Abstract
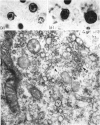
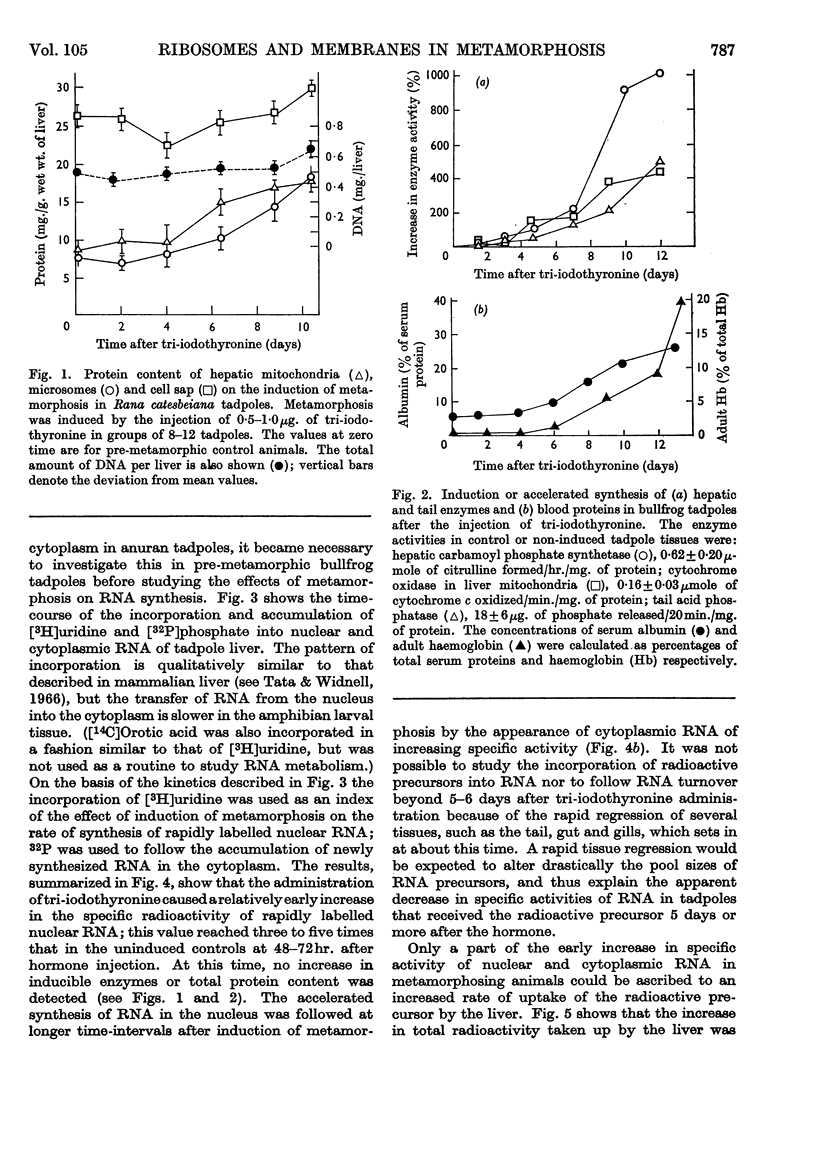
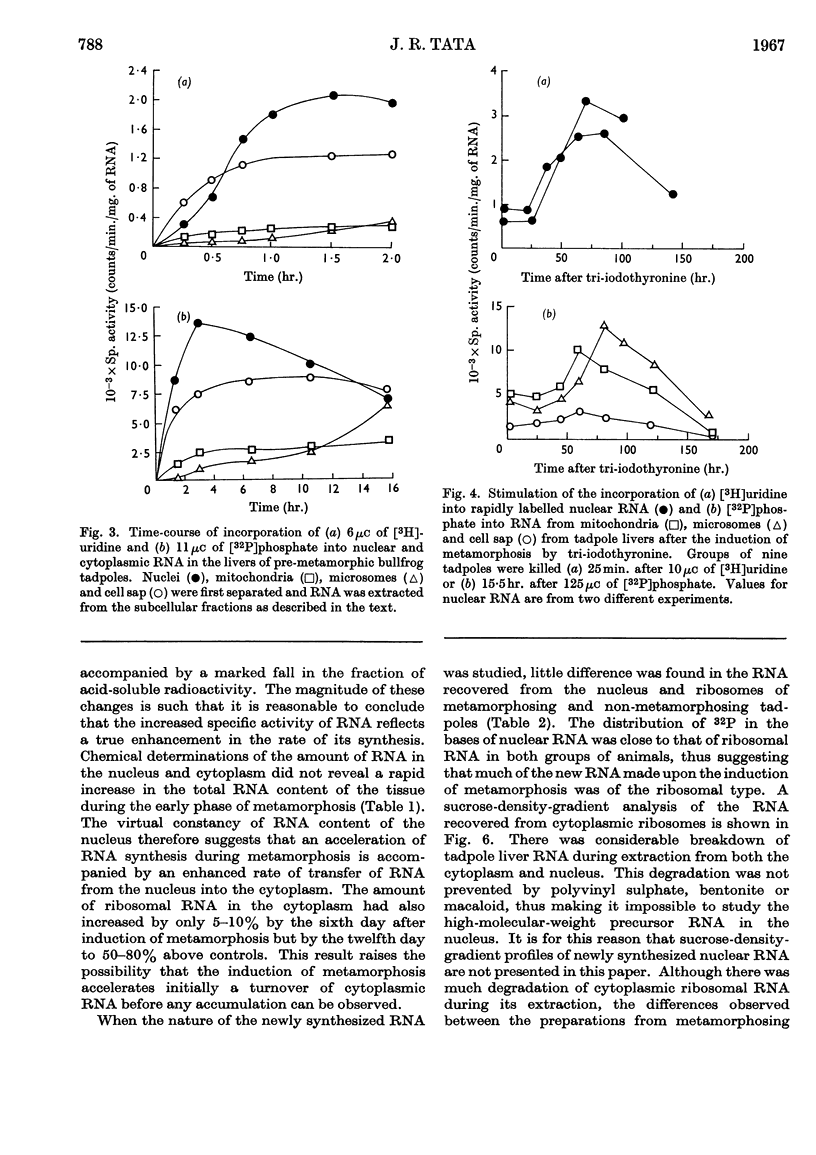
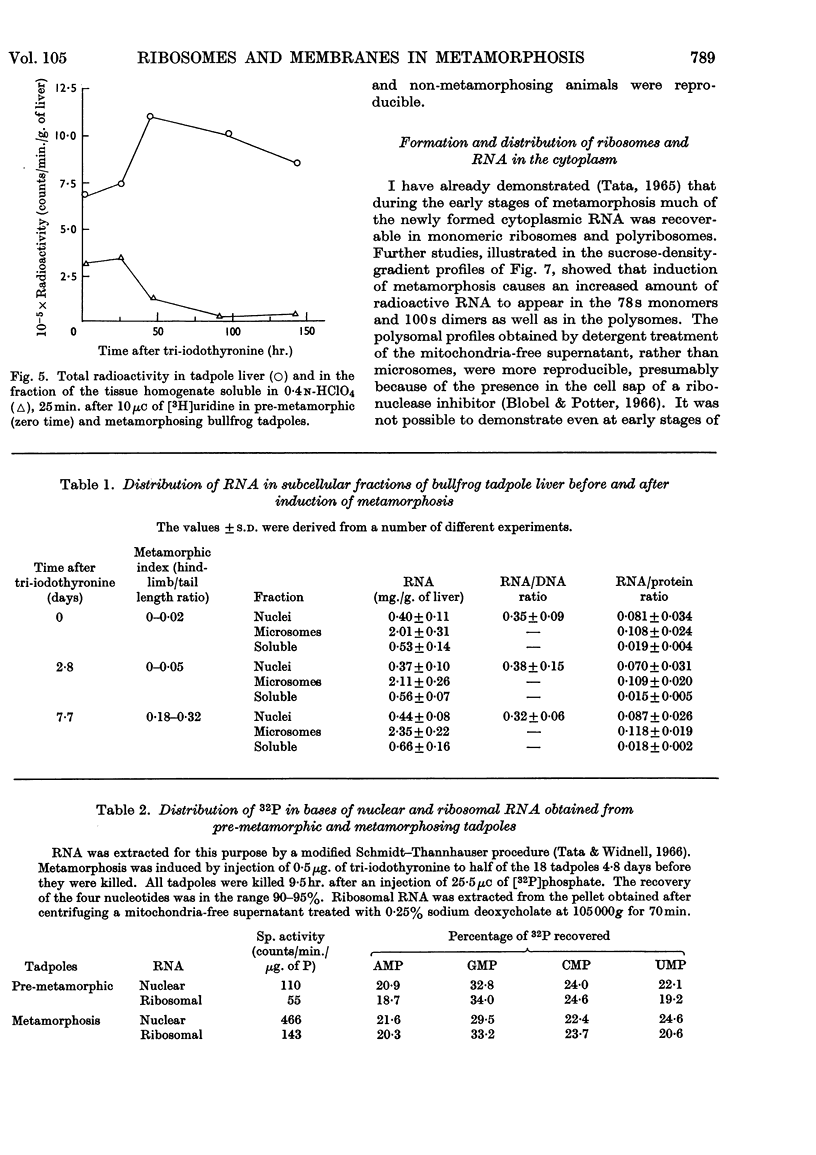
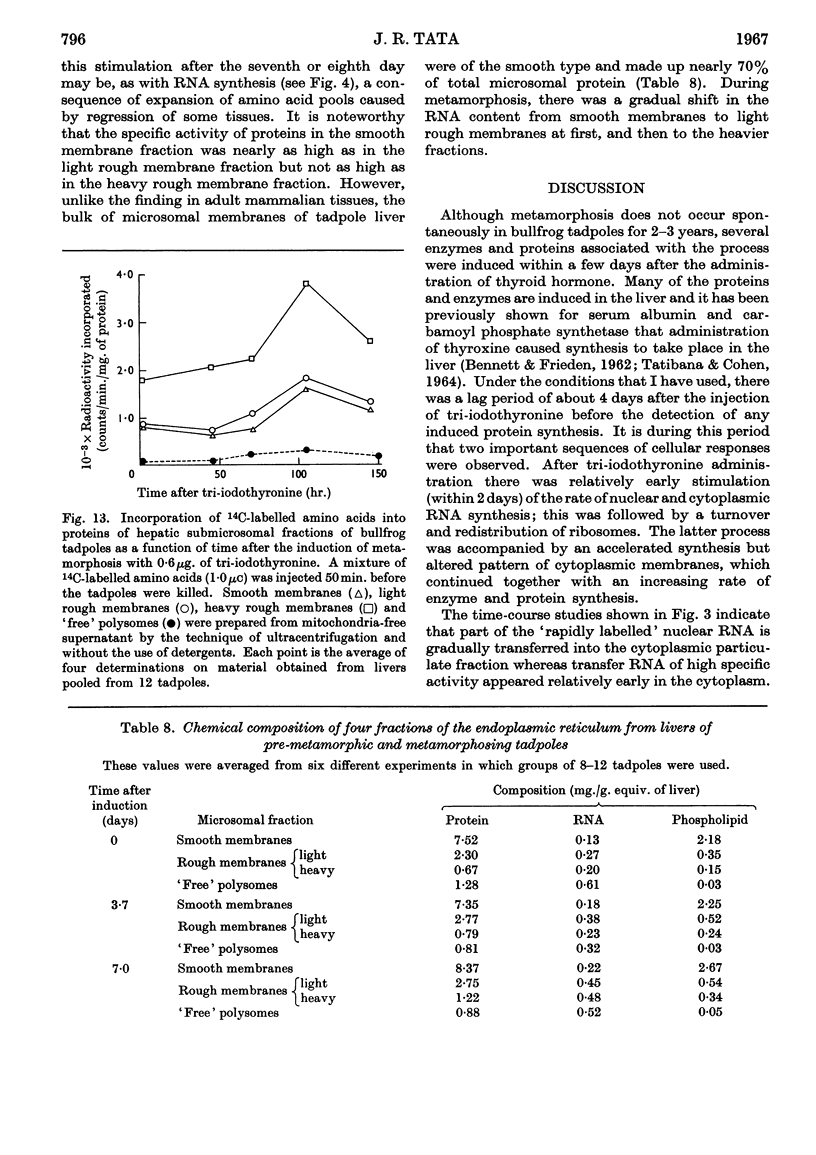
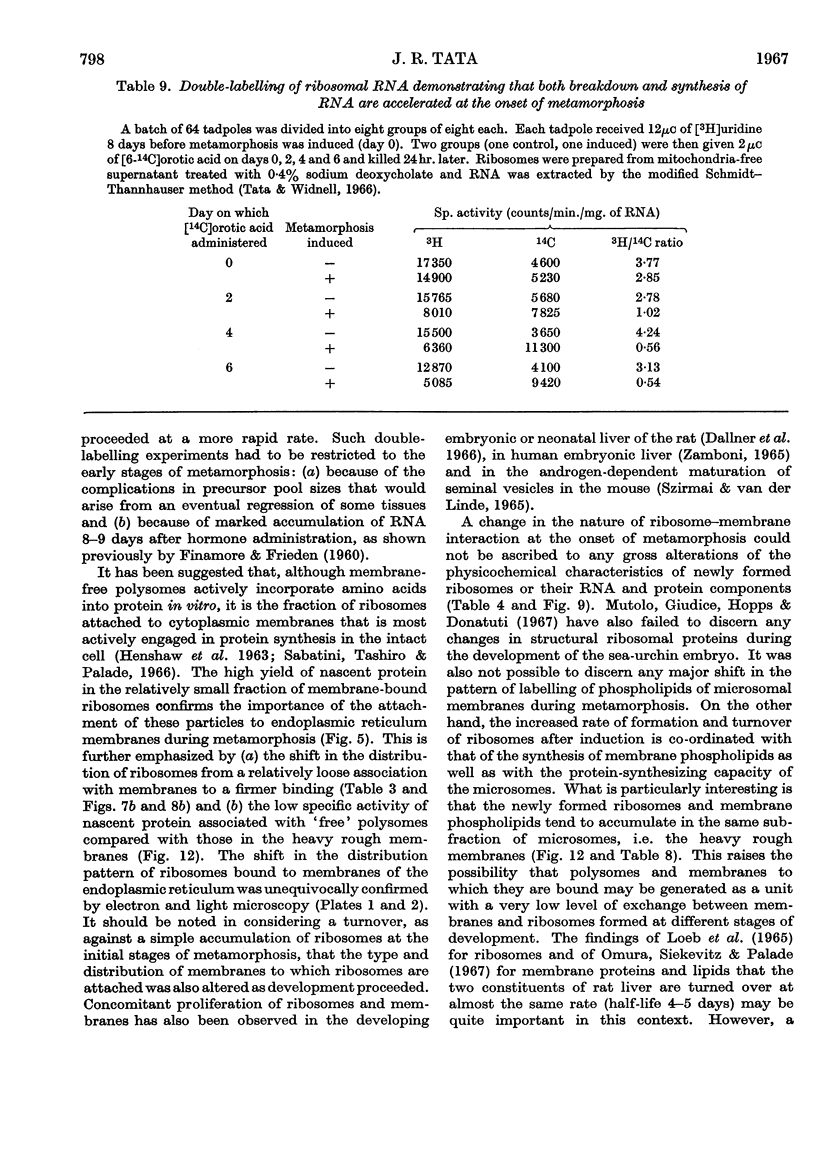
1. A lag period of about 4 days preceded the onset of metamorphosis precociously induced by tri-iodothyronine in tadpoles of the giant American bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana). It was established by the accelerated synthesis or induction of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase and cytochrome oxidase in the liver, serum albumin and adult haemoglobin in the blood, acid phosphatase in the tail, and the increase in the hindleg/tail length ratio. 