Abstract
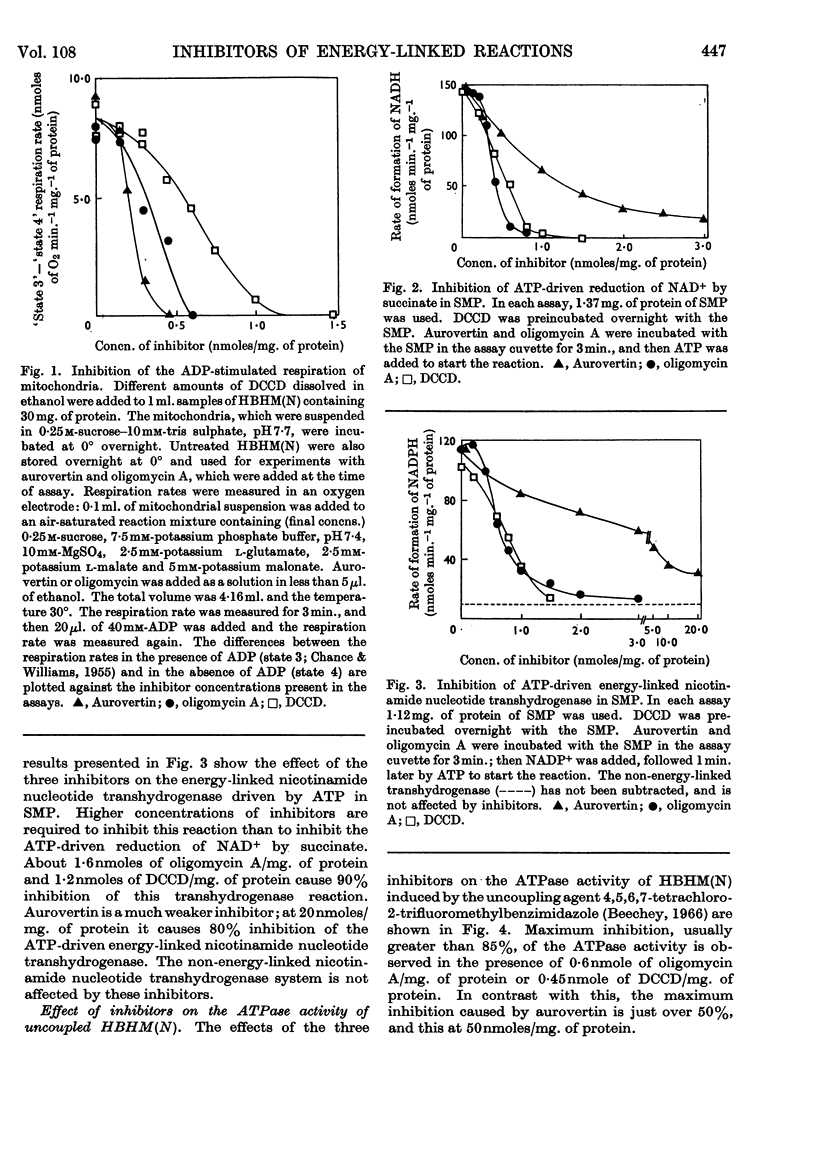
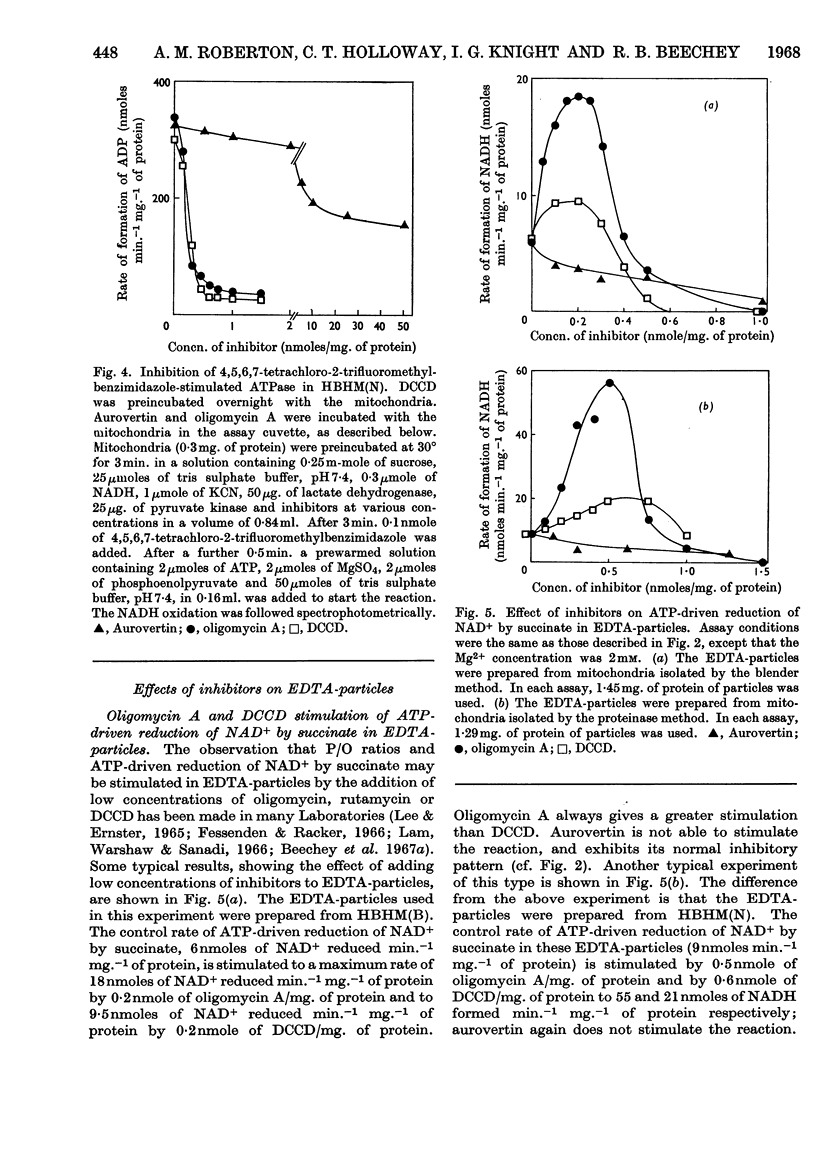
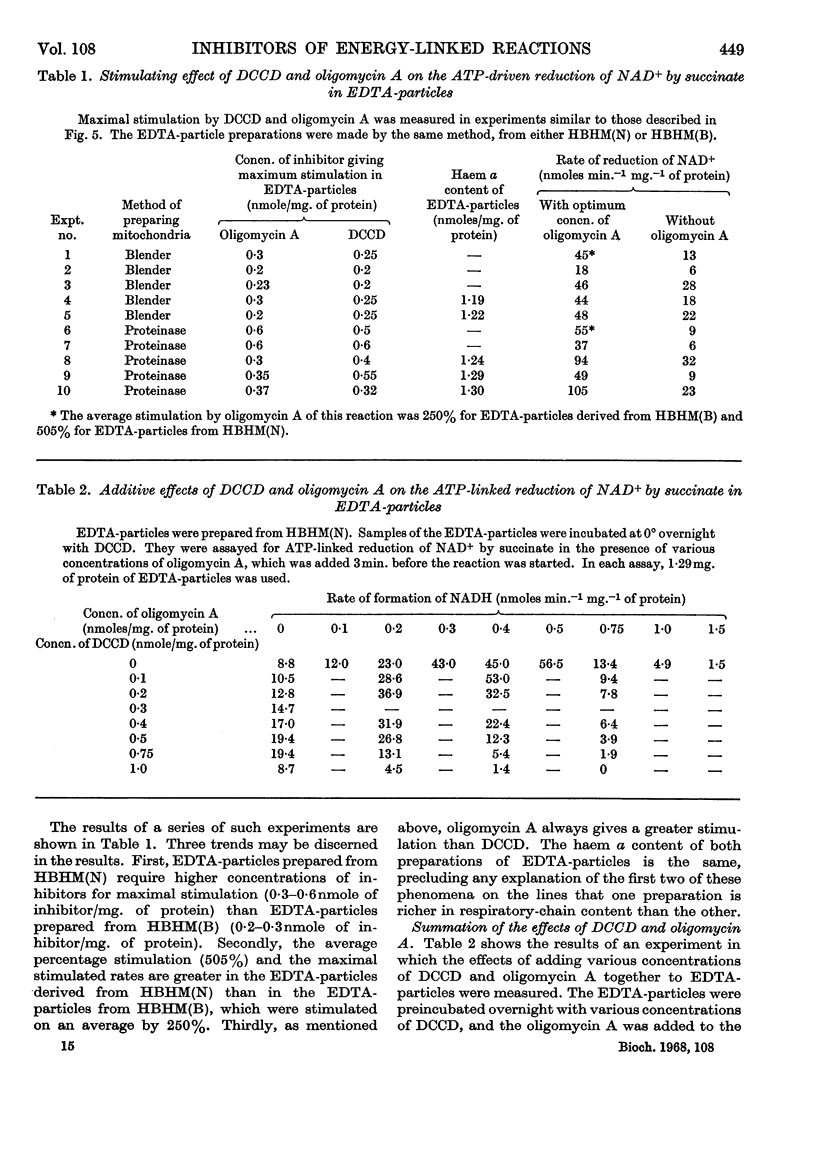
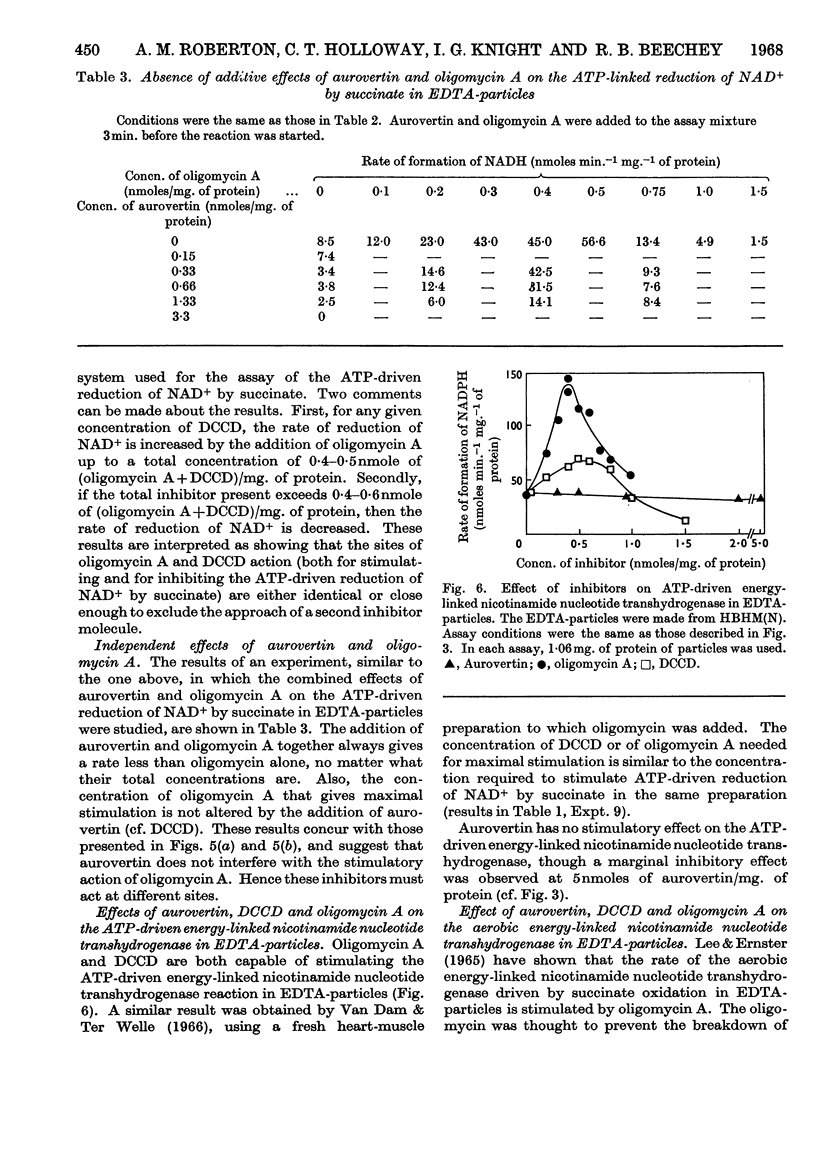
1. The effects of dicyclohexylcarbodi-imide, oligomycin A and aurovertin on enzyme systems related to respiratory-chain phosphorylation were compared. Dicyclohexylcarbodi-imide and oligomycin A have very similar functional effects, giving 50% inhibition of ATP-utilizing and ATP-generating systems at concentrations below 0·8nmole/mg. of submitochondrial-particle protein. Aurovertin is a more potent inhibitor of ATP synthesis, giving 50% inhibition at 0·2nmole/mg. of protein. However, aurovertin is a less potent inhibitor of ATP-utilizing systems: the ATP-driven energy-linked nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase is 50% inhibited at 3·0nmoles/mg. of protein and the ATP-driven reduction of NAD+ by succinate is 50% inhibited at 0·95nmole/mg. of protein. 2. With EDTA-particles (prepared by subjecting mitochondria to ultrasonic radiation at pH9 in the presence of 2mm-EDTA) the maximum stimulation of the ATP-driven partial reactions is effected by similar concentrations of oligomycin A and dicylcohexylcarbodi-imide, but the latter is less effective. The stimulatory effects of suboptimum concentrations of dicyclohexylcarbodi-imide and oligomycin A are additive. Aurovertin does not stimulate these reactions or interfere with the stimulation by the other inhibitors. 