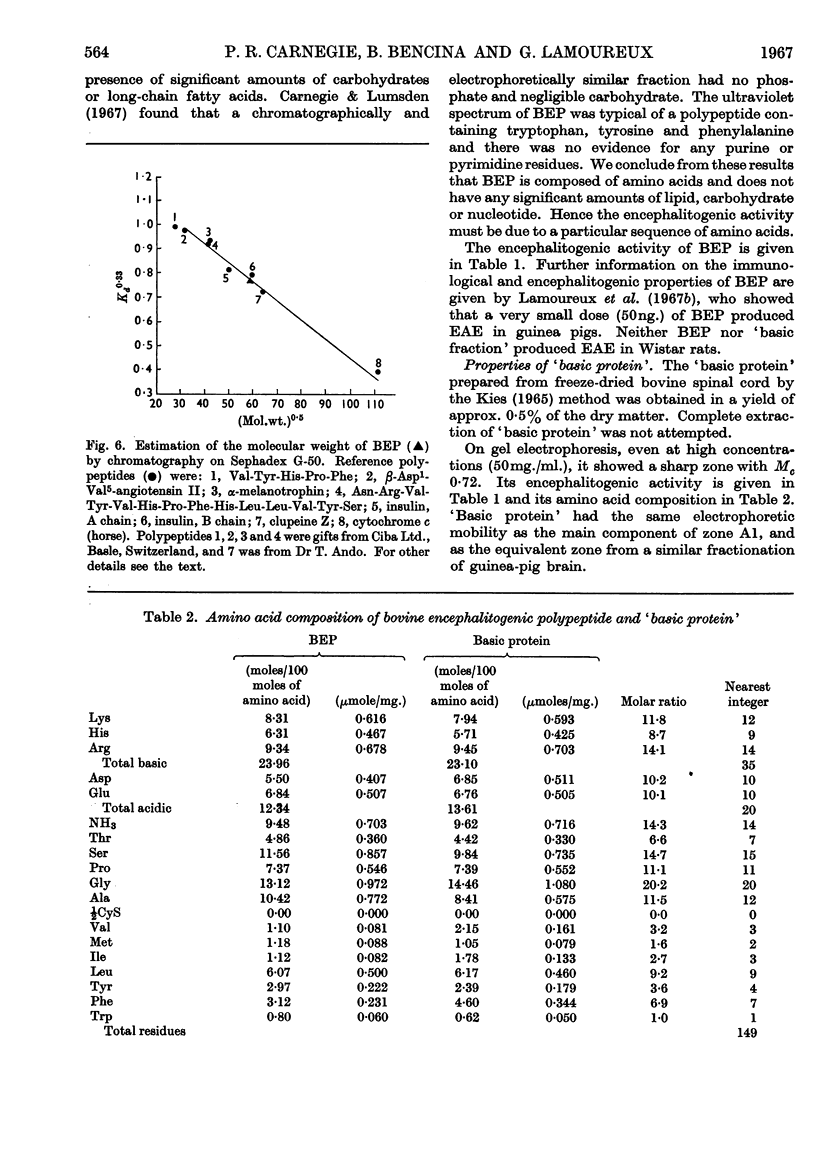
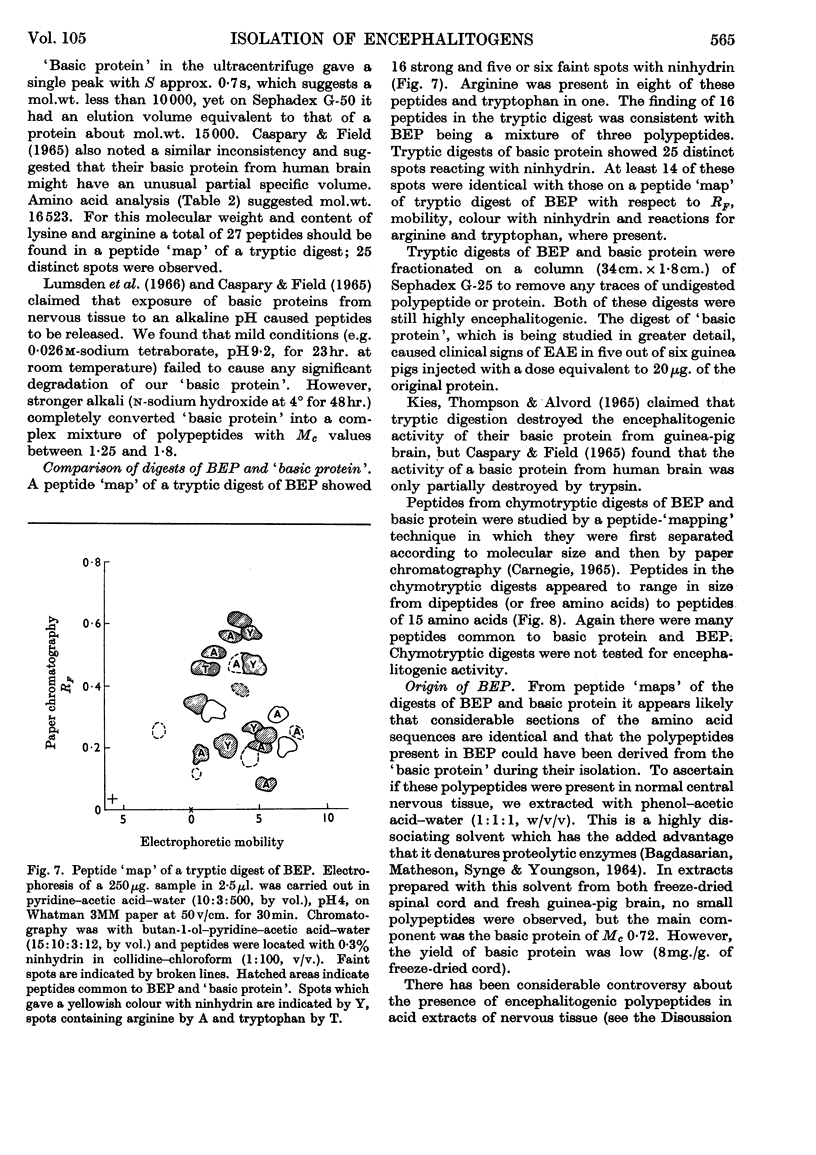
1. Basic protein (mol.wt. 16500) and polypeptides (mol.wt. 3500) were isolated from bovine spinal cord by a procedure involving defatting, acid extraction of the defatted material and repeated chromatography on Sephadex G-50. Similar fractions were isolated from guinea-pig brain. 2. These fractions produced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in guinea pigs. 3. The polypeptides appeared to be derived from a basic protein of myelin as a result of the action of an acid proteinase during extraction with acid. Similar proteolysis might also occur in the isolation of other biologically active polypeptides from acetone-dried powders of nervous tissue. The activity of the acid proteinase was lowered by defatting with chloroform–methanol. 4. Peptides from tryptic digests of encephalitogenic polypeptides and protein were also encephalitogenic, which suggests that the encephalitogenic determinant may be quite a short sequence of amino acids. 5. These encephalitogenic polypeptides are further examples of antigens of low molecular weight.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEAVEN G. H., HOLIDAY E. R. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of proteins and amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1952;7:319–386. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M., Matheson N. A., Synge R. L., Youngson M. A. New procedures for isolating polypeptides and proteins from tissues. Metabolic incorporation of L-[14C]valine into fractions of intermediate molecular weight in broad-bean (Vicia faba L.) leaves. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):91–105. doi: 10.1042/bj0910091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPARY E. A., FIELD E. J. AN ENCEPHALITOGENIC PROTEIN OF HUMAN ORIGIN: SOME CHEMICAL AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:182–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R. A peptide-mapping technique for the estimation of molecular size. Nature. 1965 Jun 12;206(989):1128–1130. doi: 10.1038/2061128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R., Lamoureux G., Bencina B. Proposed technique for classifying and identifying encephalitogens. Nature. 