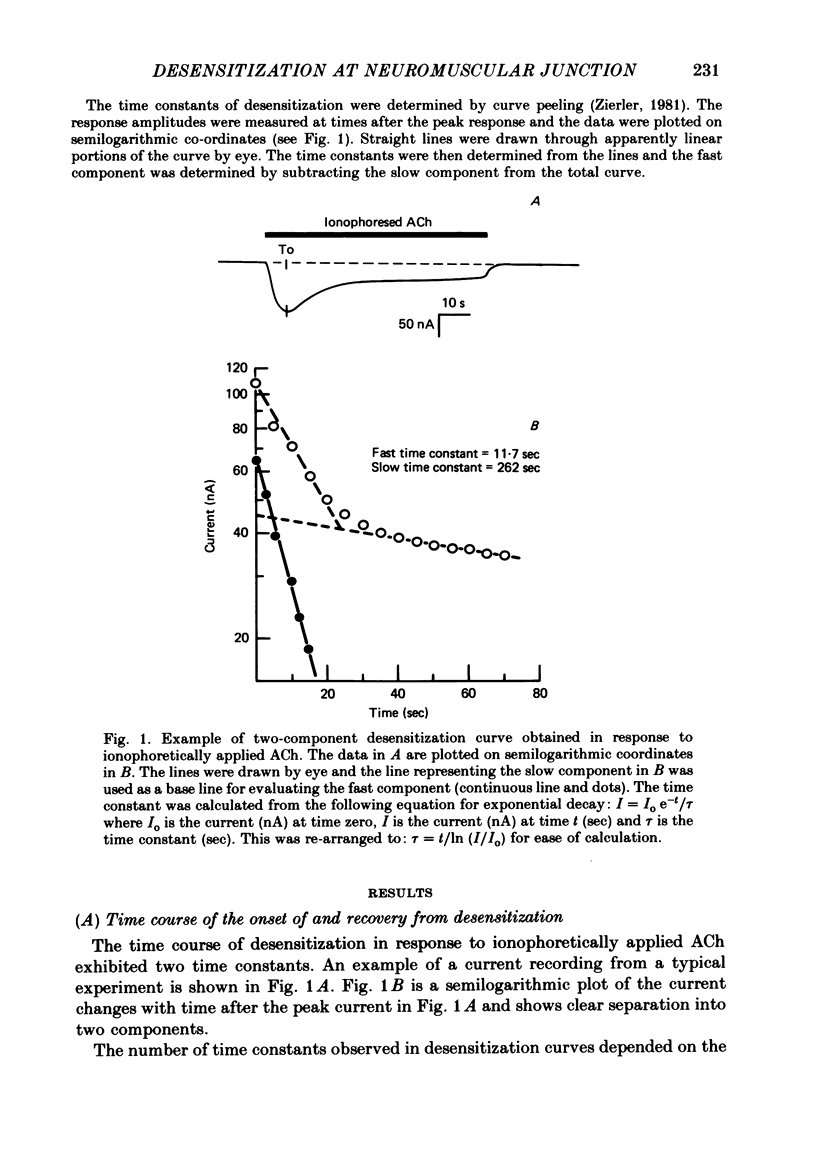
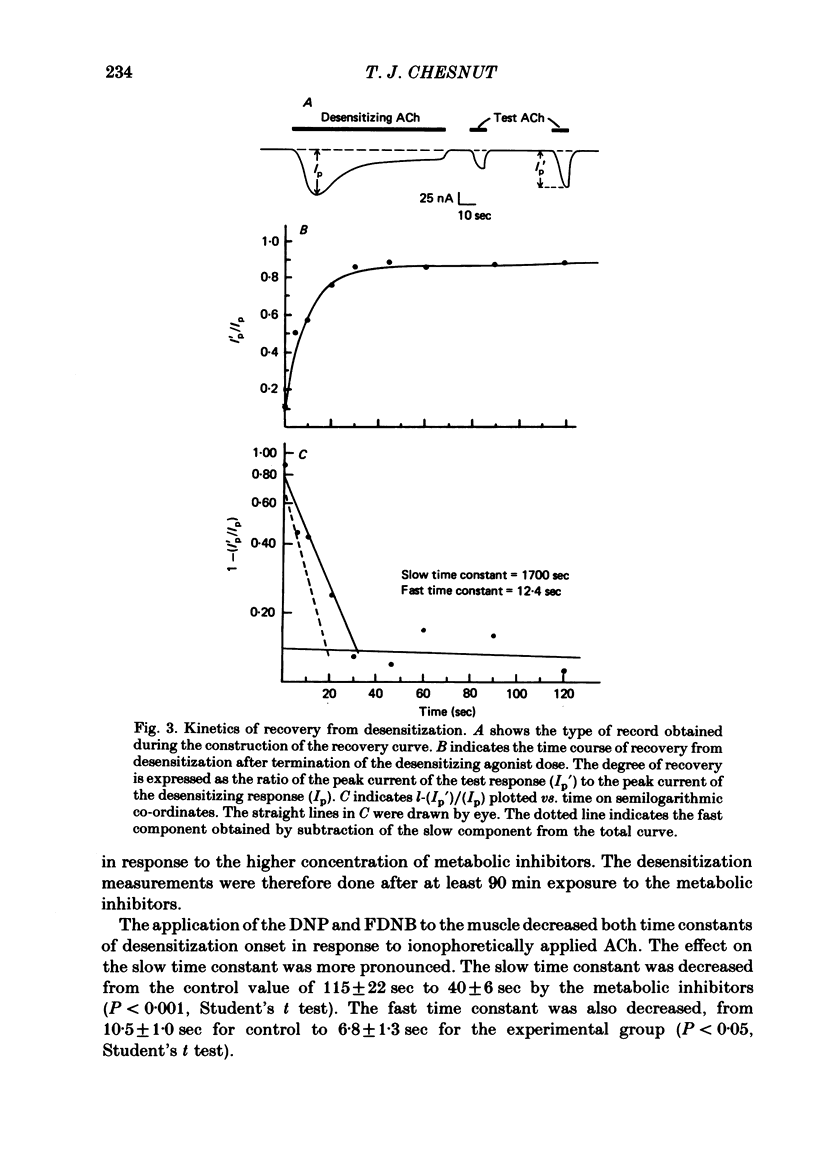
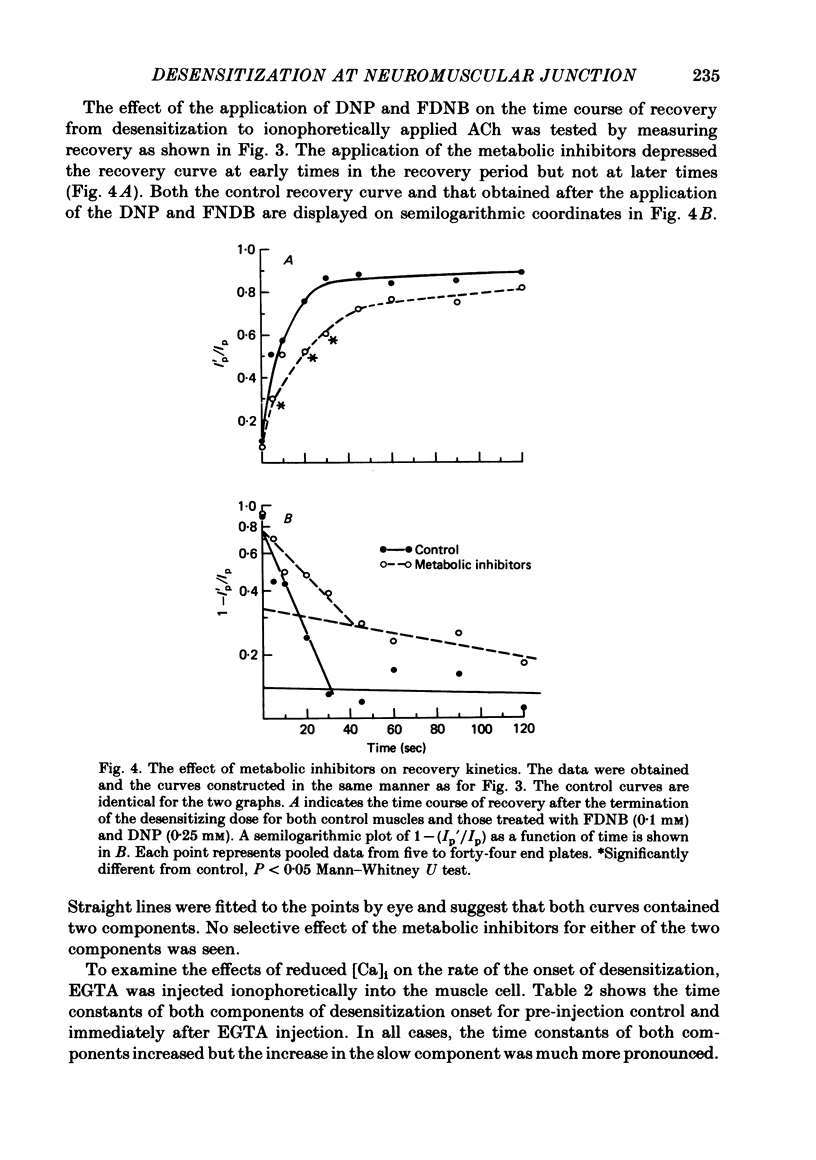
Abstract
Desensitization to ionophoretically applied ACh has been studied at voltage-clamped neuromuscular junctions of Rana pipiens. The time courses of both the onset of and recovery from desensitization displayed two components. The application of metabolic inhibitors to the preparation decreased the degree of recovery and also decreased both time constants of onset. The effect on onset was more pronounced on the slow component while no effect selective for either of the two components of recovery was seen. Intracellular injection of EGTA into the muscle cell increased both time constants of desensitization onset. The effect was much more pronounced on the slow component. Increasing the dose of ACh selectively decreased the fast time constant of desensitization onset. The effect was more selective in low-calcium than normal Ringer solution. These observations suggest that there are at least two independent mechanisms in the process of desensitization at the neuromuscular junction. These mechanisms differ in time course, degree of dependency on [Ca]i, and sensitivity to acetylcholine dose.