2. A 4- to 6-fold stimulation, 2 days after the induction of metamorphosis, of the rate of synthesis of rapidly labelled nuclear RNA in liver cells was followed by an increasing amount of RNA appearing in the cytoplasm. Most of the newly formed RNA on induction of metamorphosis was of the ribosomal type. An accelerated turnover at early stages of development preceded a net accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm, with no change in the amount of DNA per liver. 3. Most hepatic ribosomes of the pre-metamorphic tadpoles were present as 78s monomers and 100s dimers; metamorphosis caused a shift towards larger polysomal aggregates with newly formed ribosomes that were relatively more tightly bound to membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum. 4. The appearance of new polyribosomes in the cytoplasm on induction of metamorphosis was co-ordinated in time with a stimulation of synthesis of phospholipids of the smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, followed by a gradual shift in preponderance from the smooth to the rough type of microsomal membranes. 5. Electron- and optical-microscopic examination of intact hepatocytes revealed a striking change in the distribution and nature of ribosomes and microsomal membranes during metamorphosis. 6. Ribosomes prepared from non-metamorphosing and metamorphosing animals were identical in their sedimentation coefficients and in the structural ribosomal proteins. The base composition and sedimentation coefficients of ribosomal RNA were also identical. Induction of metamorphosis also did not alter the incorporation of 32P into the different phospholipid constituents of microsomal membranes. 7. Nascent 14C-labelled protein with the highest specific activity was recovered in the `heavy' rough membrane fraction of microsomes, whereas little 14C was associated with `free' polysomes. Protein synthesis in vivo was most markedly stimulated during metamorphosis in the tightly membrane-bound ribosomal fraction after the appearance of new ribosomes. 8. The rate of synthesis of macromolecules in vivo could not be followed beyond 7–8 days after induction because of variable shifts in precursor pools due to regression of larval tissues. 9. The stimulation of RNA and ribosome formation was specifically associated with the process of metamorphosis since no similar response to thyroid hormones occurred in those species (Axolotl and Necturus) in which the hormones failed to induce metamorphosis.
