Abstract
The membrane at the tendinous ends of frog muscle fibres has acetylcholine (ACh) receptors that are blocked by alpha-bungarotoxin. The properties of ACh-activated channels in the myotendinous region were investigated by noise analysis. These channels displayed the same characteristics in normal, denervated and reinnervated muscles. The mean lifetime and conductance of ACh-induced channels at the myotendinous junction resembled those of channels at the normal neuromuscular junction. Both channels opened with a lifetime shorter than that of extrajunctional receptors. Channels of short lifetime could be detected at distances of several hundred micrometres from the tendon junction. The similarity of ACh-activated channels at neuromuscular and myotendon junctions was found both in the fast, 'singly' innervated sartorius and cutaneous pectoris muscle and in the intermediate, multiply innervated submaxillaris muscle.
Full text
PDF

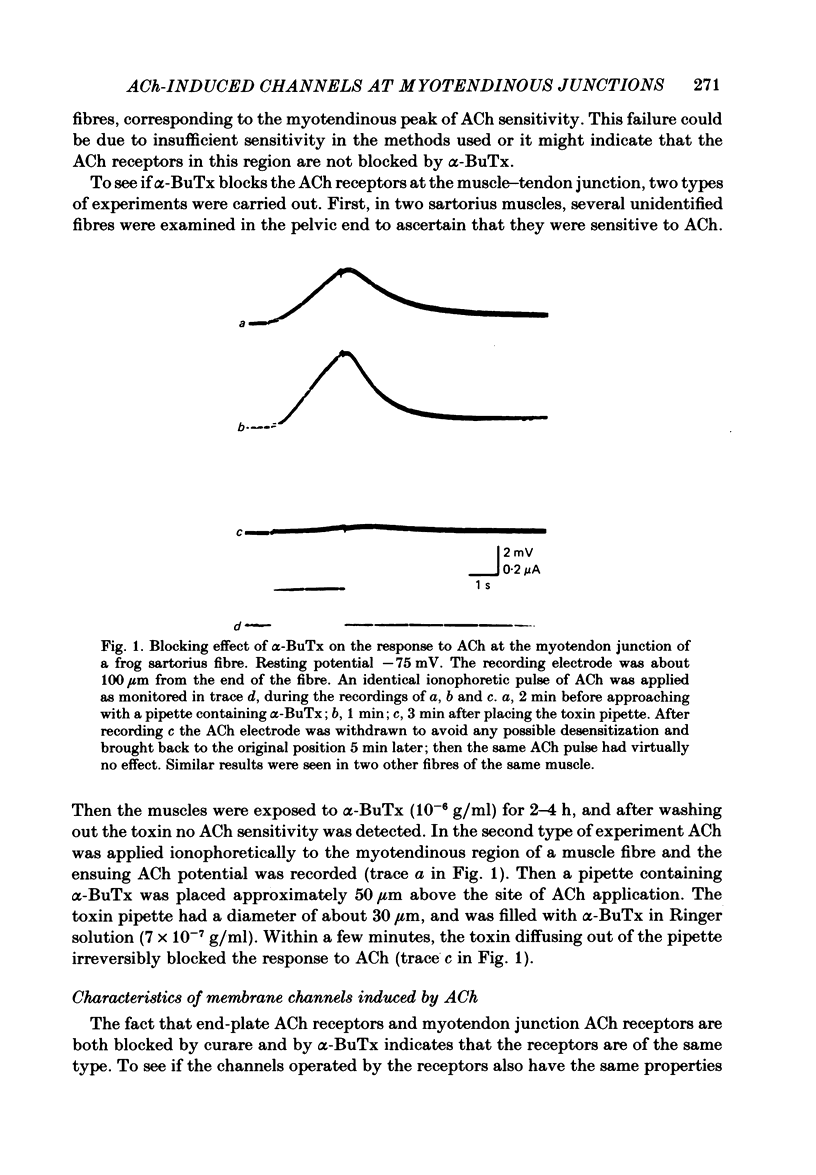
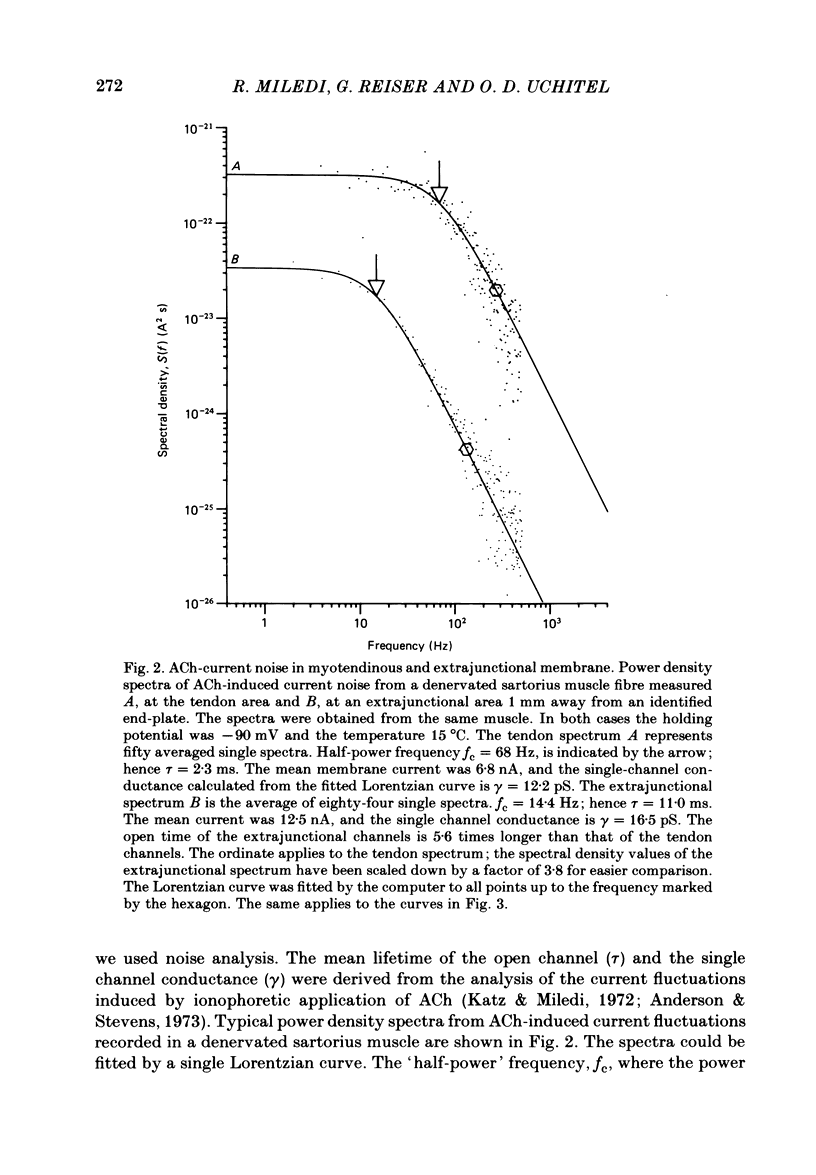
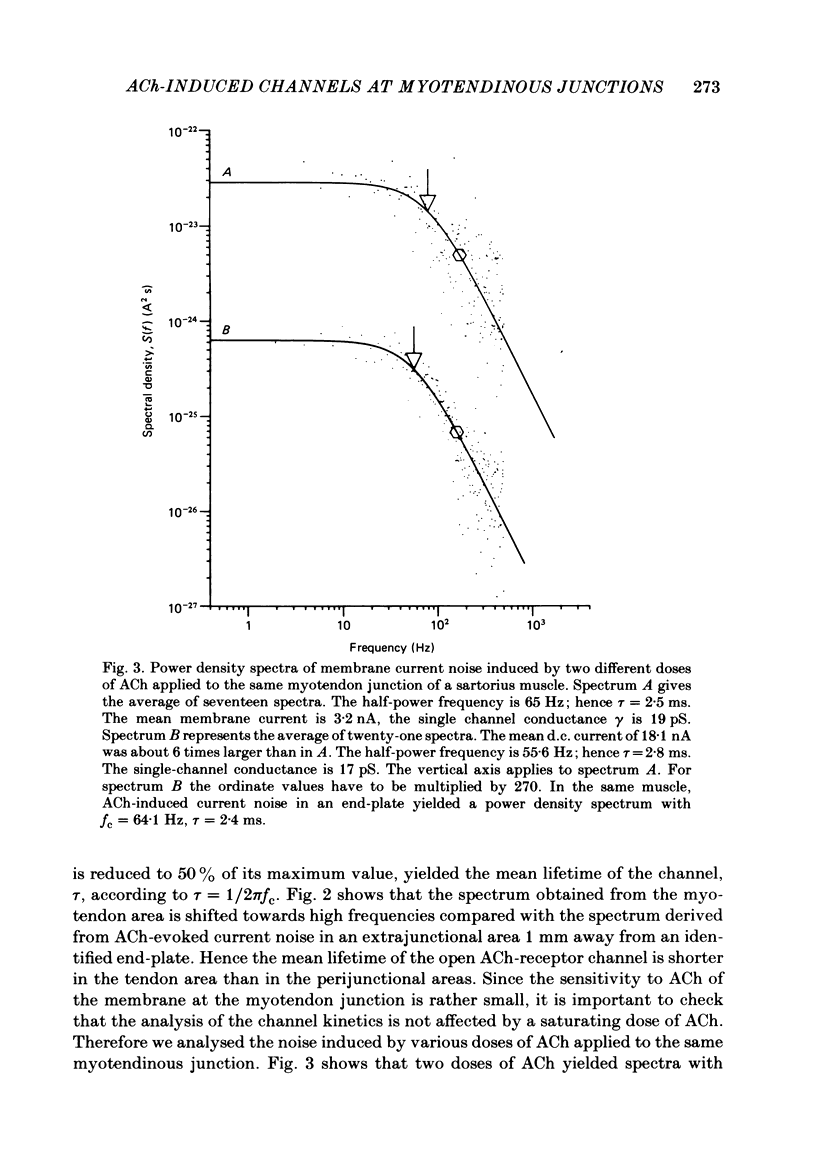




