Abstract
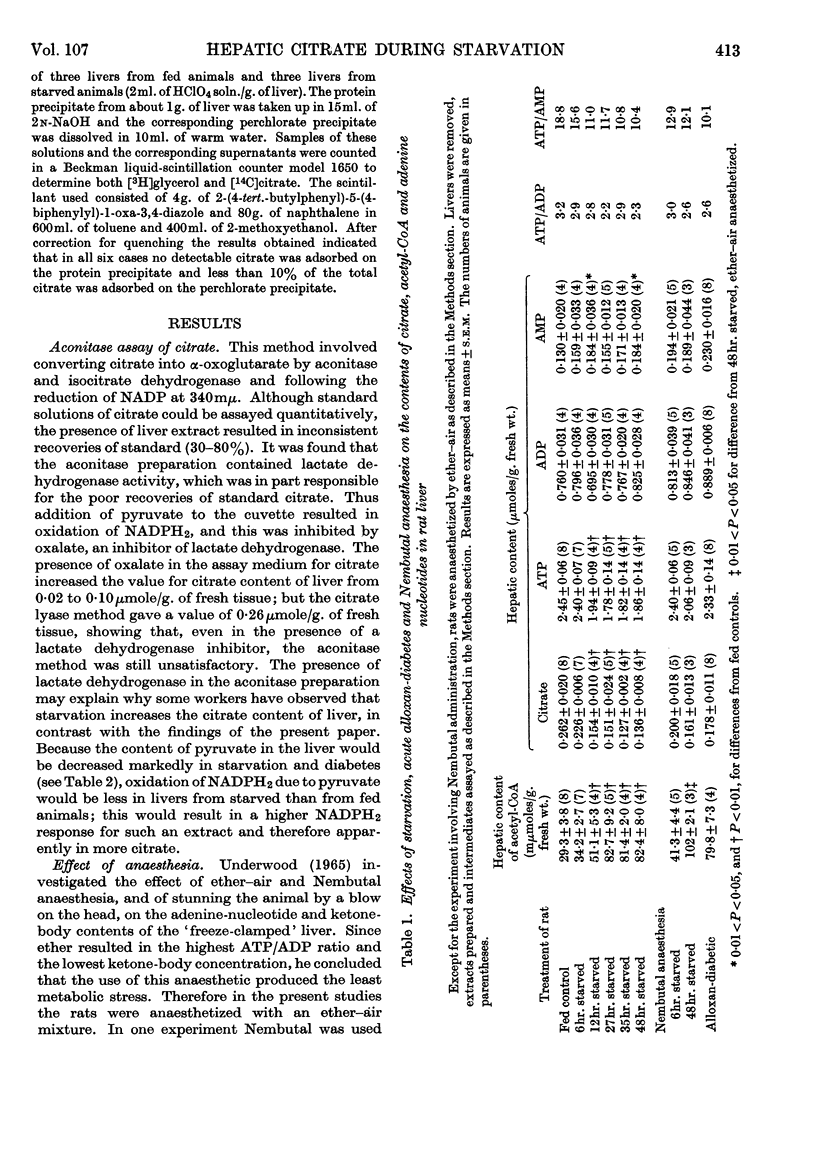
1. The content of citrate in `freeze-clamped' livers from starved and alloxan-diabetic rats was measured by using the specific citrate assay method of Gruber & Moellering (1966). 2. The content of citrate fell progressively during a period of 48hr. starvation to reach a plateau value that is 50% of the value for livers from fed rats. Some possible explanations for the conflicting reports of changes in hepatic citrate content during starvation are discussed. 3. The hepatic contents of ATP, pyruvate, lactate, glycogen and the hexose phosphates were decreased during starvation, whereas those of acetyl-CoA and AMP were increased. 4. Acute alloxan-diabetes produced similar changes in the contents of these metabolic intermediates. 5. The effects of starvation and diabetes on the citrate and acetyl-CoA contents are discussed in relation to control of gluconeogenesis, fatty acid synthesis and the activity of citrate synthase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DALZIEL K. Kinetic studies of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:244–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0840244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Yorke R. E., Randle P. J. Measurement of concentrations of metabolites in adipose tissue and effects of insulin, alloxan-diabetes and adrenaline. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):407–419. doi: 10.1042/bj1000407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit P. K., DeVilliers D. C., Jr, Lazarow A. Citrate metabolism in diabetes. II. Tissue citrate content, citrate synthase and oxidation in alloxan-diabetic rat. Metabolism. 1967 Mar;16(3):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland P. B., Randle P. J. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscles. 10. Effects of alloxan-diabetes, starvation, hypophysectomy and adrenalectomy, and of fatty acids, ketone bodies and pyruvate, on the glycerol output and concentrations of free fatty acids, long-chain fatty acyl-coenzyme A, glycerol phosphate and citrate-cycle intermediates in rat heart and diaphragm muscles. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):678–687. doi: 10.1042/bj0930678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gevers W., Krebs H. A. The effects of adenine nucleotides on carbohydrate metabolism in pigeon-liver homogenates. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):720–735. doi: 10.1042/bj0980720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg N. D., Passonneau J. V., Lowry O. H. Effects of changes in brain metabolism on the levels of citric acid cycle intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):3997–4003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A., BENNETT D. A., DE GASQUET P., GASQUET P., GASCOYNE T., YOSHIDA T. Renal gluconeogenesis. The effect of diet on the gluconeogenic capacity of rat-kidney-cortex slices. Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86:22–27. doi: 10.1042/bj0860022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynen F., Matsuhashi M., Numa S., Schweizer E. The cellular control of fatty acid synthesis at the enzymatic level. Biochem Soc Symp. 1963;24:43–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON J. F. The purification of aconitase. Biochem J. 1954 Jan;56(1):99–105. doi: 10.1042/bj0560099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Gevers W. Control of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in liver and kidney cortex. Vitam Horm. 1967;25:1–87. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Randle P. J. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscle. 7. Effects of fatty acids, ketone bodies and pyruvate, and of alloxan-diabetes, starvation, hypophysectomy and adrenalectomy, on the concentrations of hexose phosphates, nucleotides and inorganic phosphate in perfused rat heart. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):641–651. doi: 10.1042/bj0930641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numa S., Ringelmann E., Lynen F. Zur Hemmung der Acetyl-CoA-Carboxylase durch Fettsäure-Coenzym A-Verbindungen. Biochem Z. 1965 Dec 1;343(3):243–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARMEGGIANI A., BOWMAN R. H. REGULATION OF PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE ACTIVITY BY CITRATE IN NORMAL AND DIABETIC MUSCLE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 1;12:268–273. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER V. R., ONO T. Enzyme patterns in rat liver and Morris hepatoma 5123 during metabolic transitions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:355–362. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolleston F. S., Newsholme E. A. Control of glycolysis in cerebral cortex slices. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):524–533. doi: 10.1042/bj1040524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER A. F., LOWENSTEIN J. M. The supply of precursors for the synthesis of fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1962 Dec;237:3640–3648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRERE P. A., KOSICKI G. W. The purification of citrate-condensing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2557–2559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINER D. F., WILLIAMS R. H. Some observations concerning hepatic glucose 6-phosphate content in normal and diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1342–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd D., Garland P. B. ATP controlled acetoacetate and citrate synthesis by rat liver mitochondria oxidising palmitoyl-carnitine, and the inhibition of citrate synthase by ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jan 4;22(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90607-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer A. F., Lowenstein J. M. Citrate content of liver and kidney of rat in various metabolic states and in fluoroacetate poisoning. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):342–348. doi: 10.1042/bj1030342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Start C., Newsholme E. A. Effects of starvation and alloxan diabetes on the content of citrate in the livers of the rat. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):46P–47P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubbs P. K., Garland P. B. Variations in tissue contents of coenzyme A thio esters and possible metabolic implications. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):550–557. doi: 10.1042/bj0930550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNDERWOOD A. H., NEWSHOLME E. A. PROPERTIES OF PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE FROM RAT LIVER AND THEIR RELATION TO THE CONTROL OF GLYCOLYSIS AND GLUCONEOGENESIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:868–875. doi: 10.1042/bj0950868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood A. H., Newsholme E. A. Control of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in rat kidney cortex slices. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):300–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1040300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Herczeg B., Coles H., Danish R. Studies on the ketogenic effect of glucagon in intact rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Aug 12;24(3):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


