Abstract
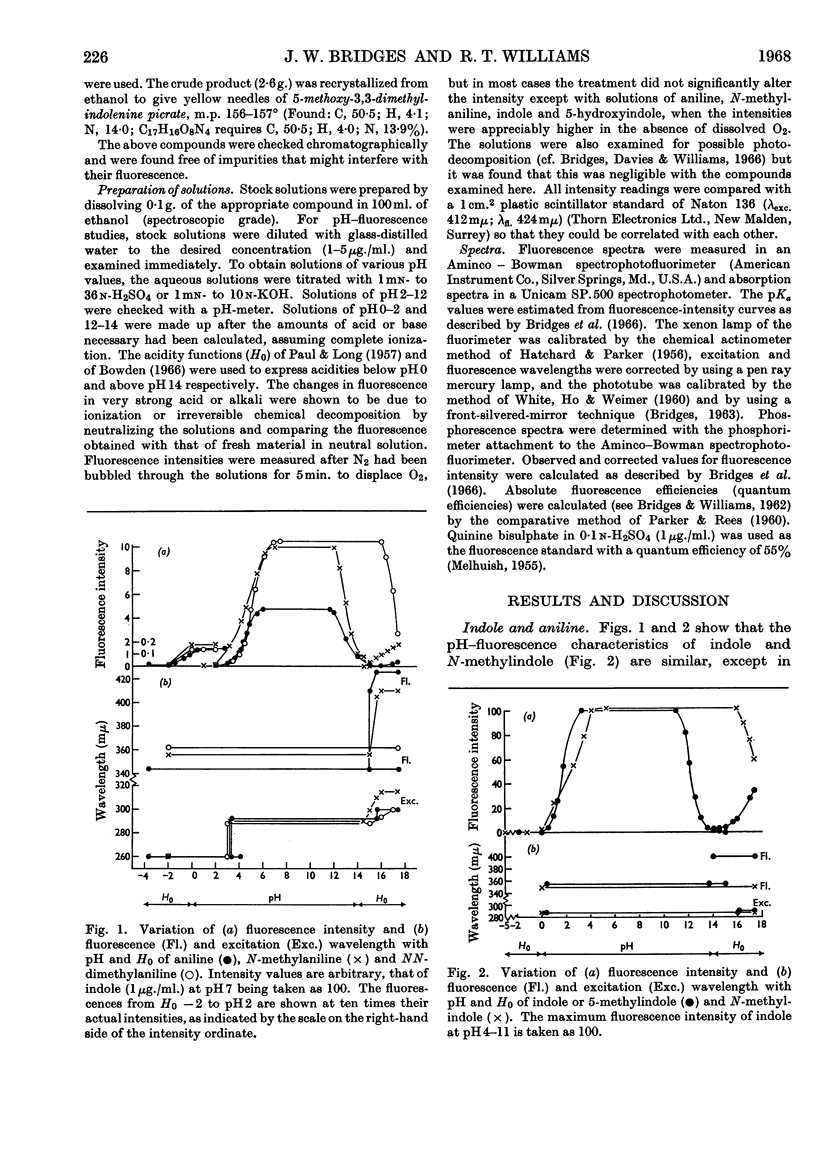
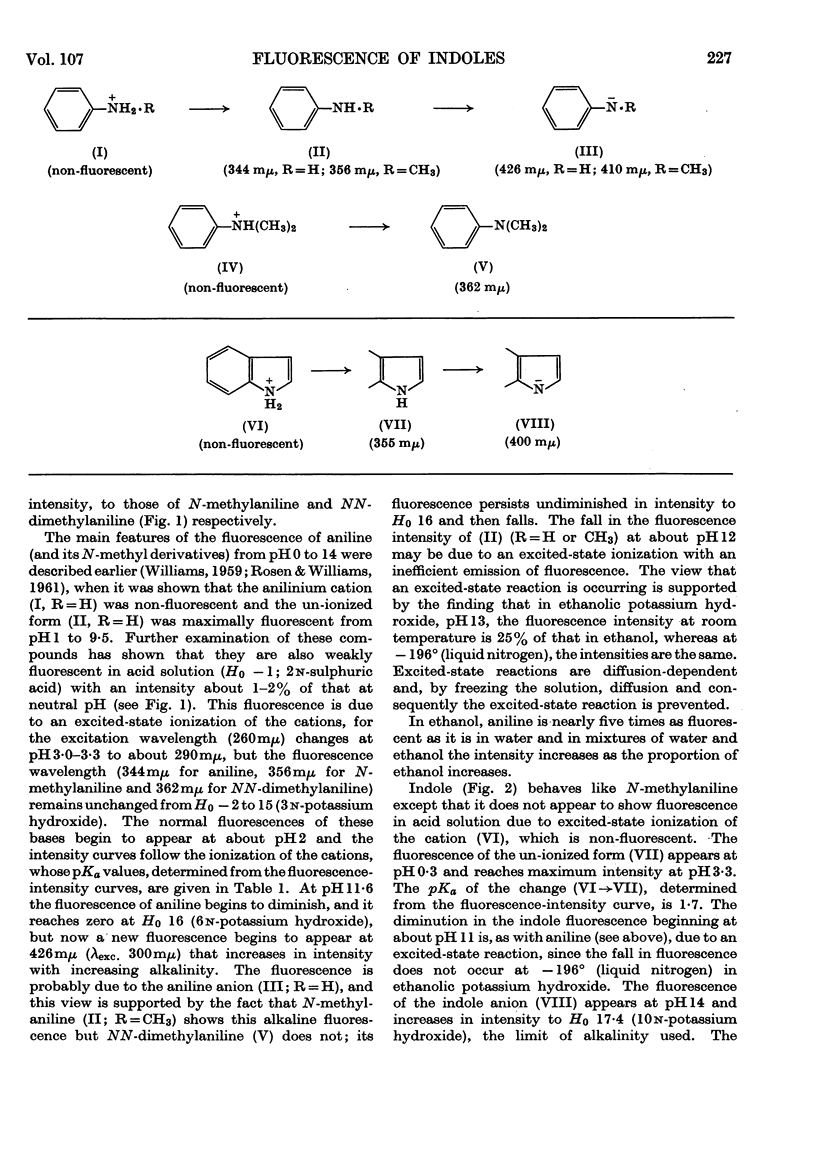
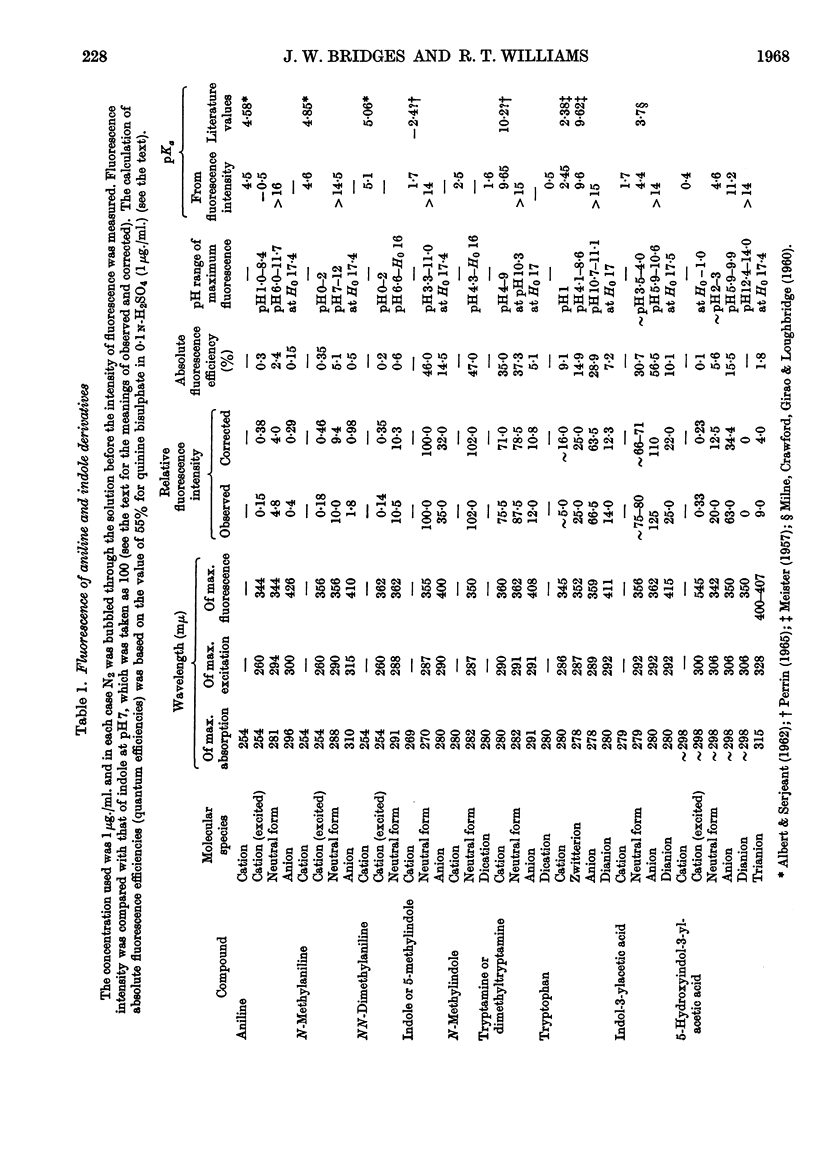
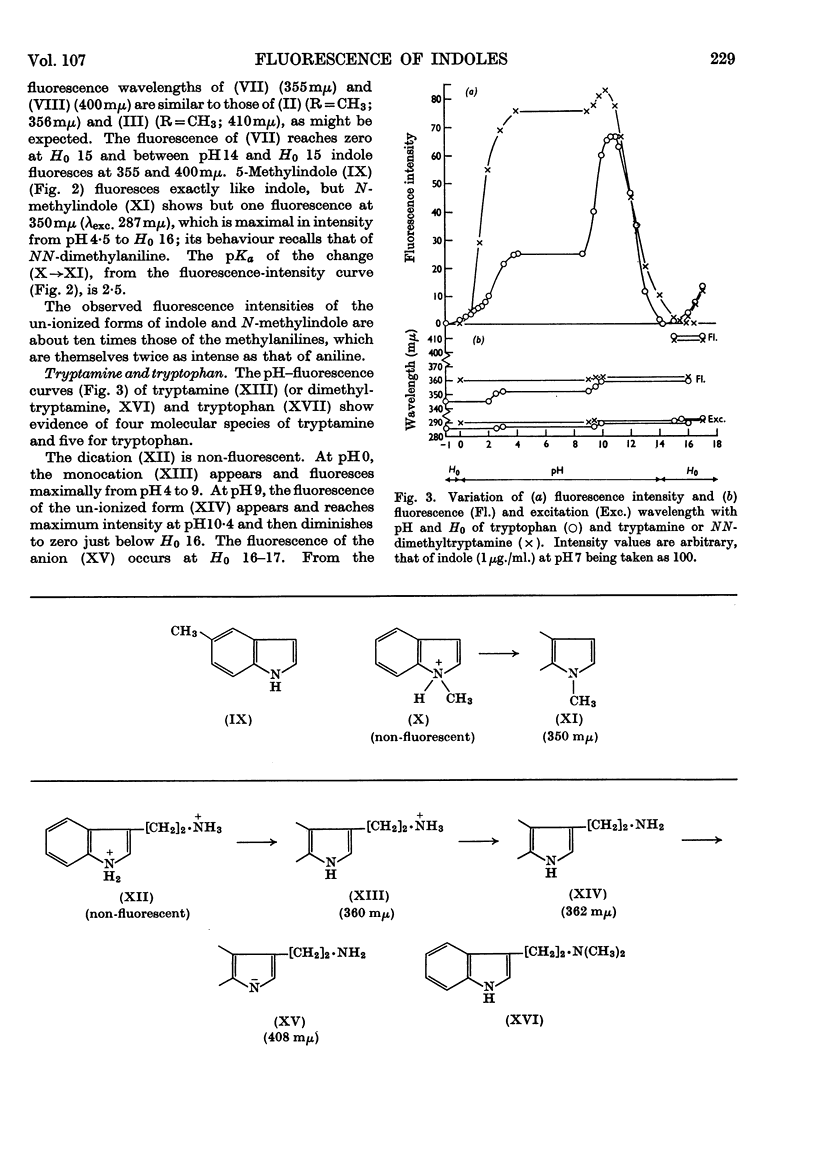
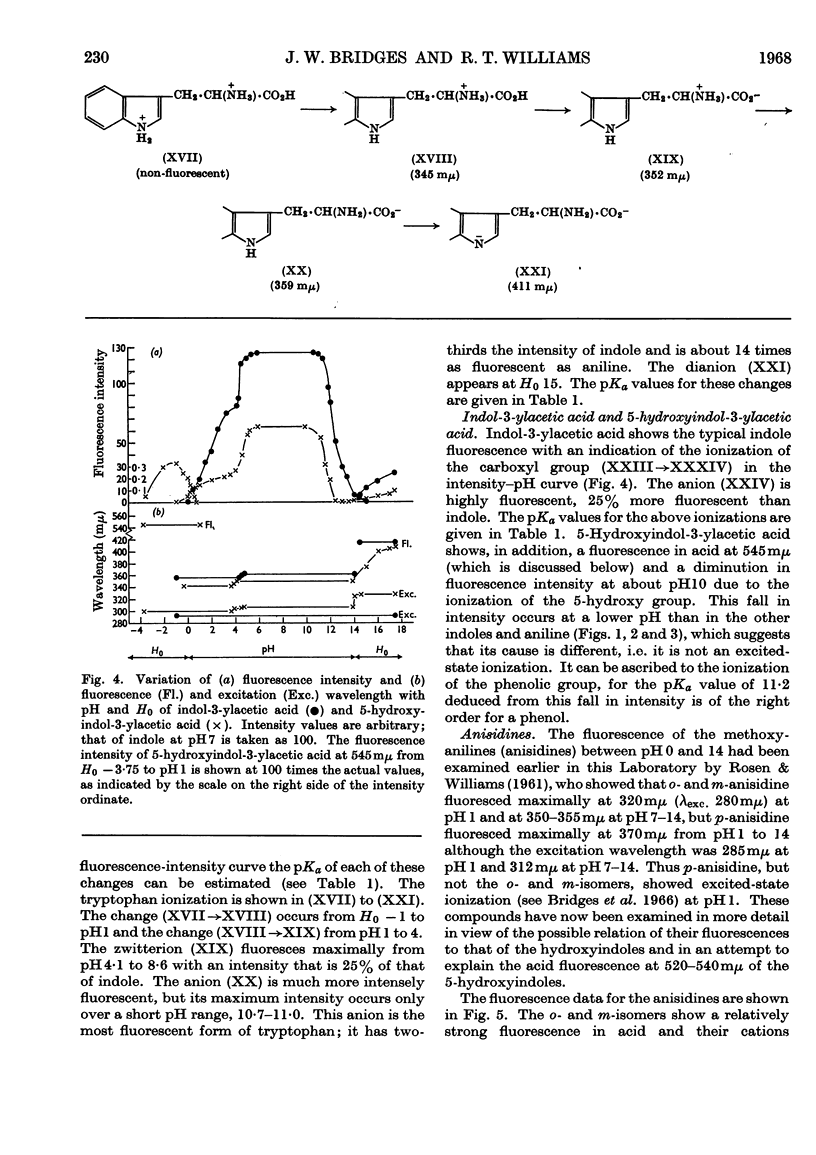
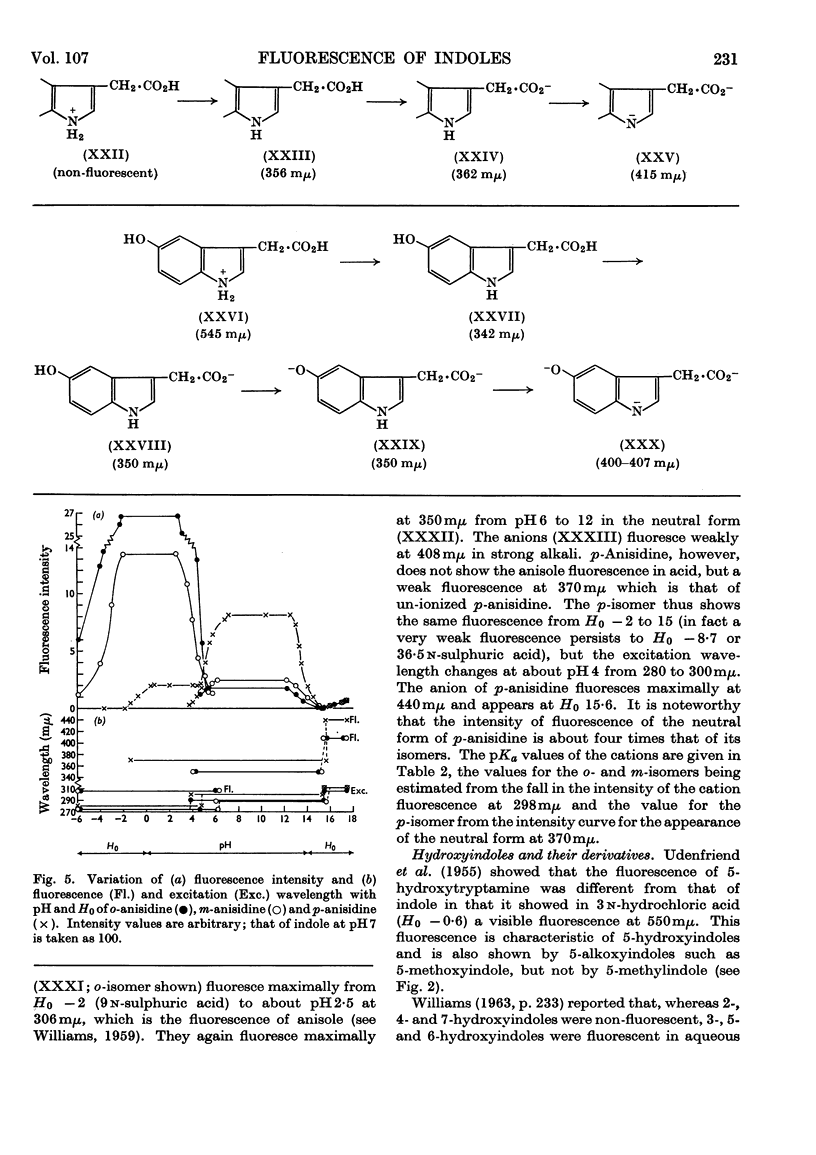
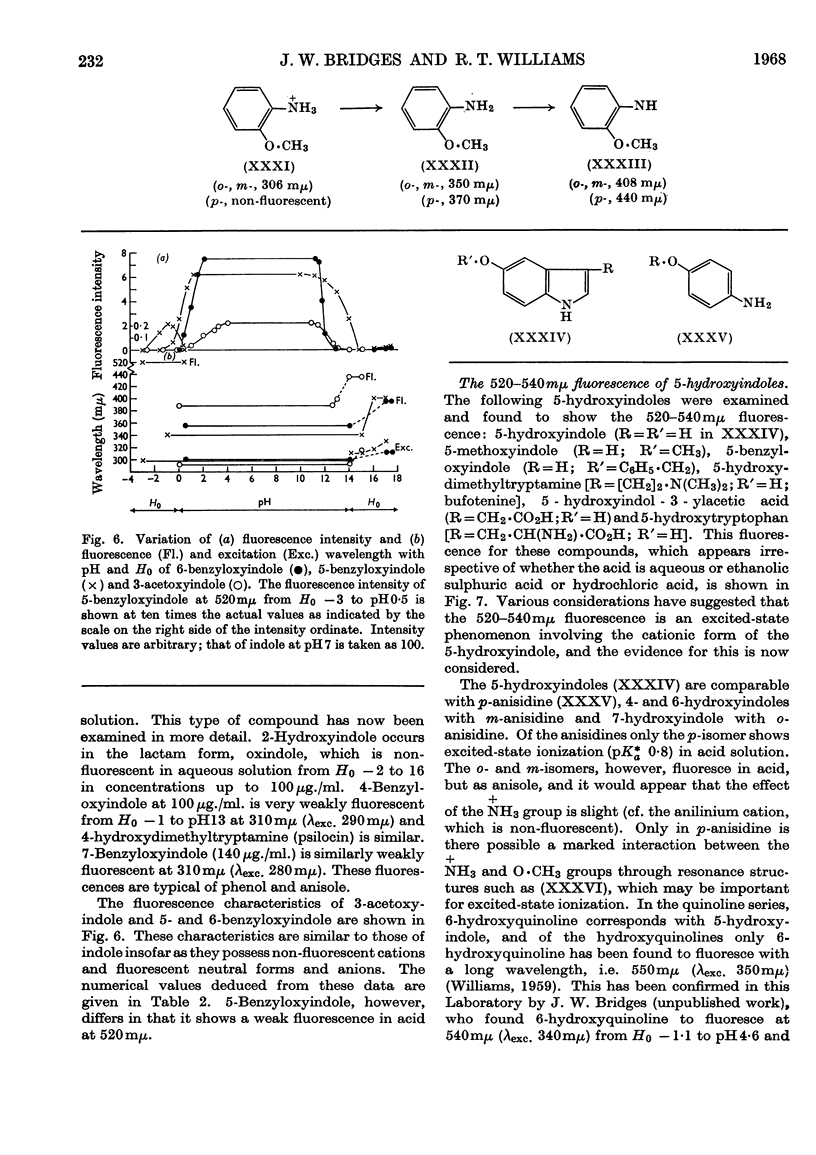
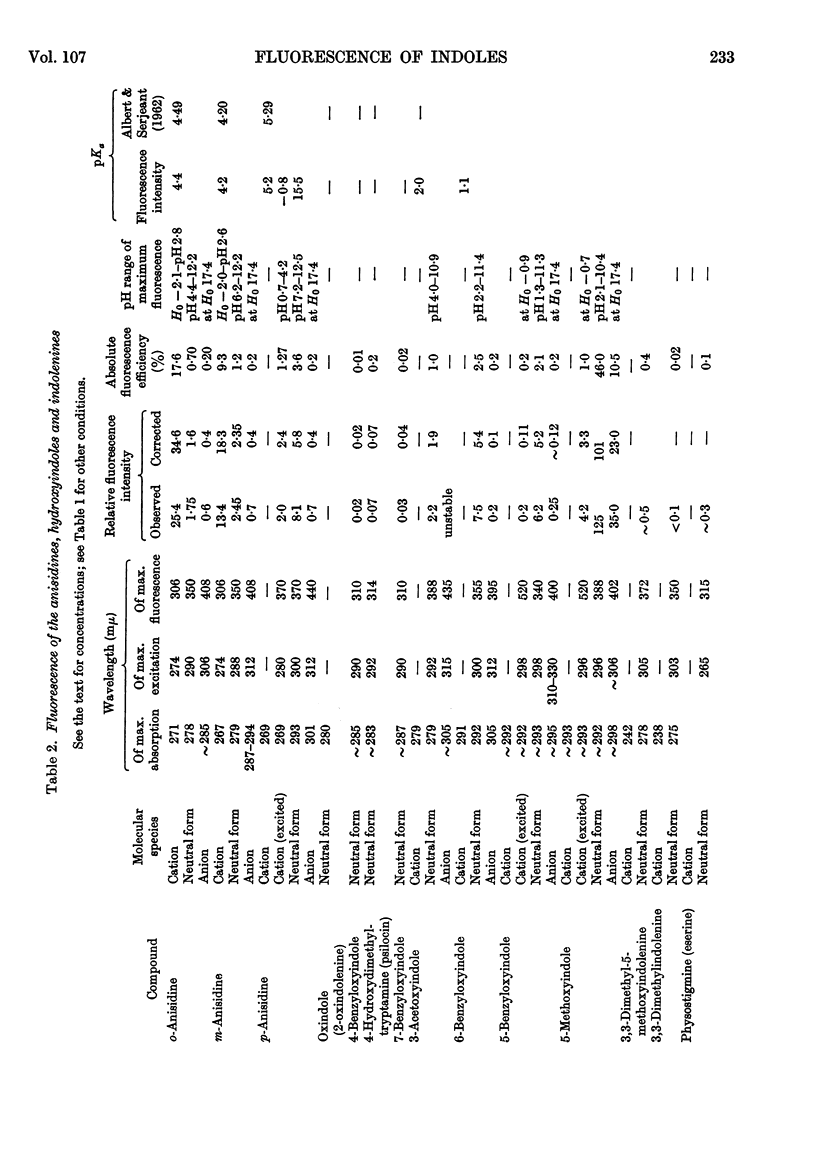
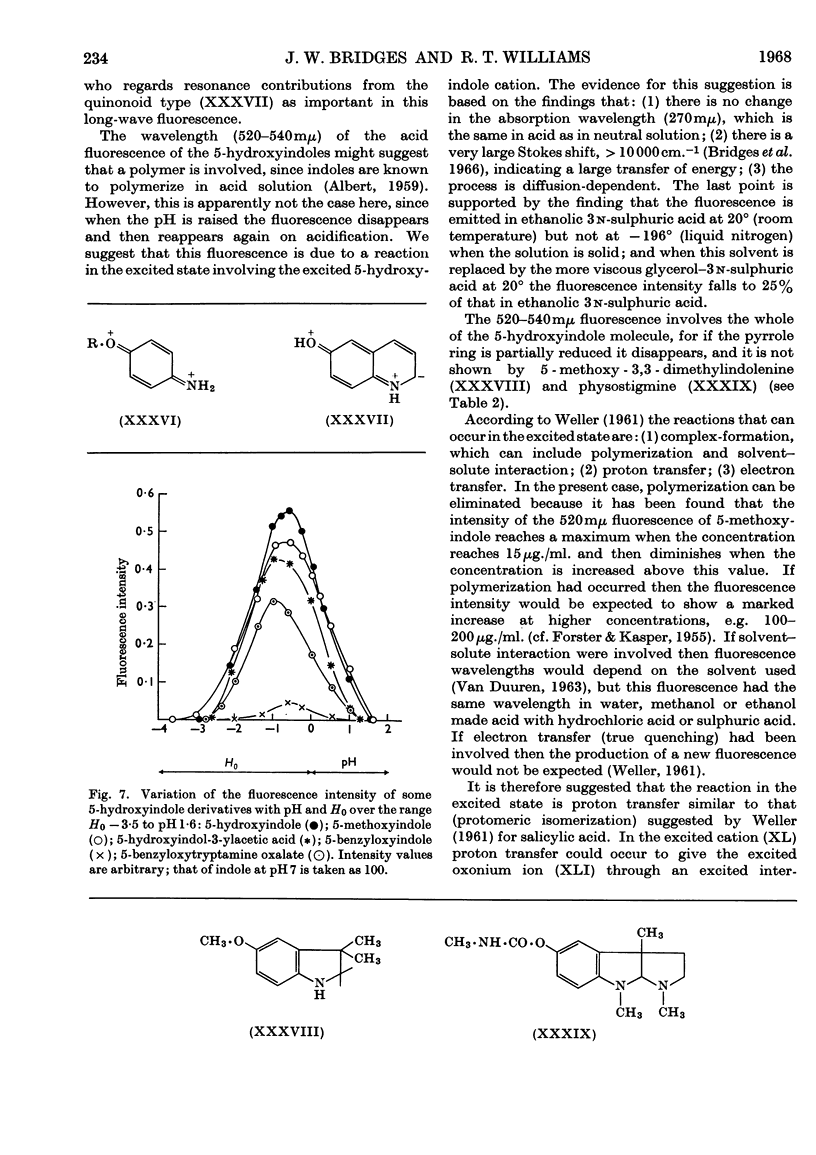
