Abstract
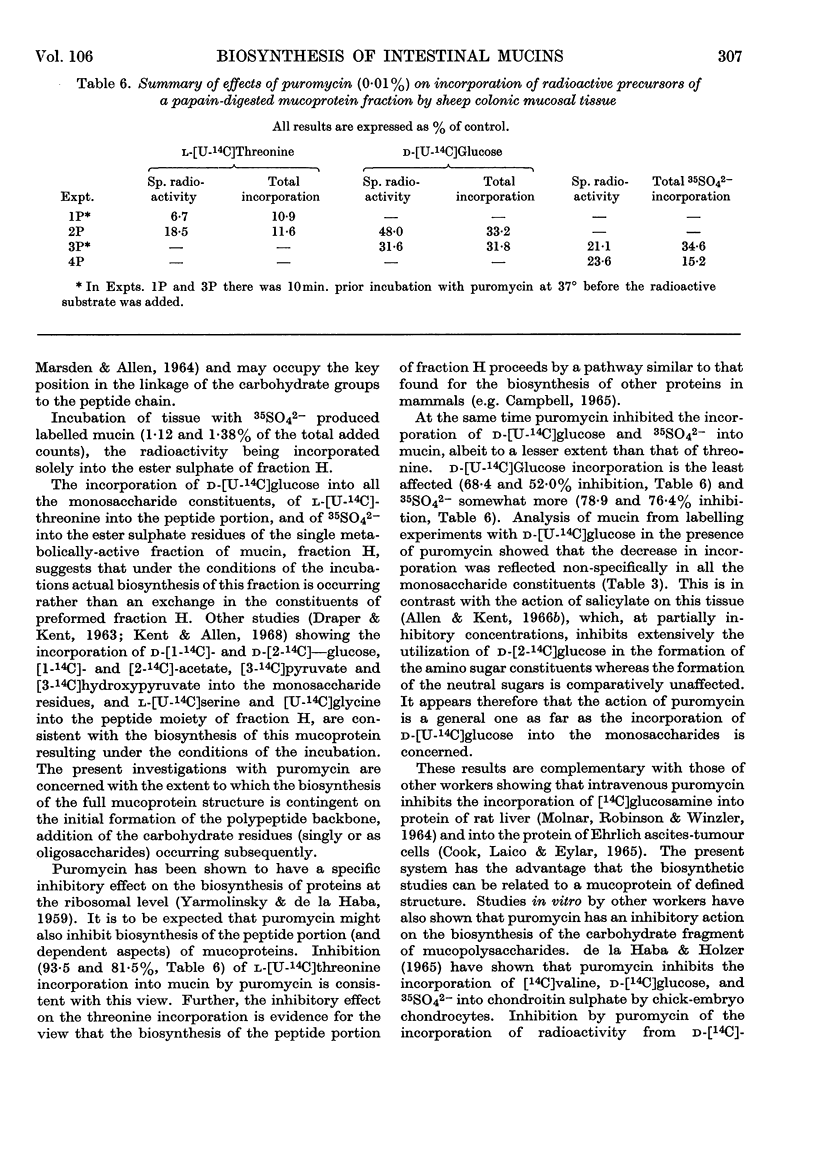
1. Surviving sheep colonic mucosal tissue incorporated l-[U-14C]threonine when incubated in Krebs medium III at 37° in an atmosphere of oxygen, into a well-characterized mucoprotein fraction, isolated by papain digestion of the incubated scrapings. 2. Acidic hydrolysis and chromatography of the labelled mucoprotein showed that threonine was the only constituent to become labelled. In the presence of puromycin the incorporation of l-[U-14C]threonine was considerably diminished (6·7 and 18·5% of control in duplicate experiments). Furthermore, puromycin also decreased incorporation of radioactivity from d-[U-14C]-glucose (48·0 and 31·6% of control) and 35SO42− (21·2 and 23·6% of control) into the mucoprotein fraction. 3. In a puromycin-inhibited system, with d-[U-14C]-glucose, where the overall specific radioactivity of the mucoprotein was 48% of control, the labelling of the individual monosaccharide constituents (as% of control) was: N-acetylneuraminic acid, 44%; N-glycollylneuraminic acid, 61%; hexosamines, 46%; fucose, 68%; galactose, 34%.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Haba G., Holtzer H. Chondroitin sulfate: inhibition of synthesis by puromycin. Science. 1965 Sep 10;149(3689):1263–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3689.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper P., Kent P. W. Biosynthesis of intestinal mucins. 4. Utilization of [1-C]glucose by sheep colonic mucosa in vitro. Biochem J. 1963 Feb;86(2):248–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0860248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOREY H. W. The secretion and function of intestinal mucus. Gastroenterology. 1962 Sep;43:326–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDELL S. Determination of hexosamines. Methods Biochem Anal. 1958;6:289–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. A., ROBERTS G. P. Some aspects of the structure of macromolecular constituents of epithelial mucus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 30;106:218–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb16640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK A. The basic structure of glycoproteins and problems of their chemical and physiochemical analysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 30;106:168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb16636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO Y., TSUIKI S., NISIZAWA K., PIGMAN W. Action of proteolytic enzymes on purified bovine submaxillary mucin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 30;106:233–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb16641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT P. W. The chemistry of mucoproteins: an introduction to gastrointestinal mucus. Gastroenterology. 1962 Sep;43:292–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNFELD S., KORNFELD R., NEUFELD E. F., O'BRIEN P. J. THE FEEDBACK CONTROL OF SUGAR NUCLEOTIDE BIOSYNTHESIS IN LIVER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:371–379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A. Body size and tissue respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):249–269. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVVY G. A., MCALLAN A. The N-acetylation and estimation of hexosamines. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:127–132. doi: 10.1042/bj0730127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLNAR J., ROBINSON G. B., WINZLER R. J. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF GLYCOPROTEINS. 3. GLUCOSAMINE INTERMEDIATES IN PLASMA GLYCOPROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN LIVERS OF PUROMYCIN-TREATED RATS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3157–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN W. T., WATKINS W. M. Some aspects of the biochemistry of the human blood-group substances. Br Med Bull. 1959 May;15(2):109–113. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. M. Filter-paper partition chromatography of sugars: 1. General description and application to the qualitative analysis of sugars in apple juice, egg white and foetal blood of sheep. with a note by R. G. Westall. Biochem J. 1948;42(2):238–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0420238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarcione E. J., Carmody P. J. Incorporation of D-galactose into liver microsomal protein in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Mar 22;22(6):689–694. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins W. M. Blood-group substances. Science. 1966 Apr 8;152(3719):172–181. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3719.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmolinsky M. B., Haba G. L. INHIBITION BY PUROMYCIN OF AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Dec;45(12):1721–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.12.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



