Abstract
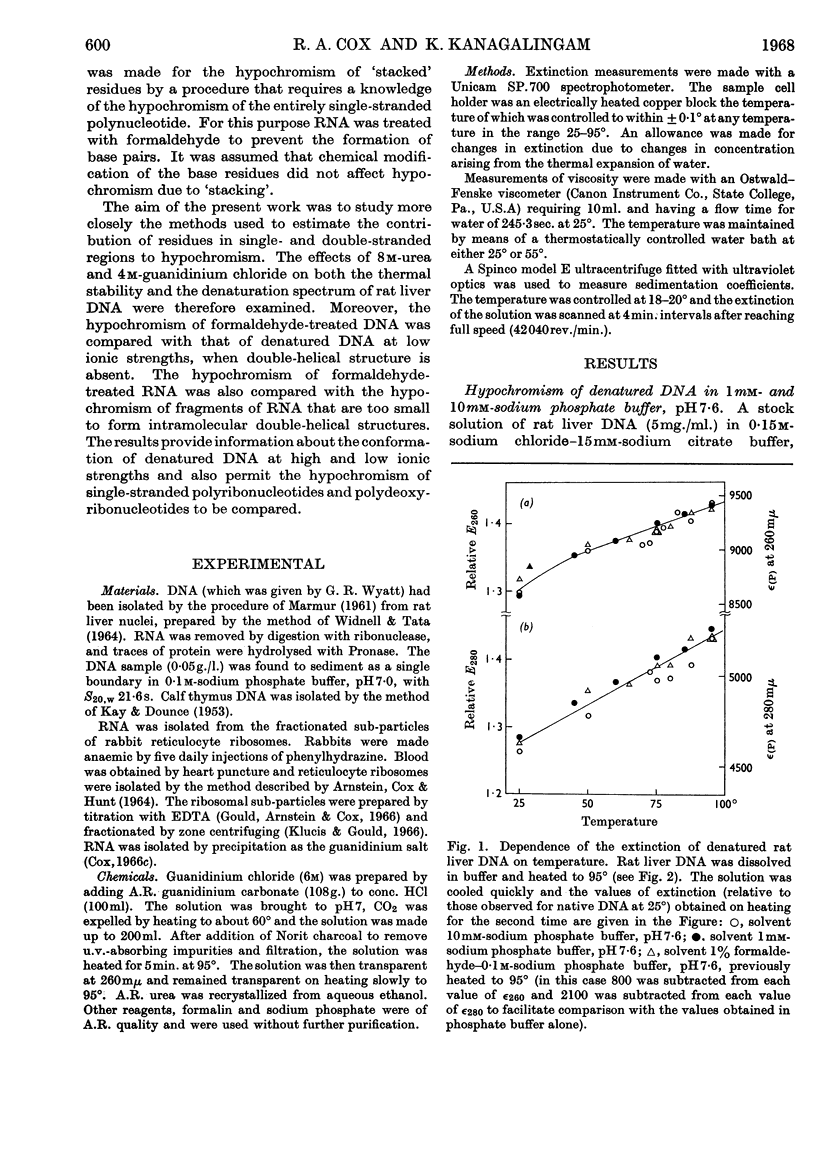
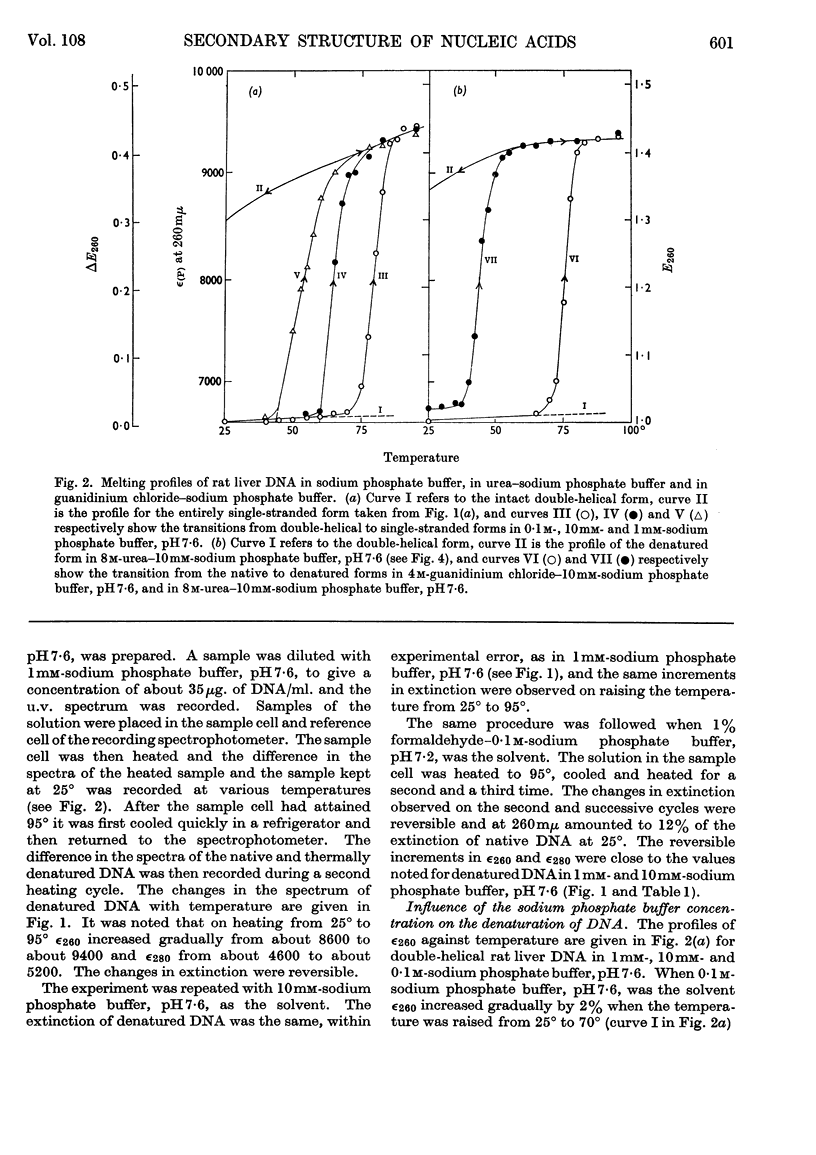
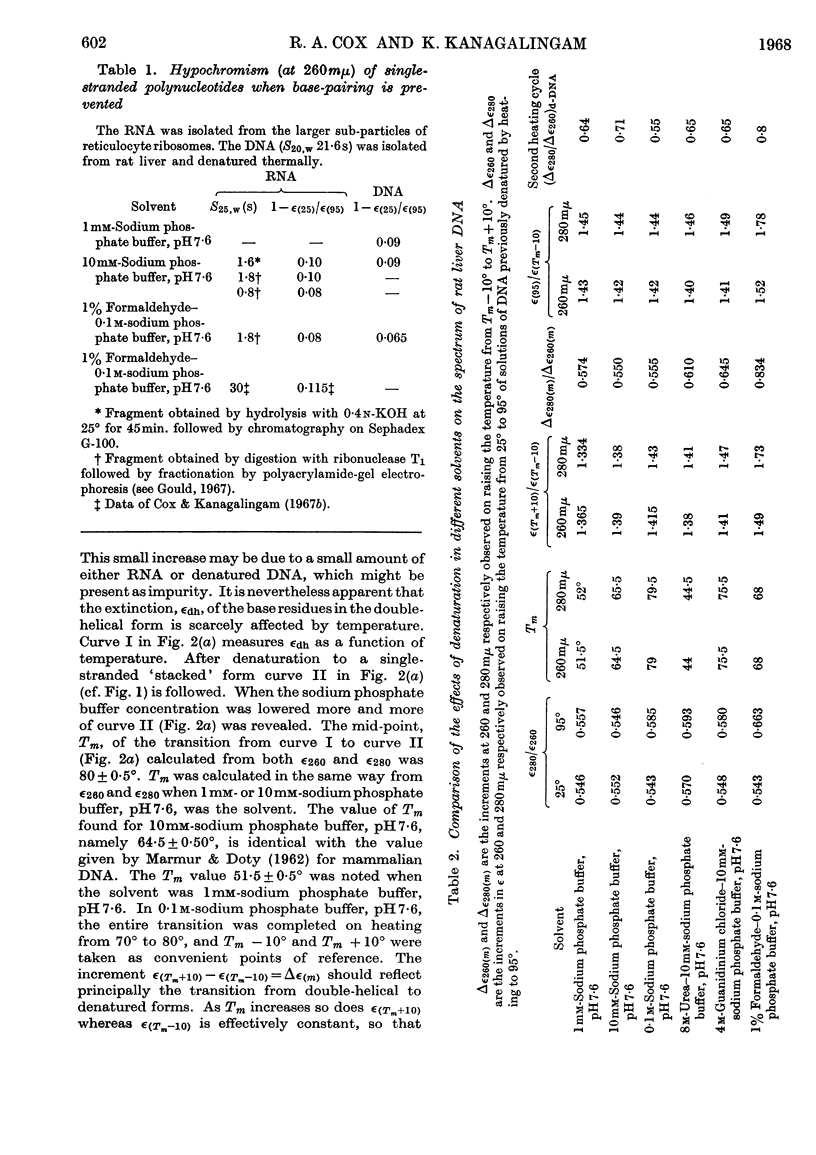
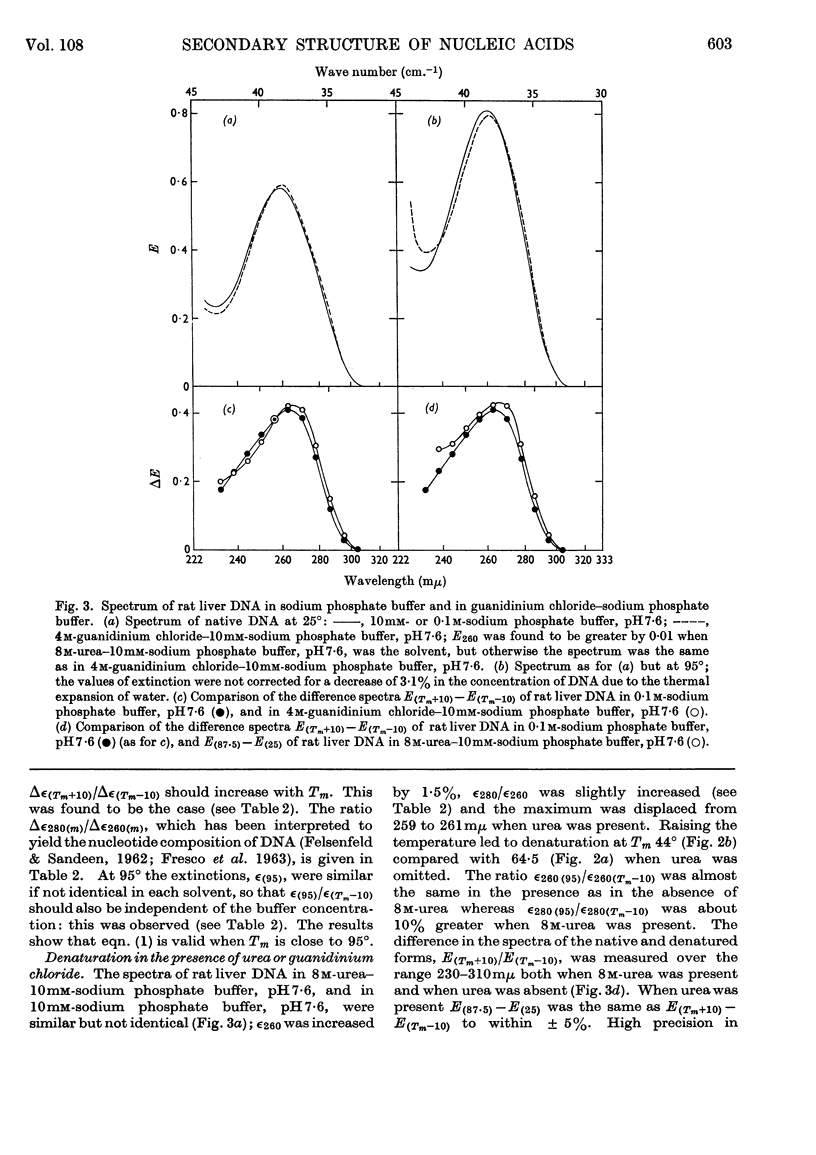
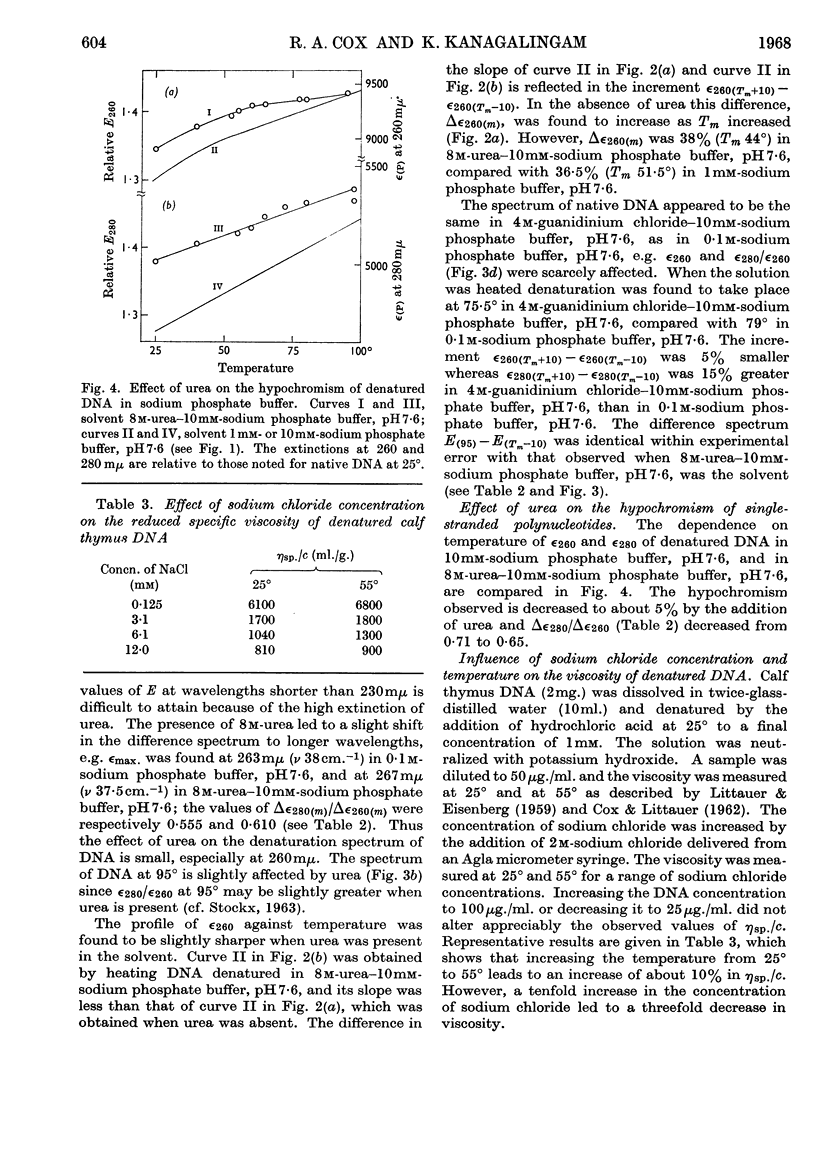
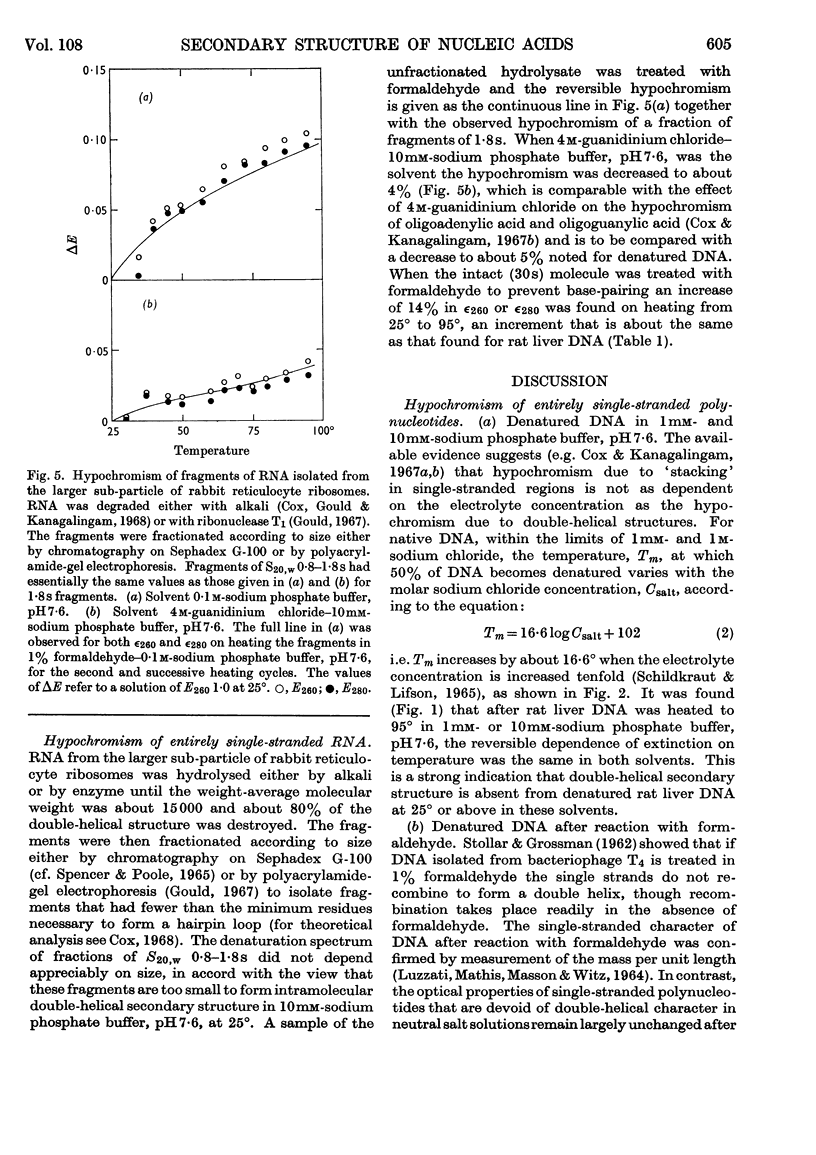
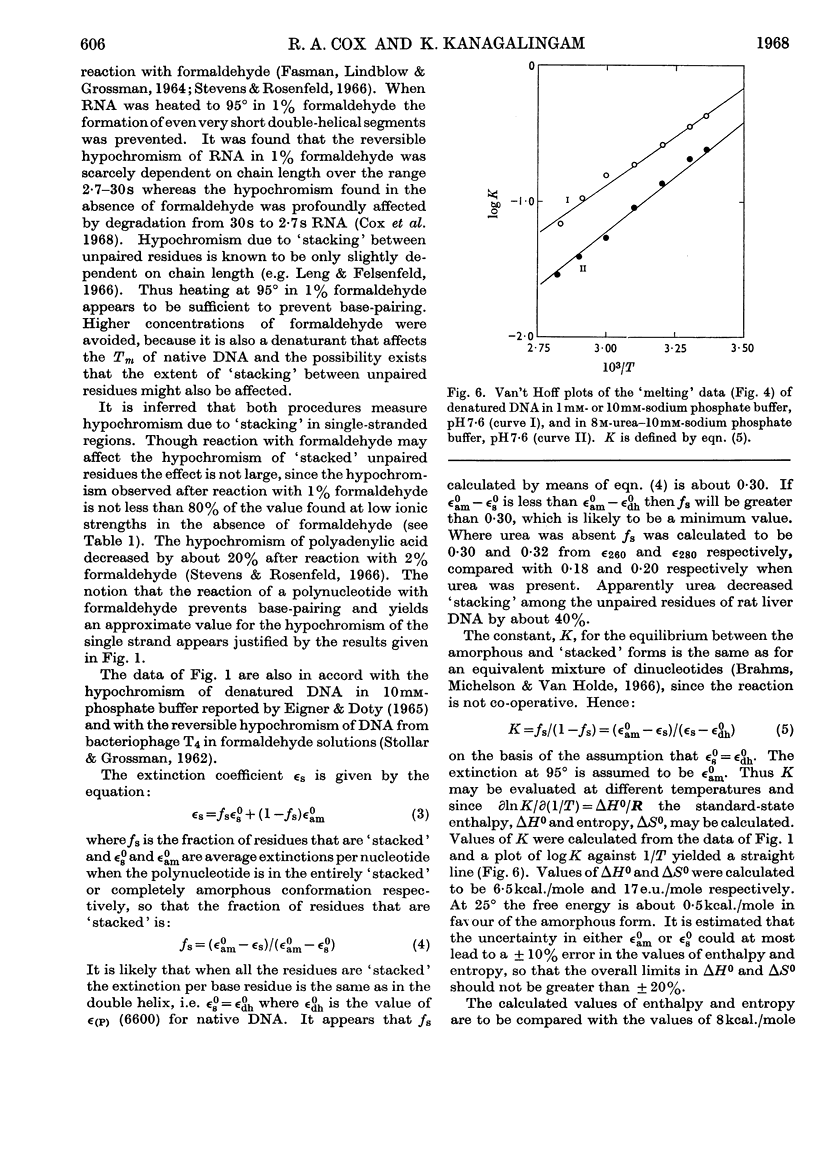
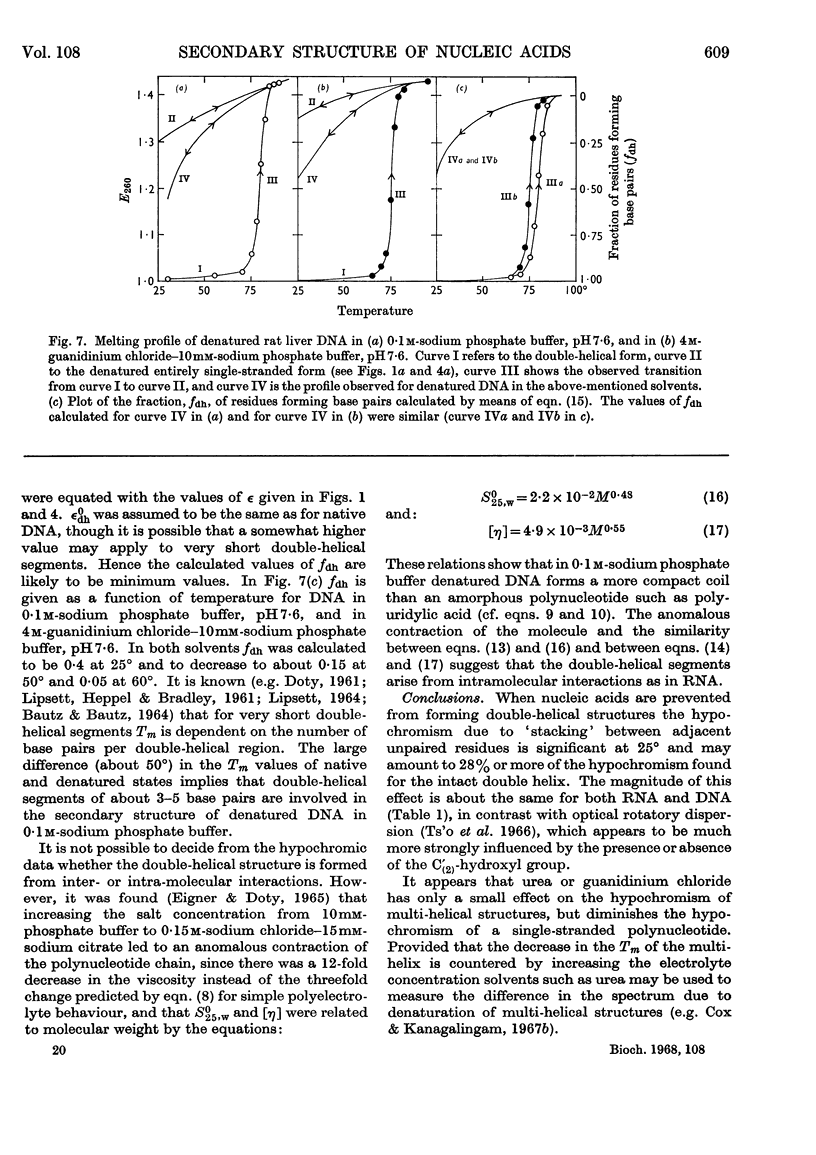
1. The thermal denaturation of DNA from rat liver was studied spectrophotometrically. In sodium phosphate buffers denaturation led to a single-stranded form having, at 25°, about 25% of the hypochromism of the intact double helix. 2. The hypochromism of the denatured form was the same in 1mm- as in 10mm-sodium phosphate buffer and was scarcely affected by reaction with formaldehyde. The hypochromism was decreased by about 40% in the presence of 8m-urea. 3. The hypochromism of denatured DNA at low ionic strengths was about the same as that of fragments of reticulocyte ribosomal RNA that were too short to form double-helical secondary structure and about the same as that of RNA after reaction with formaldehyde. 