Abstract
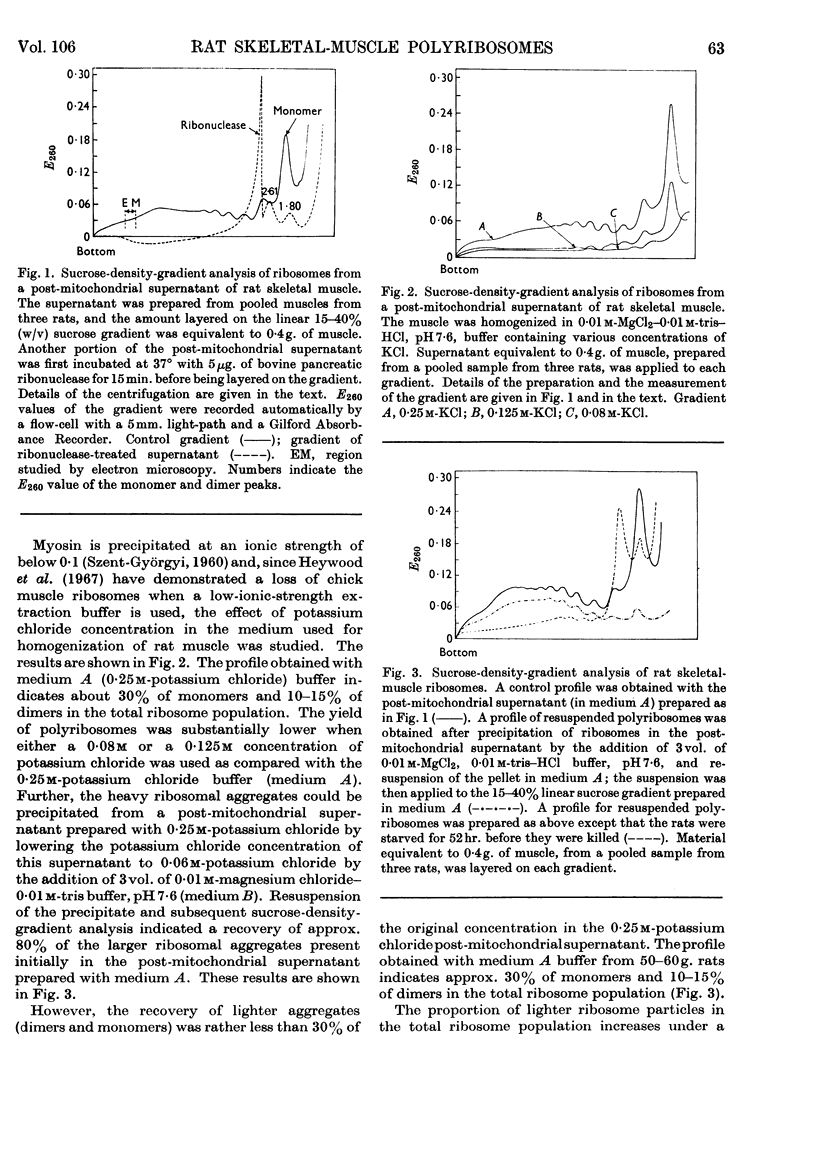
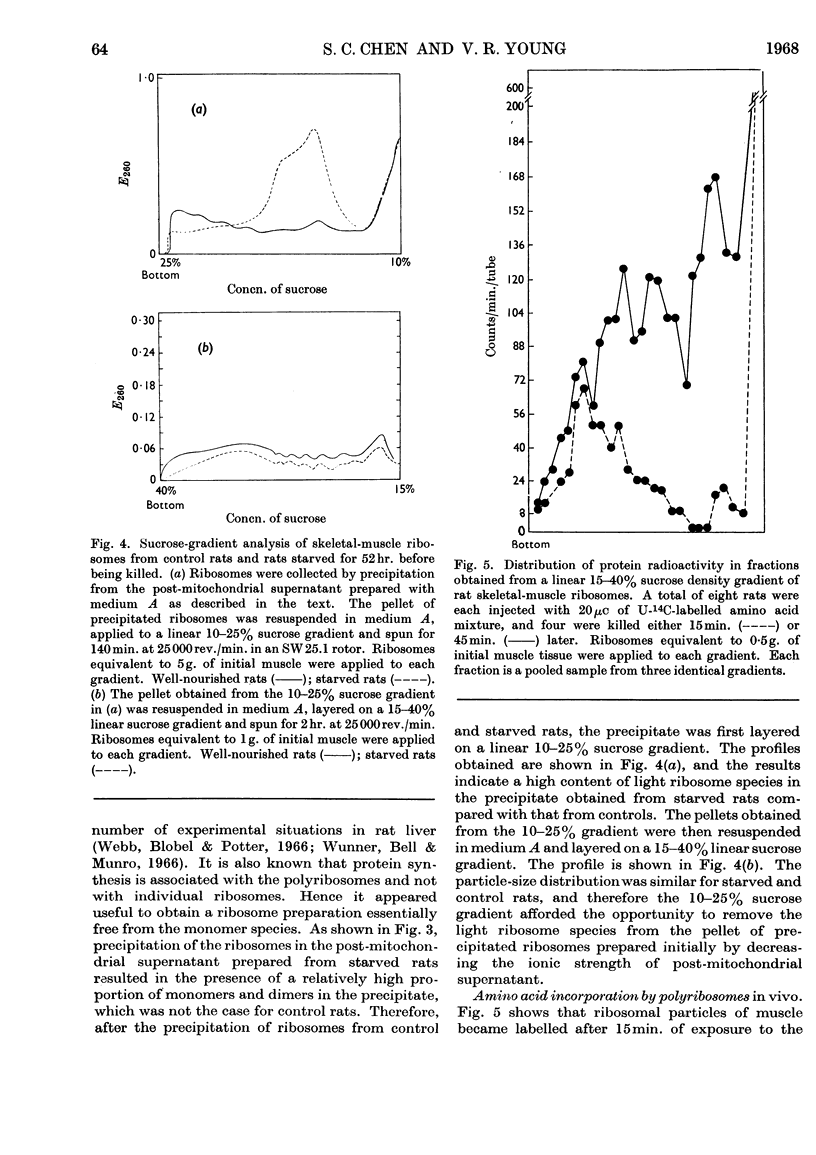
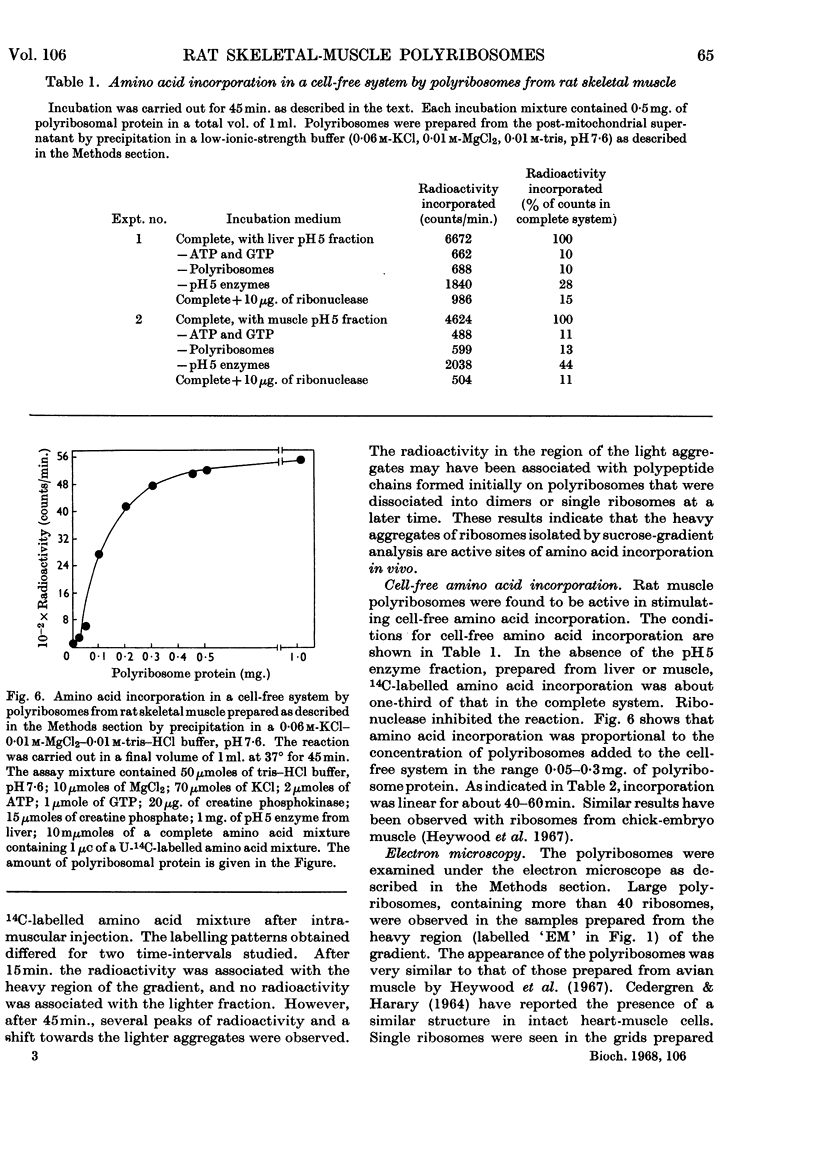
1. A method is described for the sucrose-gradient sedimentation analysis of ribosomes in a post-mitochondrial supernatant of rat skeletal muscle. 2. An essential feature of the method involves the use of buffer of ionic strength 0·3 for homogenization of the muscle tissue. 3. Polyribosomes can be prepared by precipitation from post-mitochondrial supernatant of skeletal muscle by adjustment of the potassium chloride content of the medium. These polyribosomes stimulate cell-free amino acid incorporation in vitro in an energy-dependent system. 4. Ribosome aggregates of uniform size distribution can be obtained by adjustment of the ionic strength of the post-mitochondrial supernatant, followed by differential sucrose-gradient centrifugation. 5. In vivo, rat skeletal-muscle polyribosomes became labelled by 14C-labelled amino acid within 15min., and radioactivity was associated with the light ribosome species within 45min. 6. Electron microscopy of the polyribosomes revealed aggregations containing more than 40 single ribosomes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BREUER C. B., DAVIES M. C., FLORINI J. R. AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEIN BY CELL-FREE PREPARATIONS FROM RAT SKELETAL MUSCLE. II. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF MUSCLE RIBOSOMES AND POLYRIBOSOMES. Biochemistry. 1964 Nov;3:1713–1719. doi: 10.1021/bi00899a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuer C. B., Florini J. R. Amino acid incorporation into protein by cell-free systems from rat skeletal muscle. IV. Effects of animal age, androgens, and anabolic agents on activity of muscle ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1965 Aug;4(8):1544–1550. doi: 10.1021/bi00884a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Roberts R. B. High-Resolution Density Gradient Sedimentation Analysis. Science. 