Abstract
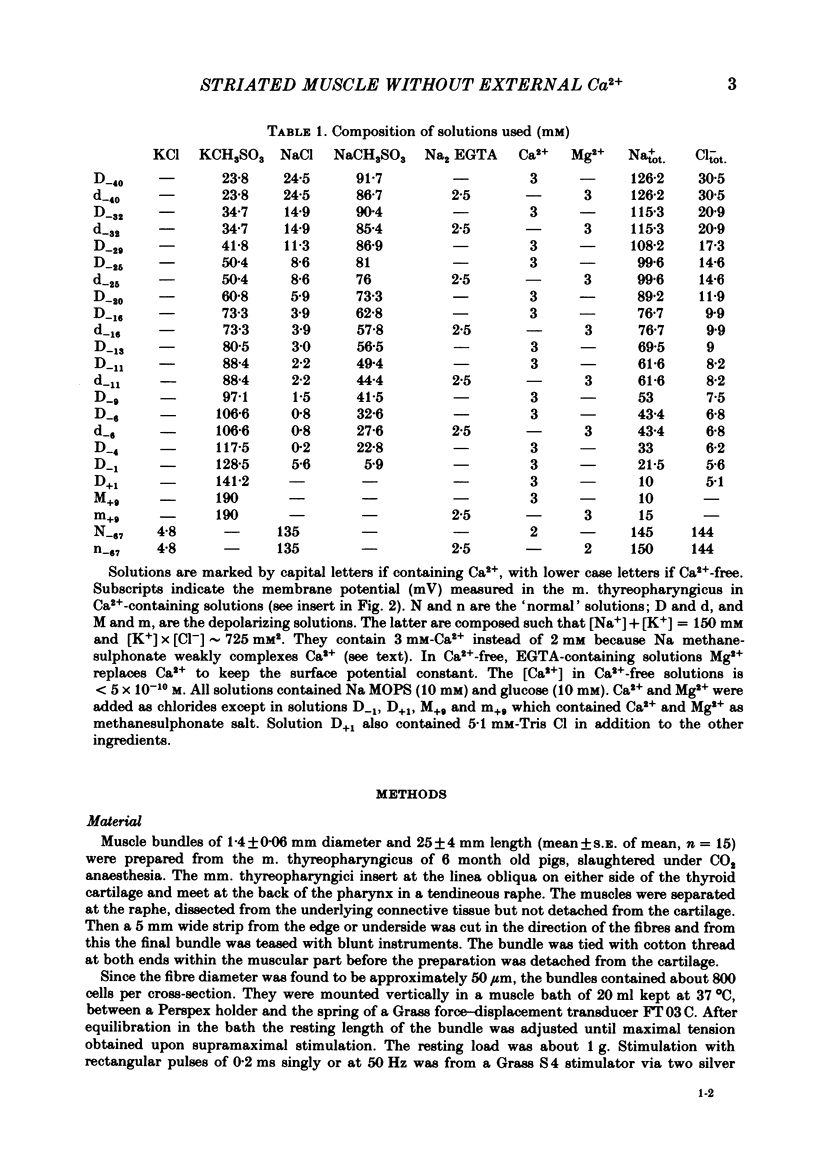
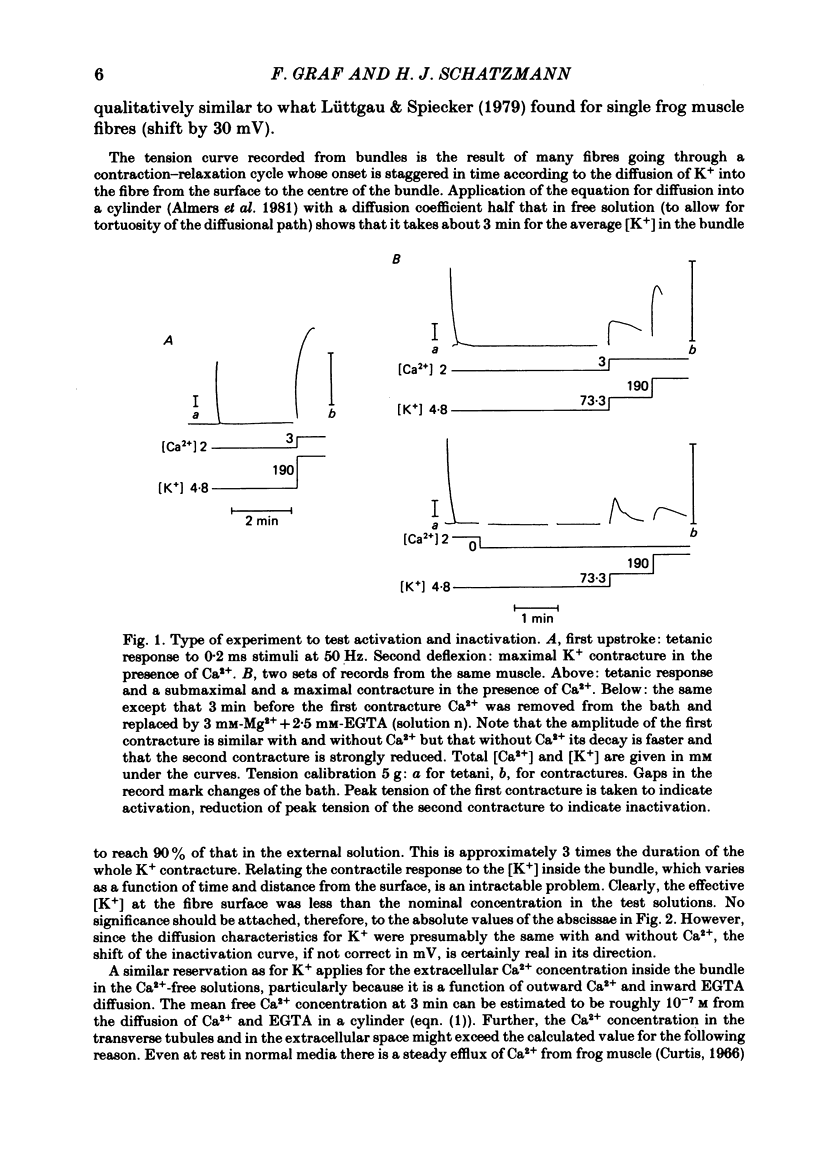
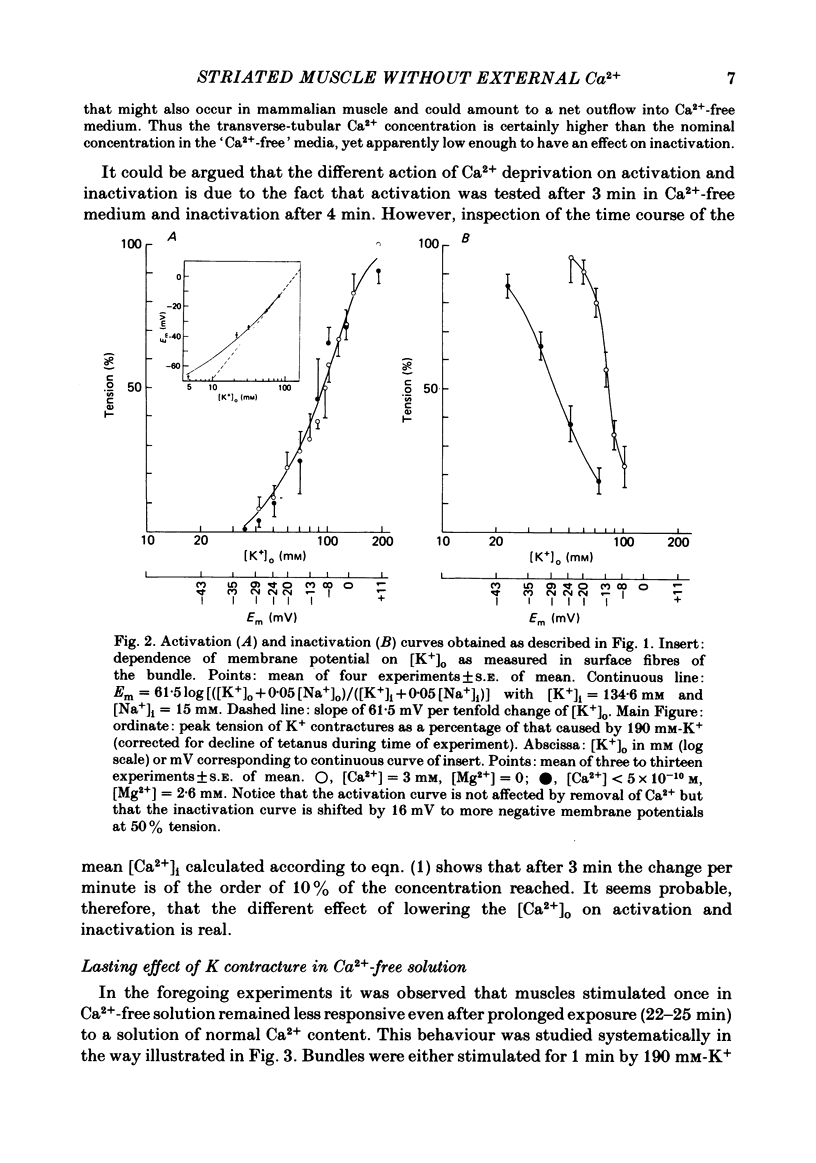
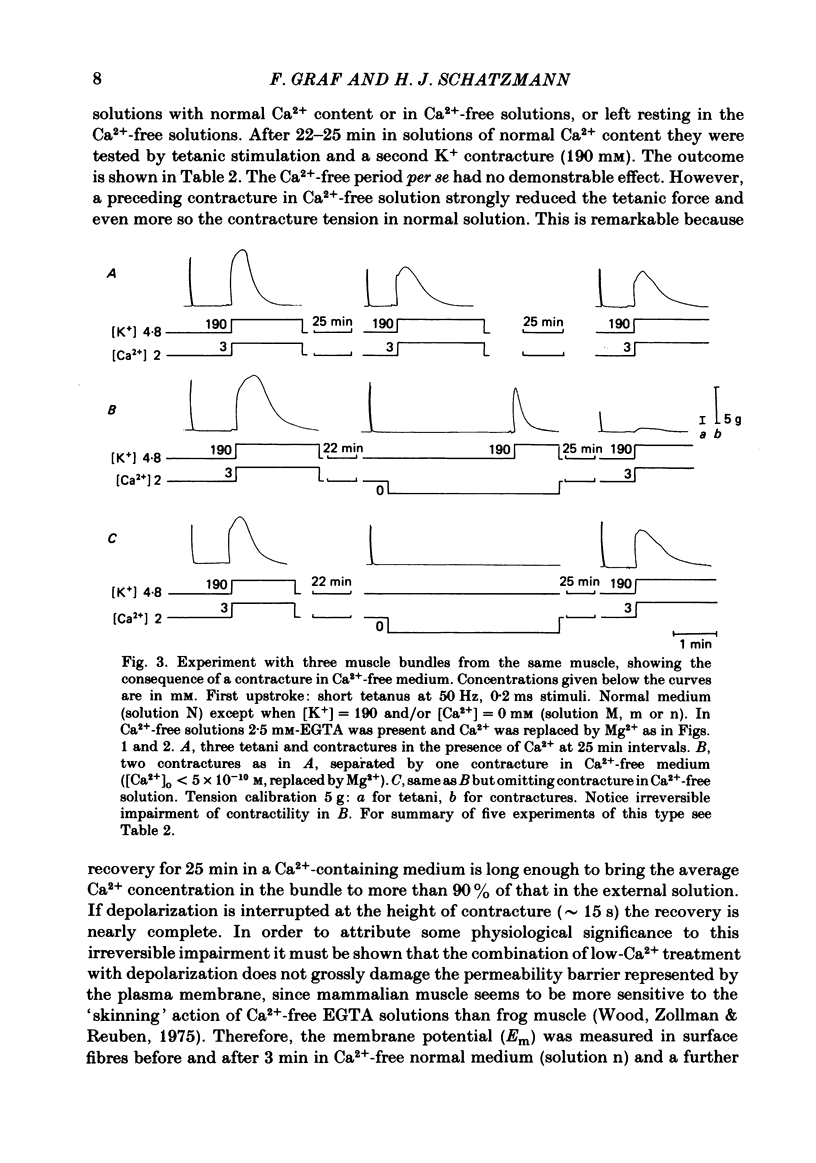
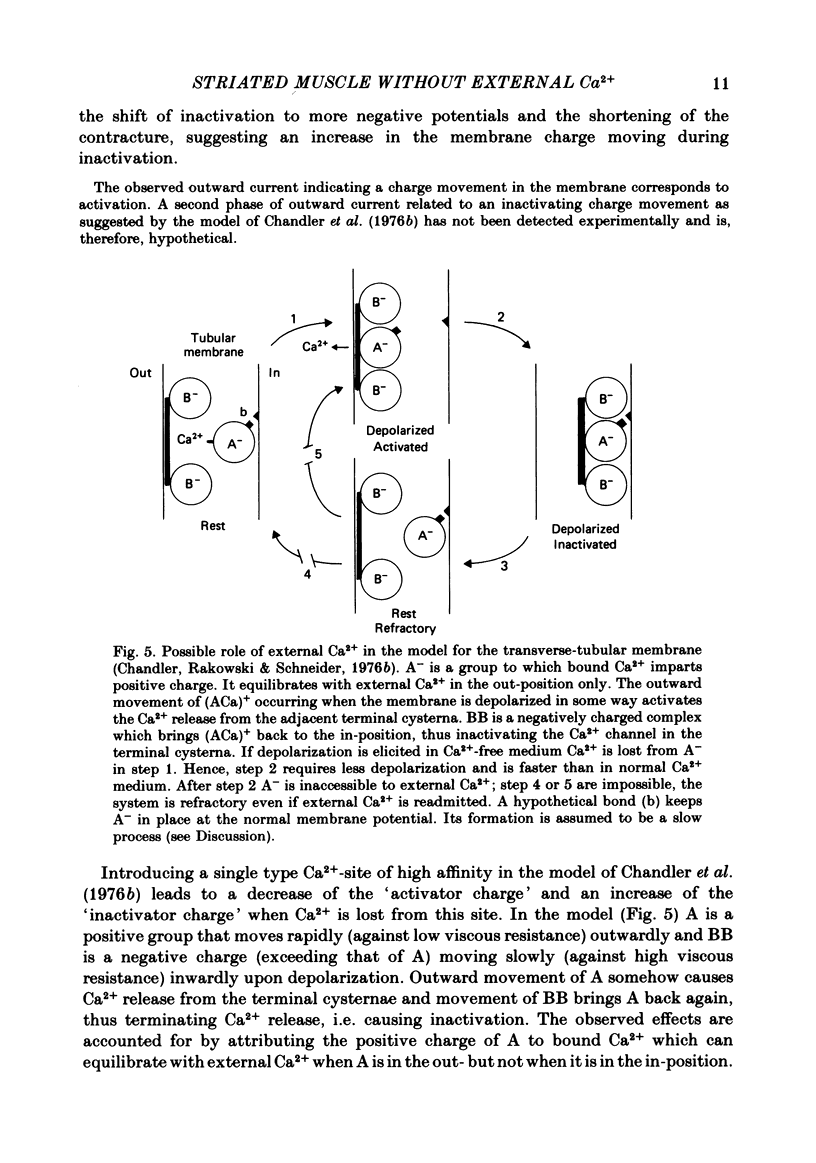
Bundles of about 800 cells from the m. thyreopharyngicus of pigs were used to measure activation and inactivation during contracture by K+ depolarization. When [Ca2+] in the medium was lowered to less than 5 X 10(-10) M for 3 min (replacing Ca2+ by Mg2+) the activation occurred at the same [K+] in the medium as in normal solution (3 mM-Ca2+) but inactivation was shifted to lower external [K+]. The absolute value of this shift in terms of membrane potential is uncertain, because [K+] at the cell surface is unknown. Exposure for 4 min to Ca2+-free medium (Ca2+ being replaced by Mg2+) had no effect on contractility tested after a subsequent rest of 22-25 min in normal solution ( [Ca2+] = 2 mM). However, if the muscle underwent one maximal K+ contracture in Ca2+-free medium the response (tetanus or K+ contracture) after the same interval in normal solution was strongly reduced, although the membrane potential recovered fully. K+ contractures in normal solution could be repeated without loss of contractile force. A K+ contracture in Ca2+-free medium had very little effect on the response to