Abstract
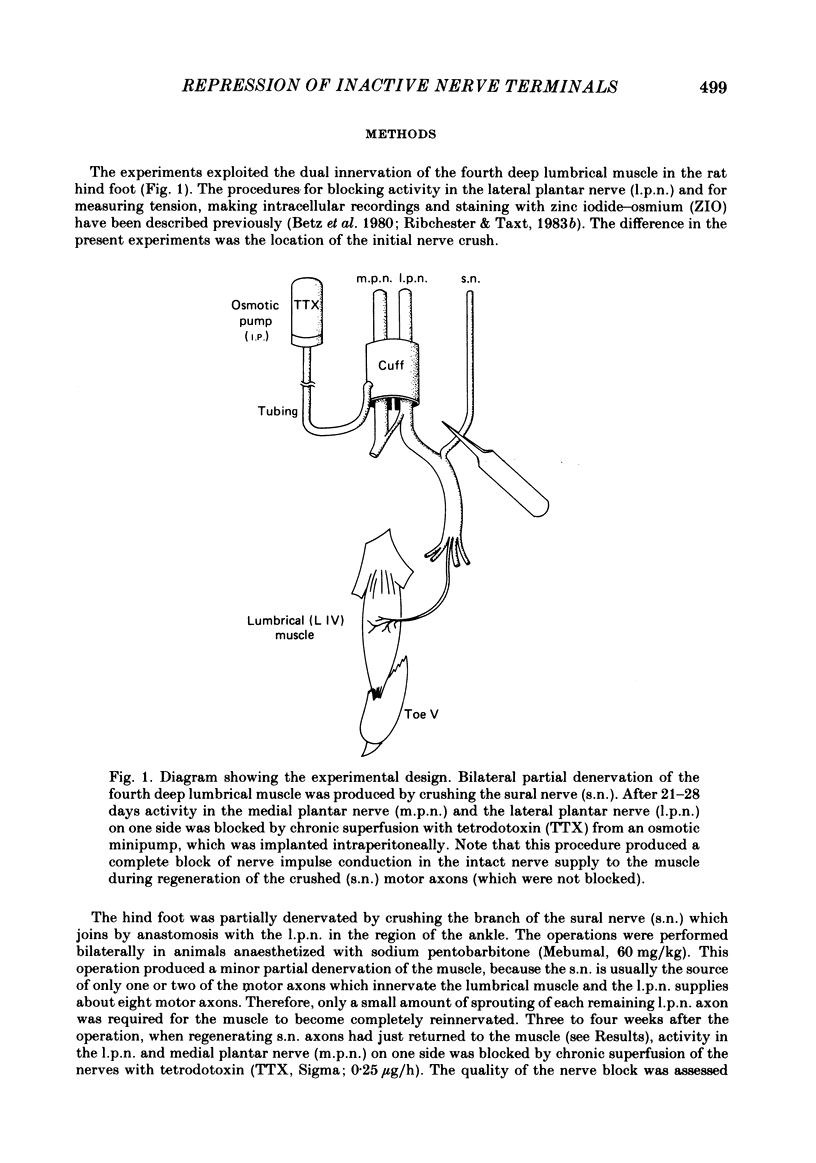
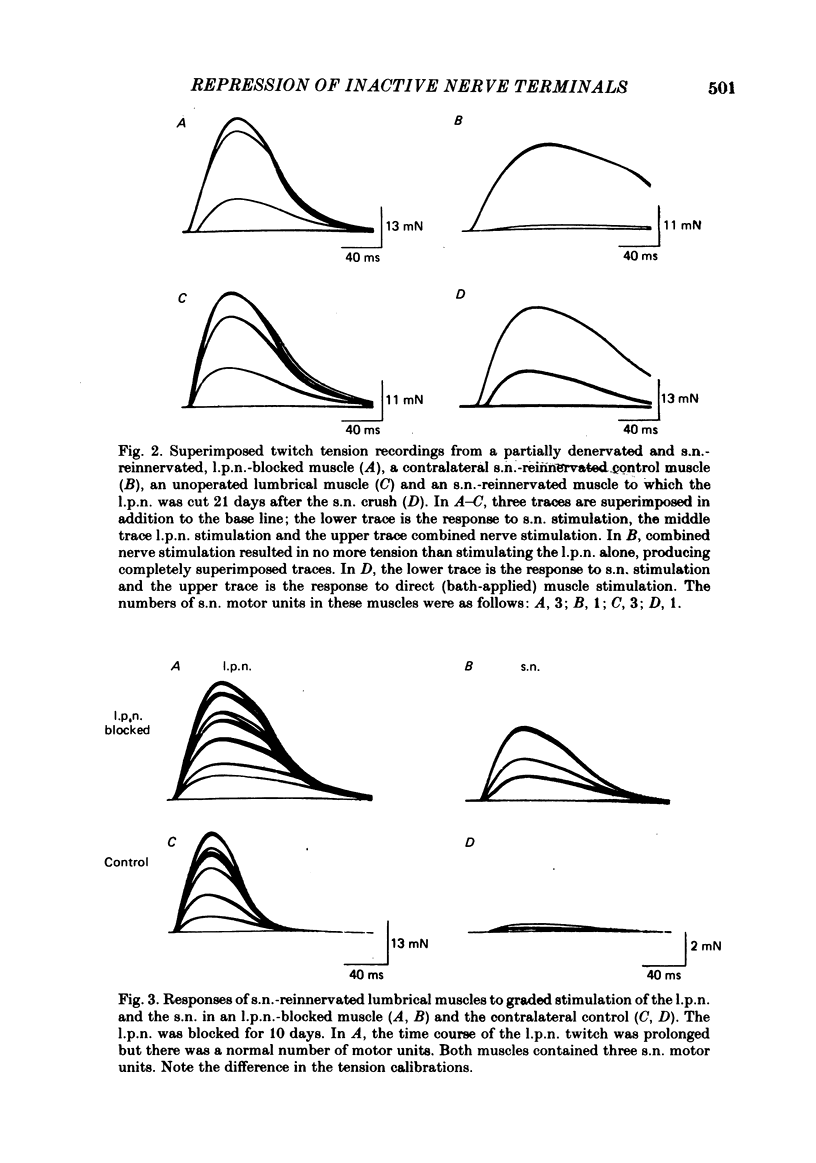
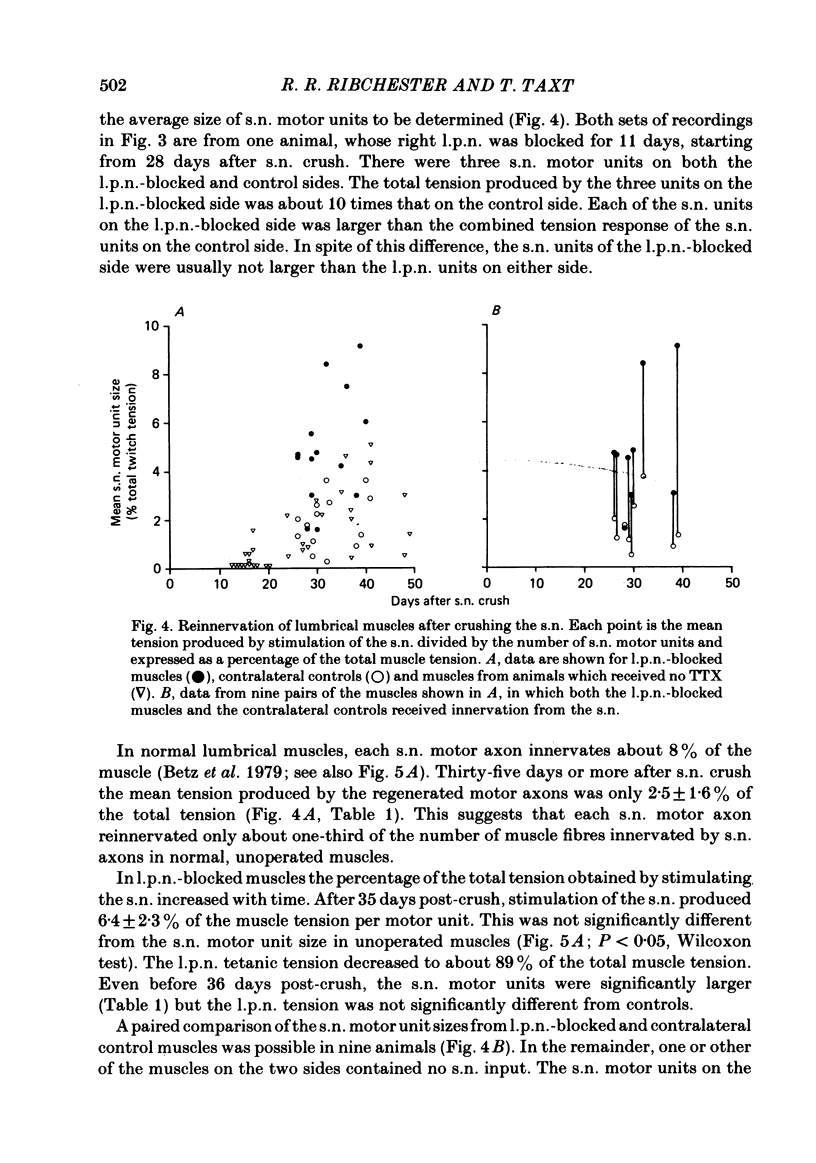
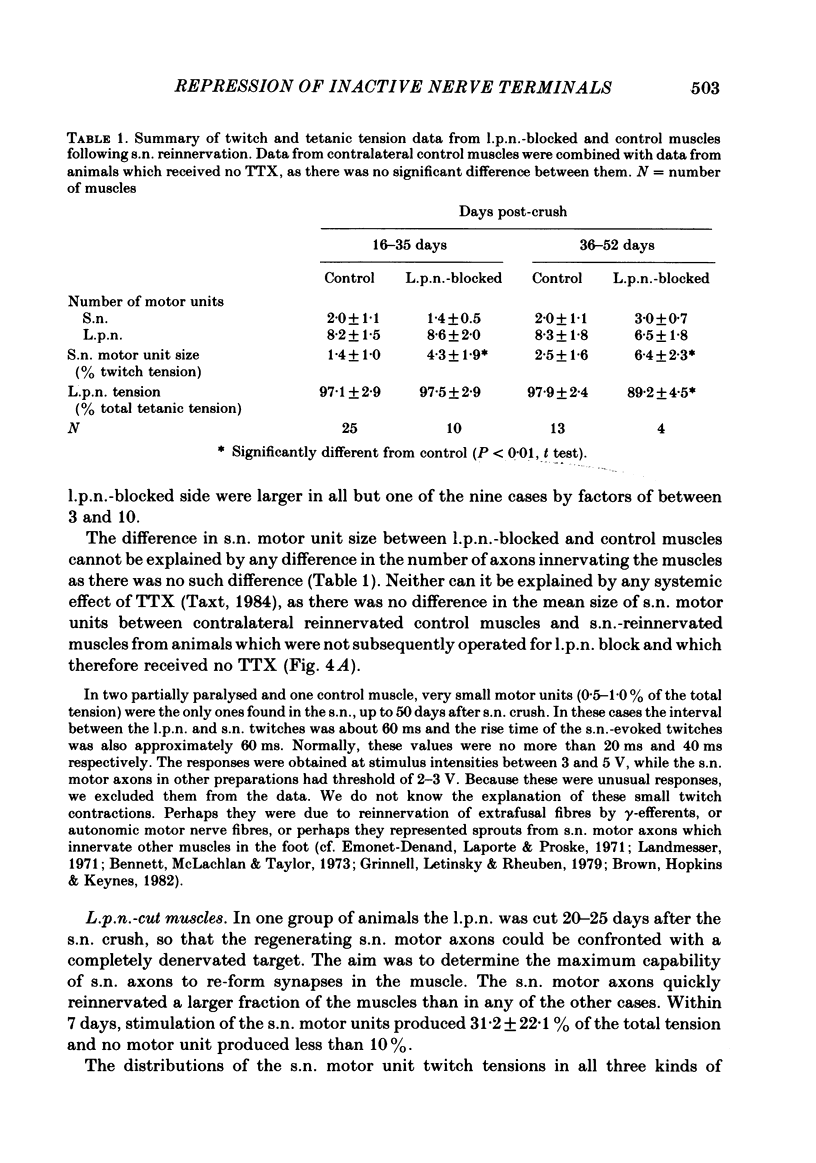
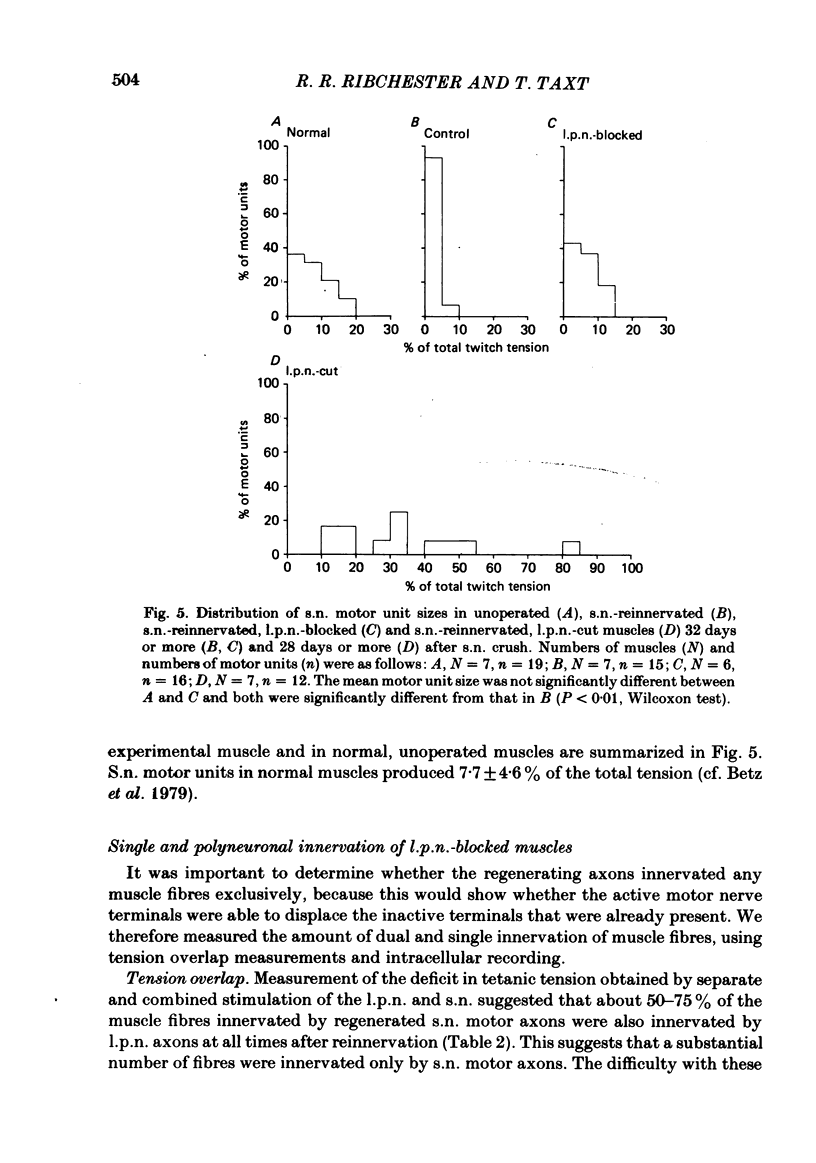
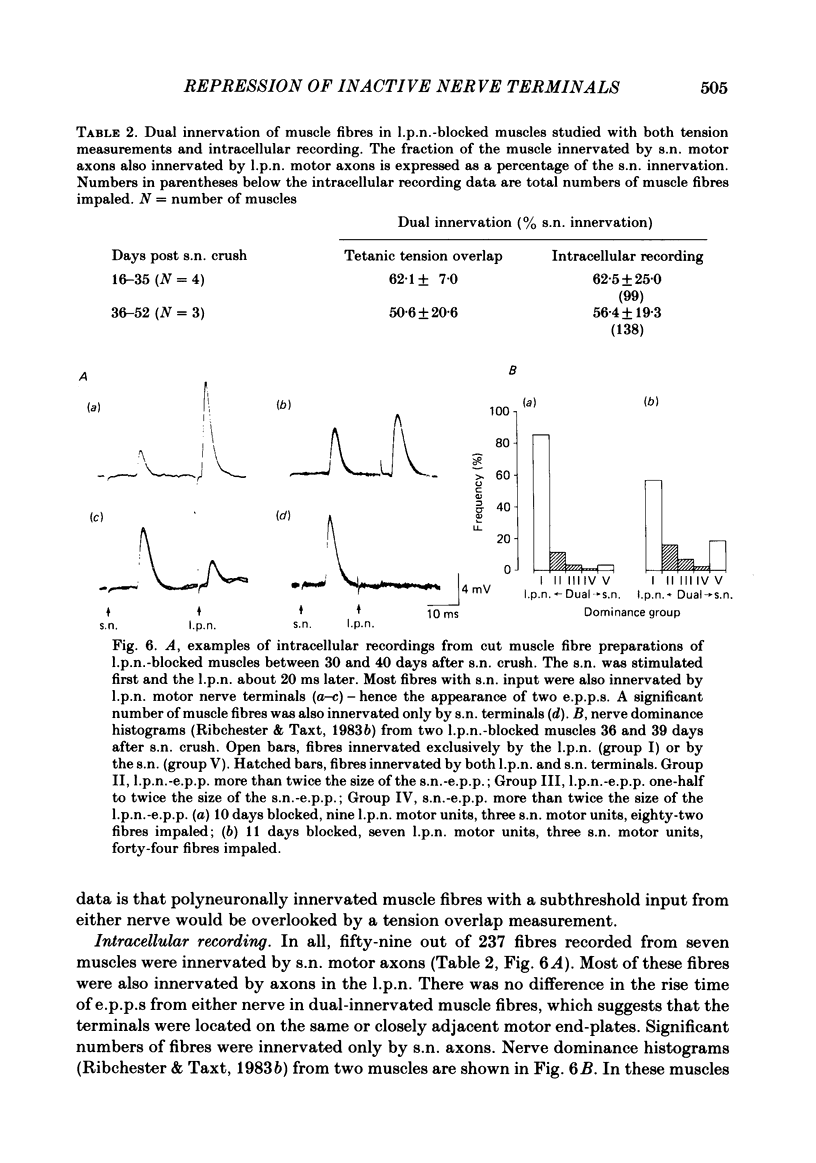
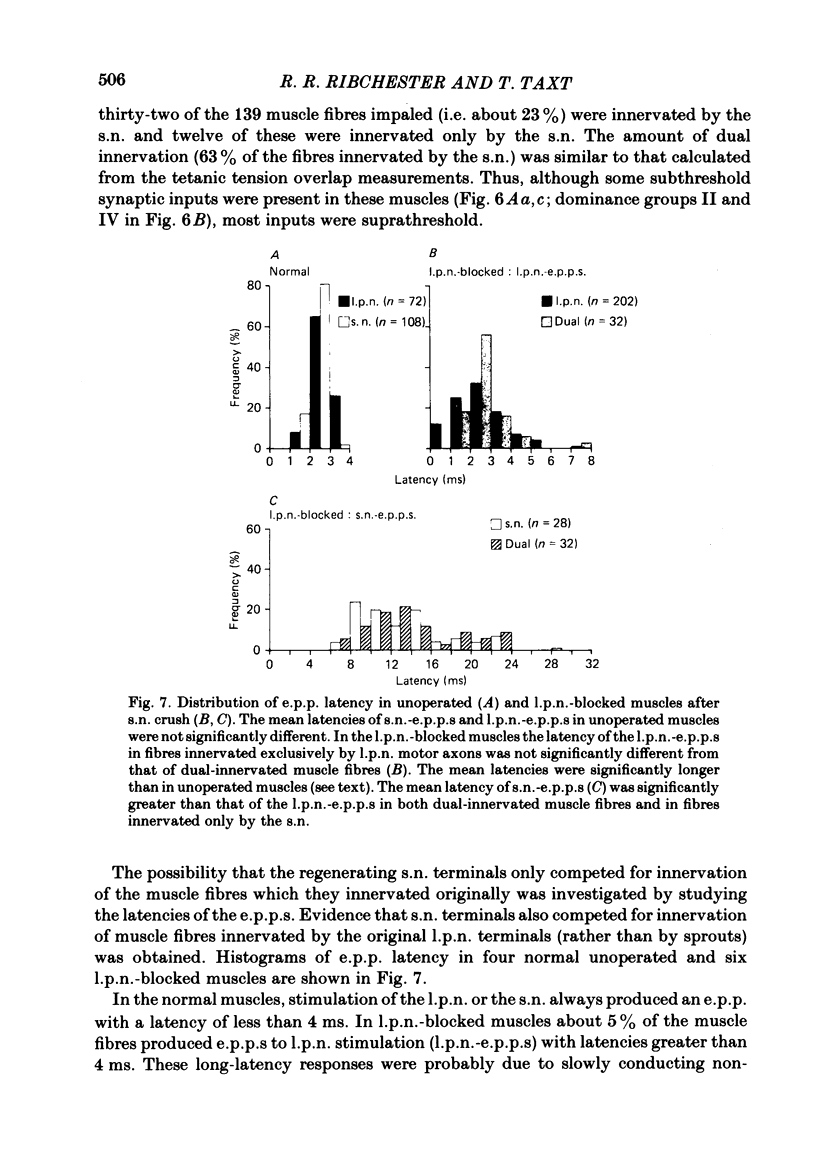
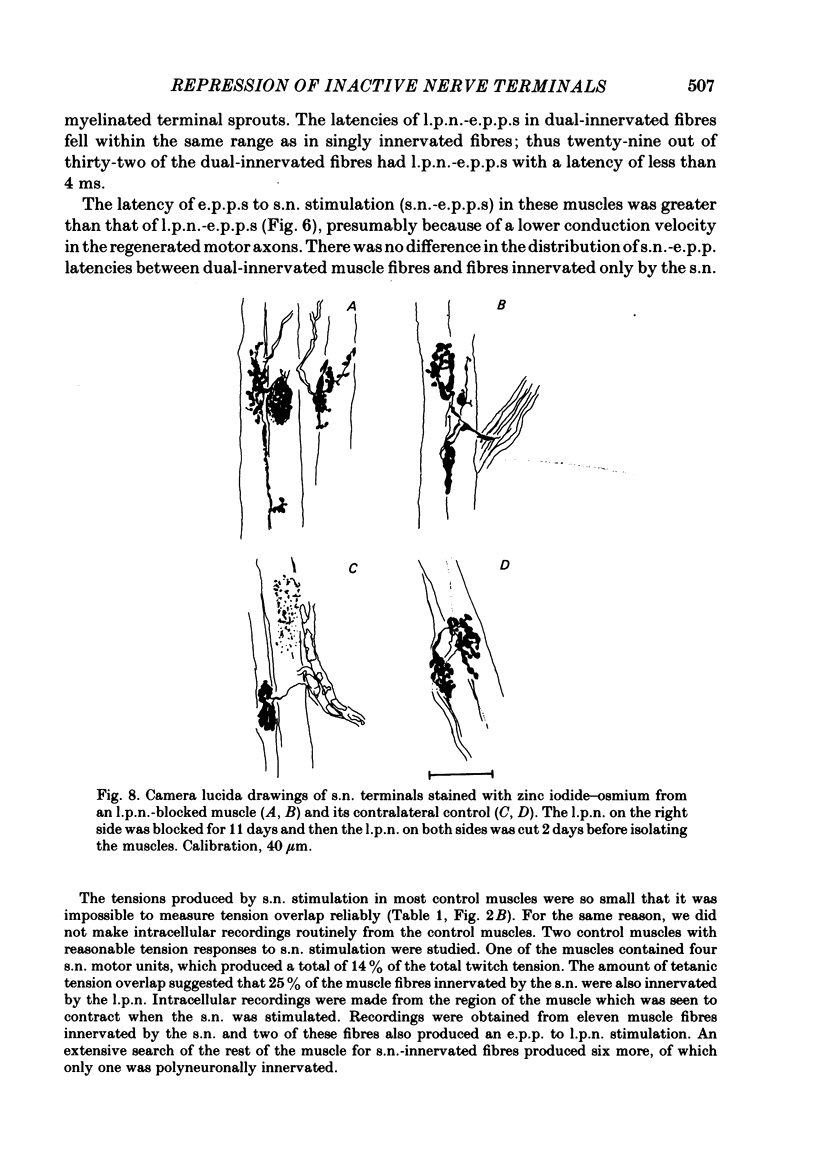
The fourth deep lumbrical muscle in the hind foot of adult rats was partially denervated by crushing the sural nerve (s.n.). The denervated muscle fibres became completely reinnervated by sprouts from lateral plantar nerve (l.p.n.) motor axons. By about 20 days after the nerve crush, s.n. motor axons started to reinnervate the muscle. In control muscles, a small proportion of the muscle fibres--about 2.5% of the muscle per motor unit--was reinnervated by s.n. motor axons over the following 20 days. Hence the regenerating terminals were able to re-establish functional synapses, despite the fact that all the muscle fibres were functionally innervated by l.p.n. terminals. When nerve impulse conduction in the l.p.n. was blocked with tetrodotoxin