Abstract
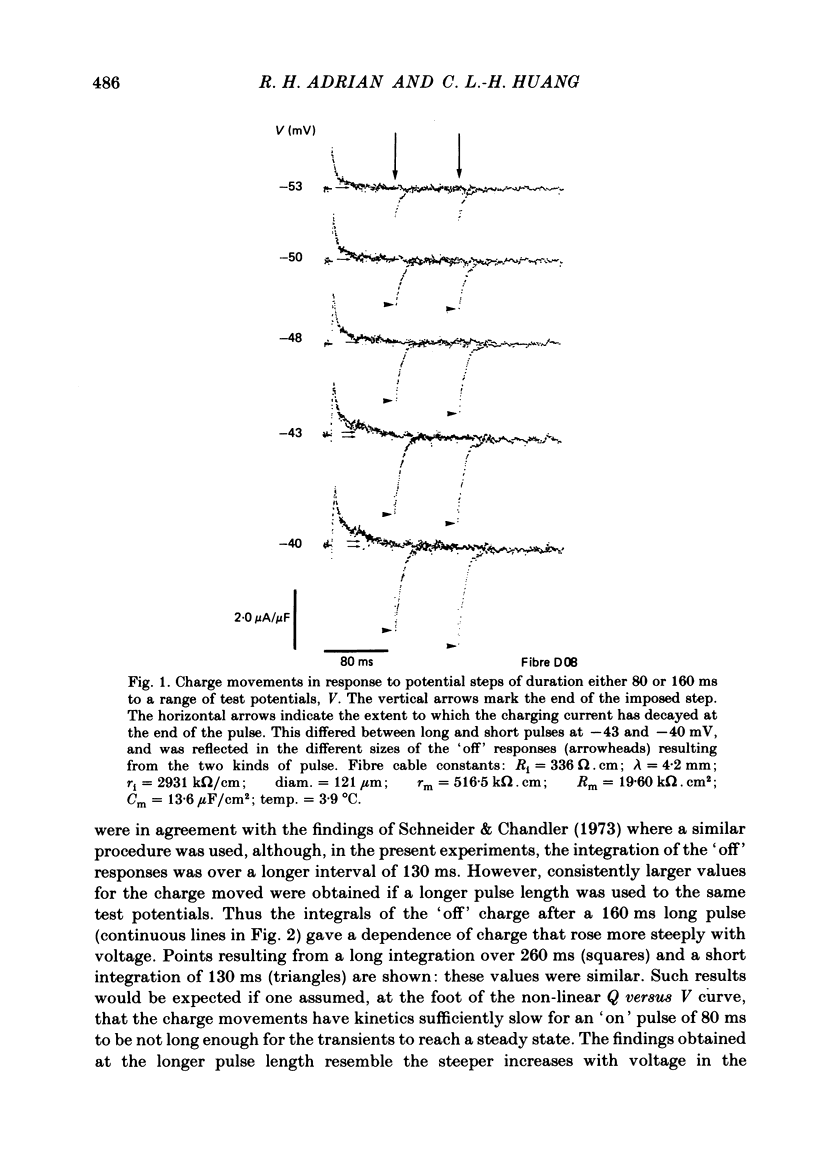
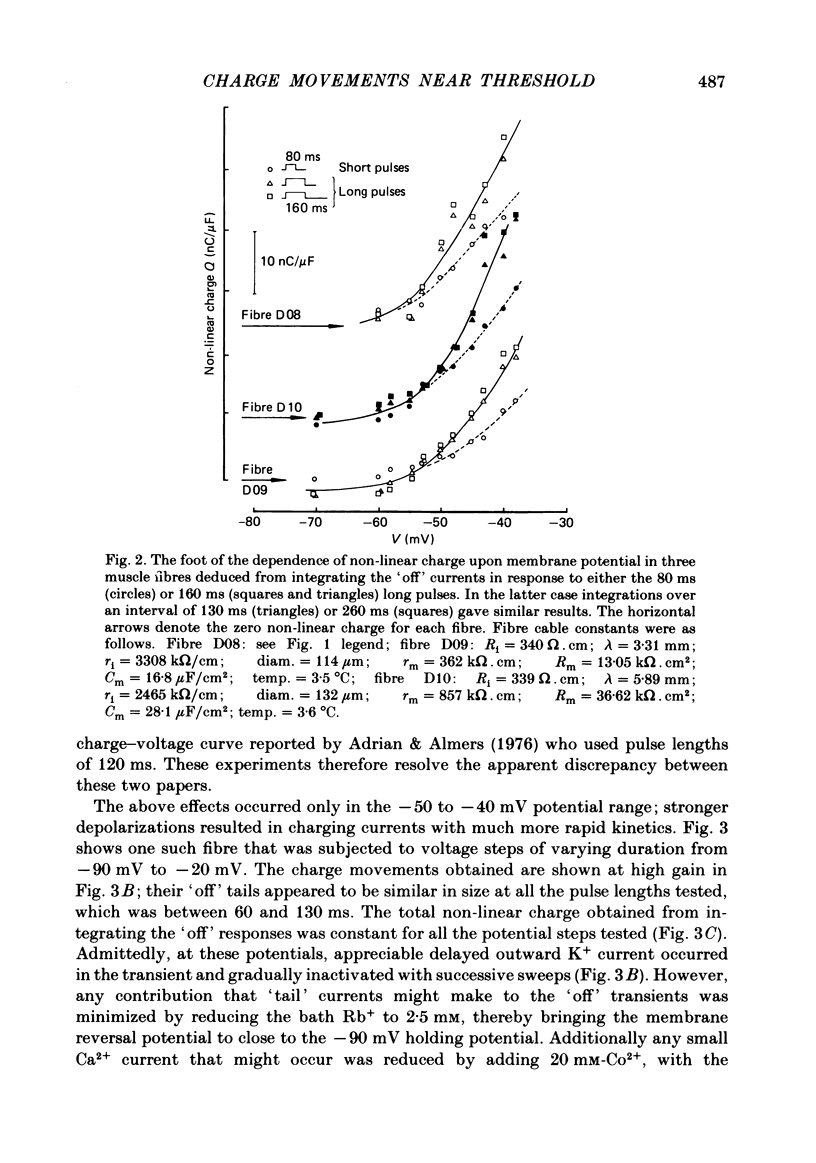
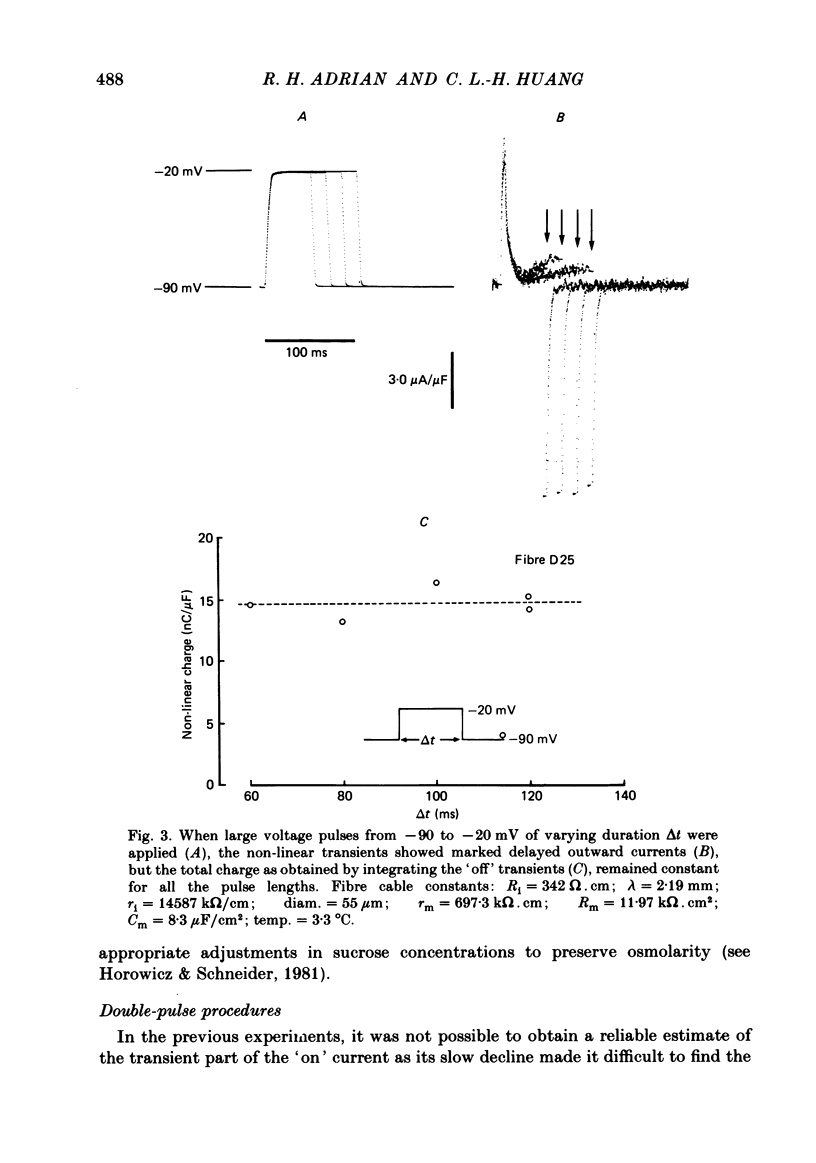
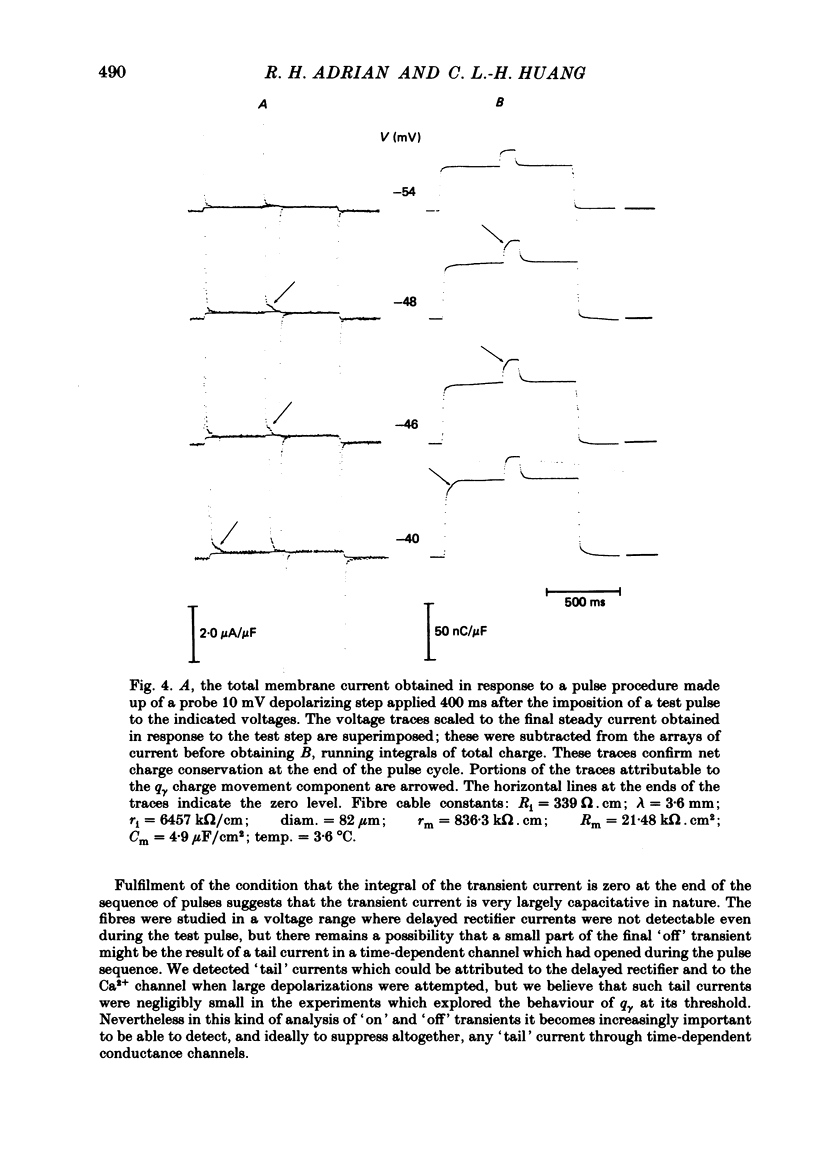
Charge movement was investigated over a range of potentials close to the mechanical threshold in voltage-clamped frog skeletal muscle. The delayed (q gamma) component of the charging currents appeared with a time course lasting well over 100 ms at around -50 to -40 mV, but the currents became larger and faster with further depolarization. The slow charging current was investigated using a 10 mV probe step intercepting the time course of these currents. This procedure showed that the charging currents could last as long as 100-300 ms. The total charge was conserved when the charging current was small and prolonged. The results can be related directly to earlier findings concerning contractile activation of muscle by applied voltage steps to potentials near threshold ( Adrian , Chandler & Hodgkin, 1969).
