Abstract
1. The N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase of human spleen has been separated by gel electrophoresis into two components, an acidic form A and a basic form B. 2. The two forms are readily separated on DEAE-cellulose and have been concentrated 50-fold and sevenfold respectively. 3. They show similar Km values towards 4-methylumbelliferyl N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminide, and have the same pH optima when compared in citrate, phosphate or acetate buffers. They are inhibited to a similar extent by acetate, heparin, N-acetylgalactosaminolactone, N-acetyl-β-d-galactosamine and N-acetyl-β-d-glucosamine. Specificity for C-4 orientation is not absolute and p-nitrophenyl β-galactosaminide is also hydrolysed but at a rate only 11·6% of that for the corresponding glucosaminide. 4. N-Acetyl-β-glucosaminidase B is stable over a wider pH range than is N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase A, and is less easily denatured by heat. 5. Tissue fractionation indicates that both the A and B forms are present in the lysosomal fraction, whereas the supernatant contains the A form only. 6. Evidence is presented to indicate that the A form contains a number of sialic acid residues.
Full text
PDF



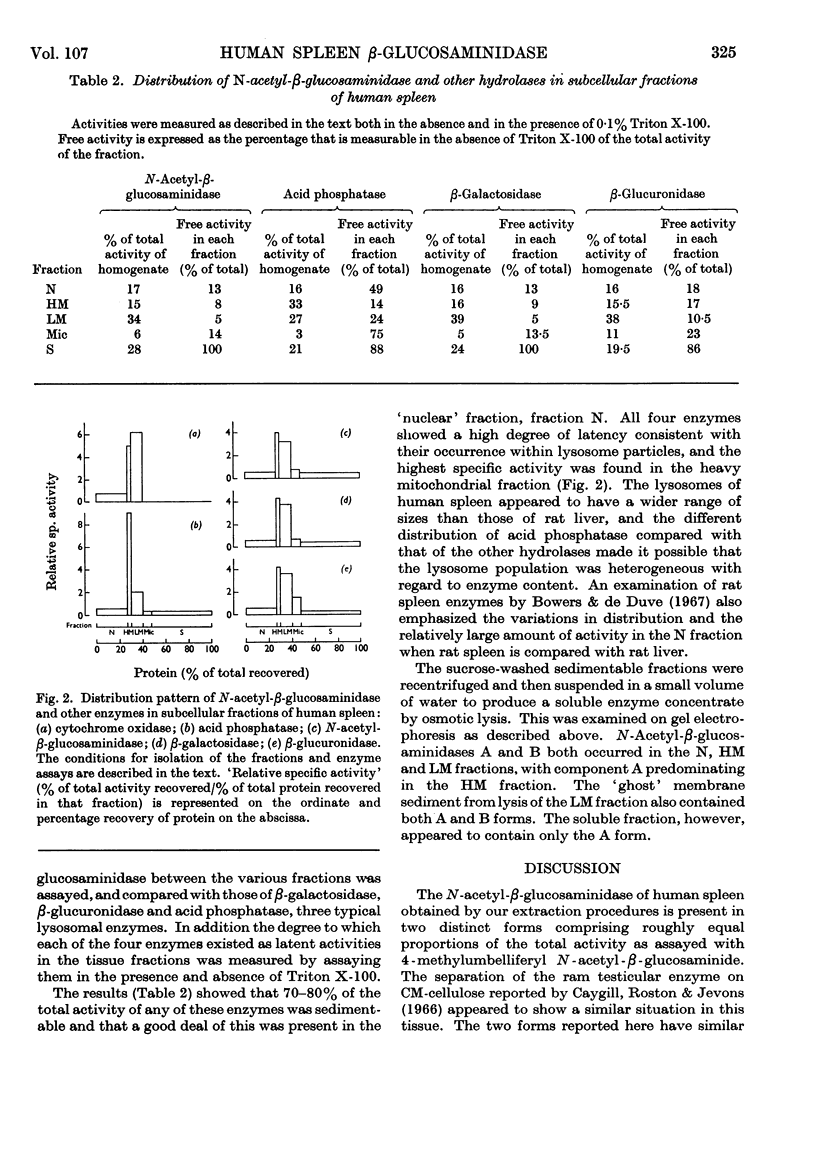
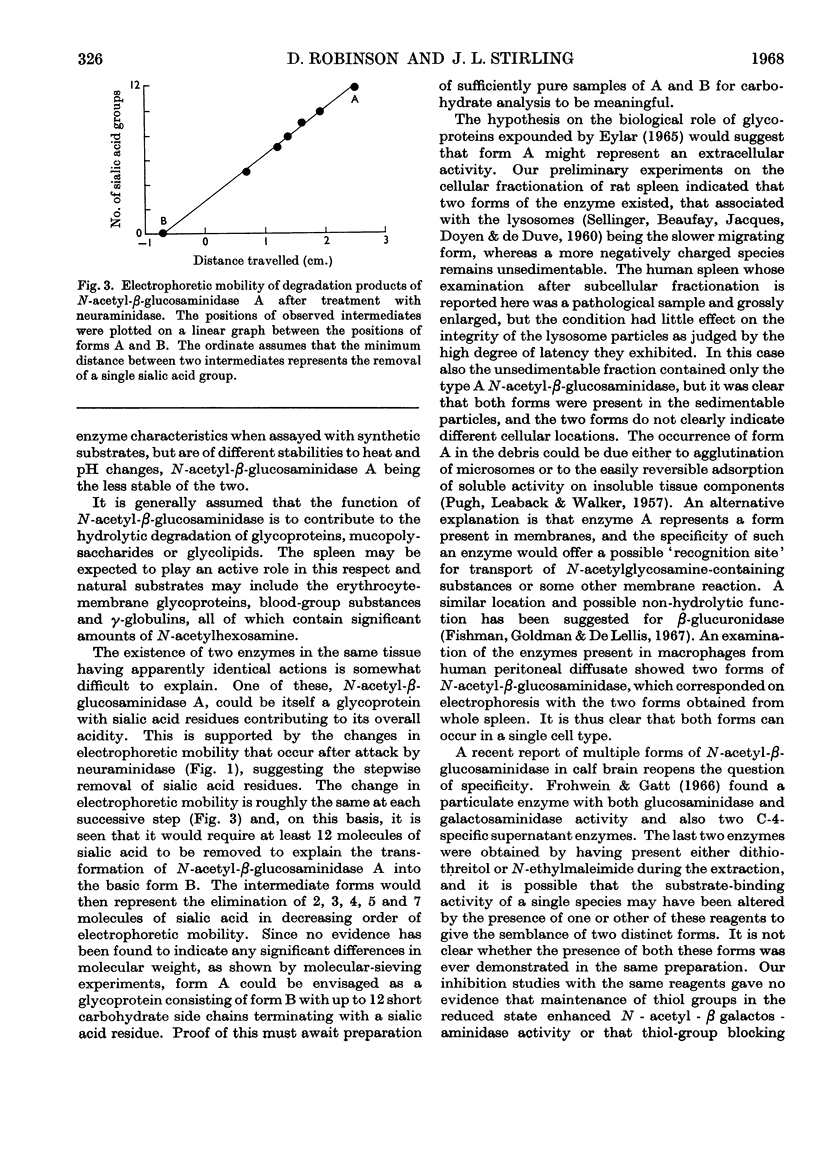

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUDDECKE E., WERRIES E. REINIGUNG UND EIGENSCHAFTEN EINER BETA-N-ACETYL-D-HEXOSAMINIDASE AUS RINDERMILZ. Z Naturforsch B. 1964 Sep;19:798–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers W. E., de Duve C. Lysosomes in lymphoid tissue. II. Intracellular distribution of acid hydrolases. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):339–348. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONCHIE J., FINDLAY J., LEVVY G. A. Mammalian glycosidases; distribution in the body. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):318–325. doi: 10.1042/bj0710318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPERSTEIN S. J., LAZAROW A. A microspectrophotometric method for the determination of cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caygill J. C., Roston C. P., Jevons F. R. Purification of beta-acetylglucosaminase and beta-galactosidase from ram testis. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):405–409. doi: 10.1042/bj0980405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINDLAY J., LEVVY G. A., MARSH C. A. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. 