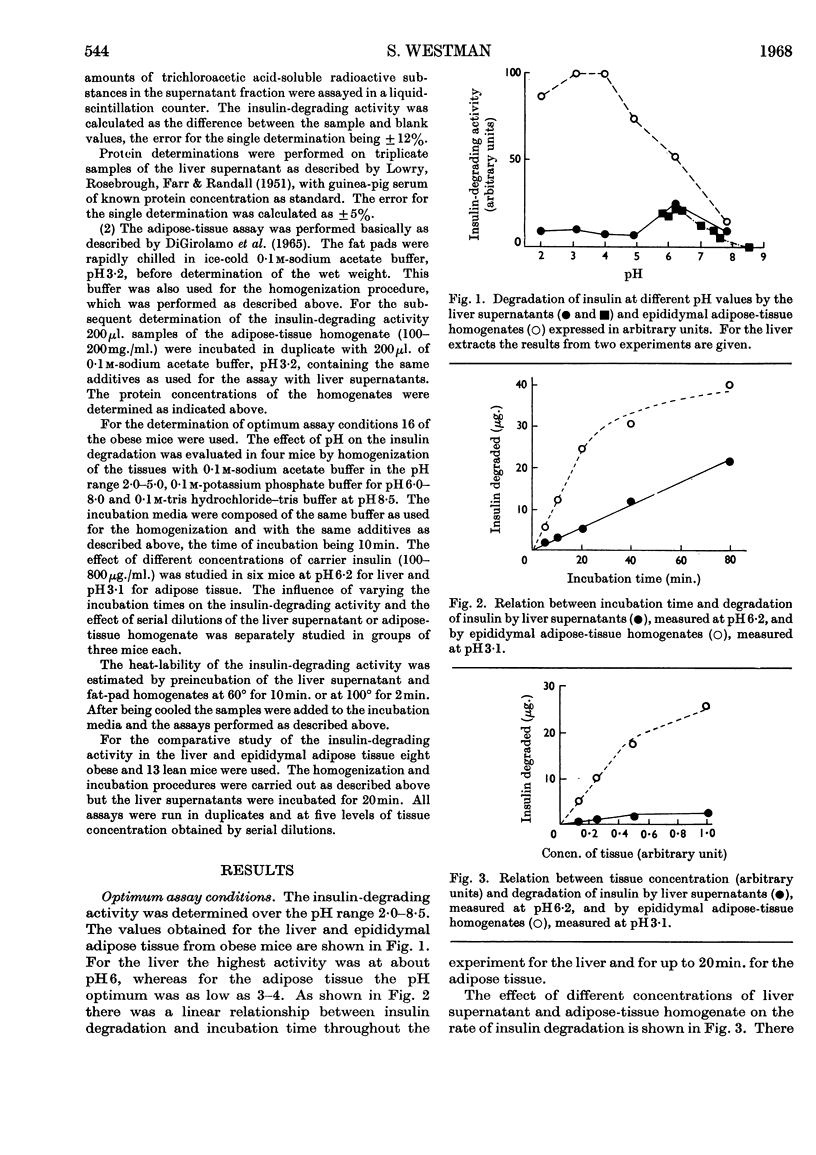
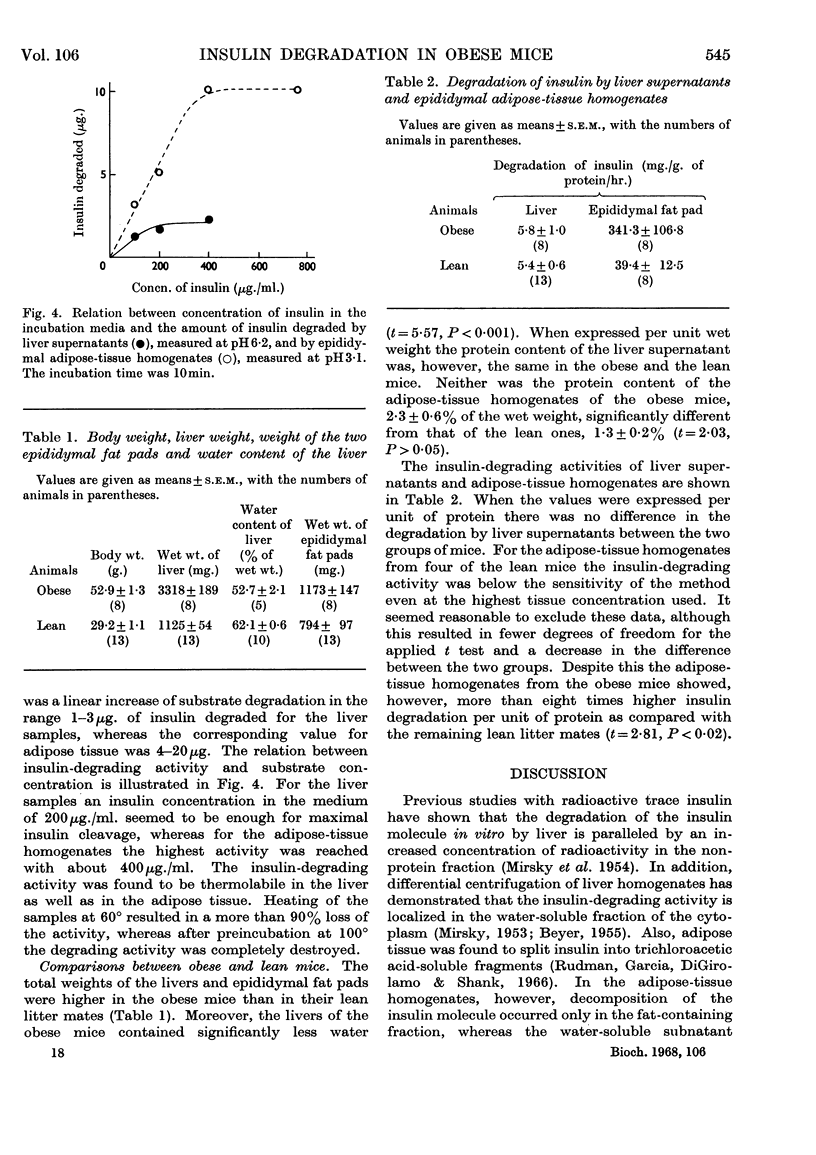
Abstract
The insulin-degrading activity of liver supernatants and epididymal adipose-tissue homogenates from genetically obese–hyperglycaemic mice (ob ob) and their lean litter mates was studied by measurement of radioactive trichloroacetic acid-soluble degradation products of the insulin molecule. Optimum assay conditions for the decomposition of the hormone were devised. The properties of the degrading activity suggested the presence of enzymic insulin destruction in both the liver and epididymal adipose tissue. There was no difference in insulin degradation in liver samples from obese and lean mice when the results were related to the protein content of the supernatants. The epididymal adipose-tissue homogenates from obese mice displayed about eightfold higher degrading activity per unit of protein than did homogenates from lean animals. The physiological significance of this finding is discussed in the light of the increased fat depots, hyperphagia, raised serum insulin concentrations and increased insulin tolerance previously recorded in this strain of mice.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATES M. W., NAUSS S. F., HAGMAN N. C., MAYER J. Fat metabolism in three forms of experimental obesity; body composition. Am J Physiol. 1955 Feb;180(2):301–303. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.180.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROH-KAHN R. H., SIMKIN B., MIRSKY A. The inactivation of insulin by tissue extracts. V. The effect of the composition of the diet on the restoration of the liver insulinase activity of the fasted rat. Arch Biochem. 1950 Jun;27(1):174–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIENGOTT D., MIRSKY I. A., PERISUTTI G. Effect of fasting on insulinase activity and on hypoglycemic response to insulin. Endocrinology. 1957 Feb;60(2):303–307. doi: 10.1210/endo-60-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIGIROLAMO M., RUDMAN D., MALKIN M. F., GARCIA L. A. INACTIVATION OF INSULIN BY ADIPOSE TISSUE. Diabetes. 1965 Feb;14:87–92. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.2.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLMAN B., LARSSON S., WESTMAN S. The metabolism of variously labelled glucose in fatty livers from mice with congenital hyperglycaemia and obesitas. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1962 Mar;39:457–464. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0390457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZEN H. M., STETTEN D., Jr Hepatic glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Diabetes. 1962 Jul-Aug;11:271–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER J., BATES M. W., DICKIE M. M. Hereditary diabetes in genetically obese mice. Science. 1951 Jun 29;113(2948):746–747. doi: 10.1126/science.113.2948.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY I. A. Insulinase, insulinase-inhibitors, and diabetes mellitus. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1957;13:429–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY I. A., PERISUTTI G., DIXON F. J. Destruction of I131 labeled insulin by liver slices. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Jun;86(2):228–230. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Garcia L. A., DiGirolamo M., Shank P. W. Cleavage of bovine insulin by rat adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1966 Jan;78(1):169–185. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABO I. DIE ROLLE DER INSULINASE IN DER PATHOGENESE DES DIABETES MELLITUS. Endokrinologie. 1964 May;46:111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schucher R. Studies on the metabolism of insulin by pancreas in vitro. I. Degradation of exogenous insulin by calf pancreas slices. Can J Biochem. 1965 Jul;43(7):1143–1156. doi: 10.1139/o65-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffacher W., Lambert A. E., Vecchio D., Renold A. E. Measurements of insulin activities in pancreas and serum of mice with spontaneous ("Obese" and "New Zealand Obese") and induced (Goldthioglucose) obesity and hyperglycemia, with considerations on the pathogenesis of the spontaneous syndrome. Diabetologia. 1967 Apr;3(2):230–237. doi: 10.1007/BF01222200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMIZAWA H. H. Mode of action of an insulin-degrading enzyme from beef liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:428–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMIZAWA H. H., VARANDANI P. T. GLUTATHIONE-INSULIN TRANSHYDROGENASE OF HUMAN LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:3191–3194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Mode of action of glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Studies on the precipitate produced by its action on insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 12;118(1):198–201. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