for up to 2 weeks, starting from the time when s.n. axons returned to the muscle, s.n. motor axons retrieved a much larger proportion of the muscle fibres--about 6.5% of the muscle per motor unit. There was a concomitant decrease in the tension produced by the sprouted l.p.n. motor axons. Intracellular recordings showed that many muscle fibres became innervated exclusively by regenerated s.n. motor nerve terminals. Measurements of end-plate potentials suggested that l.p.n. sprouts and the original nerve terminals were eliminated non-selectively. These results suggest that regenerating, active motor nerve terminals have an additional competitive advantage in reinnervating innervated muscles, if the intact terminals are inactive. When the l.p.n. was cut, rather than blocked, extensive reinnervation by the s.n. occurred-about 30% of the muscle per motor unit. This suggests that the absence of an intact nerve terminal in the motor end-plate provides a stronger stimulus than inactivity for synapse formation by regenerating motor axons.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer S. M., Dubin M. W., Stark L. A. Abnormal development of kitten retino-geniculate connectivity in the absence of action potentials. Science. 1982 Aug 20;217(4561):743–745. doi: 10.1126/science.7100921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., McLachlan E. M., Taylor R. S. The formation of synapses in mammalian striated muscle reinnervated with autonomic preganglionic nerves. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):501–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Raftos J. The formation and regression of synapses during the re-innervation of axolotl striated muscles. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):261–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixby J. L., Van Essen D. C. Competition between foreign and original nerves in adult mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):726–728. doi: 10.1038/282726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Holland R. L., Hopkins W. G. Motor nerve sprouting. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:17–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Hopkins W. G., Keynes R. J. Short- and long-term effects of paralysis on the motor innervation of two different neonatal mouse muscles. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:439–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Ironton R. Sprouting and regression of neuromuscular synapses in partially denervated mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:325–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Nieto-Sampedro M., Harris E. W. Synapse replacement in the nervous system of adult vertebrates. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jul;61(3):684–784. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.3.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Yip J. W. Formation and elimination of foreign synapses on adult salamander muscle. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:299–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Proske U. Contraction of muscle fibers in two adjacent muscles innervated by branches of the same motor axon. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):132–138. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Jansen J. K., Lomo T., Westgaard R. H. The interaction between foreign and original motor nerves innervating the soleus muscle of rats. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):725–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTH L. Neuromuscular function after regeneration of interrupted nerve fibers into partially denervated muscle. Exp Neurol. 1962 Aug;6:129–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(62)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell A. D., Letinsky M. S., Rheuben M. B. Competitive interaction between foreign nerves innervating frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:241–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N., LeVay S. Plasticity of ocular dominance columns in monkey striate cortex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr 26;278(961):377–409. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1977.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Lomo T., Nicolaysen K., Westgaard R. H. Hyperinnervation of skeletal muscle fibers: dependence on muscle activity. Science. 1973 Aug 10;181(4099):559–561. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4099.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Thompson W., Kuffler D. P. The formation and maintenance of synaptic connections as illustrated by studies of the neuromuscular junction. Prog Brain Res. 1978;48:3–19. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)61012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko C. P., Roper S. Disorganised and 'excessive' reinnervation of frog cardiac ganglia. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):286–288. doi: 10.1038/274286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmesser L. Contractile and electrical responses of vagus-innervated frog sartorius muscles. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):707–725. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. L. Tetrodotoxin blocks the formation of ocular dominance columns in goldfish. Science. 