Abstract
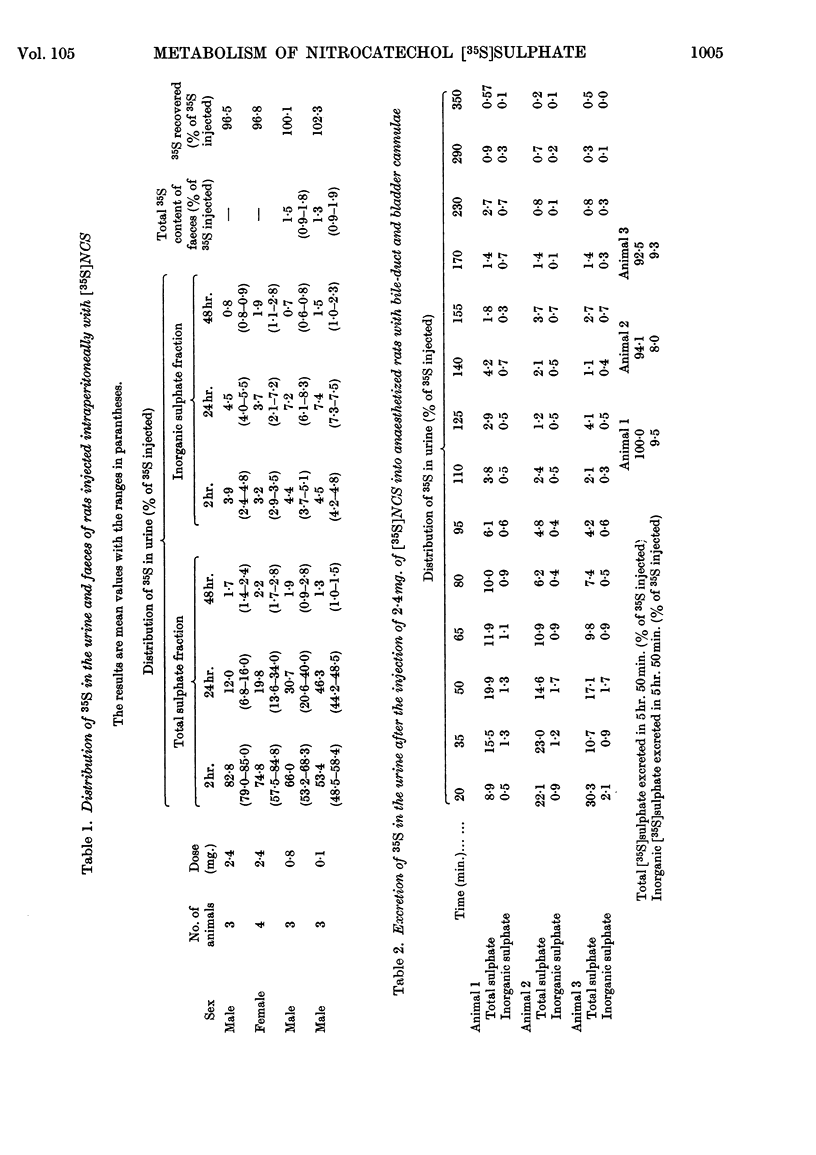
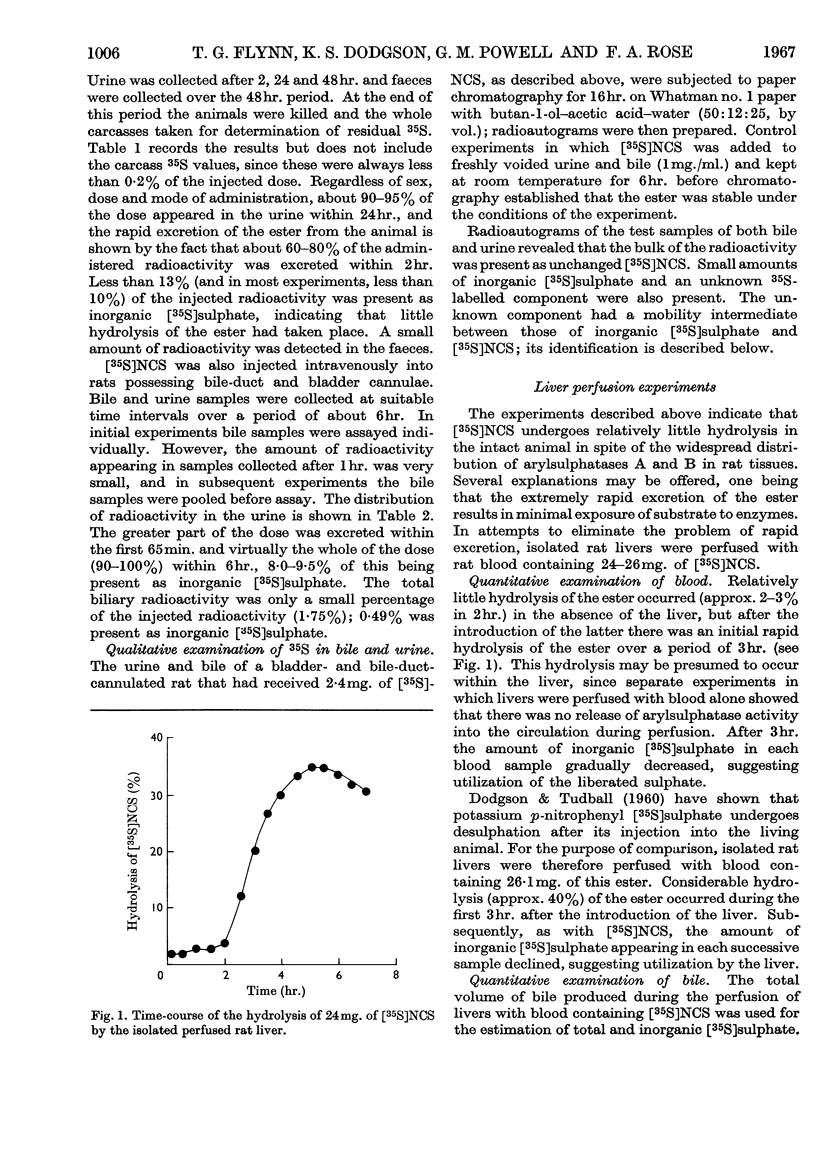
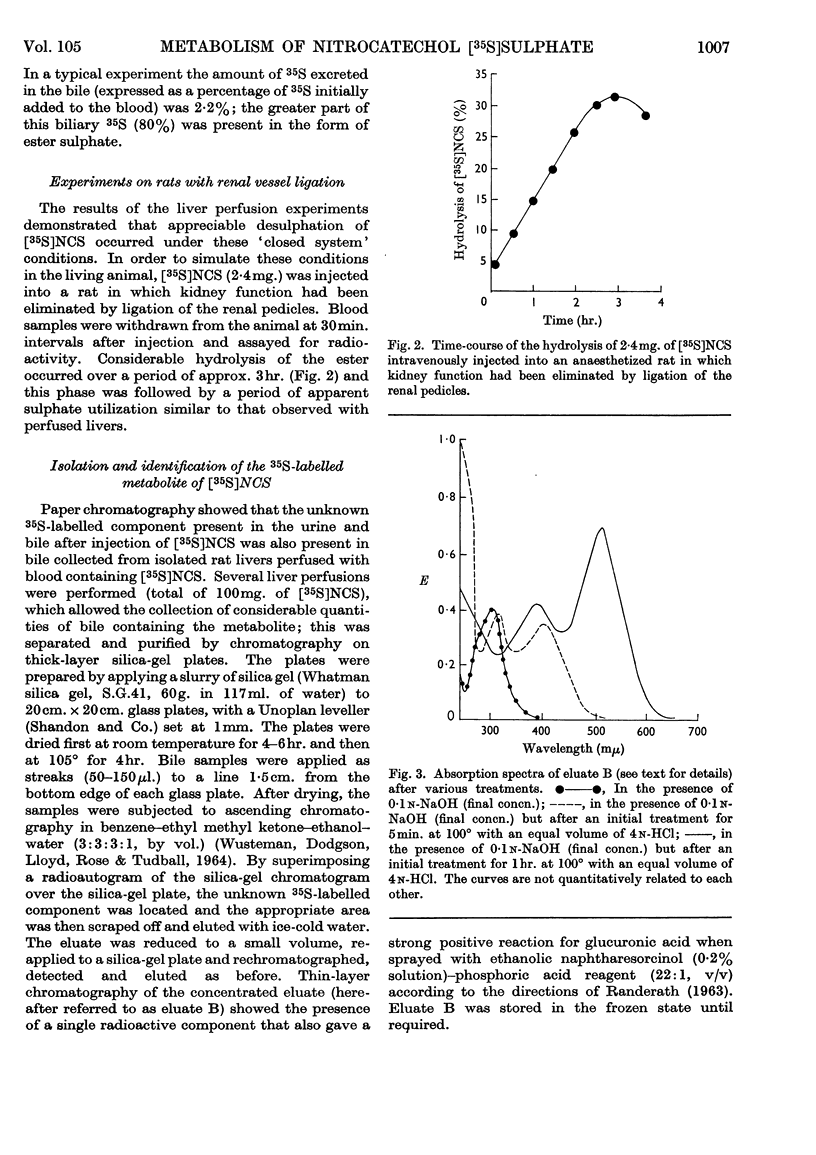
The metabolic fate of dipotassium 2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl [35S]sulphate ([35S]NCS), a chromogenic substrate for lysosomal arylsulphatases A and B, has been studied in rats. Intraperitoneal injection of [35S]NCS into free-ranging animals is followed by excretion of the bulk of the radioactivity in the urine within 24hr., less than 13% being eliminated as inorganic [35S]sulphate. Most of the urinary radioactivity can be accounted for as [35S]NCS, but small amounts of a labelled metabolite are also present. Experiments in which [35S]NCS was injected intravenously into anaesthetized rats with bile-duct and bladder cannulae confirm that the ester is rapidly excreted in the urine. However, small amounts of radioactivity appear in bile, mainly in the form of the metabolite detected in urine. When [35S]NCS is perfused through the isolated rat liver, about 35% of the dose is hydrolysed within 3hr. Similar results are obtained if [35S]NCS is injected into anaesthetized rats in which kidney function has been eliminated by ligature of the renal pedicles. The labelled metabolite has been isolated from bile obtained by perfusing several rat livers with blood containing a total of 100mg. of [35S]NCS. It has been identified as 2-β-glucuronosido-5-nitrophenyl [35S]sulphate. The implications of the various findings are discussed. The Appendix describes the preparation of [35S]NCS.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DODGSON K. S., ROSE F. A., SPENCER B. Studies on sulphatases. 10. The isolation and characterization of biosynthetic arylsulphates. Biochem J. 1955 Jun;60(2):346–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0600346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., ROSE F. A., TUDBALL N. Studies on sulphatases. 23. The enzymic desulphation of tyrosine O-sulphate. Biochem J. 1959 Jan;71(1):10–15. doi: 10.1042/bj0710010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., SPENCER B., THOMAS J. Studies on sulphatases. 