Full text
PDF



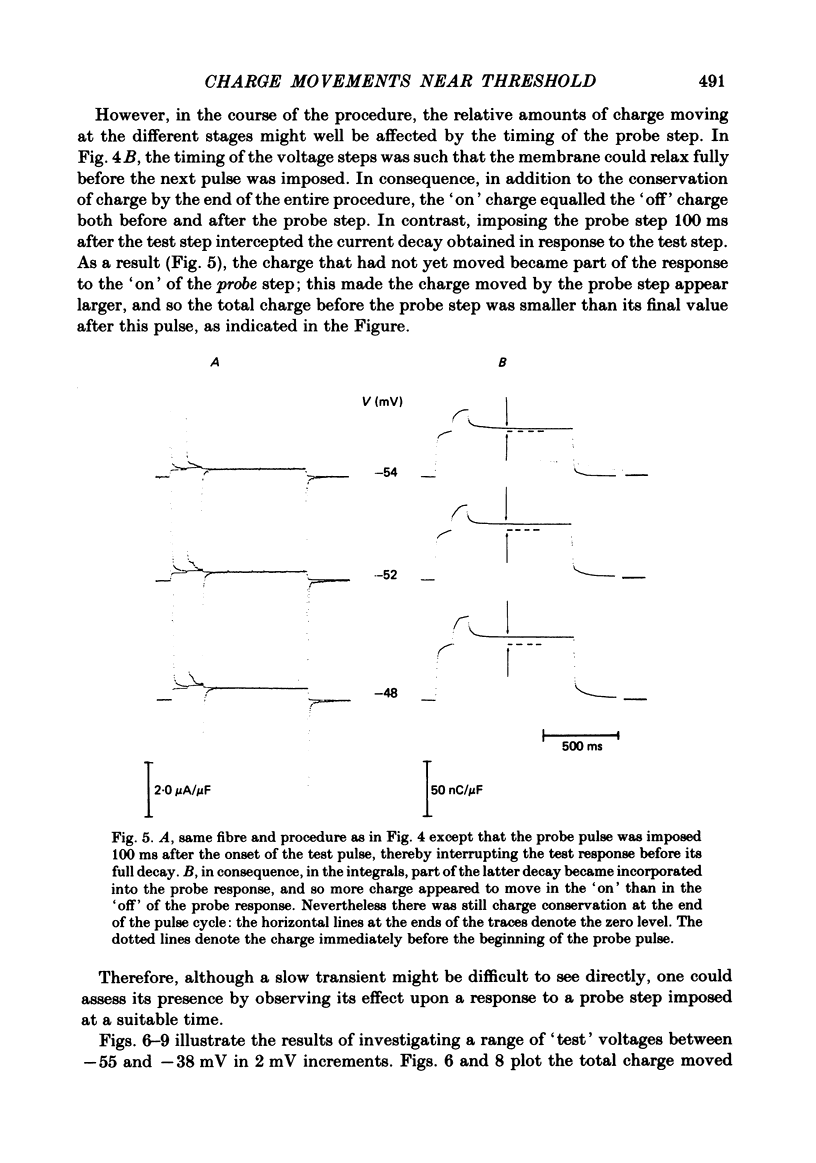
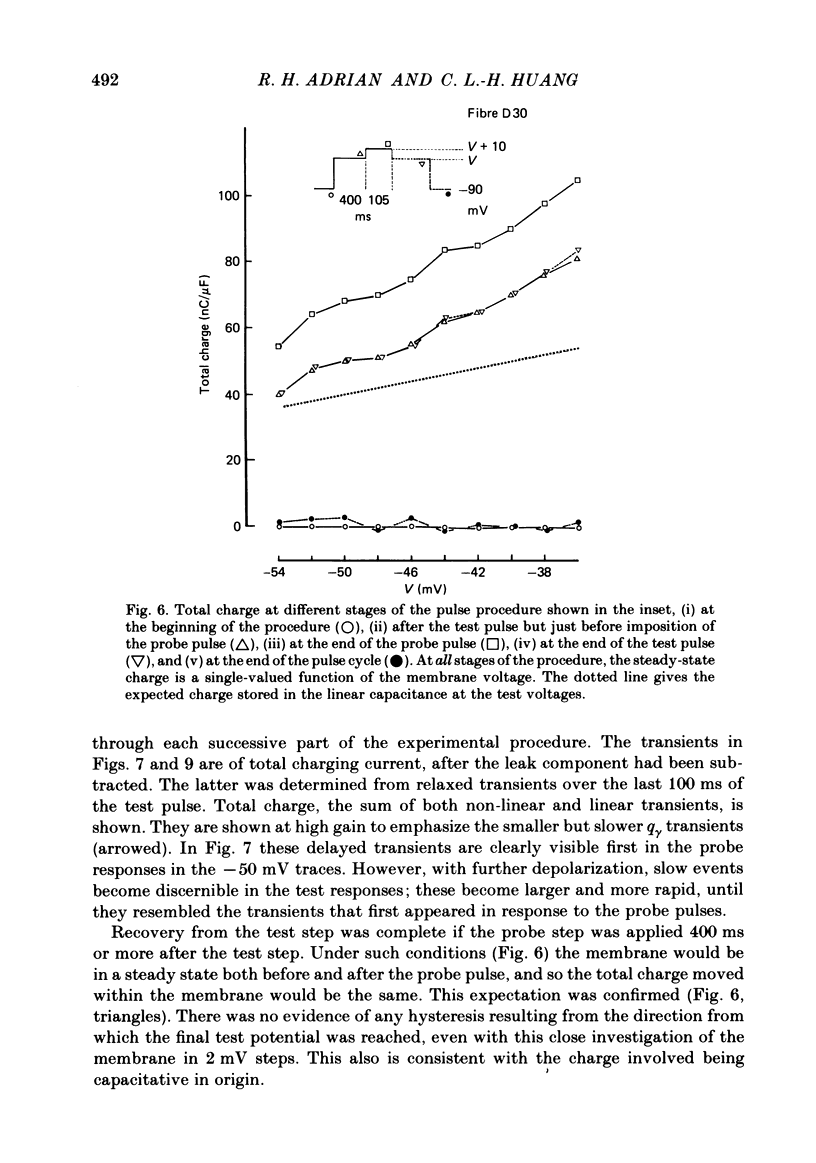
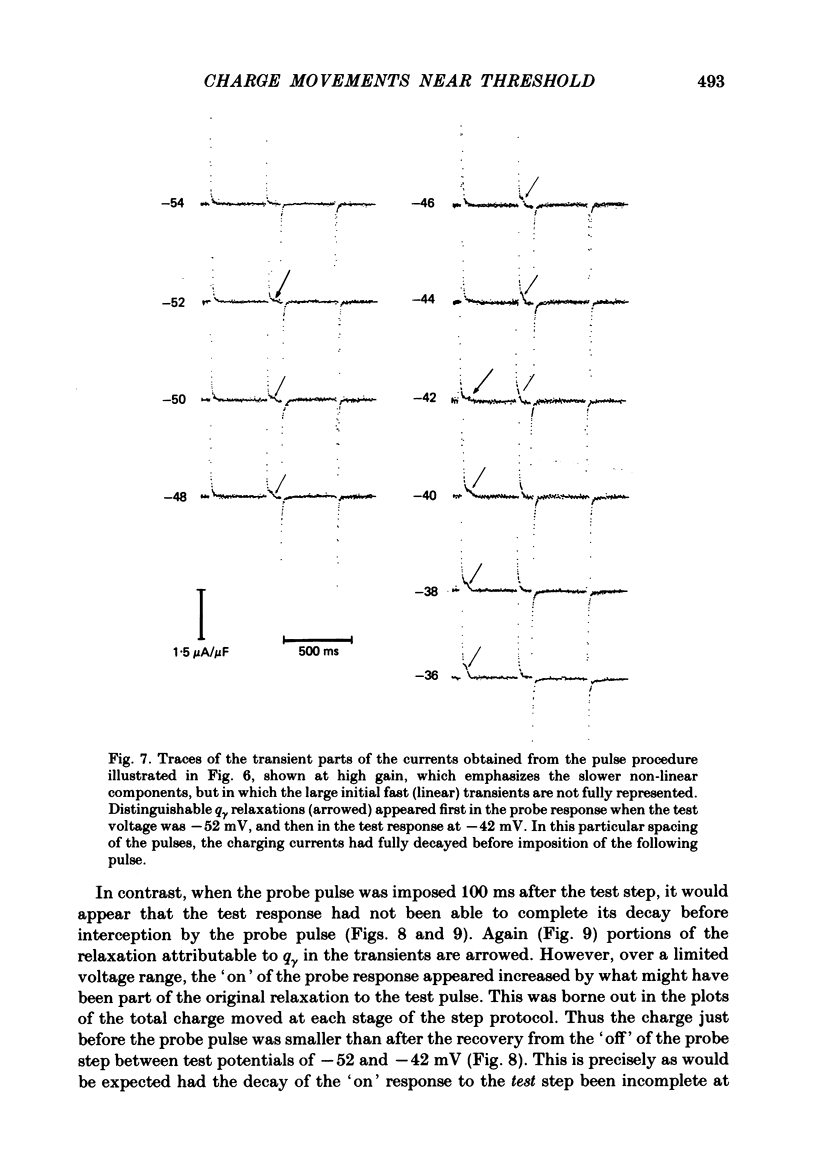
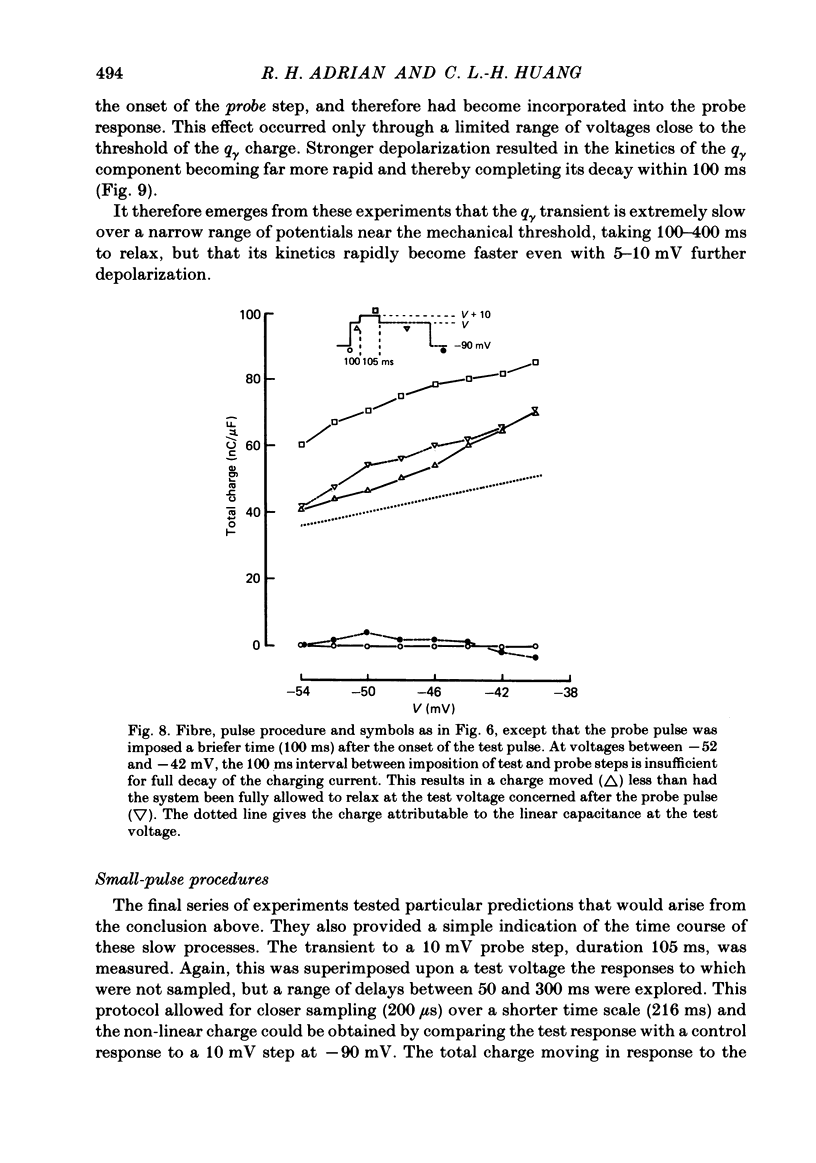
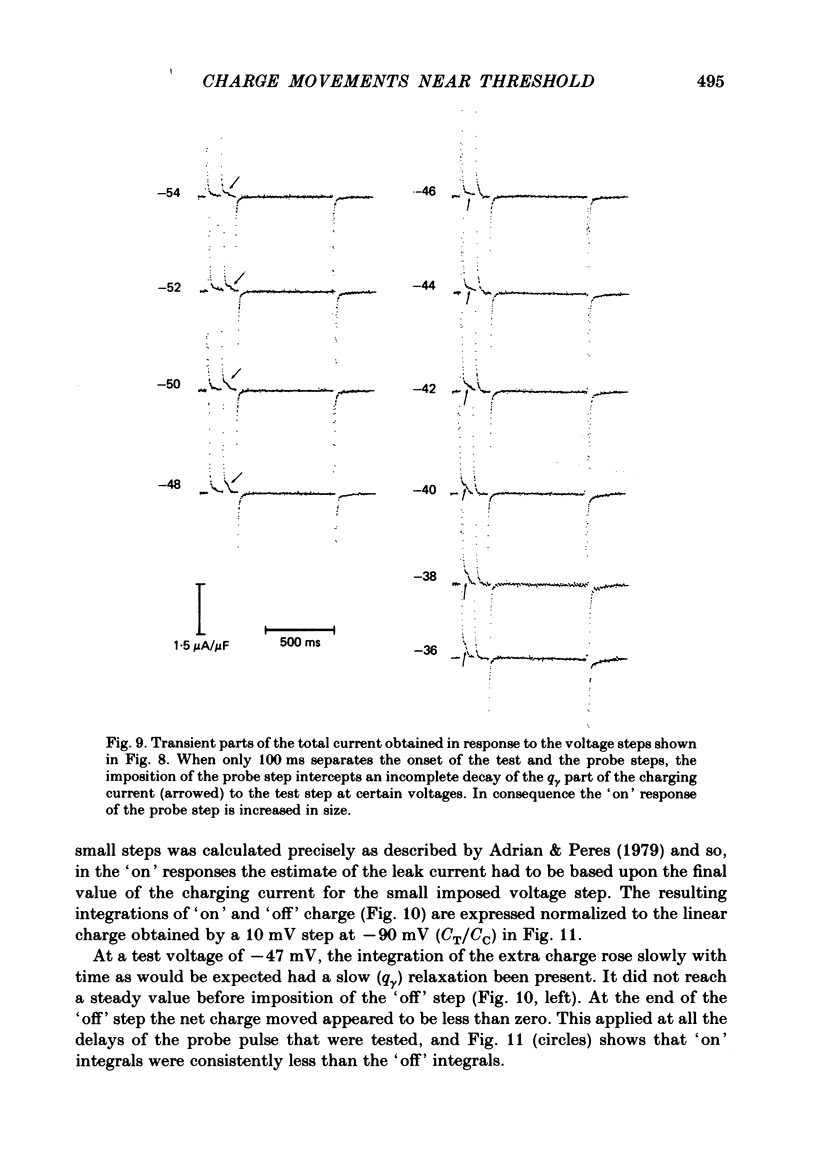
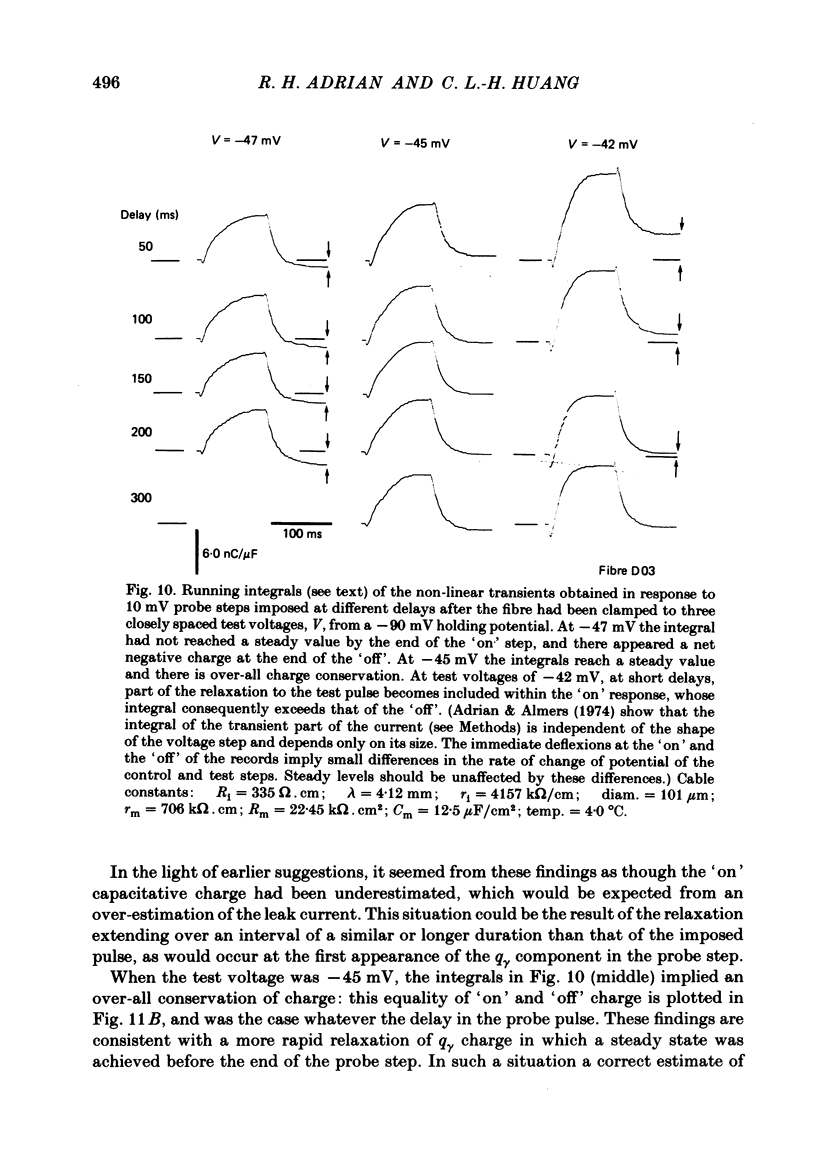
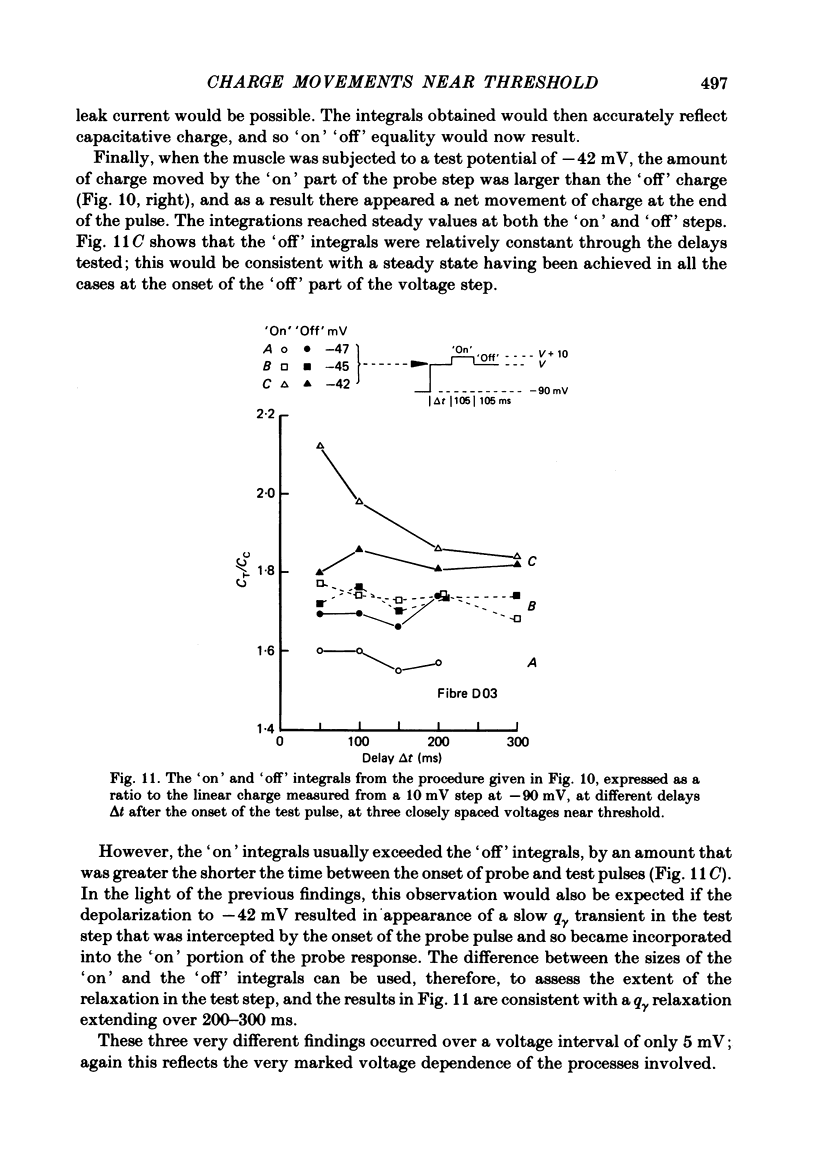



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Membrane capacity measurements on frog skeletal muscle in media of low ion content. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(3):573–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peres A. Charge movement and membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:83–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Rakowski R. F. Reactivation of membrane charge movement and delayed potassium conductance in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:533–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W. Gating currents and charge movements in excitable membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;82:96–190. doi: 10.1007/BFb0030498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. Effects of glycerol treatment and maintained depolarization on charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):285–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duane S., Huang C. L. A quantitative description of the voltage-dependent capacitance in frog skeletal muscle in terms of equilibrium statistical mechanics. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Apr 22;215(1198):75–94. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. The effect of diameter on the electrical constants of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):105–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowicz P., Schneider M. F. Membrane charge movement in contracting and non-contracting skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:565–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Dielectric components of charge movements in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1981;313:187–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Effects of local anaesthetics on the relationship between charge movements and contractile thresholds in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:381–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Experimental analysis of alternative models of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:527–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Pharmacological separation of charge movement components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:375–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Time domain spectroscopy of the membrane capacitance in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:1–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Pharmacological studies of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:509–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Zhu P. H. Calcium transients studied under voltage-clamp control in frog twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:649–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