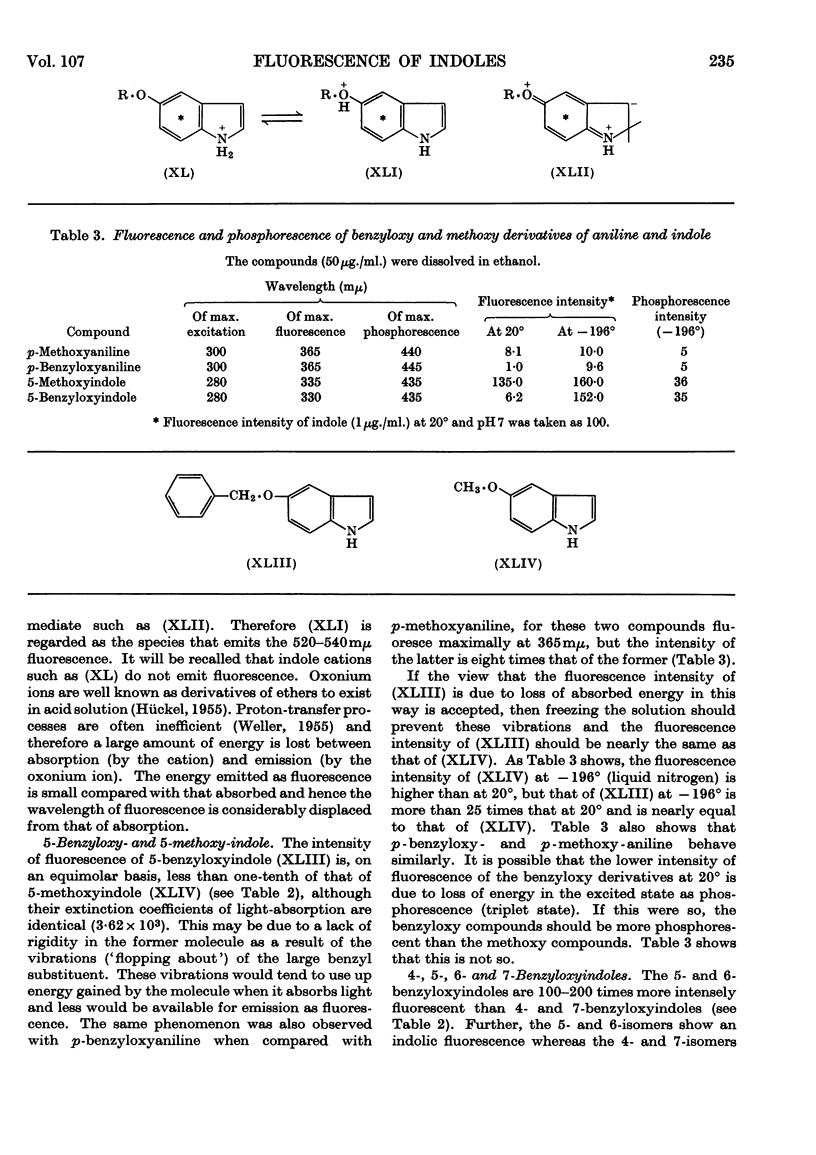
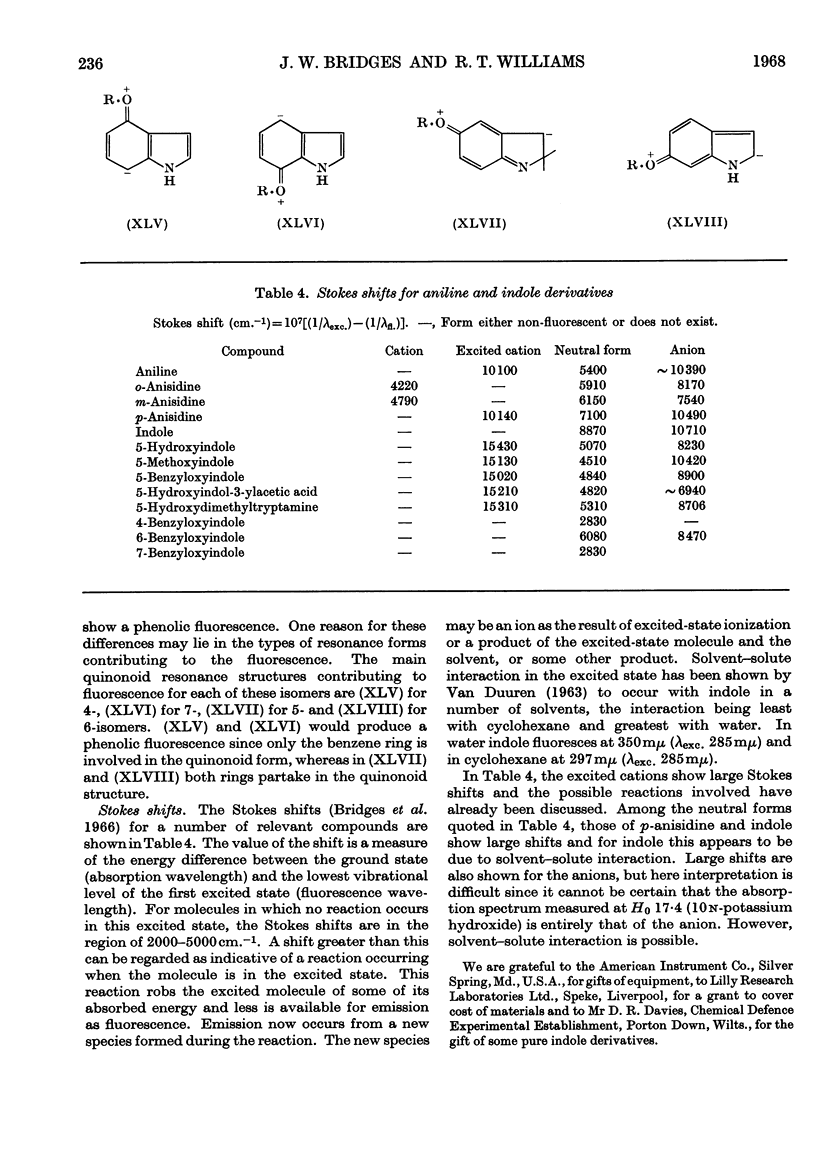
1. The variations in the excitation and fluorescence wavelengths and fluorescence intensities of a number of indole and aniline derivatives over a wide range of acidity and alkalinity (36n-sulphuric acid to 10n-potassium hydroxide) have been studied. 2. The changes in fluorescence with pH of the indoles and