6. The localization of arylsulphatase in the rat-liver cell. Biochem J. 1954 Feb;56(2):177–181. doi: 10.1042/bj0560177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., SPENCER B., THOMAS J. Studies on sulphatases. IX. The arylsulphatases of mammalian liver. Biochem J. 1955 Jan;59(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj0590029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., SPENCER B. The impure nature of nitrocatechol sulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Jul;21(1):175–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., SPENCER B., WILLIAMS K. Studies on sulphatase. II. The purification and properties of the arylsulphatase of Alcaligenes metalcaligenes. Biochem J. 1955 Nov;61(3):374–380. doi: 10.1042/bj0610374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., TUDBALL N. The metabolic fate of the ester sulphate group of potassium p-nitrophenyl [35S]sulphate. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:154–159. doi: 10.1042/bj0740154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C., Wattiaux R. Functions of lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1966;28:435–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.28.030166.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garton G. A., Robinson D., Williams R. T. Studies in detoxication. 25. The characterization of phenylglucuronide, and its rate of hydrolysis compared with that of phenylsulphuric acid. Biochem J. 1949;45(1):65–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garton G. A., Williams R. T. Studies in detoxication. 26. The fates of phenol, phenylsulphuric acid and phenylglucuronide in the rabbit, in relation to the metabolism of benzene. Biochem J. 1949;45(2):158–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAHAN D. J., EVERETT N. B. The metabolism of S35-sodium estrone sulfate in the adult female rat. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):919–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWKINS J. B., YOUNG L. Biochemical studies of toxic agents. V. Observations on the fate of 35S-labelled arylsulphuric acids following their administration of the rat. Biochem J. 1954 Jan;56(1):166–170. doi: 10.1042/bj0560166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSELBACHER K. J., CHRABAS M. F., QUINN R. C. The solubilization and partial purification of a glucuronyl transferase from rabbit liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3033–3036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. G. The metabolism of exogenous N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 6-O[S]-sulphate in the normal rat. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80(3):572–578. doi: 10.1042/bj0800572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEHL E., JATZKEWITZ H. EVIDENCE FOR THE GENETIC BLOCK IN METACHROMATIC LEUCODYSTROPHY (ML). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:407–411. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER L. L., BLY C. G., WATSON M. L., BALE W. F. The dominant role of the liver in plasma protein synthesis; a direct study of the isolated perfused rat liver with the aid of lysine-epsilon-C14. J Exp Med. 1951 Nov;94(5):431–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.94.5.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY A. B. Comparative studies on the liver sulphatases. Biochem J. 1958 Mar;68(3):519–528. doi: 10.1042/bj0680519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY A. B. The sulphatase of ox liver. 3. Further observations on sulphatase B and an investigation of the origin of fractions A and B. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):465–470. doi: 10.1042/bj0570465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY A. B. The sulphatase of ox liver. I. The complex nature of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):12–15. doi: 10.1042/bj0530012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY A. B. The sulphatase of ox liver. I. The complex nature of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):12–15. doi: 10.1042/bj0530012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROEN P., NILSSON B., WIQVIST N., DICZFALUSY E. Pattern of oestriol conjugates in human cord blood, amniotic fluid, and urine of newborns. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1961 Nov;38:361–382. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0380361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIALA R., GIANETTO R. The binding of sulphatase by rat-liver particles as compared to that of acid phosphatase. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1955 Sep;33(5):839–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WUSTEMAN F. S., DODGSON K. S., LLOYD A. G., ROSE F. A., TUDBALL N. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY IN THE STUDY OF ESTER SULPHATES. J Chromatogr. 1964 Nov;16:334–339. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82495-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Edson M., McCarter J. A. The measurement of radioactive sulphur (S) in biological material. Biochem J. 1949;44(2):179–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


