Abstract
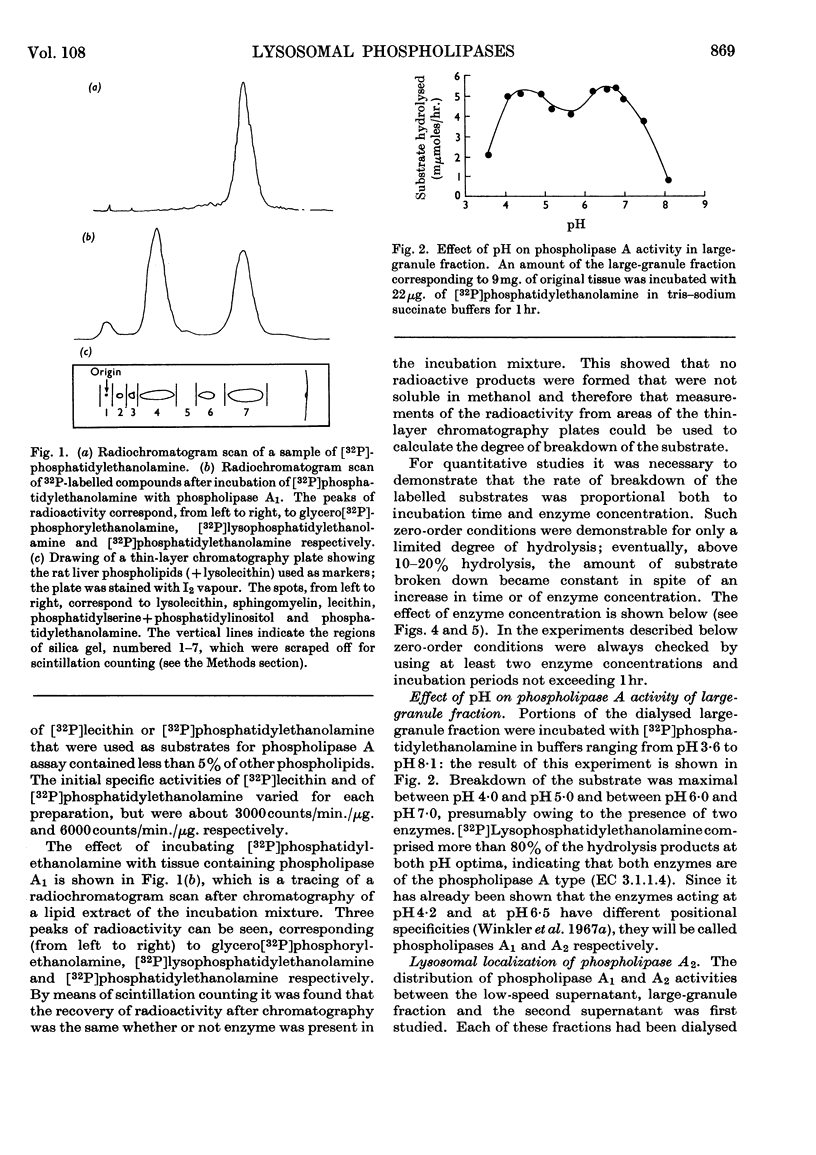
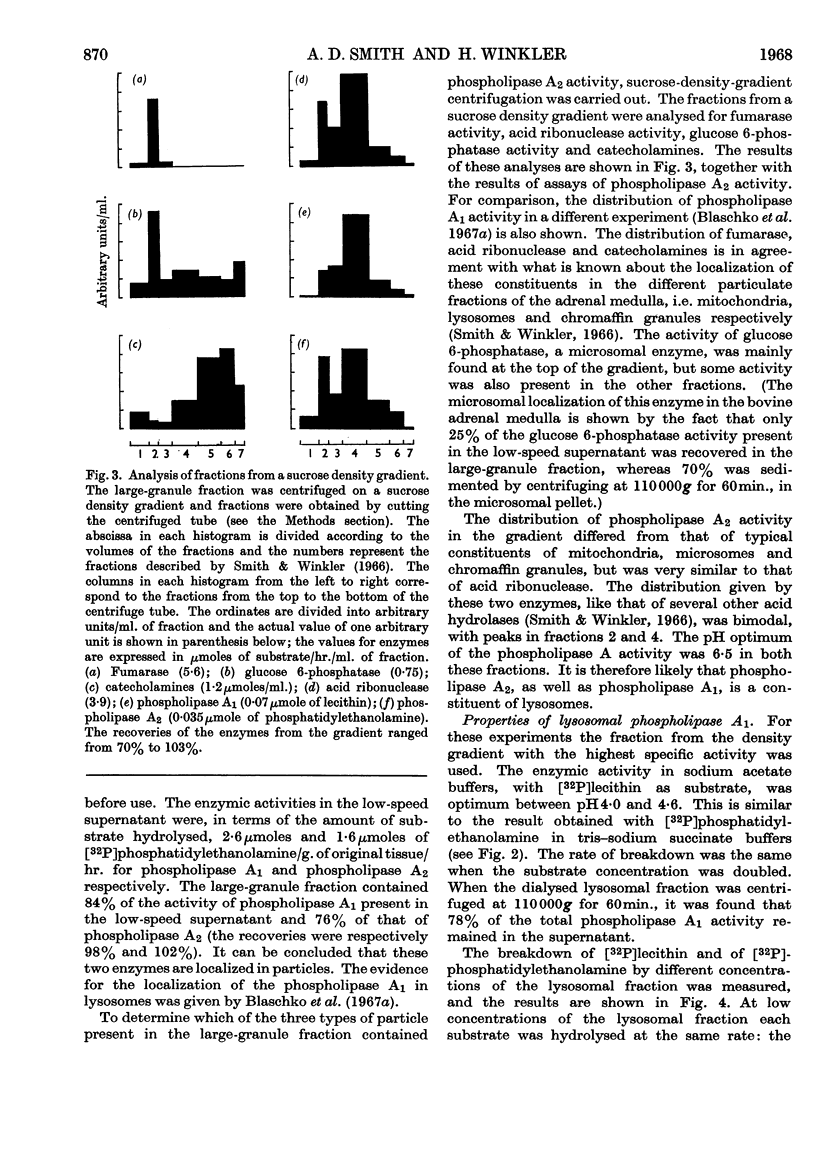
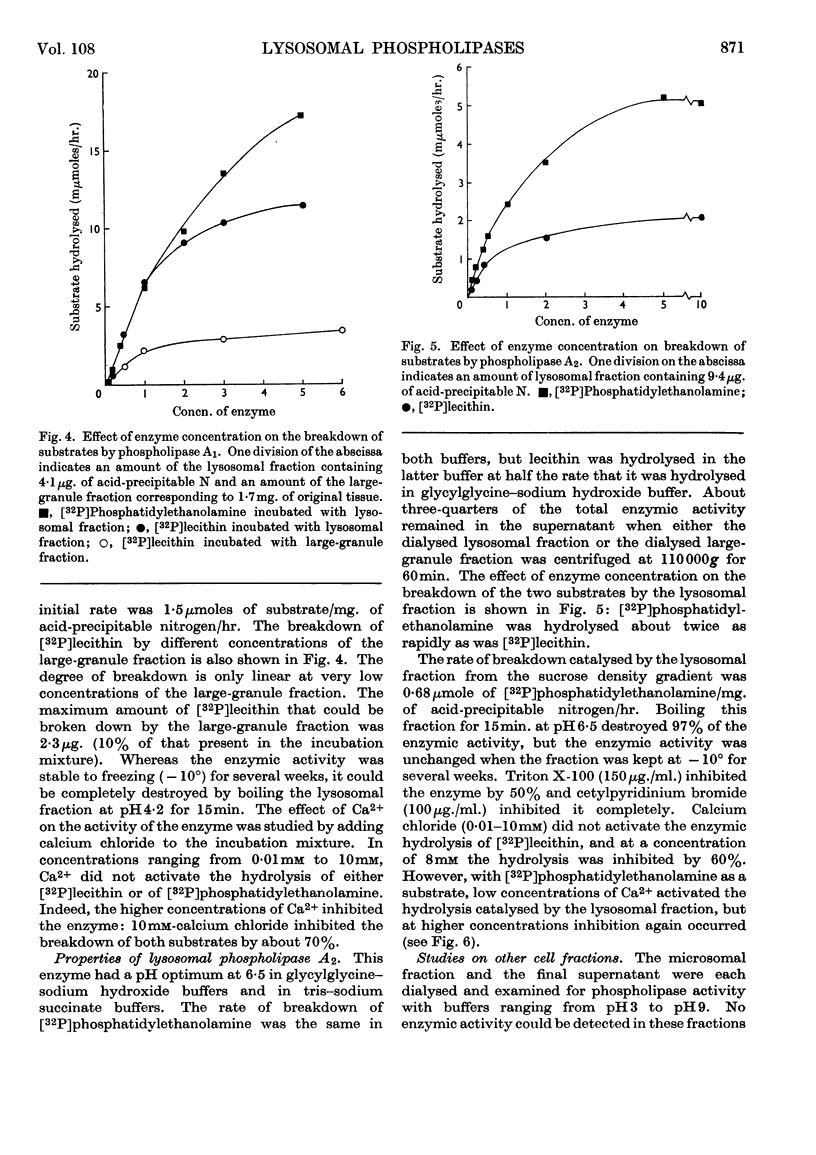
1. [32P]Lecithin and [32P]phosphatidylethanolamine were prepared by incubating rat liver mince with [32P]phosphate. With these 32P-labelled phospholipids conditions for the quantitative assay of phospholipase A activity were established. 2. The distribution of phospholipase A activity between subcellular fractions of the bovine adrenal medulla was determined. Phospholipases A1 and A2, with pH optima at 4·2 and 6·5 respectively, were found in the large-granule fraction. By means of sucrose-density-gradient centrifugation it was shown that both these phospholipases were localized in lysosomes. 3. Lysosomal phospholipase A1 catalysed the hydrolysis of [32P]lecithin and [32P]phosphatidylethanolamine at the same rate. The enzymic activity was inhibited by 70% in the presence of 10mm-calcium chloride. 4. Lysosomal phospholipase A2 catalysed the hydrolysis of [32P]phosphatidylethanolamine more rapidly than it hydrolysed [32P]lecithin. The hydrolysis of [32P]phosphatidylethanolamine, but not that of [32P]lecithin, by phospholipase A2 was activated by 0·8mm-calcium chloride. However, the hydrolysis of both substrates was inhibited by 8mm-calcium chloride. 5. The significance of the presence of phospholipase activity in lysosomes is discussed in relation to the functions of lysosomes in general and in the adrenal medulla.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornstad P. Phospholipase activity in rat-liver microsomes studied by the use of endogenous substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 1;116(3):500–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H., Firemark H., Smith A. D., Winkler H. Lipids of the adrenal medulla. Lysolecithin, a characteristic constituent of chromaffin granules. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):545–549. doi: 10.1042/bj1040545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., WIENER E. THE PARTICULATE HYDROLASES OF MACROPHAGES. I. COMPARATIVE ENZYMOLOGY, ISOLATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Exp Med. 1963 Dec 1;118:991–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS F. D. STUDIES ON PHOSPHOLIPIDS. 9. THE COMPOSITION OF RAT-LIVER LECITHINS. Biochem J. 1963 Aug;88:319–324. doi: 10.1042/bj0880319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C., Wattiaux R. Functions of lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1966;28:435–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.28.030166.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN B., SHAPIRO B. Lecithinase and lysolecithinase of intestinal mucosa. Biochem J. 1959 Apr;71(4):615–619. doi: 10.1042/bj0710615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P. Phospholipid metabolism by phagocytic cells. I. A comparison of conversion of [32P]lysolecithin to lecithin and glycerylphosphorylcholine by homogenates of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes and alveolar macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 7;125(3):510–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., van den Berg J. W., van den Bosch H., van Deenen L. L. Metabolism of phospholipids by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):338–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt S., Barenholz Y., Roitman A. Isolation of rat brain lecithinase-A, specific for the alpha'-position of lecithin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 20;24(2):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90714-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOVERAS J., DOUSTE-BLAZY L., VALDIGUIE P. [Mode of action of splenic phospholipase]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 18;256:1861–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors A., Tappel A. L. Hydrolysis of phospholipids by a lysosomal enzyme. J Lipid Res. 1967 Sep;8(5):479–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutter L. J., Privett O. S. Phospholipase a properties of several snake venom preparations. Lipids. 1966 Jul;1(4):258–262. doi: 10.1007/BF02531612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. Spectrophotometric measurements of the enzymatic formation of fumaric and cis-aconitic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI C. R., SARTORELLI L., TATO L., BARETTA L., SILIPRANDI N. PHOSPHOLIPASE A ACTIVITY OF RAT-LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 1;98:207–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERPHOF G. L., VANDEENEN L. L. PHOSPHOLIPASE A ACTIVITY OF RAT-LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 1;98:204–206. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider F. H., Smith A. D., Winkler H. Secretion from the adrenal medulla: biochemical evidence for exocytosis. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):94–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. The localization of lysosomal enzymes in chromaffin tissue. J Physiol. 1966 Mar;183(1):179–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DEN BOSCH H., VAN DEENEN L. THE FORMATION OF ISOMERIC LYSOLECITHINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 20;84:234–236. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M., van Deenen L. L. Hydrolysis of phospholipids and glycerides by rat-liver preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 6;137(3):498–517. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Strieder N., Ziegler E. Lysolecithin und Phospholipasen im chromaffinen Gewebe. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1967;257(1):77–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H., van Deenen L. L. Chemical structure and biochemical significance of lysolecithins from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):326–337. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