1967 Apr 22;214(5086):407–408. doi: 10.1038/214407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R., Lumsden C. E. Encephalitogenic peptides from spinal cord. Nature. 1966 Mar 26;209(5030):1354–1355. doi: 10.1038/2091354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R., Lumsden C. E. Fractionation of encephalitogenic polypeptides from bovine spinal cord by gel filtration in phenol--acetic acid--water. Immunology. 1967 Feb;12(2):133–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easley C. W. Combinations of specific color reactions useful in the peptide mapping technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 13;107(2):386–388. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUILLEMIN R. HYPOTHALAMIC FACTORS RELEASING PITUITARY HORMONES. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1964;20:89–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTTLE G. A., NEDZEL G. A. Allergic encephalitis following injection of dialysate of brain tissue. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1949 Nov;72(2):289–291. doi: 10.3181/00379727-72-17410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIBLER R. F., FOX R. H., SHAPIRA R. ISOLATION OF A HIGHLY PURIFIED ENCEPHALITOGENIC PROTEIN FROM BOVINE CORD. Nature. 1964 Dec 26;204:1273–1275. doi: 10.1038/2041273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIES M. W., THOMPSON E. B., ALVORD E. C., Jr THE RELATIONSHIP OF MYELIN PROTEINS TO EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:148–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth S. E., Anderson J. W. Localization of a basic protein in the myelin of various species with the aid of fluorescence and electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jul;26(1):157–166. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUMSDEN C. E., ROBERTSON D. M., BLIGHT R. NEW AND UNEXPECTED FINDINGS ON THE CHEMICAL NATURE OF THE ECM-PROMOTING FACTOR(S) IN BOVINE SPINAL CORD. Z Immunitats Allergieforsch. 1964 Mar;126:168–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux G., McPherson T. A., Carnegie P. R. Attempts to transfer experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in guinea-pigs by lymph node fragments in millipore chambers. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Mar;2(2):253–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowden J. A., Moscarello M. A., Morecki R. The isolation and characterization of an acid-soluble protein from myelin. Can J Biochem. 