3. Dicyclohexylcarbodi-imide and oligomycin A stimulate the aerobic energy-linked nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase of EDTA-particles, but the optimum concentration is higher than that required for the ATP-driven partial reactions. Aurovertin has no effect on this reaction. 4. The site of action of dicyclohexylcarbodi-imide is in CF0, the mitochondrial fraction that confers oligomycin sensitivity on F1 mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase.
Full text
PDF

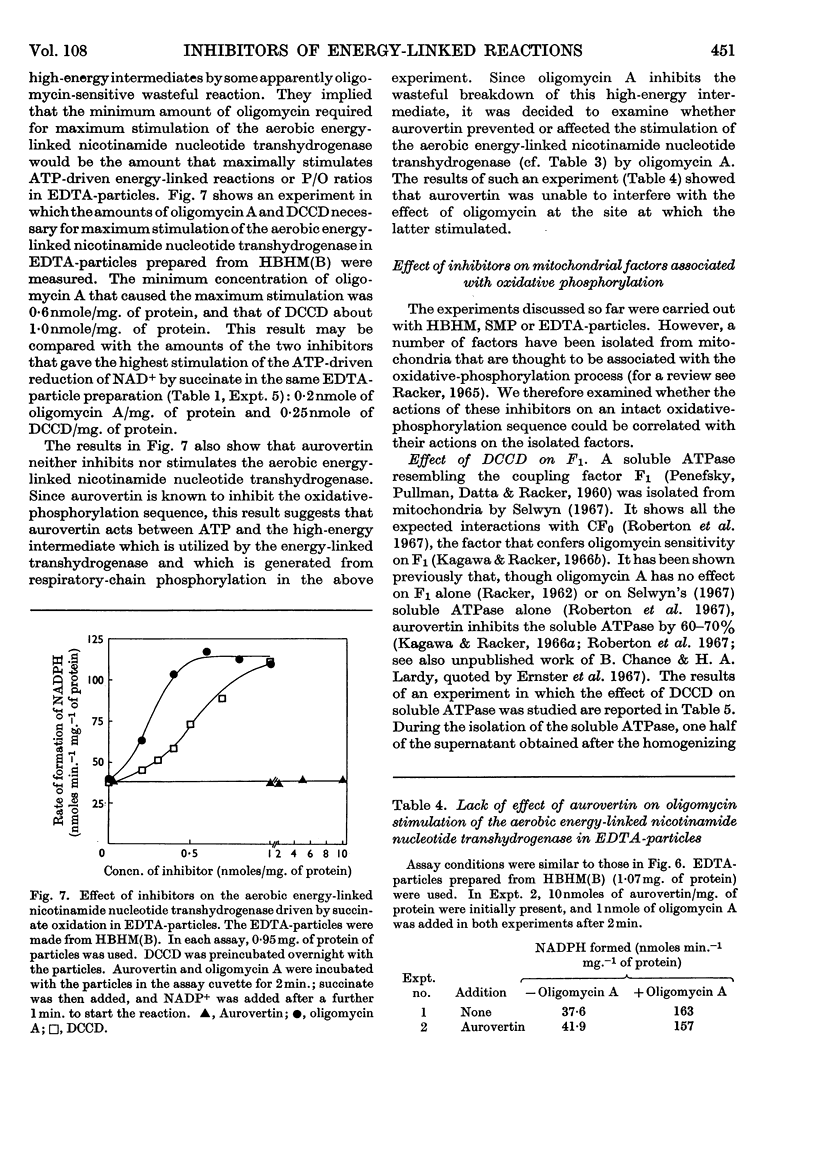
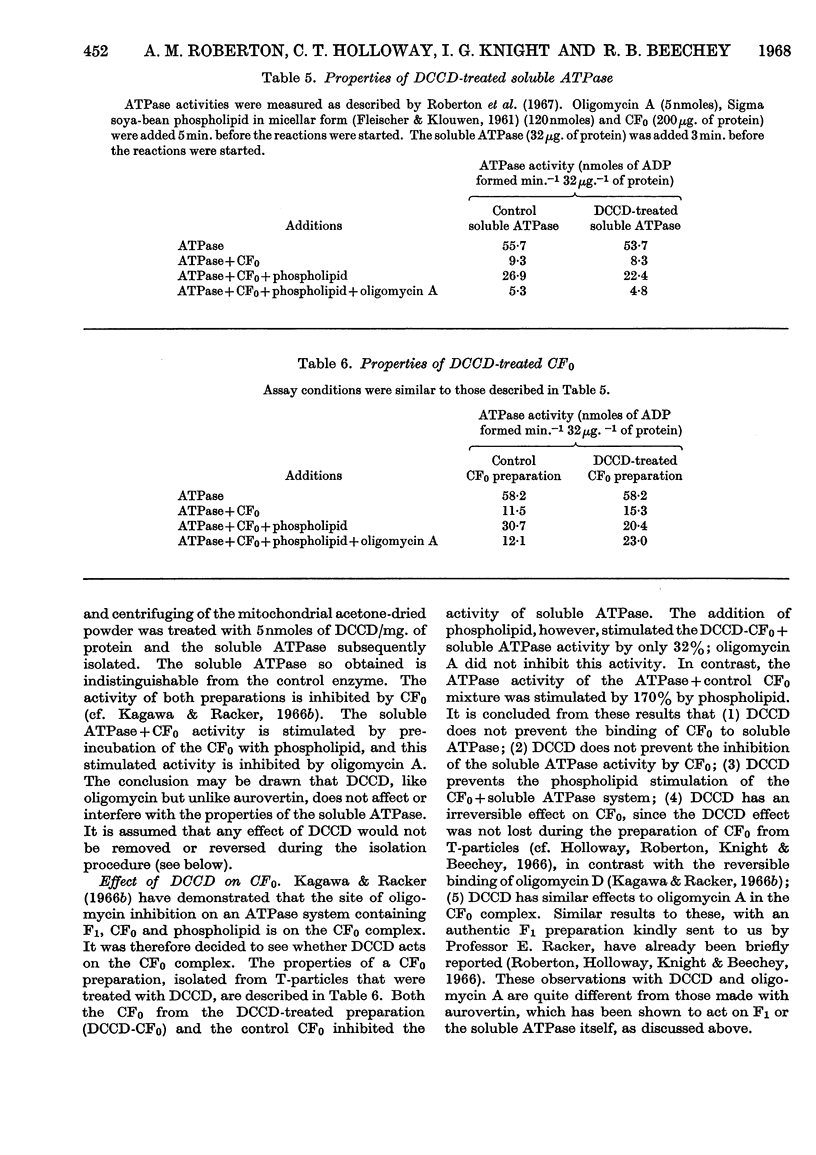




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAIR P. V., ODA T., GREEN D. E. STUDIES ON THE ELECTRON TRANSFER SYSTEM. LIV. ISOLATION OF THE UNIT OF ELECTRON TRANSFER. Biochemistry. 1963 Jul-Aug;2:756–764. doi: 10.1021/bi00904a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechey R. B., Roberton A. M., Holloway C. T., Knight I. G. The properties of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide as an inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3867–3879. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechey R. B. The uncoupling of respiratory-chain phosphorylation by 4,5,6,7-tetrachloro-2-trifluoromethylbenzimidazole. