Abstract
1. The reaction of pig heart lactate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.27) with NAD+ and lactate to form pyruvate and NADH was followed by rapid spectrophotometric methods. The distinct spectrum of enzyme-bound NADH permits the measurement of the rate of dissociation of this compound. 2. The reduction of the first mole equivalent of NAD+ per mole of enzyme sites can also be observed, and is much more rapid than the steady-state rate of NADH production. 3. At pH8 the dissociation of the enzyme–NADH complex is rate-determining for the steady-state oxidation of lactate. At lower pH some other step after the interconversion of the ternary complex and before the dissociation of NADH is rate-determining. Other evidence for a compulsory-order mechanism is provided.
Full text
PDF
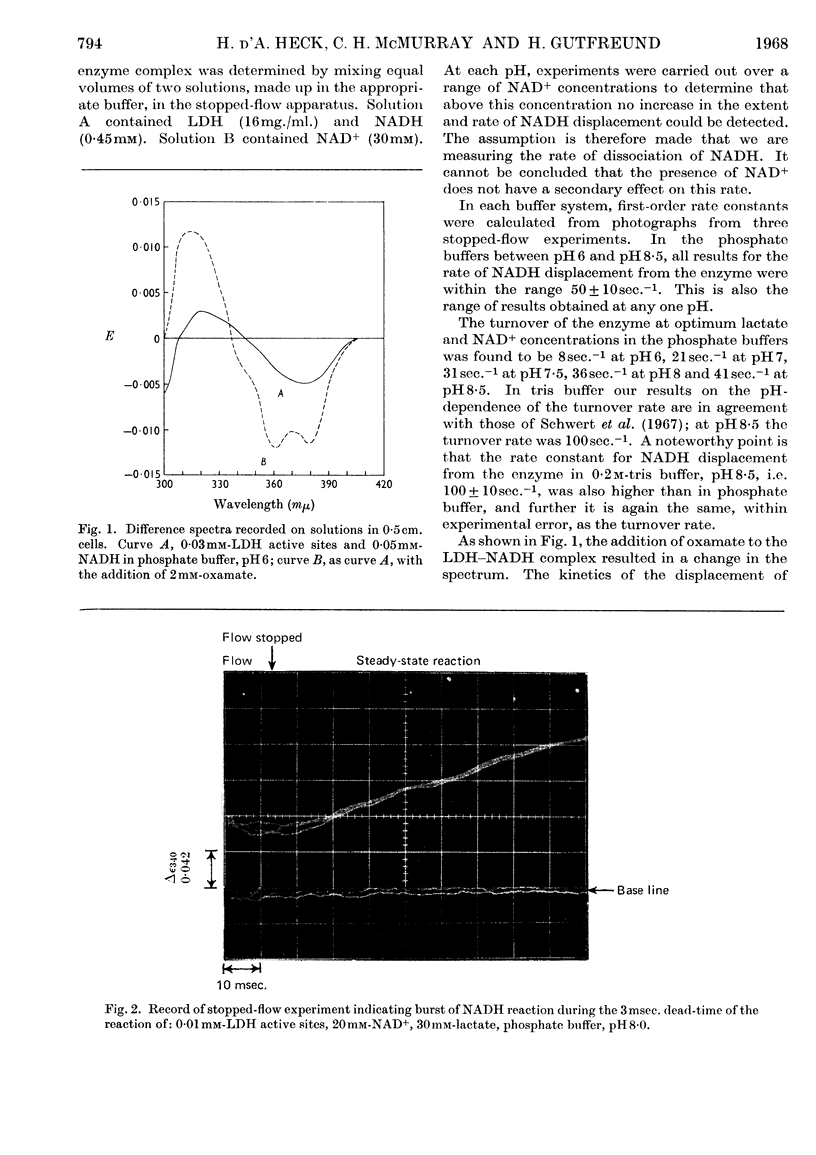
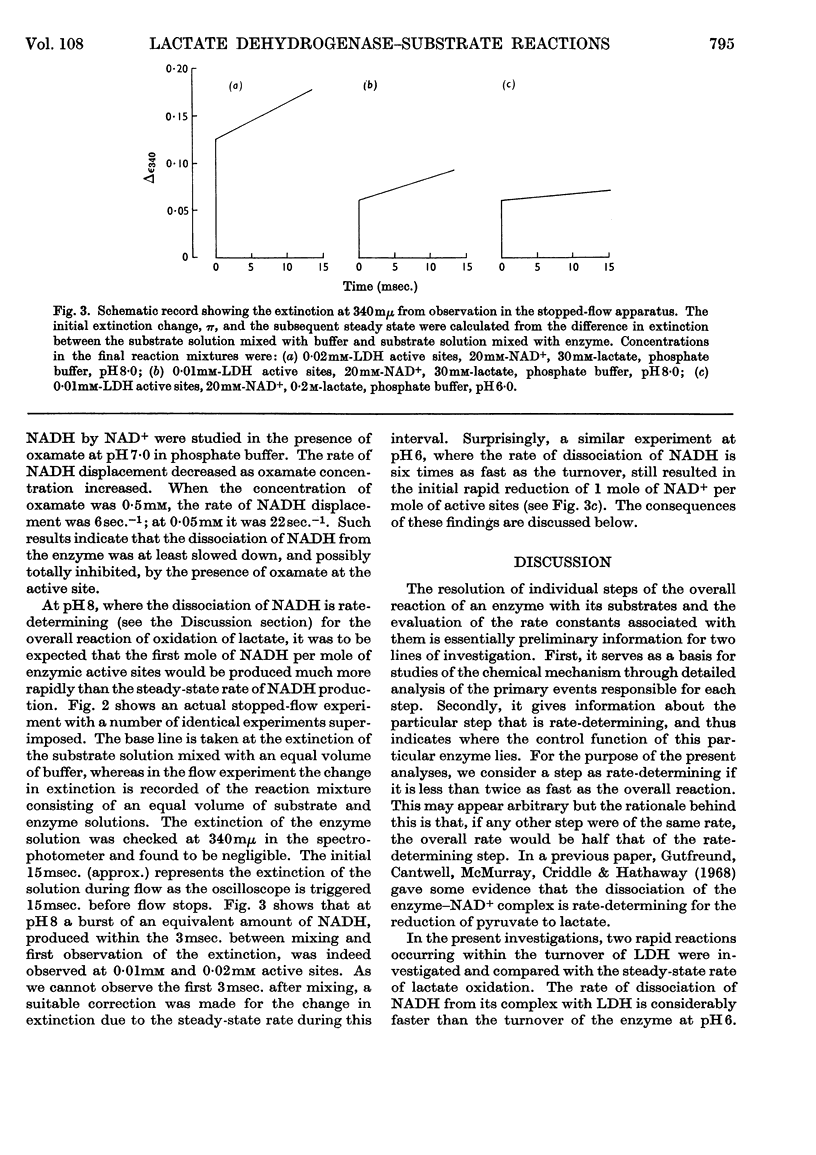

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barman T. E., Gutfreund H. Optical and chemical identification of kinetic steps in trypsin- and chymotrypsin-catalysed reactions. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):411–416. doi: 10.1042/bj1010411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., NEILANDS J. B. Studies on lactic dehydrogenase of heart. II. A compound of lactic dehydrogenase and reduced pyridine nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1952 Nov;199(1):383–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZERLINSKI G. H., SCHRECK G. FLUORESCENCE DETECTION OF THE CHEMICAL RELAXATION OF THE REACTION OF LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE WITH REDUCED NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:913–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraci G., Gibson Q. H. The reaction of liver alcohol dehydrogenase with reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4275–4278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutfreund H., Cantwell R., McMurray C. H., Criddle R. S., Hathaway G. The kinetics of the reversible inhibition of heart lactate dehydrogenase through the formation of the enzyme-oxidized nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide-pyruvate compounds. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(3):683–687. doi: 10.1042/bj1060683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J. The importance of SH-groups for enzymic activity. V. The coenzyme-binding capacity of pig heart lactate dehydrogenase, isozyme I, after inhibition by various maleinimides. Biochem Z. 1966 Mar 28;344(2):141–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsubo M., Pantaloni D. Régulation de l'activité de la glutamate déshydrogènase par les effecteurs GTP et ADP: étude par "stopped flow". Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1967 Dec 18;49(11):1563–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JECKEL D., PFLEIDERER G., WIELAND T. Uber die Einwirkung von Sulfit auf einige DPN hydrierende Enzyme. Biochem Z. 1956;328(3):187–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwert G. W., Miller B. R., Peanasky R. J. Lactic dehydrogenase. X. A re-evaluation of the effects of pH upon the kinetics of the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 25;242(14):3245–3252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