caffeine, tested after 25 min in normal solution. It seems that Ca2+ is lost into Ca2+-free medium only during depolarization, from a site which is not accessible to Ca2+ from outside at the resting membrane potential, or from inside at any membrane potential. This site might be located inside the transverse-tubular membrane and, when loaded with Ca2+, might represent the positive group of the model of Chandler, Rakowski & Schneider ( 1976b ), the movement of which during depolarization activates and inactivates the Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F. Charge movement and mechanical repriming in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):361–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Fink R., Palade P. T. Calcium depletion in frog muscle tubules: the decline of calcium current under maintained depolarization. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:177–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W. Observations on intramembrane charge movements in skeletal muscle. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):507–513. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Palade P. T. Slow calcium and potassium currents across frog muscle membrane: measurements with a vaseline-gap technique. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:159–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. M., Horowicz P. Twitches in the presence of ethylene glycol bis( -aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetracetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C. The time course of potassium contractures of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):483–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. Effects of glycerol treatment and maintained depolarization on charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):285–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Effect of calcium withdrawal on mechanical threshold in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:153–163. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. A. Ca fluxes in single twitch muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Nov;50(2):255–267. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockry M., Kernan R. P., Tangney A. Active transport of sodium and potassium in mammalian skeletal muscle and its modification by nerve and by cholinergic and adrenergic agents. J Physiol. 1966 Sep;186(1):187–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F. Potassium contractures and mechanical activation in mammalian skeletal muscles. J Membr Biol. 1980 Dec 