Abstract
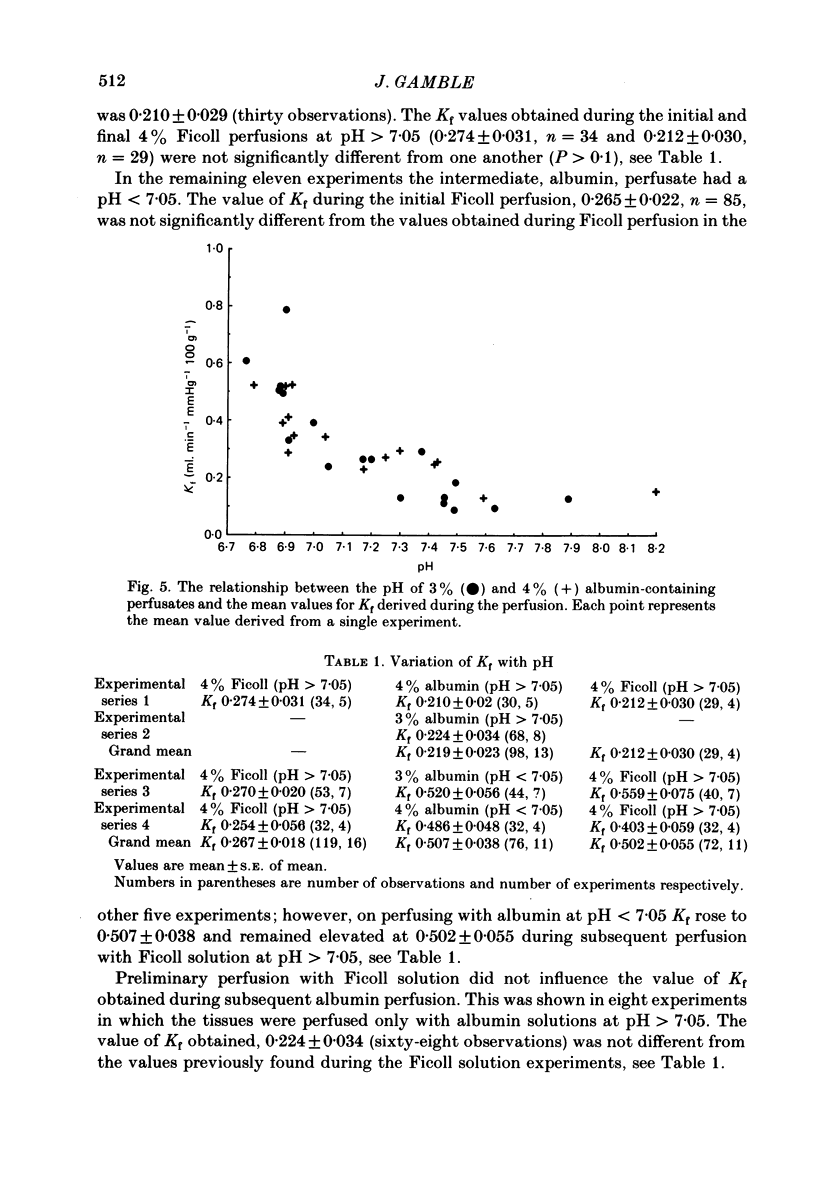
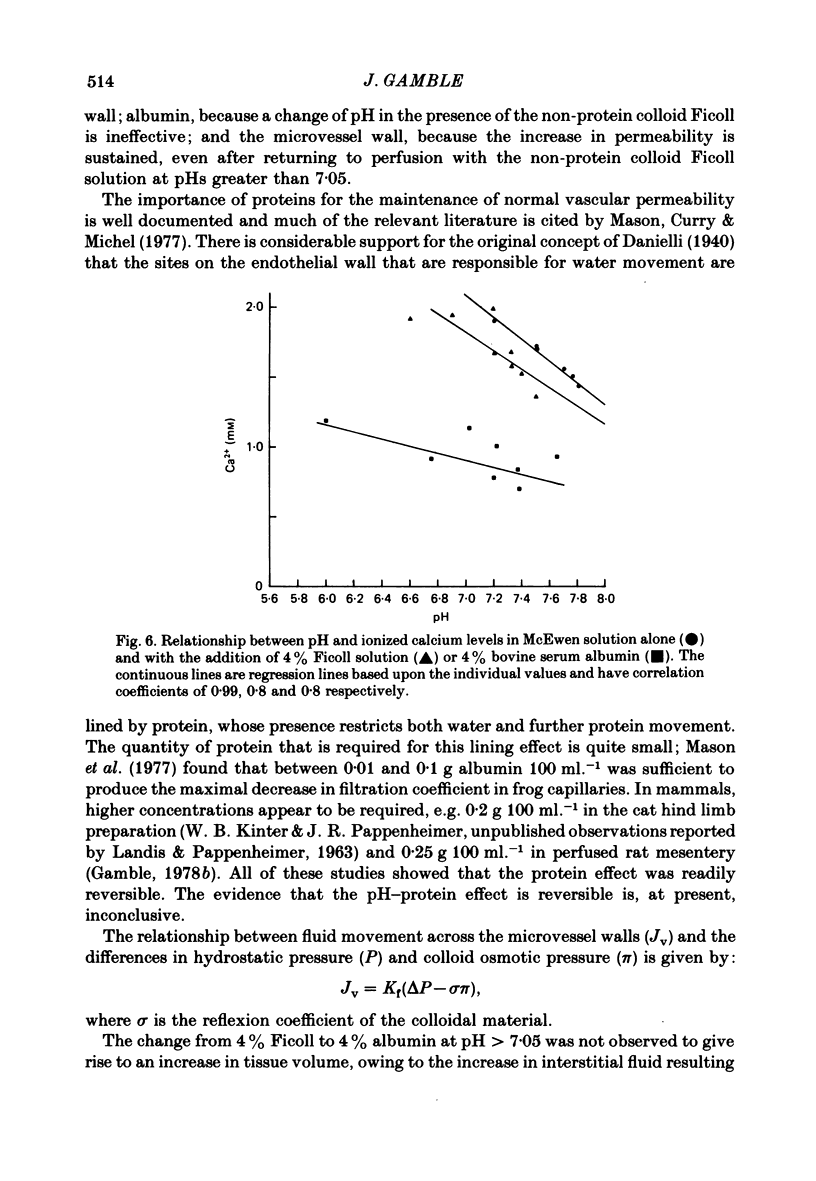
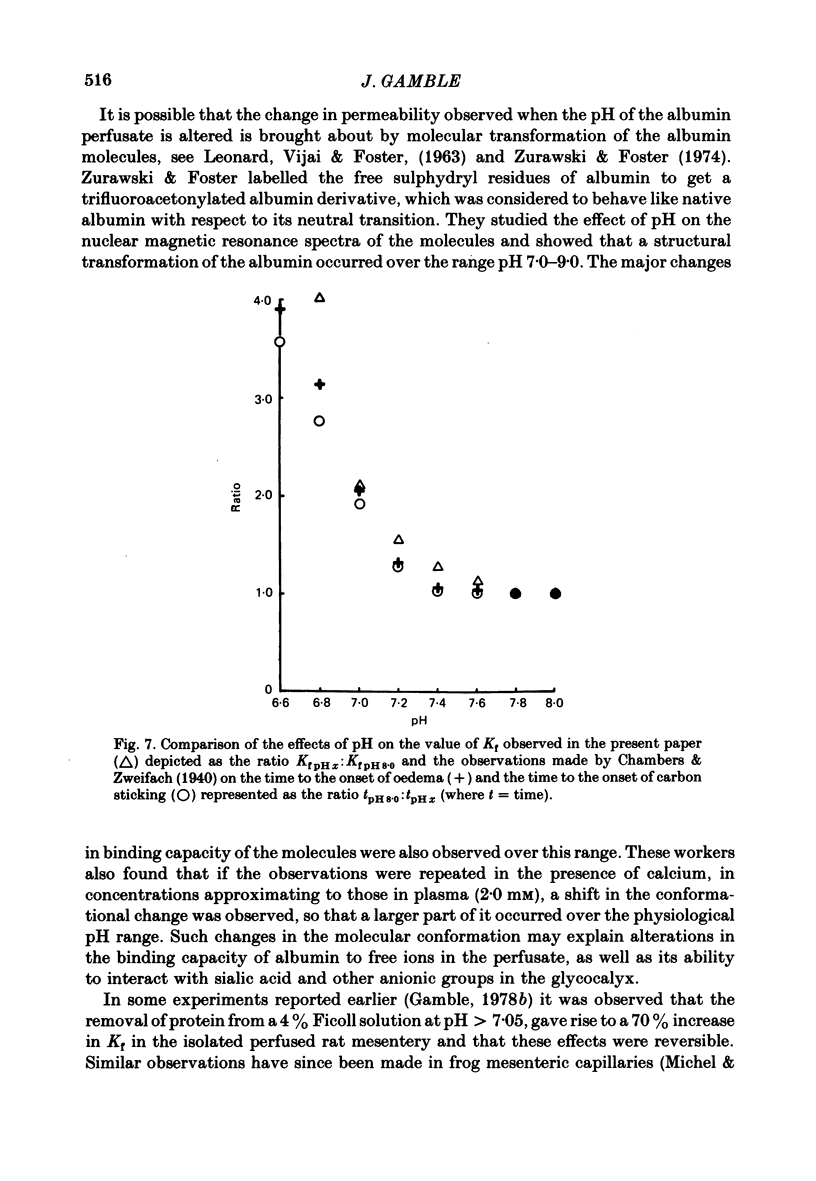
A preparation of rat mesentery was vascularly isolated from the intestine and perfused with a physiological salt solution containing either Ficoll 70 or bovine serum albumin, to act as colloidal agents. The capillary filtration coefficient (Kf; units, ml. min-1 100 g-1 mmHg-1) was measured by following the weight change after graded increases in venous pressure. At pH values greater than 7.05, Kf, during perfusion with 3 and 4% bovine serum albumin solutions, was 0.219 +/- 0.023 (mean +/- S.E. of mean), ninety-eight observations in thirteen experiments, which was significantly less than the value of 0.507 +/- 0.038 which was obtained during perfusion with albumin solutions at pH less than 7.05, seventy-six observations in eleven experiments, (P less than 0.05). The value of Kf obtained during perfusion with 4% Ficoll solutions was 0.267 +/- 0.018, 119 observations in sixteen