Abstract
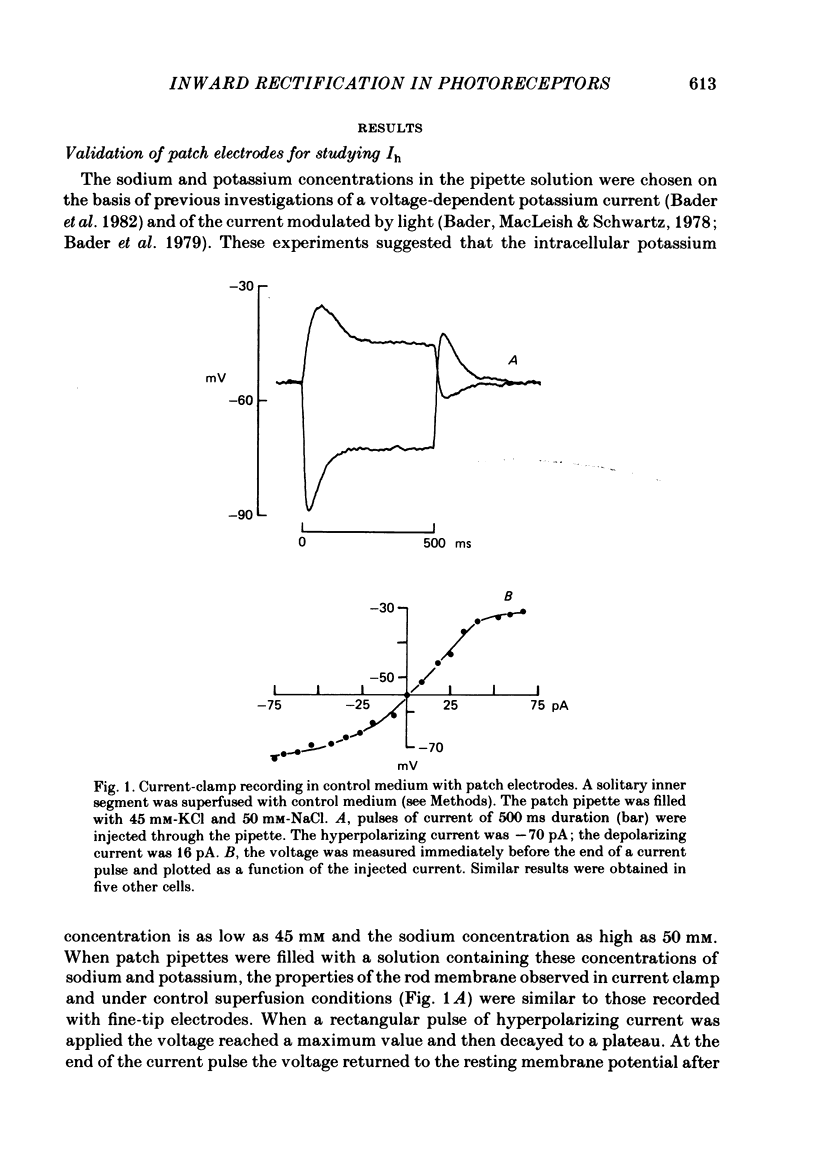