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R. Glutamate current noise: post-synaptic channel kinetics investigated under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:219–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUTEAUX R. Sur le mode de terminaison des myofibrilles et leurs connexions avec la membrane sarcoplasmique au niveau de la jonction musculo-tendineuse. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1958 Jan 13;246(2):307–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R., Uchitel O. D. Properties of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine-receptor channels in organ cultured human muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:251–267. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. P., Miledi R., Perez de la Mora M., Vincent A. Acetylcholine receptors. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):551–559. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE DISTRIBUTION OF ACTYLCHOLINE-REACTIVE SITES IN SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:379–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE DEVELOPMENT OF ACETYLCHOLINE SENSITIVITY IN NERVE-FREE SEGMENTS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:389–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. Junctional and extra-junctional acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:24–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete or partial devervation. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Uchitel O. D. Properties of postsynaptic channels induced by acetylcholine in different frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1981 May 14;291(5811):162–165. doi: 10.1038/291162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Zelená J. Sensitivity to acetylcholine in rat slow muscle. Nature. 1966 May 21;210(5038):855–856. doi: 10.1038/210855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Noise analysis of drug induced voltage clamp currents in denervated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;258(3):705–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J. A., Corbett K., Avner B. P. Structure and function of the murine muscle-tendon junction. Anat Rec. 1981 Oct;201(2):293–302. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092010209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