2. Inhibitors of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):467–476. doi: 10.1042/bj0690467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINDLAY J., LEVVY G. A. Purification of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from the pig epididymis. Biochem J. 1960 Oct;77:170–175. doi: 10.1042/bj0770170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURIYA S., FUKUDA A. ESTIMATION OF SERUM BETA-ACETYLAMINODEOXYGLUCOSIDASE. J Biochem. 1963 Nov;54:398–402. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Goldman S. S., DeLellis R. Dual localization of beta-glucuronidase in endoplasmic reticulum and in lysosomes. Nature. 1967 Feb 4;213(5075):457–460. doi: 10.1038/213457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth A. J., Robinson D. Specificity and multiple forms of beta-galactosidase in the rat. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):59–66. doi: 10.1042/bj0970059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEABACK D. H., WALKER P. G. Studies on glucosaminidase. 4. The fluorimetric assay of N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:151–156. doi: 10.1042/bj0780151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER W. C., BEARN A. G. Studies on the transferrins of adult serum, cord serum, and cerebrospinal fluid. The effect of neuraminidase. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:83–105. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON J. C., PIERCE J. E. DIFFERENTIAL ACTION OF NEURAMINIDASE ON HUMAN SERUM ALKALINE PHOSPHATASES. Nature. 1964 Oct 31;204:472–473. doi: 10.1038/204472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Price R. G., Dance N. Separation and properties of beta-galactosidase, beta-glucosidase, beta-glucuronidase and N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase from rat kidney. Biochem J. 1967 Feb;102(2):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1020525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLINGER O. Z., BEAUFAY H., JACQUES P., DOYEN A., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 15. Intracellular distribution and properties of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase and beta-galactosidase in rat liver. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:450–456. doi: 10.1042/bj0740450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER P. G., WOOLLEN J. W., HEYWORTH R. Studies on glucosaminidase. 5. Kidney N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase and N-acetyl-beta-galactosaminidase. Biochem J. 1961 May;79:288–294. doi: 10.1042/bj0790288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woollen J. W., Turner P. Plasma N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase and beta-glucuronidase in health and disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1965 Dec;12(6):671–683. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(65)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