anilines had many characteristics in common, and the most fluorescent species were found to be the non-ionized or neutral forms showing fluorescence maxima at about λ 350mμ. 3. In 10n-potassium hydroxide most of the compounds examined, except those containing a tertiary nitrogen atom, showed a bathochromic shift in fluorescence wavelength attributable to an anion due to a negatively charged nitrogen, but in strong acid (3n-sulphuric acid) these compounds were non-fluorescent, except the anisidines and the 5-hydroxyindoles. 4. p-Anisidine but not the o- and m-isomers showed excited-state ionization in acid solution. 5. Of the hydroxyindoles only the 5-hydroxy derivatives showed a fluorescence (λmax. 520–540mμ) in acid solution. It is suggested that this fluorescence is due to a proton-transfer reaction in the excited state, and various arguments for this suggestion are given. 6. Stokes shifts for the various ionic and neutral species of the indoles and anilines have been calculated, and the large shifts found with indole and p-anisidine may be due to solvent–solute interaction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRIDGES J. W., WILLIAMS R. T. Fluorescence of some substituted benzenes. Nature. 1962 Oct 6;196:59–61. doi: 10.1038/196059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges J. W., Davies D. S., Williams R. T. Fluorescence studies on some hydroxypyridines including compounds of the vitamin B6 group. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):451–468. doi: 10.1042/bj0980451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILNE M. D., CRAWFORD M. A., GIRAO C. B., LOUGHRIDGE L. The excretion of indolylacetic acid and related indolic acids in man and the rat. Clin Sci. 1960 Feb;19:165–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UDENFRIEND S., BOGDANSKI D. F., WEISSBACH H. Fluorescence characteristics of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Science. 1955 Nov 18;122(3177):972–973. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3177.972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE A. Effect of pH on fluorescence of tryosine, tryptophan and related compounds. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):217–220. doi: 10.1042/bj0710217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