Full text
PDF



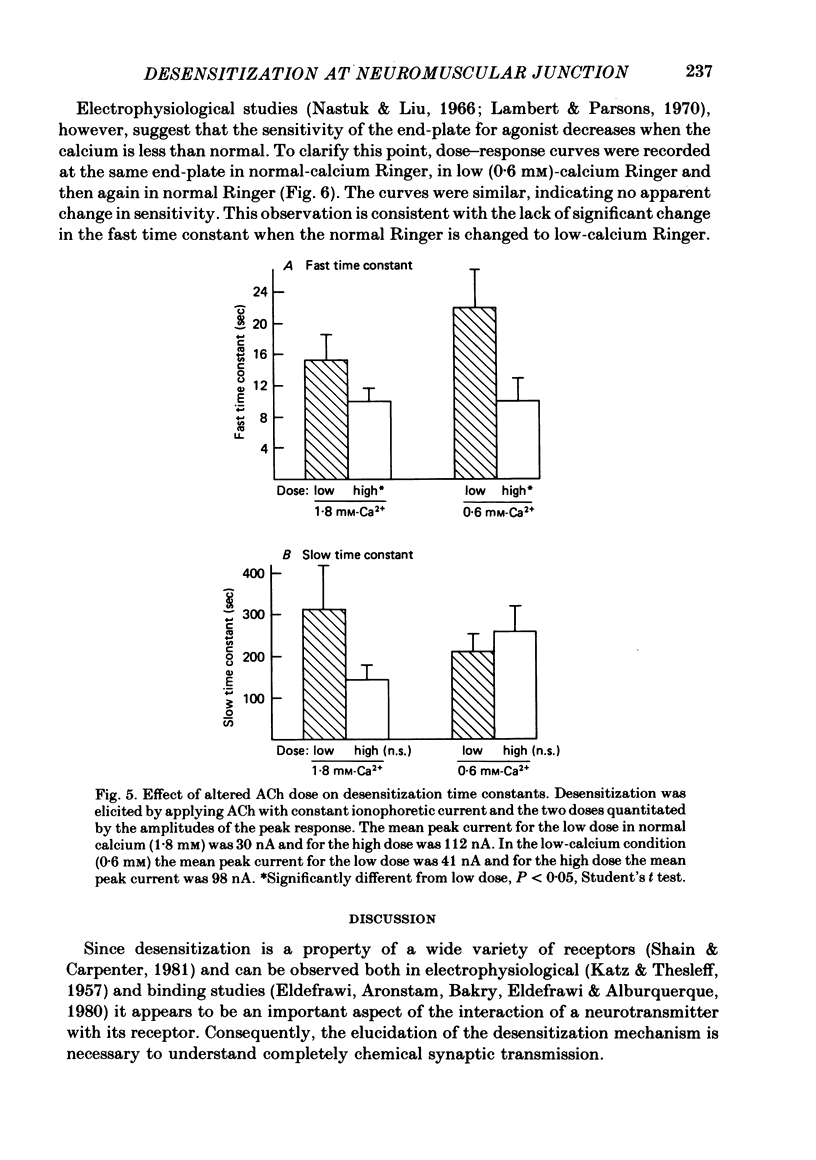
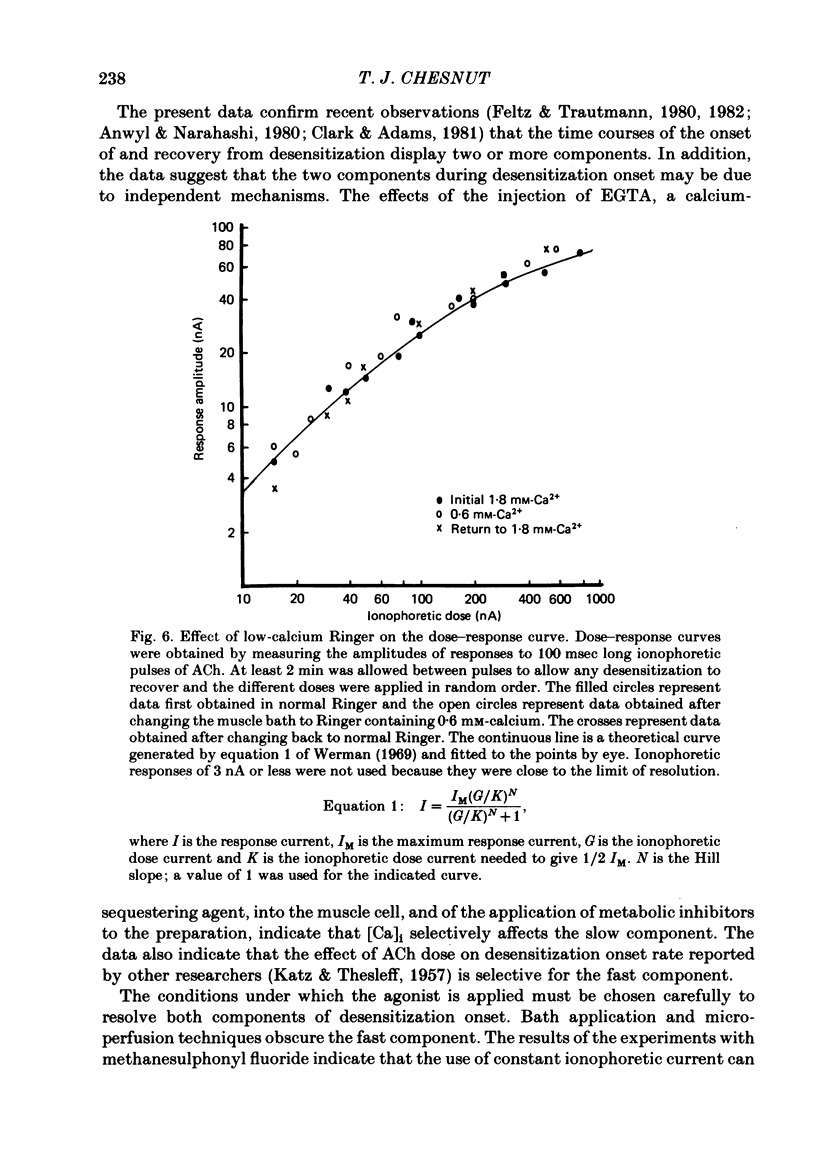



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. A study of desensitization using voltage clamp. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Oct 28;360(2):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00580536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwyl R., Narahashi T. Desensitization of the acetylcholine receptor of denervated rat soleus muscle and the effect of calcium. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 May;69(1):91–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Crompton M. The regulation of intracellular calcium by mitochondria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:269–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Neumann E. Dynamic properties of isolated acetylcholine receptor proteins: release of calcium ions caused by acetylcholine binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3364–3368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBassio W. A., Parsons R. L., Schnitzler R. M. Effect of ionophore X-537A on desensitization rate and tension development in potassium-depolarized muscle fibres. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;57(4):565–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb10386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Aronstam R. S., Bakry N. M., Eldefrawi A. T., Albuquerque E. X. Activation, inactivation, and desensitization of acetylcholine receptor channel complex detected by binding of perhydrohistrionicotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2309–2313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltz A., Trautmann A. Desensitization at the frog neuromuscular junction: a biphasic process. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:257–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltz A., Trautmann A. Interaction between nerve-related acetylcholine and bath applied agonists at the frog end-plate. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:533–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Effects of the intracellular Ca ion concentration upon the excitability of the muscle fiber membrane of a barnacle. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):807–818. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. H., Parsons R. L. Influence of polyvalent cations on the activation of muscle end plate receptors. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Sep;56(3):309–321. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthey A. A. The effect of calcium on the desensitization of membrane receptors at the neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):963–976. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. The mechanism of action of DNP on phospholipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1972;9(4):361–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Intracellular calcium and desensitization of acetylcholine receptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Sep 26;209(1176):447–452. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastuk W. L., Liu J. H. Muscle postjunctional membrane: changes in chemosensitivity produced by calcium. Science. 1966 Oct 14;154(3746):266–267. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3746.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTZEHL H., CALDWELL P. C., RUEEGG J. C. THE DEPENDENCE OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBRES FROM THE CRAB MAIA SQUINADO ON THE INTERNAL CONCENTRATION OF FREE CALCIUM IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 25;79:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shain W., Carpenter D. O. Mechanisms of synaptic modulation. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1981;22:205–250. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan R. E., Lester H. A. Rates and equilibria at the acetylcholine receptor of Electrophorus electroplaques: a study of neurally evoked postsynaptic currents and of voltage-jump relaxations. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):187–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Active phase of frog's end-plate potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):395–411. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R. An electrophysiological approach to drug-receptor mechanisms. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Sep 15;30(6):997–1017. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)91038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler K. A critique of compartmental analysis. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:531–562. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