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):284–289. doi: 10.1042/bj0980284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechey R. B., Williams V., Holloway C. T., Knight I. G., Roberton A. M. Estimation of the molecular weights and molecular formulae of oligomycin-A, rutamycin & aurovertin by mass spectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 8;26(3):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., WILLIAMS G. R. Respiratory enzymes in oxidative phosphorylation. III. The steady state. J Biol Chem. 1955 Nov;217(1):409–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cañas-Rodriguez A., Smith H. W. The identification of the antimicrobial factors of the stomach contents of sucking rabbits. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):79–82. doi: 10.1042/bj1000079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIELSON L., ERNSTER L. ENERGY-DEPENDENT REDUCTION OF TRIPHOSPHOPYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE BY REDUCED DIPHOSPHOPYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE, COUPLED TO THE ENERGY-TRANSFER SYTEM OF THE RESPIRATORY CHAIN. Biochem Z. 1963;338:188–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESNOUF M. P., WILLIAMS W. J. The isolation and purification of a bovine-plasma protein which is a substrate for the coagulant fraction of Russell's-viper venom. Biochem J. 1962 Jul;84:62–71. doi: 10.1042/bj0840062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessenden J. M., Racker E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. XI. Stimulation of oxidative phosphorylation by coupling factors and oligomycin; inhibition by an antibody against coupling factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2483–2489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa Y., Racker E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. 8. Properties of a factor conferring oligomycin sensitivity on mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2461–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa Y., Racker E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. IX. Reconstruction of oligomycin-sensitive adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2467–2474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARDY H. A., CONNELLY J. L., JOHNSON D. ANTIBIOTIC STUDIES. II. INHIBITION OF PHOSPHORYL TRANSFER IN MITOCHONDRIA BY OLIGOMYCIN AND AUROVERTIN. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1961–1968. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARDY H. A., JOHNSON D., McMURRAY W. C. Antibiotics as tools for metabolic studies. I. A survey of toxic antibiotics in respiratory, phosphorylative and glycolytic systems. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Dec;78(2):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90383-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARDY H. A., WITONSKY P., JOHNSON D. ANTIBIOTICS AS TOOLS FOR METABOLIC STUDIES. IV. COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS OF OLIGOMYCINS A, B, C, AND RUTAMYCIN AS INHIBITORS OF PHOSPHORYL TRANSFER REACTIONS IN MITOCHONDRIA. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:552–554. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE C. P., AZZONE G. F., ERNSTER L. EVIDENCE FOR ENERGY-COUPLING IN NON-PHOSPHORYLATING ELECTRON TRANSPORT PARTICLES FROM BEEF-HEART MITOCHONDRIA. Nature. 1964 Jan 11;201:152–155. doi: 10.1038/201152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE C. P., ERNSTER L. RESTORATION OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN NON-PHOSPHORYLATING SUBMITOCHONDRIAL PARTICLES BY OLIGOMYCIN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 17;18:523–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90785-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENEFSKY H. S., PULLMAN M. E., DATTA A., RACKER E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. II. Participation of a soluble adenosine tolphosphatase in oxidative phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3330–3336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULLMAN M. E., PENEFSKY H. S., DATTA A., RACKER E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. I. Purification and properties of soluble dinitrophenol-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3322–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Horstman L. L. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. 13. Structure and function of submitochondrial particles completely resolved with respect to coupling factor. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2547–2551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANADI D. R., FLUHARTY A. L. ON THE MECHANISM OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION. VII. THE ENERGY-REQUIRING REDUCTION OF PYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE BY SUCCINATE AND THE ENERGY-YIELDING OXIDATION OF REDUCED PYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE BY FUMARATE. Biochemistry. 1963 May-Jun;2:523–528. doi: 10.1021/bi00903a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz G., Penefsky H. S., Racker E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. XIV. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2552–2560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn M. J. Preparation and general properties of a soluble adenosine triphosphatase from mitochondria. Biochem J. 1967 Oct;105(1):279–288. doi: 10.1042/bj1050279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN GELDERB, SLATER E. C. TITRATION OF CYTOCHROME C OXIDASE WITH NADH AND PHENAZINE METHOSULPHATE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 6;73:663–665. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90342-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


