Abstract
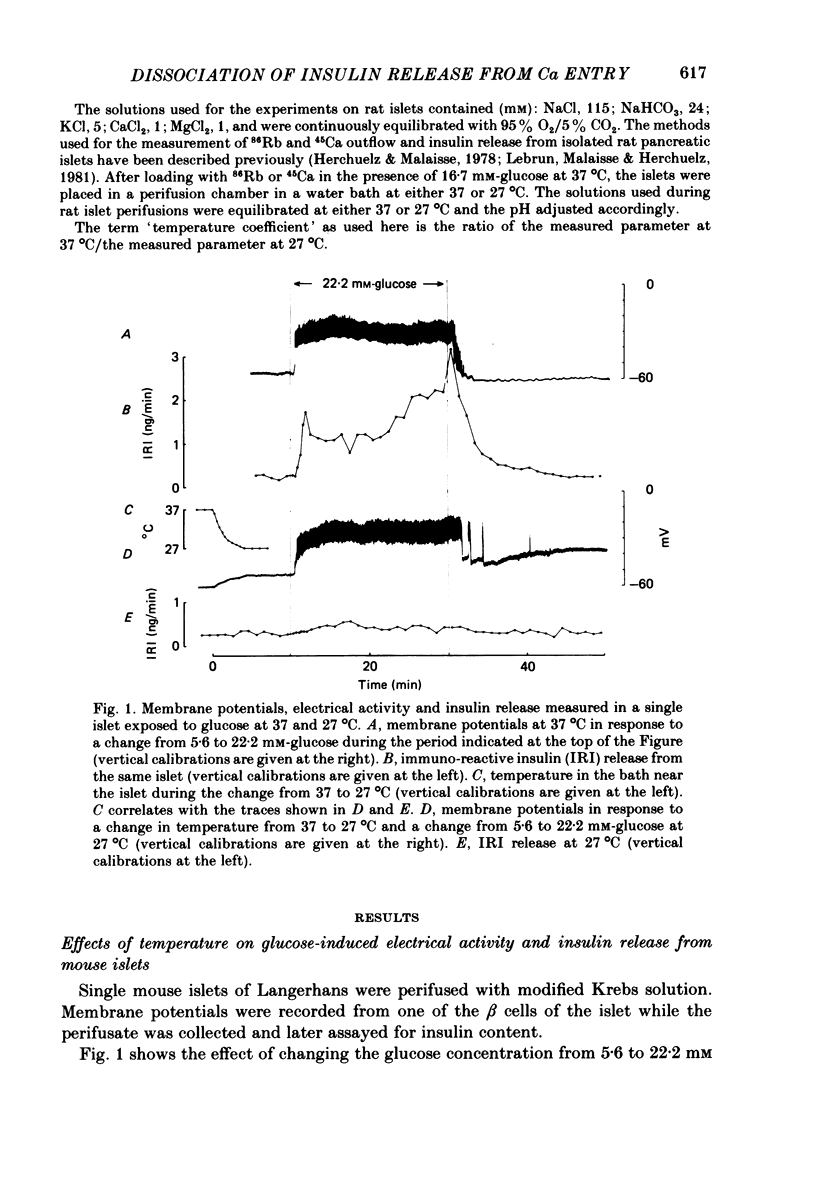
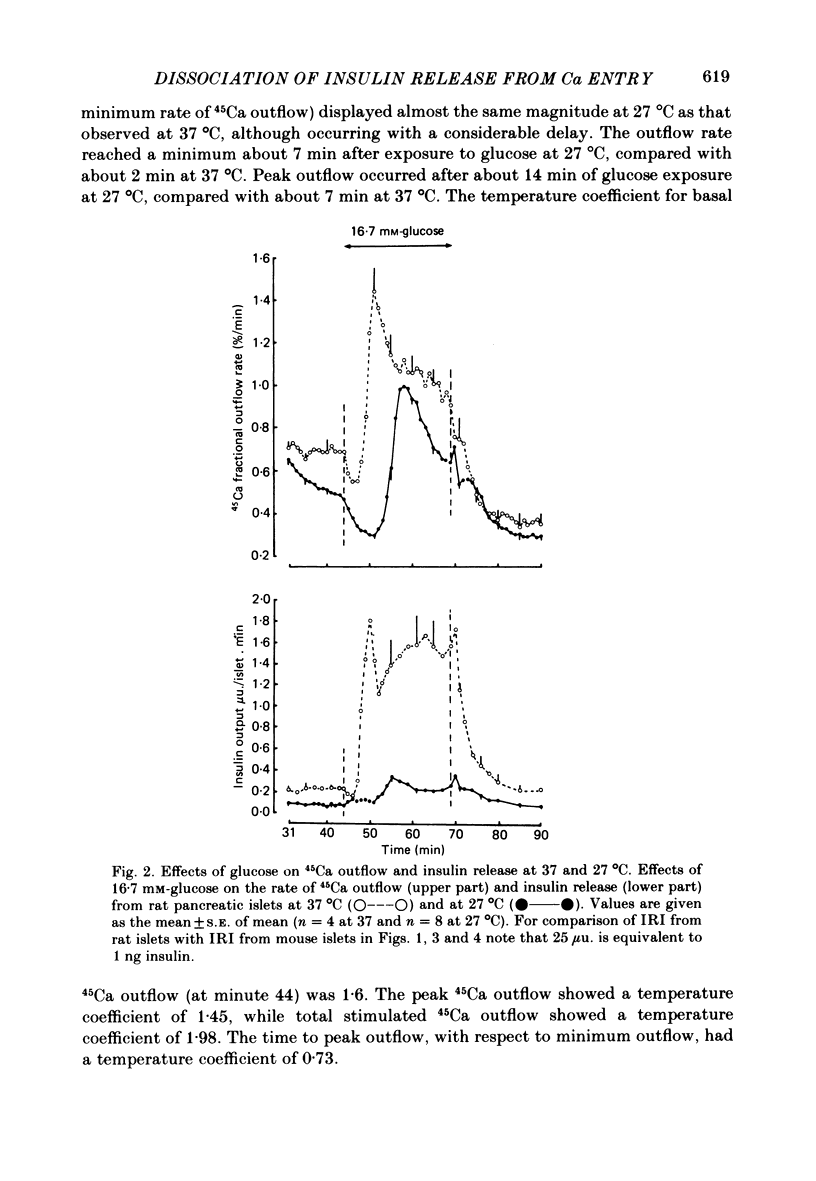
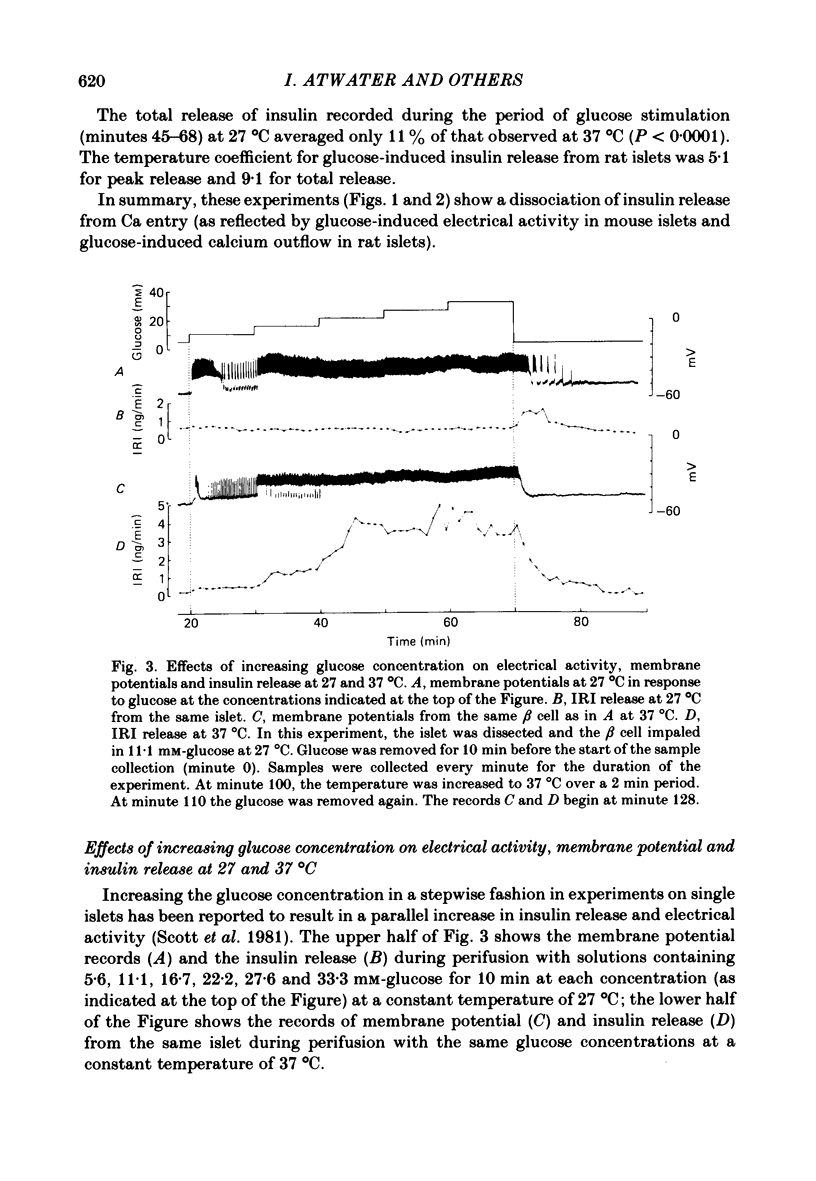
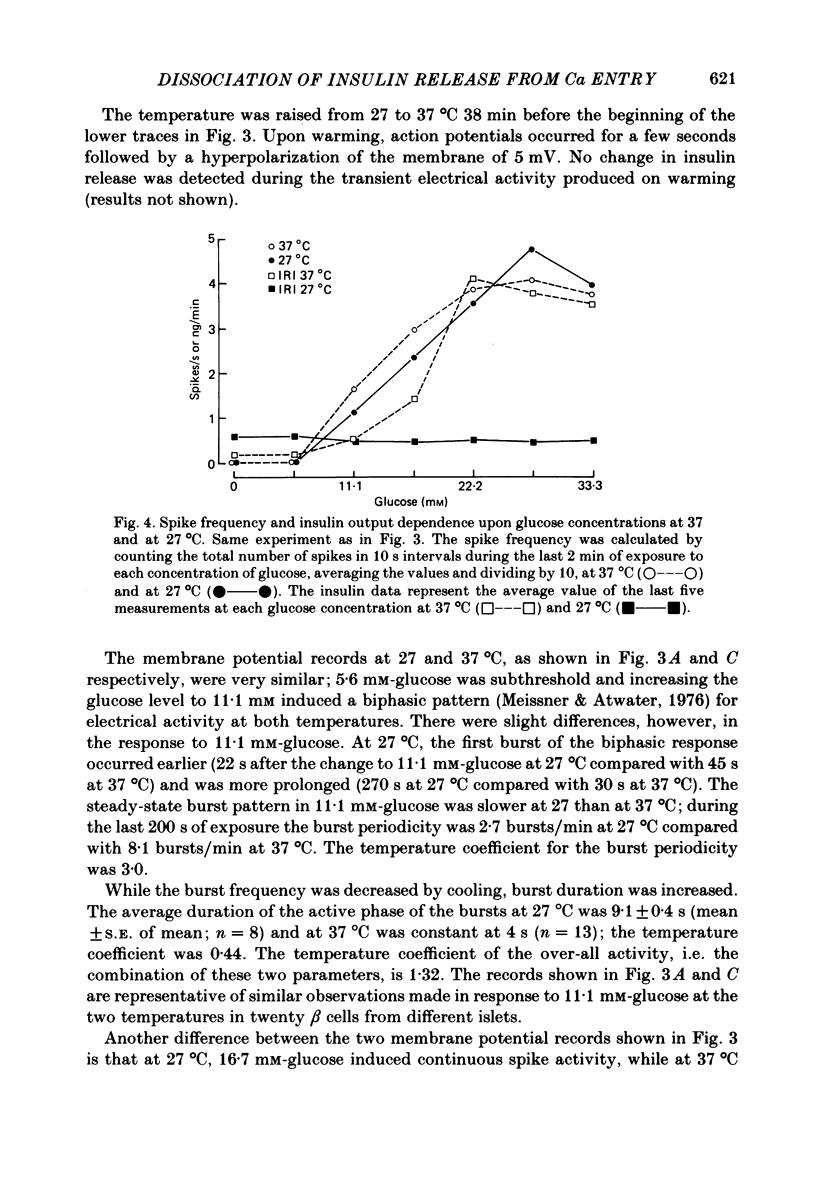
Insulin release and beta-cell membrane potentials in response to glucose at 37 and 27 degrees C have been measured simultaneously in single, micro-dissected, perifused islets of Langerhans from normal mice. Insulin release and 45Ca outflow in response to glucose at 37 and 27 degrees C have been measured simultaneously from perfused islets isolated by collagenase digestion from normal rats. The effect of cooling on beta-cell membrane potassium permeability was assessed by changes in measured membrane potential and input resistance (in the mouse) and by changes in 86Rb outflow (in the rat). Resting and active beta-cell membrane parameters (i.e. membrane potential, spike frequency, input resistance, 45Ca outflow and 86Rb outflow), in both mouse and rat islets, were affected only slightly by cooling to 27 degrees C, with temperature coefficients of 2 or lower. At 27 degrees C glucose-stimulated insulin release was inhibited completely in mouse islets and almost completely in rat islets. The temperature coefficients in both preparations were greater than 5. It is concluded that beta-cell electrical activity and changes in membrane permeability induced by glucose are not consequences of insulin release.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Potassium permeability activated by intracellular calcium ion concentration in the pancreatic beta-cell. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:575–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Scott A., Eddlestone G., Rojas E. The nature of the oscillatory behaviour in electrical activity from pancreatic beta-cell. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Cyclic changes in potential and resistance of the beta-cell membrane induced by glucose in islets of Langerhans from mouse. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:117–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschero A. C., Malaisse W. J. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXIX. Regulation of 86Rb+ efflux from perfused islets. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):E139–E146. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.2.E139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpinelli A. R., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of 86Rb+ outflow from pancreatic islets III. Possible significance of ATP. J Endocrinol Invest. 1980 Oct-Dec;3(4):365–370. doi: 10.1007/BF03349372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. A., Rojas E. Temperature dependence of the sodium channel gating kinetics in the node of Ranvier. Q J Exp Physiol. 1982 Jan;67(1):41–55. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1982.sp002623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl G., Henquin J. C. Cold-induced insulin release in vitro: evidence for exocytosis. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Dec 12;194(3):387–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00236160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):389–390. doi: 10.1038/219389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):255–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel B. J., Atwater I., Grodsky G. M. Calcium affects insulin release and membrane potential in islet beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):C64–C72. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.240.1.C64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Andersson T. Calcium and pancreatic beta-cell function. 4. Evidence that glucose and phosphate stimulate calcium-45 incorporation into different intracellular pools. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 17;541(4):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):271–273. doi: 10.1038/271271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Metabolic control of potassium permeability in pancreatic islet cells. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):541–550. doi: 10.1042/bj1860541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Opposite effects of intracellular Ca2+ and glucose on K+ permeability of pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):66–68. doi: 10.1038/280066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of calcium fluxes in pancreatic islets: dissociation between calcium and insulin release. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:409–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Thonnart N., Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of calcium fluxes in pancreatic islets: the role of membrane depolarization. Endocrinology. 1980 Aug;107(2):491–497. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-2-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Rojas E. Kinetics and steady-state properties of the charged system controlling sodium conductance in the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):393–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun P., Malaisse W. J., Herchuelz A. Effect of calcium antagonists on potassium conductance in islet cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Dec 15;30(24):3291–3294. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A., Lebrun P., Herchuelz A., Leclercq-Meyer V., Malaisse W. J. Réponse sécrétoire, ionique et métabolique des îlots de langerhans aux anoméres du D-mannose. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1982 Mar 22;294(12):605–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G. R., Baird L. E. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. X. Effect of glucose on 45 Ca efflux from perifused islets. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):389–394. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Sakamoto Y. Electrical characteristics of pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):421–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Atwater I. J. The kinetics of electrical activity of beta cells in response to a "square wave" stimulation with glucose or glibenclamide. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Jan;8(1):11–16. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P. Electrical characteristics of the beta-cells in pancreatic islets. J Physiol (Paris) 1976 Nov;72(6):757–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Schmelz H. Membrane potential of beta-cells in pancreatic islets. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(3):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00586918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Stillings S. N., Hover B. A., Matschinsky F. M. Electrical and secretory manifestations of glucose and amino acid interactions in rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1975 May;24(5):489–496. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.5.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Cyclic variation of K+ conductance in pancreatic beta-cells: Ca2+ and voltage dependence. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):C137–C146. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.237.3.C137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. M., Atwater I., Rojas E. A method for the simultaneous measurement of insulin release and B cell membrane potential in single mouse islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia. 1981 Nov;21(5):470–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00257788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):914–973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