4. The spectrum of DNA was slightly affected by the presence of 8m-urea or 4m-guanidinium chloride. The differences in the spectrum of the native and denatured forms of DNA in 0·1m-sodium phosphate buffer, in 8m-urea–10mm-sodium phosphate buffer and in 4m-guanidinium chloride–10mm-sodium phosphate buffer, pH7·6, were similar but not identical. 5. Denatured rat liver DNA appears to have no double-helical character at 25° in 10mm-sodium phosphate buffer, pH7·6; increasing the buffer concentration to 0·1m leads to a more compact form in which about 40% of the residues form base pairs.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnstein H. R., Cox R. A., Hunt J. A. The function of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid from rabbit reticulocytes in haemoglobin biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):648–661. doi: 10.1042/bj0920648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUTZ E. K., BAUTZ F. A. THE INFLUENCE OF NONCOMPLEMENTARY BASES ON THE STABILITY OF ORDERED POLYNUCLEOTIDES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1476–1481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boedtker H. The reaction of ribonucleic acid with formaldehyde. I. Optical absorbance studies. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2718–2727. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahms J., Michelson A. M., Van Holde K. E. Adenylate oligomers in single- and double-strand conformation. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):467–488. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX R. A., LITTAUER U. Z. Ribonucleic acid from Escherichia coli. III. The influence of ionic strength and temperature on hydrodynamic and optical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:197–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. A possible method for characterizing the secondary structure of ribonucleic acids. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):146–168. doi: 10.1042/bj1000146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Gould H. J., Kanagalingam K. A study of the alkaline hydrolysis of fractionated reticulocyte ribosomal ribonucleic acid and its relevance to secondary structure. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(3):733–741. doi: 10.1042/bj1060733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. Hydrolysis of polynucleotides and the characterization of their secondary structure. A theoretical study. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(3):725–731. doi: 10.1042/bj1060725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kanagalingam K. A spectrophotometric study of the secondary structure of ribonucleic acid based on a method for diminishing single-stranded base-'stacking' without affecting multi-helical structures. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):749–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1030749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kanagalingam K. A study of the hydrolysis of unfractionated reticulocyte ribosomal ribonucleic acid by pancreatic ribonuclease and its relevance to secondary structure. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):431–452. doi: 10.1042/bj1030431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. The secondary structure of ribosomal ribonucleic acid in solution. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):841–857. doi: 10.1042/bj0980841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigner J., Doty P. The native, denatured and renatured states of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):549–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FASMAN G. D., LINDBLOW C., GROSSMAN L. THE HELICAL CONFORMATIONS OF POLYCYTIDYLIC ACID: STUDIES ON THE FORCES INVOLVED. Biochemistry. 1964 Aug;3:1015–1021. doi: 10.1021/bi00896a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSENFELD G., CANTONI G. L. USE OF THERMAL DENATURATION STUDIES TO INVESTIGATE THE BASE SEQUENCE OF YEAST SERINE SRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:818–826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould H. J., Arnstein H. R., Cox R. A. The dissociation of reticulocyte polysomes into subunits and the location of messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):600–618. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guschlbauer W. Helical regions in transfer ribonucleic acid. Biophysik. 1966;3(2):156–164. doi: 10.1007/BF01191609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanlon S. The importance of London dispersion forces in the maintenance of the deoxyribonucleic acid helix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 21;23(6):861–867. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90567-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klucis E. S., Gould H. J. Zonal ultracentrifuge for the separation of ribosomal subunits. Science. 1966 Apr 15;152(3720):378–378. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3720.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSETT M. N. COMPLEX FORMATION BETWEEN POLYCYTIDYLIC ACID AND GUANINE OLIGONUCLEOTIDES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1256–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSETT M. N., HEPPEP L. A., BRADLEY D. F. Complex formation between oligonucleotides and polymers. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:857–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTAUER U. Z., EISENBERG H. Ribonucleic acid from Escherichia coli; preparation, characterization and physical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:320–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90604-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng M., Felsenfeld G. A study of polyadenylic acid at neutral pH. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):455–466. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHLER H. R., KLINE B., MEHROTRA B. D. SOME OBSERVATIONS ON THE HYPOCHROMISM OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1964 Sep;9:801–811. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER M., POOLE J. ON THE ORIGIN OF CRYSTALLIZABLE RNA FROM YEAST. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:314–326. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKX J. The influence of strong solutions of uerea and poly alcohols on the spectroscopic behavior of ribonucleic acid and nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Apr 30;68:535–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut C. Dependence of the melting temperature of DNA on salt concentration. Biopolymers. 1965;3(2):195–208. doi: 10.1002/bip.360030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. L., Rosenfeld A. The secondary structure of polyadenylic acid Inferences from its reaction with formaldehyde. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2714–2721. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. A procedure for the isolation of enzymically active rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0920313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