1982 Nov 5;218(4572):589–591. doi: 10.1126/science.7123262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauschecker J. P., Singer W. The effects of early visual experience on the cat's visual cortex and their possible explanation by Hebb synapses. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:215–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribchester R. R., Taxt T. Motor unit size and synaptic competition in rat lumbrical muscles reinnervated by active and inactive motor axons. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:89–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson J. A. Abnormal axonal growth in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Jan 20;195(3):453–476. doi: 10.1002/cne.901950306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roper S., Ko C. P. Impulse blockade in frog cardiac ganglion does not resemble partial denervation in changing synaptic organization. Science. 1978 Oct 6;202(4363):66–68. doi: 10.1126/science.308697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders F. K., Whitteridge D. Conduction velocity and myelin thickness in regenerating nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1946 Sep 18;105(2):152–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimidt J. T., Cicerone C. M., Easter S. S. Expansion of the half retinal projection to the tectum in goldfish: an electrophysiological and anatomical study. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Jan 15;177(2):257–277. doi: 10.1002/cne.901770206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. Reinnervation of partially denervated rat soleus muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 May;103(1):81–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonge D. A. Effect of implantation of an extra nerve on the recovery of neuromuscular transmission from botulinum toxin. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):809–820. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigston D. J. Suppression of sprouted synapses in axolotl muscle by transplanted foreign nerves. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:355–366. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