1966 May;44(5):567–577. doi: 10.1139/o66-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden C. E., Robertson D. M., Blight R. Chemical studies on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Peptide as the common denominator in all encephalitogenic 'antigens'. J Neurochem. 1966 Mar;13(3):127–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb07507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H., Woodman R. J., Cummins J. T. Basic proteins and the potassium movements and phosphates of cerebral tissues. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81(1):79–83. doi: 10.1042/bj0810079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAO A., ROBOZ-EINSTEIN E. CHEMICAL AND IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES WITH A DIALYZABLE ENCEPHALITOGENIC COMPOUND FROM BOVINE SPINAL CORD. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:171–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piha R. S., Cuénod M., Waelsch H. Metabolism of histones of brain and liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2397–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUCH H. C., RAFFEL S. IMMUNOFLUORESCENT LOCALIZATION OF ENCEPHALITOGENIC PROTEIN IN MYELIN. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:452–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON D. M., BLIGHT R., LUMSDEN C. E. Dialysable peptide as the causative factor in experimental "allergic" encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1962 Dec 8;196:1005–1005. doi: 10.1038/1961005a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYNGE R. L. STEPS IN DEVELOPING SOME METHODS FOR SYSTEMATIC ISOLATION OF PEPTIDES FROM TISSUES, WITH FRACTIONATION ACCORDING TO MOLECULAR WEIGHT. Metabolism. 1964 Oct;13:SUPPL–SUPPL:973. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(64)80016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG S. S., CARPENTER F. H. A COMPOSITIONAL ASSAY FOR INSULIN APPLIED TO A SEARCH FOR "PROINSULIN". J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1619–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFGRAM F. MACROMOLECULAR CONSTITUENTS OF MYELIN. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:104–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]