Abstract
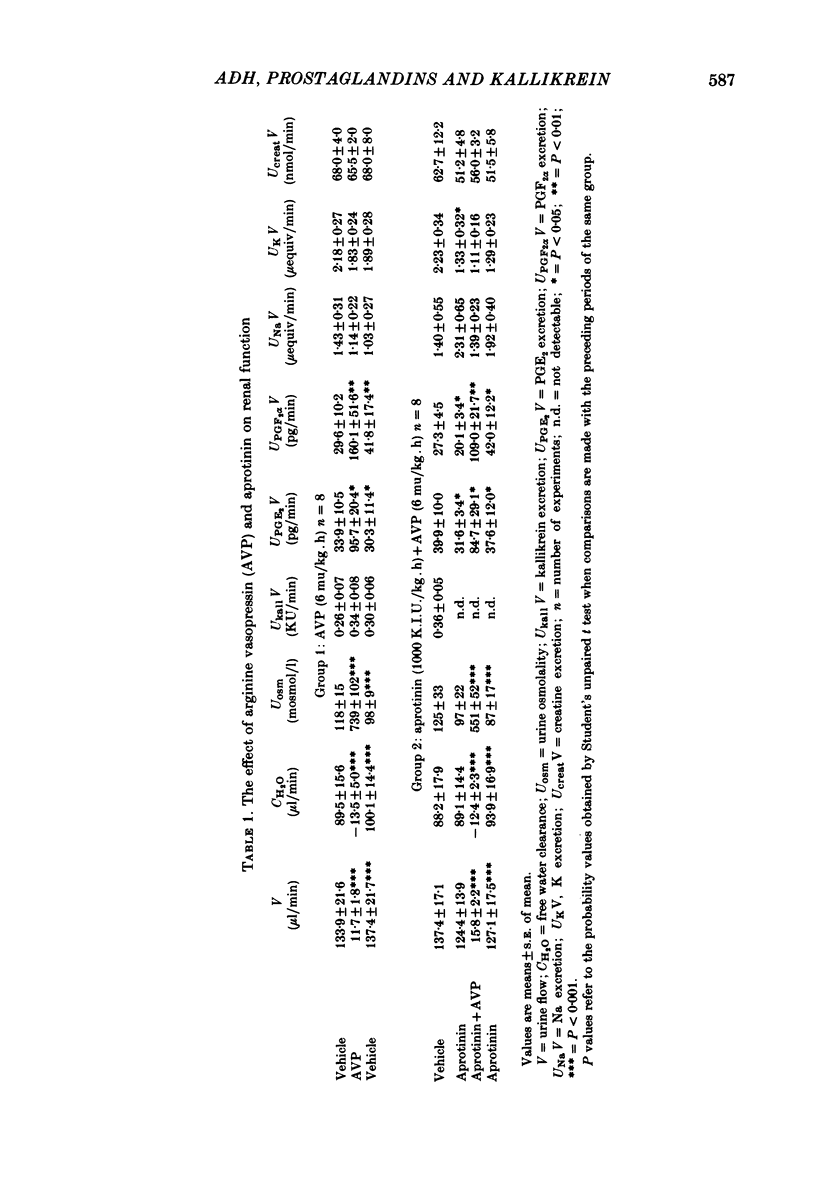
The renal response to arginine vasopressin was investigated with and without the simultaneous administration of the kallikrein inhibitor, aprotinin, in conscious Brattleboro homozygous rats with hereditary diabetes insipidus. Arginine vasopressin caused a marked antidiuretic response (urinary osmolality increased from 118 to 739 mosmol/l) which was accompanied by a significant increase in urinary prostaglandin excretion (prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha excretion increased by 182 and 441%, respectively). Kallikrein excretion remained unchanged after arginine vasopressin infusion. The infusion of aprotinin diminished urinary kallikrein activity to undetectable levels, decreased potassium excretion significantly and caused a slight fall in urinary prostaglandin excretion. However, aprotinin failed to modify the arginine vasopressin-induced enhancement in prostaglandin excretion (prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha excretion increased by 168 and 442%, respectively), and the antidiuretic response was also similar to that observed under control conditions. These results indicate that the kallikrein-kinin system is not involved in the renal response to vasopressin in the Brattleboro rat.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carvounis C. P., Carvounis G., Arbeit L. A. Role of the endogenous kallikrein-kinin system in modulating vasopressin-stimulated water flow and urea permeability in the toad urinary bladder. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1792–1796. doi: 10.1172/JCI110219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colina-Chourio J., McGiff J. C., Miller M. P., Nasjletti A. Possible influence of intrarenal generation of kinins on prostaglandin release from the rabbit perfused kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;58(2):165–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb10392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. J., Greely H. P., Valtin H., Kintner L. B., Beeuwkes R., 3rd Renal excretion of prostaglandins E2 and F2alpha in diabetes insipidus rats. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):E624–E627. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.6.E624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejes-Tóth G., Zahajszky T., Filep J. Effect of vasopressin on renal kallikrein excretion. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):F388–F392. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.4.F388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellai M., Valtin H. Chronic vascular constrictions and measurements of renal function in conscious rats. Kidney Int. 1979 Apr;15(4):419–426. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjletti A., McGiff J. C., Colina-Chourio J. Interrelations of the renal kallikrein-kinin system and renal prostaglandins in the conscious rat. Influence of mineralocorticoids. Circ Res. 1978 Nov;43(5):799–807. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.5.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen U. B., Ahnfelt-Ronne I. Bumetanide induced increase of renal blood flow in conscious dogs and its relation to local renal hormones (PGE, kallikrein and renin). Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1976 Mar;38(3):219–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1976.tb03114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtin H. Animal model of human disease: hereditary hypothalamic diabetes insipidus. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jun;83(3):633–636. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. A., Frölich J. C. Dose-dependent stimulation of renal prostaglandin synthesis by deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin in rats with hereditary diabetes insipidus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Apr;217(1):87–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. A., Whorton A. R., Smigel M., France R., Frölich J. C. Antidiuretic hormone increases renal prostaglandin synthesis in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1978 Sep;235(3):F180–F185. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.3.F180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