Full text
PDF



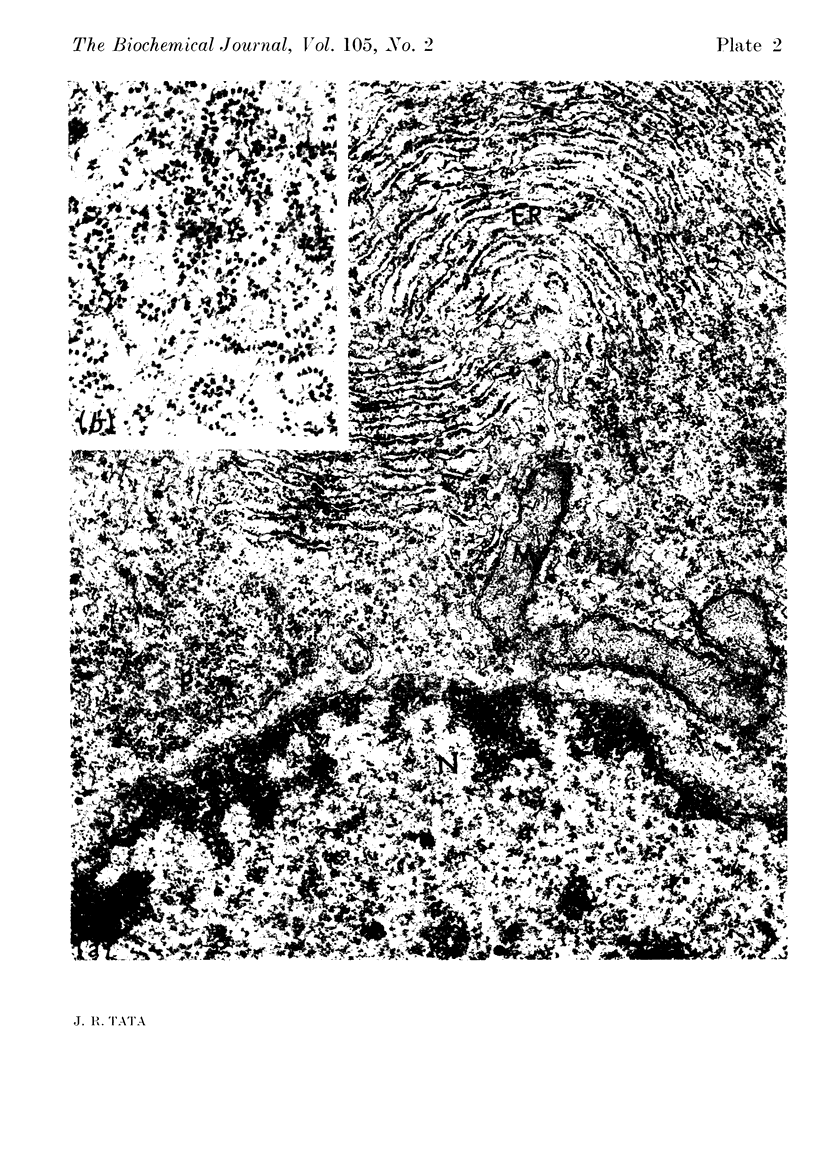
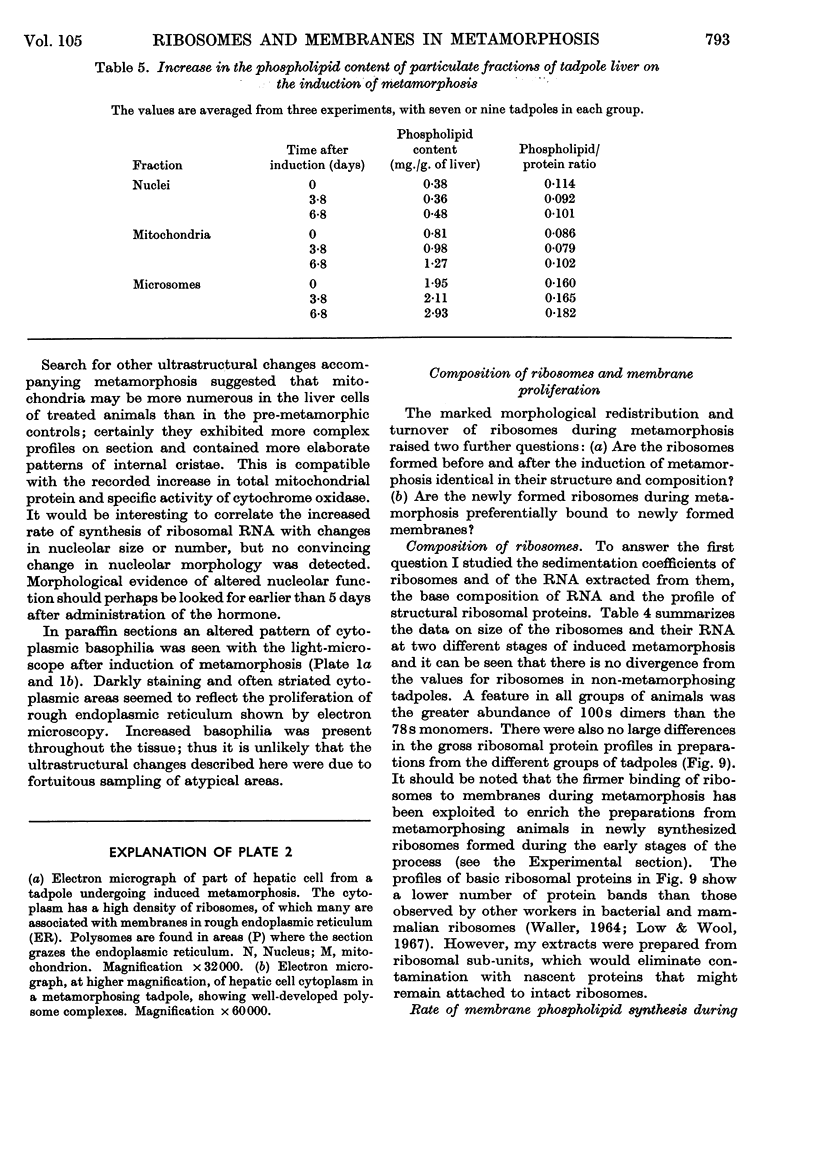
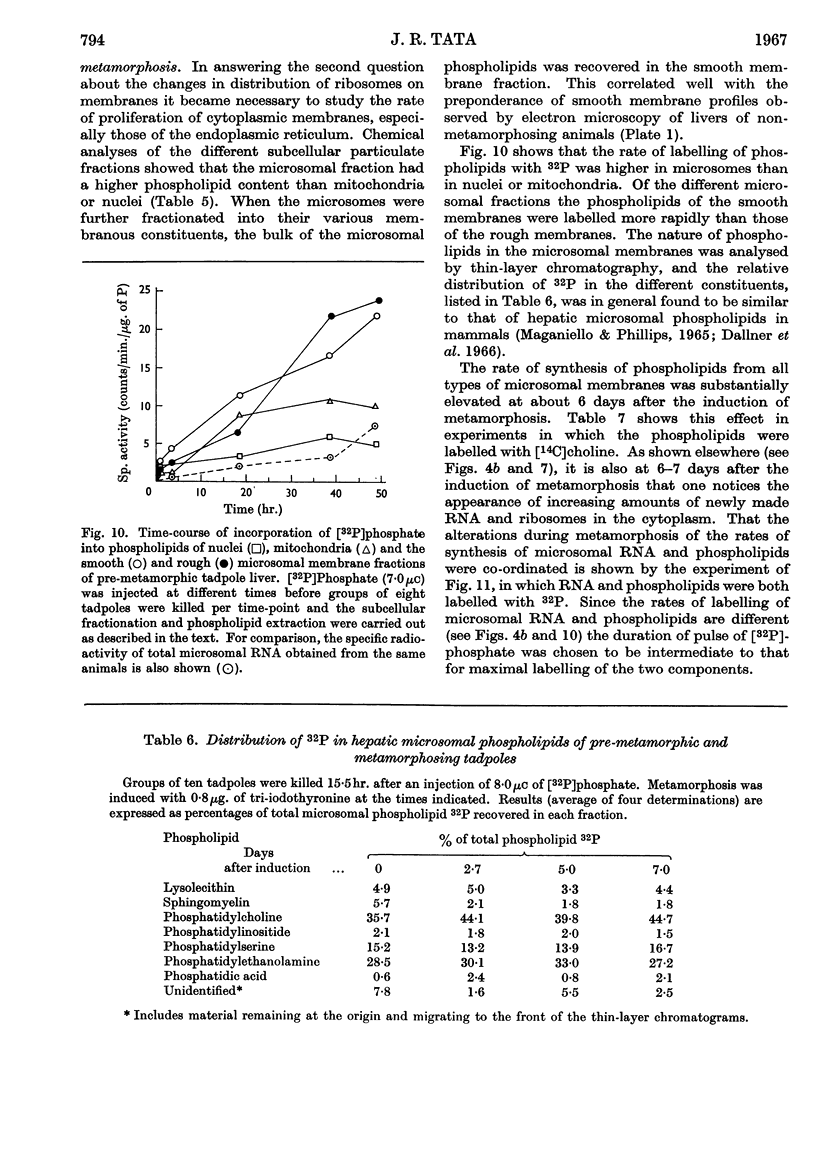
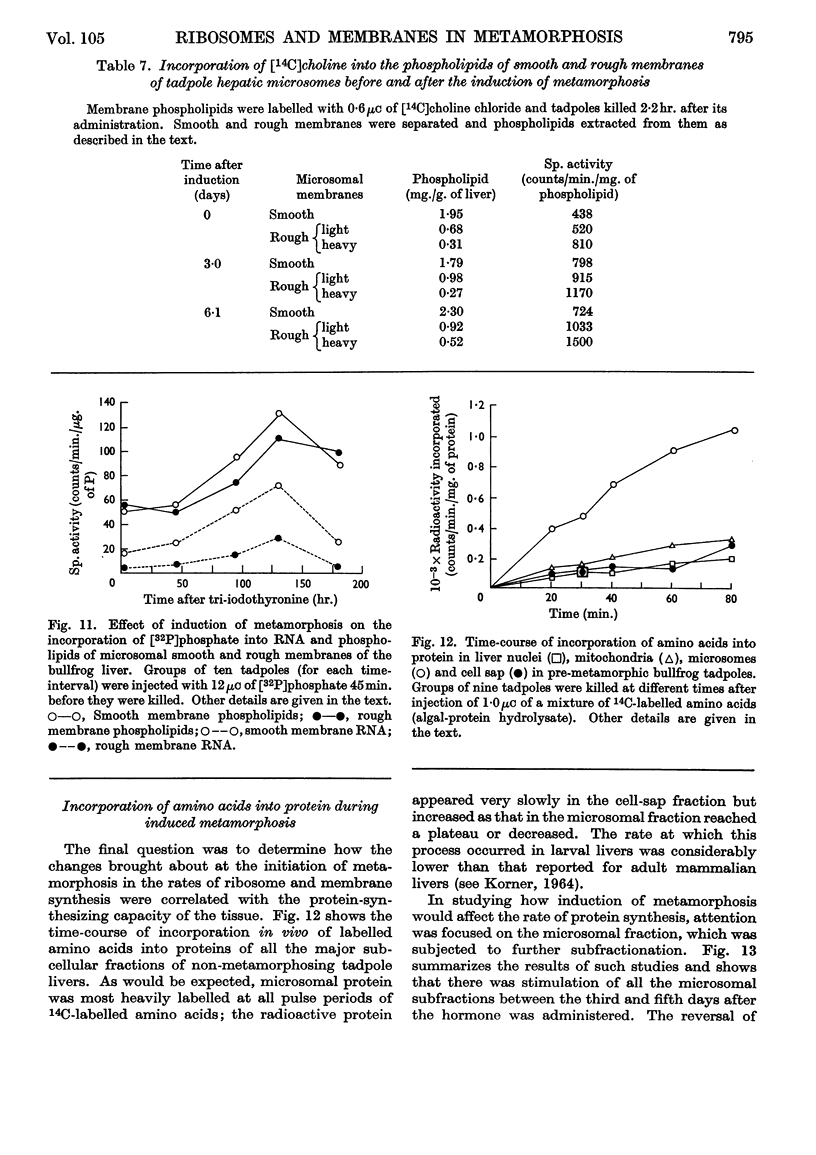




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAGLIONI C., SPARKS C. E. A STUDY OF HEMOGLOBIN DIFFERENTIATION IN RANA CATESBEIANA. Dev Biol. 1963 Dec;8:272–285. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN G. W., Jr, COHEN P. P. Comparative biochemistry of urea synthesis. I. Methods for the quantitative assay of urea cycle enzymes in liver. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jul;234(7):1769–1774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Relation of ribonuclease and ribonuclease inhibitor to the isolation of polysomes from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1283–1288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H., Bont W. S., Meisner I. Stimulation of phenylalanine incorporation in hepatic polyribosome preparations by polyuridylic acid. Nature. 1966 Mar 19;209(5029):1204–1206. doi: 10.1038/2091204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERIOTTI G. Determination of nucleic acids in animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. P. Biochemical aspects of metamorphosis: transition from ammonotelism to ureotelism. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:119–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner G., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Biogenesis of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. I. Structural and chemical differentiation in developing rat hepatocyte. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):73–96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINAMORE F. J., FRIEDEN E. Nucleic acids and induced amphibian metamorphosis. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1751–1755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDEN E., MATHEWS H. Biochemistry of amphibian metamorphosis. III. Liver and tail phosphatases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Jan;73(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDEN E., WESTMARK G. W. On the anomalous activity mf thyroxin analogs in tadpoles. Science. 1961 May 12;133(3463):1487–1489. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3463.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel R. M., Henshaw E. C., Hiatt H. H. Early changes in liver cytoplasmic RNA of hydrocortisone-treated rats. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 May;2(3):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD M., LATHAM H., PENMAN S., DARNELL J. E. ENTRANCE OF NEWLY FORMED MESSENGER RNA AND RIBOSOMES INTO HELA CELL CYTOPLASM. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:187–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSHAW E. C., BOJARSKI T. B., HIATT H. H. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY FREE AND BOUND RAT LIVER RIBOSOMES IN VIVO AND IN VITRO. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:122–129. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERNER A. E., FRIEDEN E. Biochemical changes during anuran metamorphosis. VIII. Changes in the nature of red cell proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Oct;95:25–35. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERNER A. E., FRIEDEN E. Biochemistry of anuran metamorphosis. VII. Changes in serum proteins during spontaneous and induced metamorphosis. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235:2845–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIATT H. H. A rapidly labeled RNA in rat liver nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1962 Aug;5:217–229. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henshaw E. C., Revel M., Hiatt H. H. A cytoplasmic particle bearing messenger ribonucleic acid in rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):241–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80244-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ S., COMB D. G. A NEW METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF THE BASE COMPOSITION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3065–3067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Cohen P. P. Modification of tadpole liver chromatin by thyroxine treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1251–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE B. G. The separation of adenosine, guanosine, cytidine and uridine by one-dimensional filter-paper chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 28;72:110–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS E. J. C., FRIEDEN E. Biochemistry of amphibian metamorphosis: effect of triiodothyronine, thyroxin, and dinitrophenol on the respiration of the tadpole. Endocrinology. 1959 Aug;65(2):273–282. doi: 10.1210/endo-65-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. N., Howell R. R., Tomkins G. M. Turnover of ribosomal RNA in rat liver. Science. 1965 Sep 3;149(3688):1093–1095. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3688.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low R. B., Wool I. G. Mammalian ribosomal protein: analysis by electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gel. Science. 1967 Jan 20;155(3760):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3760.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manganiello V. C., Phillips A. H. The relationship between ribosomes and the endoplasmic reticulum during protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3951–3959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H., Hopkins J. W. Subribosomal particles and the transport of messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):257–270. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Ingram V. M. The repression and induction by thyroxin of hemoglobin synthesis during amphibian metamorphosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):967–974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutolo V., Giudice G., Hopps V., Donatuti G. Species specificity of embryonic ribosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 29;138(1):214–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90609-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa H., Cohen P. P. Studies on ribonucleic acid synthesis in tadpole liver during metamorphosis induced by thyroxine. II. Analysis of ribonucleic acid fractions. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):642–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa H., Kim K. H., Cohen P. P. Studies on ribonucleic acid synthesis in tadpole liver during metamorphosis induced by thyroxine. I. Relation of synthesis of ribonucleic acid and of carbamyl phosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):635–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura T., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Turnover of constituents of the endoplasmic reticulum membranes of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2389–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAIK W. K., COHEN P. P. Biochemical studies on amphibian metamorphosis. I. The effect of thyroxine on protein synthesis in the tadpole. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Mar;43:683–696. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.4.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROODYN D. B., FREEMAN K. B., TATA J. R. THE STIMULATION BY TREATMENT IN VIVO WITH TRI-IODOTHYRONINE OF AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEIN BY ISOLATED RAT-LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:628–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0940628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZIRMAI J. A., VAN DER LINDE P. C. EFFECT OF CASTRATION ON THE ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM OF THE SEMINAL VESICLE AND OTHER TARGET EPITHELIA IN THE RAT. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Apr;12:380–395. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)80106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Tashiro Y., Palade G. E. On the attachment of ribosomes to microsomal membranes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):503–524. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TATA J. R., ERNSTER L., LINDBERG O., ARRHENIUS E., PEDERSEN S., HEDMAN R. The action of thyroid hormones at the cell level. Biochem J. 1963 Mar;86:408–428. doi: 10.1042/bj0860408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TATIBANA M., COHEN P. P. SYNTHESIS OF CARBAMYL PHOSPHATE SYNTHETASE IN LIVER SLICES FROM THYROXINE-TREATED TADPOLES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2905–2909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. Hormones and the synthesis and utilization of ribonucleic acids. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1966;5:191–250. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. Membrane phospholipid synthesis and the action of hormones. Nature. 1967 Feb 11;213(5076):566–569. doi: 10.1038/213566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. The formation and distribution of ribosomes during hormone-induced growth and development. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):1–16. doi: 10.1042/bj1040001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. Turnover of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleic acid at the onset of induced amphibian metamorphosis. Nature. 1965 Jul 24;207(995):378–381. doi: 10.1038/207378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Widnell C. C. Ribonucleic acid synthesis during the early action of thyroid hormones. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):604–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0980604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLER J. P. FRACTIONATION OF THE RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Nov;10:319–336. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber R. Inhibitory effect of actinomycin D on tail atrophy in Xenopus larvae at metamorphosis. Experientia. 1965 Nov 15;21(11):665–666. doi: 10.1007/BF02144069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. A procedure for the isolation of enzymically active rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0920313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. Additive effects of thyroid hormone, growth hormone and testosterone on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):621–629. doi: 10.1042/bj0980621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamboni L. Electron microscopic studies of blood embryogenesis in humans. I. The ultrastructure of the fetal liver. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Jun;12(5):509–524. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)80044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graeff J., Dempsey E. F., Lameyer L. D., Leaf A. Phospholipids and active sodium transport in toad bladder. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 7;106(1):155–170. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]