1960 Jan 1;131(3392):32–33. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3392.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEDERGREN B., HARARY I. IN VITRO STUDIES ON SINGLE BEATING RAT HEART CELLS. VI. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES OF SINGLE CELLS. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Dec;11:428–442. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifford J. I., Rees K. R. The action of aflatoxin B1 on the rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):65–75. doi: 10.1042/bj1020065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EARL D. C., KORNER A. THE ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC RIBOSOMES AND POLYSOMES. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:721–734. doi: 10.1042/bj0940721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Breuer C. B. Amino acid incorporation into protein by cell-free systems from rat skeletal muscle. V. Effects of pituitary growth hormone on activity of ribosomes and ribonucleic acid polymerase in hypophysectomized rats. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):1870–1876. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIERER A. Function of aggregated reticulocyte ribosomes in protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1963 Feb;6:148–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood S. M., Dowben R. M., Rich A. The identification of polyribosomes synthesizing myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1002–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLER E. B., ZAMECNIK P. C. The effect of guanosine diphosphate and triphosphate on the incorporation of labeled amino acids into proteins. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jul;221(1):45–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy M. R. Protein synthesis in growing-rat tissues. II. Polyribosome concentration of brain and liver as a function of age. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 22;119(3):599–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RISEBROUGH R. W., TISSIERES A., WATSON J. D. Messenger-RNA attachment to active ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Mar 15;48:430–436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.3.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampersad O. R., Zak R., Rabinowitz M., Wool I. G., DeSalle L. Isolation and characterization of ribonucleoprotein particles from heart muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 6;108(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Tashiro Y., Palade G. E. On the attachment of ribosomes to microsomal membranes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):503–524. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox H. C., Jr, Hoagland M. B. Functional alterations in rat liver polysomes associated with starvation and refeeding. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER J. R., KNOPF P. M., RICH A. A multiple ribosomal structure in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WETTSTEIN F. O., STAEHELIN T., NOLL H. Ribosomal aggregate engaged in protein synthesis: characterization of the ergosome. Nature. 1963 Feb 2;197:430–435. doi: 10.1038/197430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. E., Blobel G., Potter V. R. Polyribosomes in rat tissues. 3. The response of the polyribosome pattern of rat liver to physiologic stress. Cancer Res. 1966 Feb;26(2):253–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Bell J., Munro H. N. The effect of feeding with a tryptophan-free amino acid mixture on rat-liver polysomes and ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):417–428. doi: 10.1042/bj1010417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