experiments, and remained uninfluenced by pH over the same range that had been used with the albumin solutions; however, perfusion of the tissues with Ficoll solutions at pH greater than 7.05, after perfusion with albumin solution pH less than 7.05, did cause the Ficoll-derived value of Kf to rise to 0.502 +/- 0.055, seventy-two observations in eleven experiments. It was concluded that the changes in Kf were not due to pH alone, but were mediated by albumin at acidic pH.
Full text
PDF


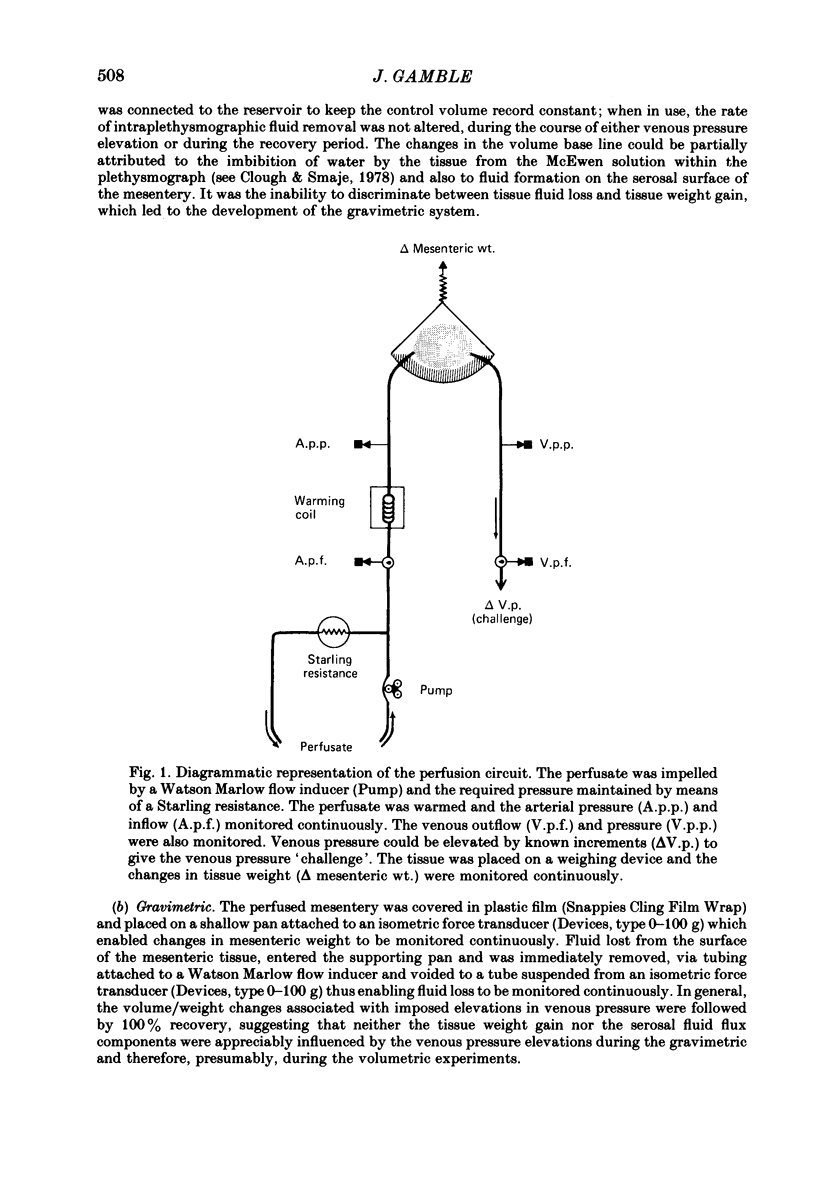
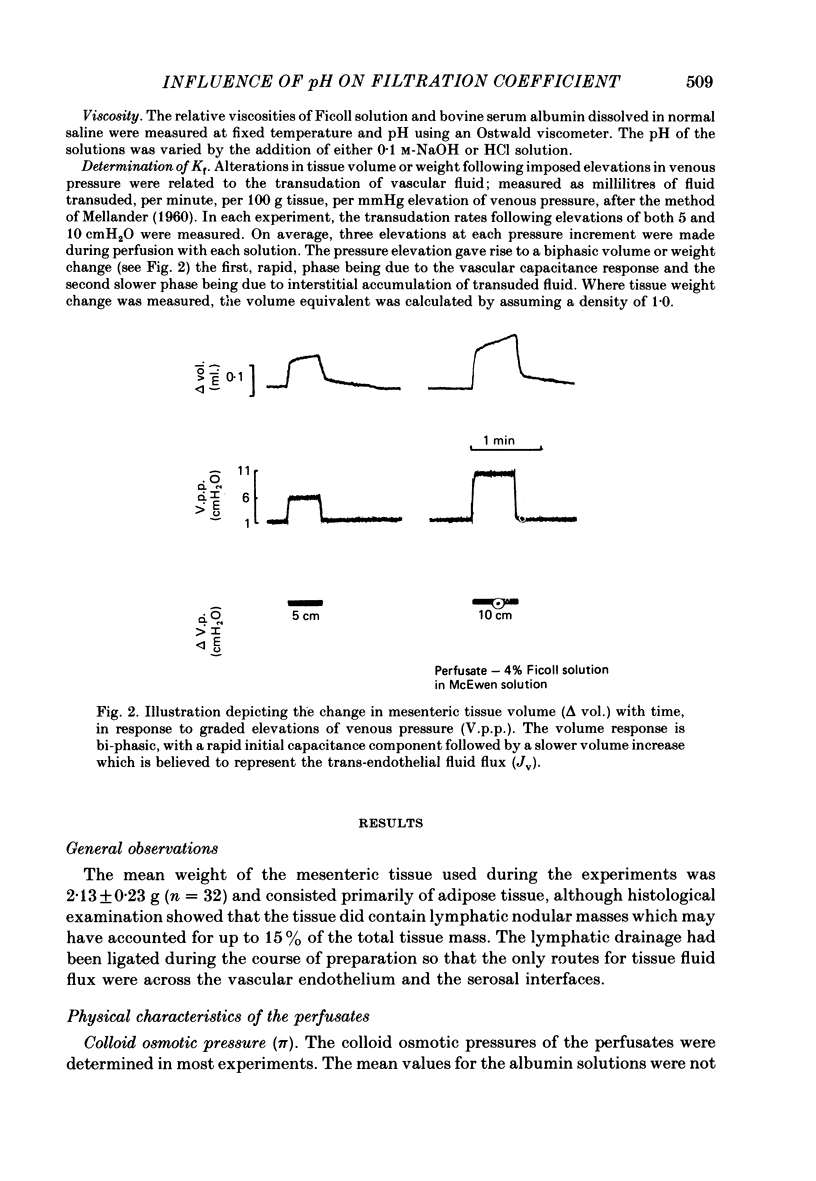
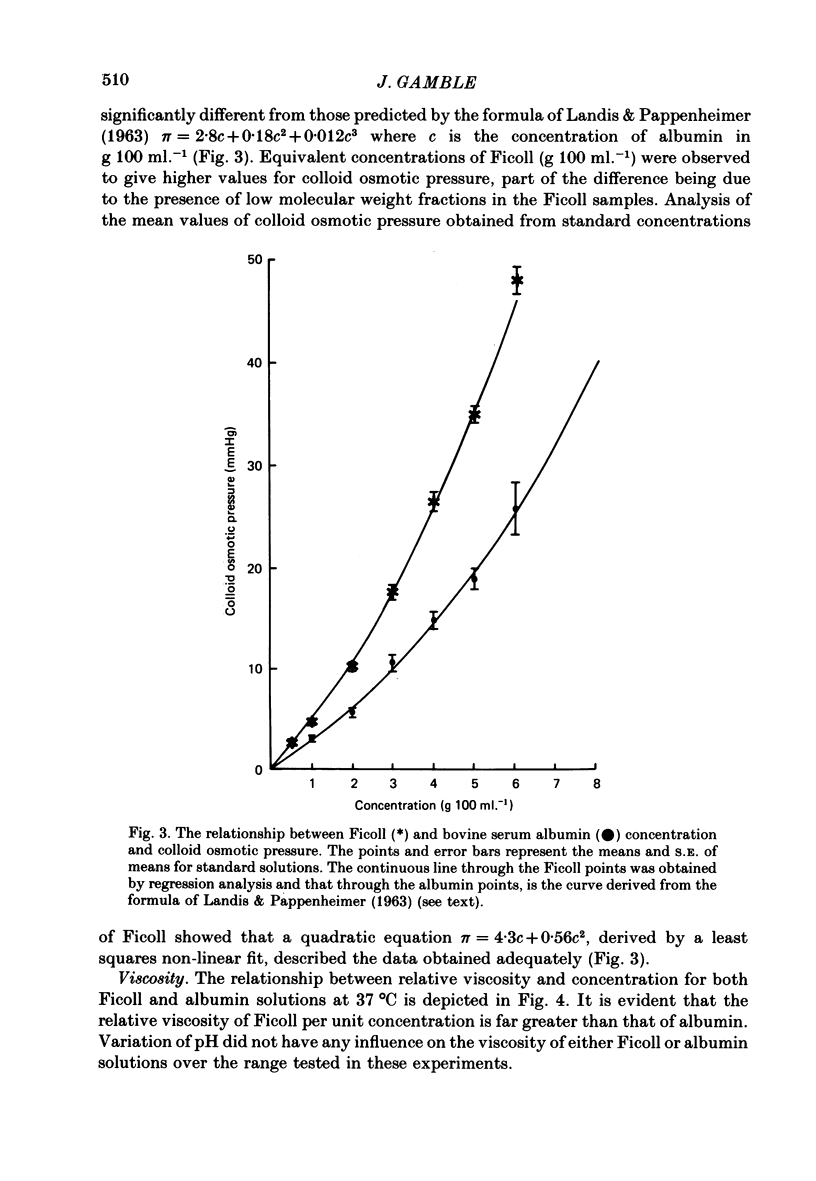
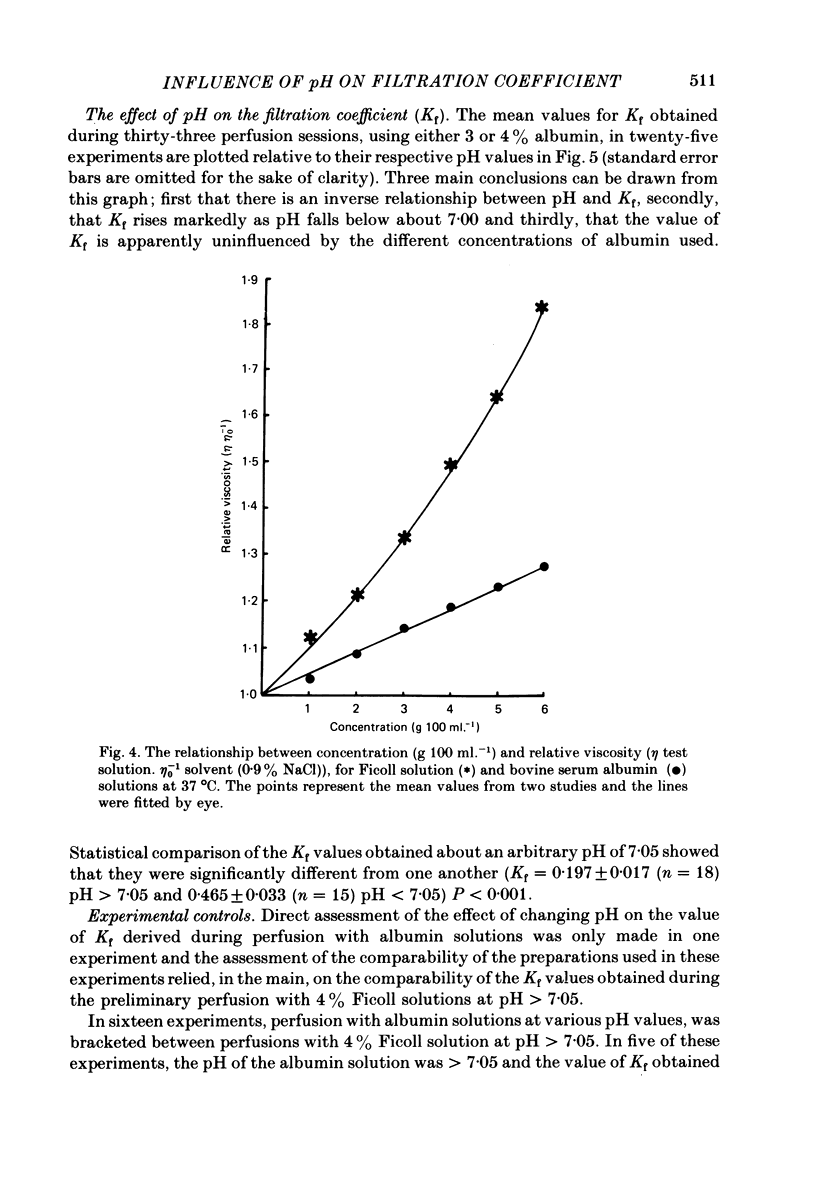




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard K., Perl W. Osmotic reflection coefficients of canine subcutaneous adipose tissue endothelium. Microvasc Res. 1978 Sep;16(2):224–236. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(78)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementi F., Palade G. E. Intestinal capillaries. II. Structural effects ofEDTA and histamine. J Cell Biol. 1969 Sep;42(3):706–714. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.3.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough G., Smaje L. H. Simultaneous measurement of pressure in the interstitium and the terminal lymphatics of the cat mesentery. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:457–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielli J. F. Capillary permeability and oedema in the perfused frog. J Physiol. 1940 Mar 14;98(1):109–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1940.sp003837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Gamble J. Changes in the rate of transudation of vascular fluid in the isolated rat mesentery following irradiation [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;266(1):71P–72P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn P. P., Michelson S. Changes in the random distribution of sialic acid at the surface of the myeloid sinusoidal endothelium resulting from the presence of diaphragmed fenestrae. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):708–714. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drinker C. K. The permeability and diameter of the capillaries in the web of the brown frog (R. temporaria) when perfused with solutions containing pituitary extract and horse serum. J Physiol. 1927 Aug 8;63(3):249–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1927.sp002401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. The effect of low concentrations of bovine albumin on the vascular transudation coefficient of the isolated perfused rat mesentery [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:63P–64P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. The effects of bovine albumin on the vascular permeability of the perfused rat mesentery [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:15P–16P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardcastle J., Hardcastle P. T., Redfern J. S. Action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on intestinal ion transport in the rat. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:41–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARD W. J., Jr, VIJAI K. K., FOSTER J. F. A structural transformation in bovine and human plasma albumins in alkaline solution as revealed by rotatory dispersion studies. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:1984–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundvall J., Holmberg J. Role of tissue hyperosmolality in functional vasodilatation in the submandibular gland. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Oct;92(2):165–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCEWEN L. M. The effect on the isolated rabbit heart of vagal stimulation and its modification by cocaine, hexamethonium and ouabain. J Physiol. 1956 Mar 28;131(3):678–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELLANDER S. Comparative studies on the adrenergic neuro-hormonal control of resistance and capacitance blood vessels in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1960;50(176):1–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. C., Curry F. E., Michel C. C. The effects of proteins upon the filtration coefficient of individually perfused frog mesenteric capillaries. Microvasc Res. 1977 Mar;13(2):185–202. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel C. C., Phillips M. E. The effects of Ficoll 70 on bovine serum albumin on the permeability properties of individually perfused frog mesenteric capillaries [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:39P–39P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Rennke H. G. The structural and molecular basis of glomerular filtration. Circ Res. 1978 Sep;43(3):337–347. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski V. R., Jr, Foster J. F. The neutral transition and the environment of the sulfhydryl side chain of bovine plasma albumin. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3465–3471. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


