Abstract
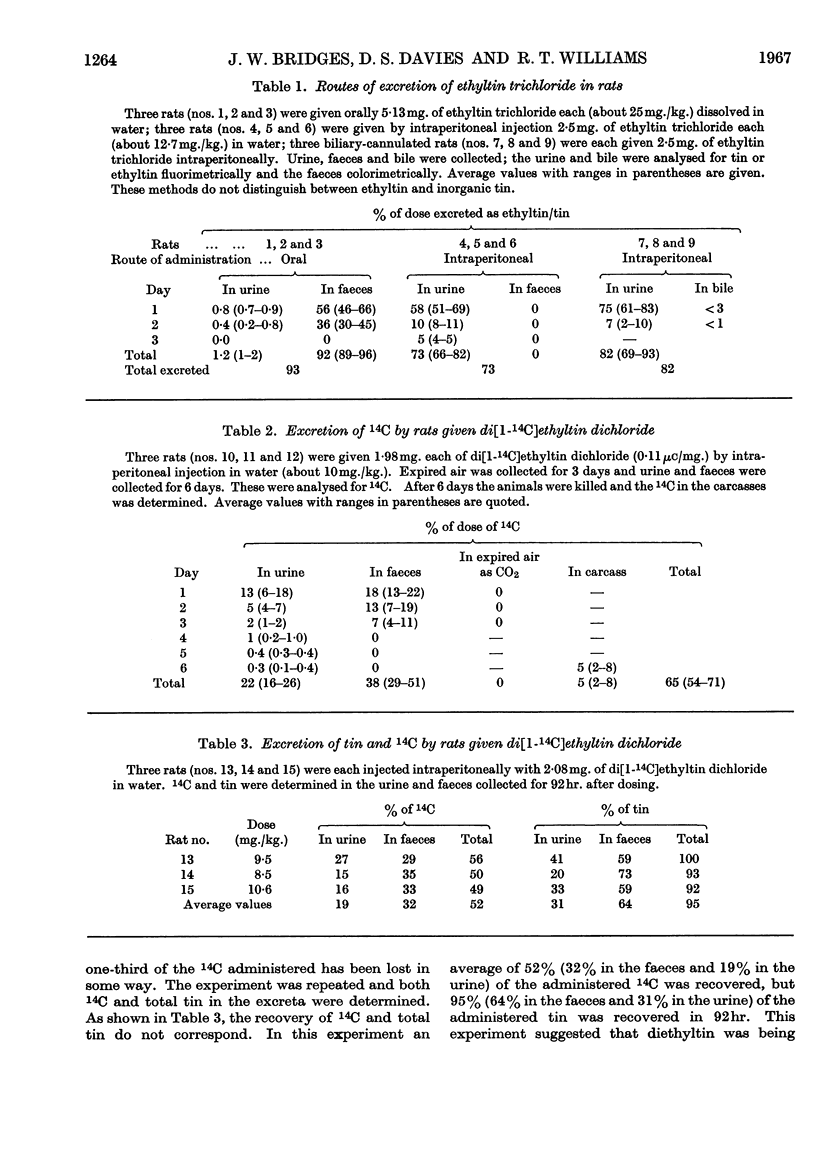
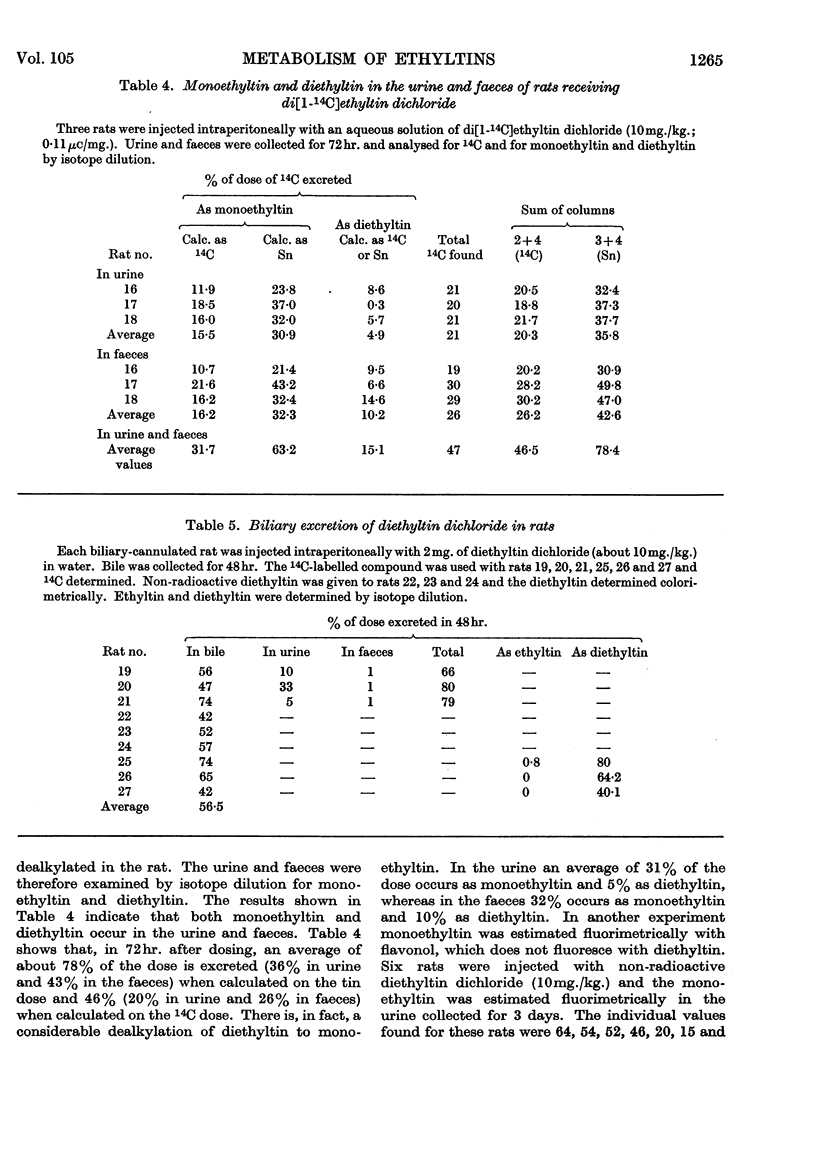
1. Ethyltin trichloride does not appear to be metabolized by the rat. When given orally excretion occurs almost entirely in the faeces, and when given intraperitoneally it occurs exclusively in the urine. Biliary excretion is almost negligible. 2. Di[1-14C]ethyltin dichloride has been synthesized. When given intraperitoneally it is excreted in the urine and faeces in the ratio about 1:2. Both the urine and faeces contain ethyltin3+ and diethyltin2+. Diethyltin is also excreted extensively in the bile. Di[14C]ethyltin is not converted into 14CO2 in the rat. 3. About 50% of the injected diethyltin dichloride is de-ethylated to ethyltin3+. Since ethyltin and diethyltin are found in the urine and faeces after intraperitoneal injection of diethyltin dichloride and since only diethyltin is excreted in the bile, then the de-ethylation of diethyltin occurs in the body tissues and the gut. 4. The conversion of diethyltin into ethyltin has been demonstrated in a preparation of rat caecal contents, but not in liver homogenates. 5. The dealkylation of diethyltin2+ to ethyltin3+ in the rat is discussed and it is suggested that the ethyl group is lost as ethane.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-El-Makarem M. M., Millburn P., Smith R. L., Williams R. T. Biliary excretion of foreign compounds. Benzene and its derivatives in the rat. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1269–1274. doi: 10.1042/bj1051269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNES J. M., STONER H. B. The toxicology of tin compounds. Pharmacol Rev. 1959 Jun;11(2 Pt 1):211–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH A. N., WILLIAMS R. T. Dehydroxylation of caffeic acid by rat and rabbit caecal contents and sheep rumen liquor. Nature. 1963 May 18;198:684–685. doi: 10.1038/198684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMER J. E. The biochemistry of organotin compounds; the conversion of tetraethyltin into triethyltin in mammals. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):685–692. doi: 10.1042/bj0680685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millburn P., Smith R. L., Williams R. T. Biliary excretion in foreign compounds. Sulphonamide drugs in the rat. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1283–1287. doi: 10.1042/bj1051283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