30;57(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF01869590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsner P., Kernan R. P., MacDermott M. Intracellular potassium activity measurements in rat skeletal muscles equilibrated with Kreb's fluid at various PCO2 values [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:47P–48P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Serratos H., Valle-Aguilera R., Lathrop D. A., Garcia M. C. Slow inward calcium currents have no obvious role in muscle excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):292–294. doi: 10.1038/298292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernan R. P., MacDermott M. Intracellular potassium concentrations and extracellular spaces in rat skeletal muscles immersed in normal, hypotonic and high-K modified Krebs fluid, determined by potassium-selective microelectrodes [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(1):158P–160P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Oetliker H. The action of caffeine on the activation of the contractile mechanism in straited muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Spiecker W. The effects of calcium deprivation upon mechanical and electrophysiological parameters in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:411–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. G., Szabo G., Eisenman G. Divalent ions and the surface potential of charged phospholipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):667–687. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Voltage-gated cation conductance channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum: steady-state electrical properties. J Membr Biol. 1978 Apr 20;40(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01909736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRETER F. A., WOO G. CELL WATER, SODIUM, AND POTASSIUM IN RED AND WHITE MAMMALIAN MUSCLES. Am J Physiol. 1963 Dec;205:1290–1294. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.6.1290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:197–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Chiarandini D. J. Skeletal muscle: dependence of potassium contractures on extracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Oct 17;343(2):143–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00585709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. S., Zollman J., Reuben J. P., Brandt P. W. Human skeletal muscle: properties of the "chemically skinned%" fiber. Science. 1975 Mar 21;187(4181):1075–1076. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4181.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


