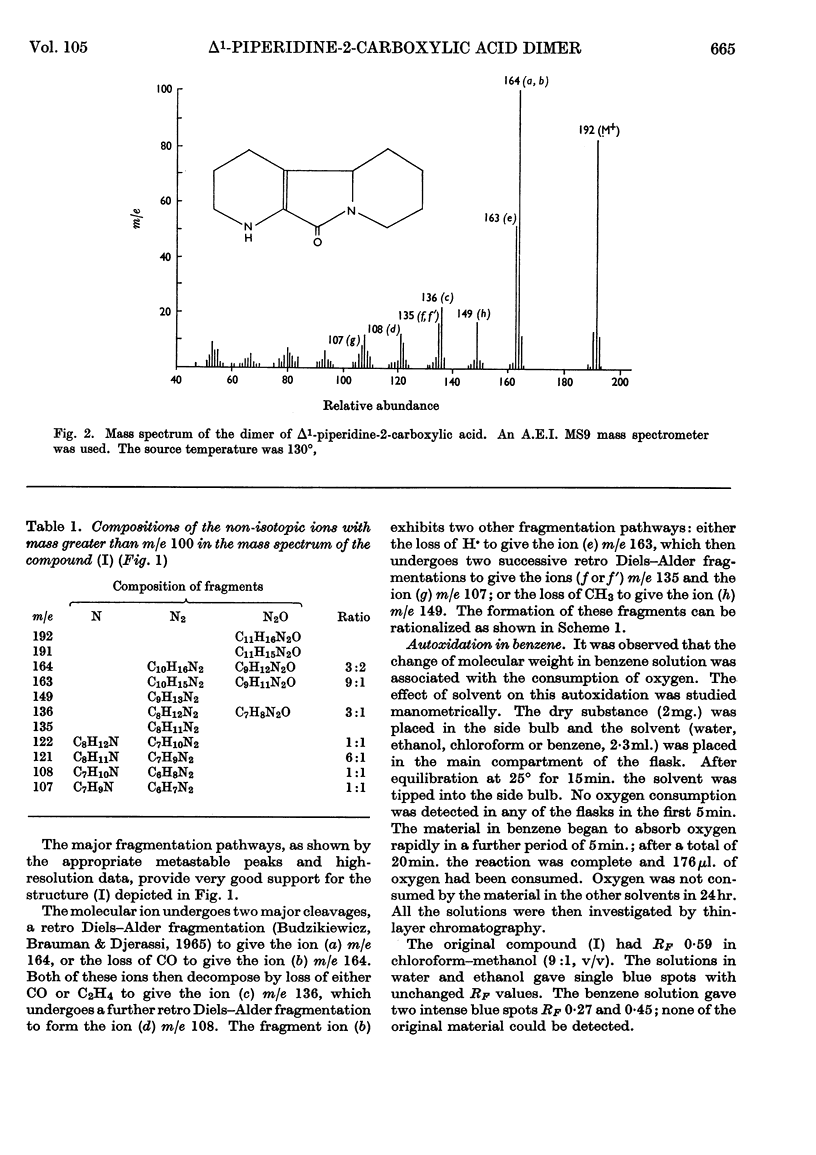
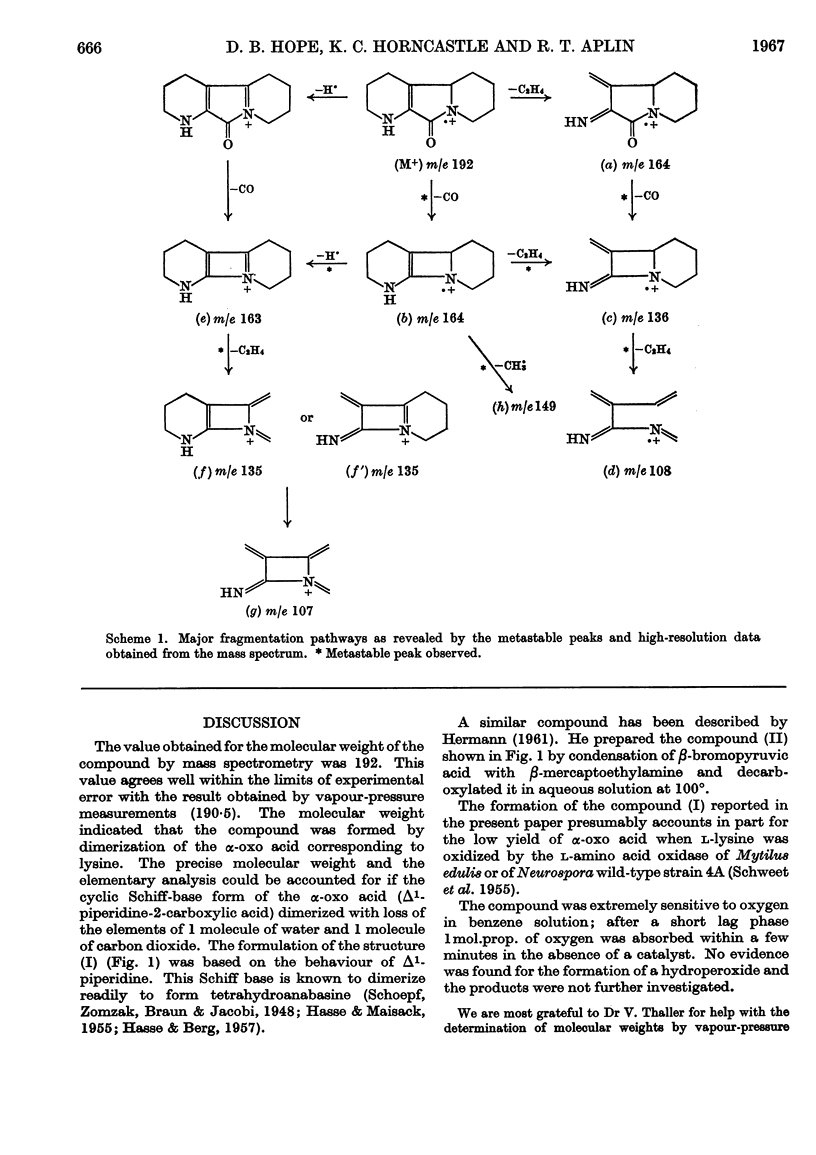
Abstract
The l-amino acid oxidase of Mytilus edulis has been used to oxidize l-lysine on a large scale in the presence of catalase. The α-oxo acid derived from lysine cyclizes to a Schiff base, which readily dimerizes. The dimer undergoes spontaneous dehydration and decarboxylation to form 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydropyrido[3,2-a]-indolizin-10(4bH)-one. This structure was established by a study of its molecular weight and infrared, nuclear-magnetic-resonance and mass spectra.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HASSE K., MAISACK H. Die Reaktionsprodukte der enzymatischen Oxydation von Putrescin und Cadaverin. Biochem Z. 1955;327(4):296–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope D. B., Horncastle K. C. The oxidation of lysine and oxalysine by Mytilus edulis: Identification of the products formed in the presence and the absence of catalase. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):910–916. doi: 10.1042/bj1020910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEISTER A. The alpha-keto analogues of arginine, ornithine, and lysine. J Biol Chem. 1954 Feb;206(2):577–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


