Abstract
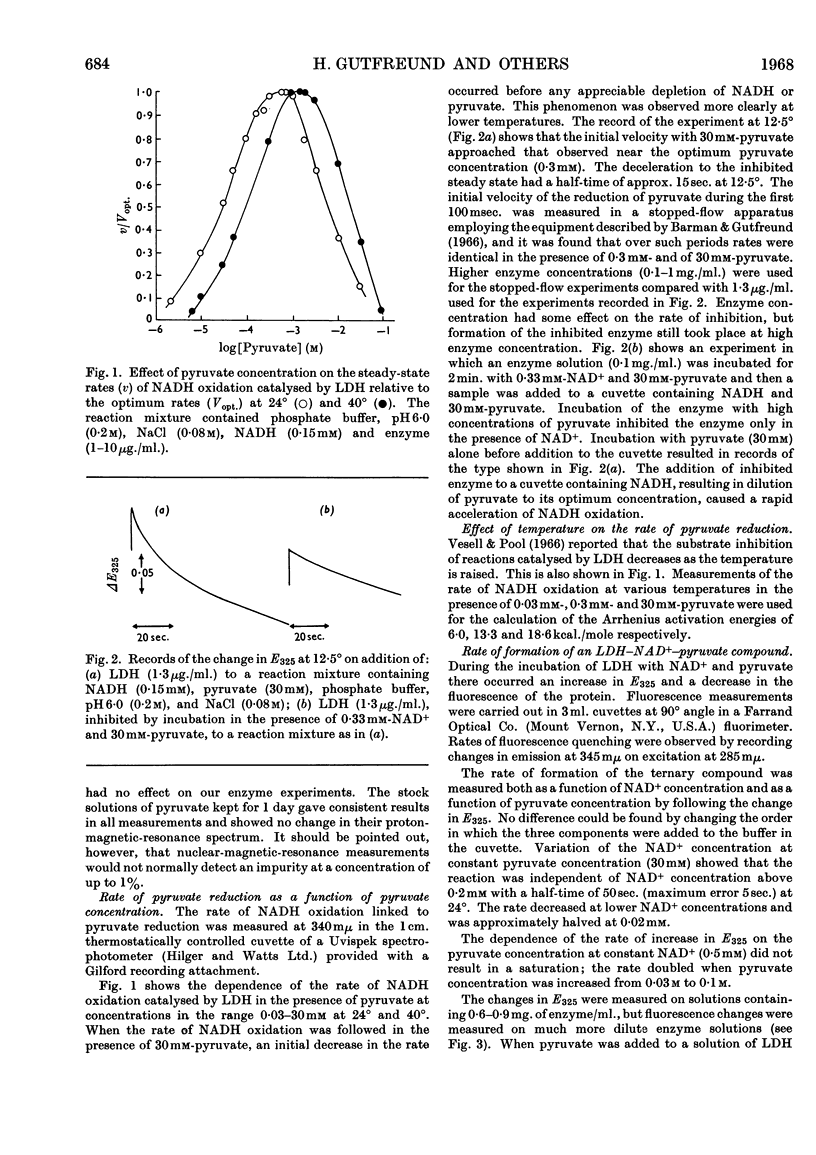
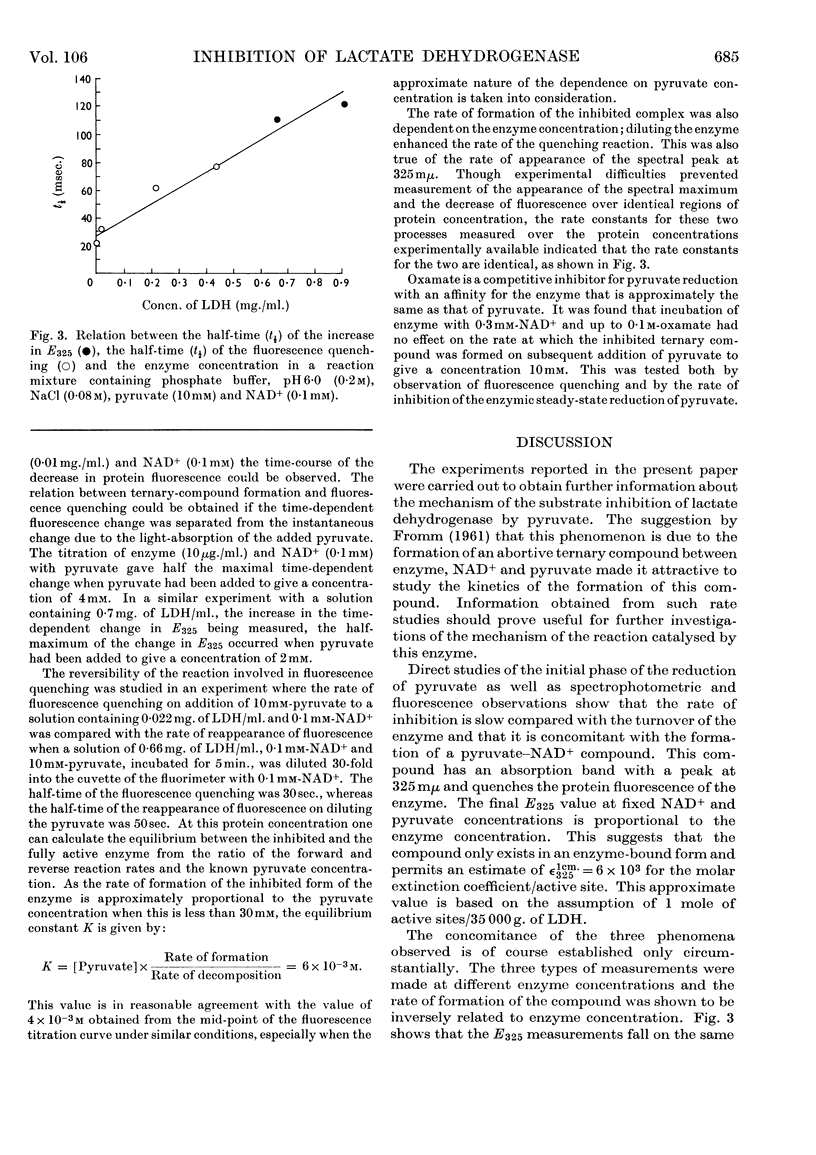
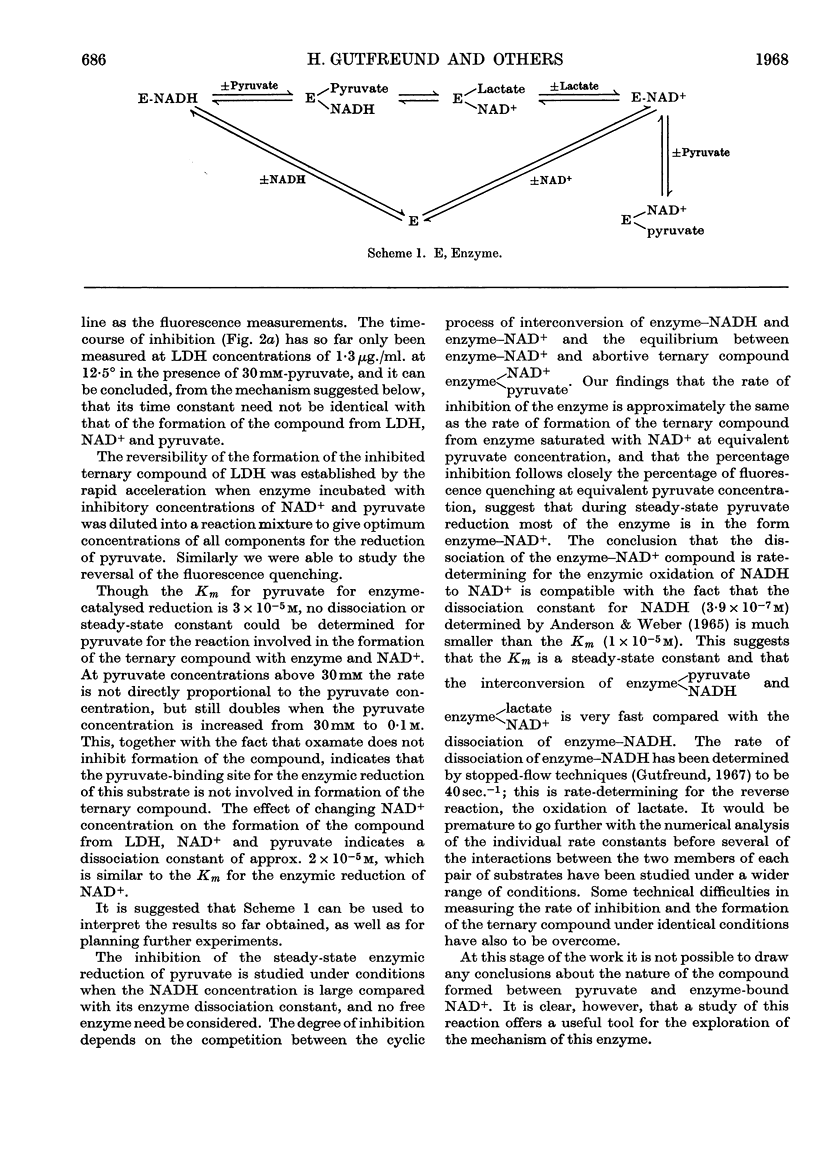
The inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase at high pyruvate concentration was studied in three ways. First, a rapid decrease in the rate of the enzyme reaction was observed; secondly, the rate of formation of a pyruvate–NAD+ compound was followed by the change in E325; thirdly, the rate of quenching of the protein fluorescence was measured. The data obtained at pH6·0 at different temperatures and ionic strengths as functions of pyruvate, NAD+ and enzyme concentrations show that the extent of inhibition can be correlated with the reversible formation of a compound between pyruvate and enzyme-bound NAD+. It is suggested that the detailed kinetic analysis of the formation of this abortive ternary compound will give pertinent information about properties of the enzyme–NAD+ compound involved in the normal catalytic process.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barman T. E., Gutfreund H. Optical and chemical identification of kinetic steps in trypsin- and chymotrypsin-catalysed reactions. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):411–416. doi: 10.1042/bj1010411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROMM H. J. Evidence for ternary-complex formation with rabbit-muscle lactic acid dehydrogenase, diphosphopyridine nucleotide and pyruvic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 2;52:199–200. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90919-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G., Criddle R. S. Substrate-dependent association of lactic dehydrogenase subunits to active tetramer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):680–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Pool P. E. Lactate and pyruvate concentrations in exercised ischemic canine muscle: relationship of tissue substrate level to lactate dehydrogenase isozyme pattern. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):756–762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