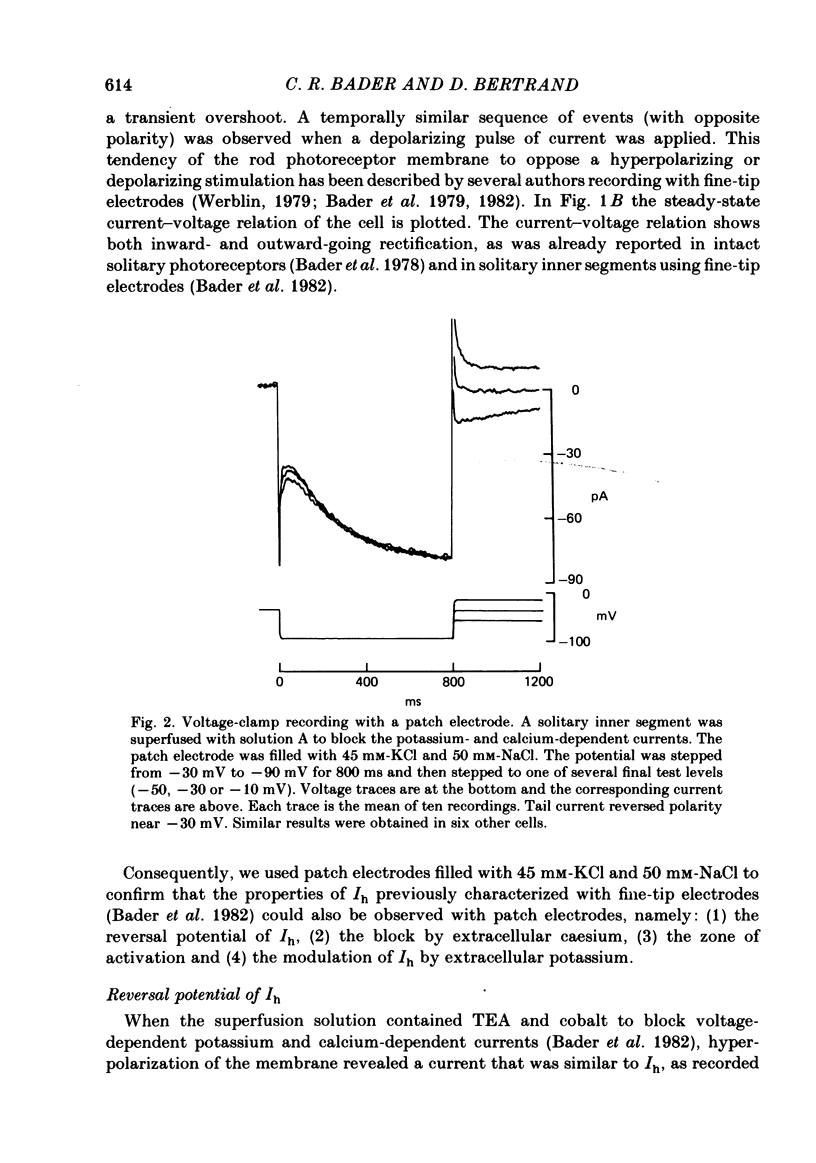
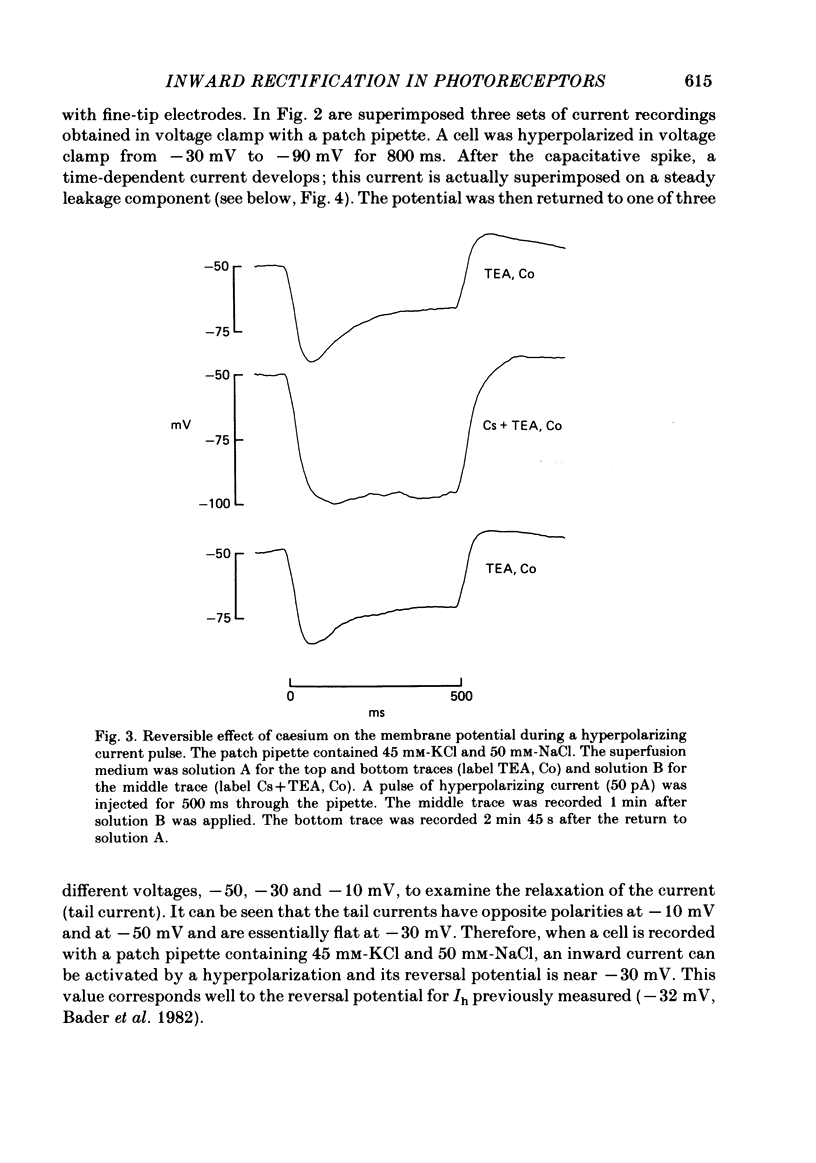
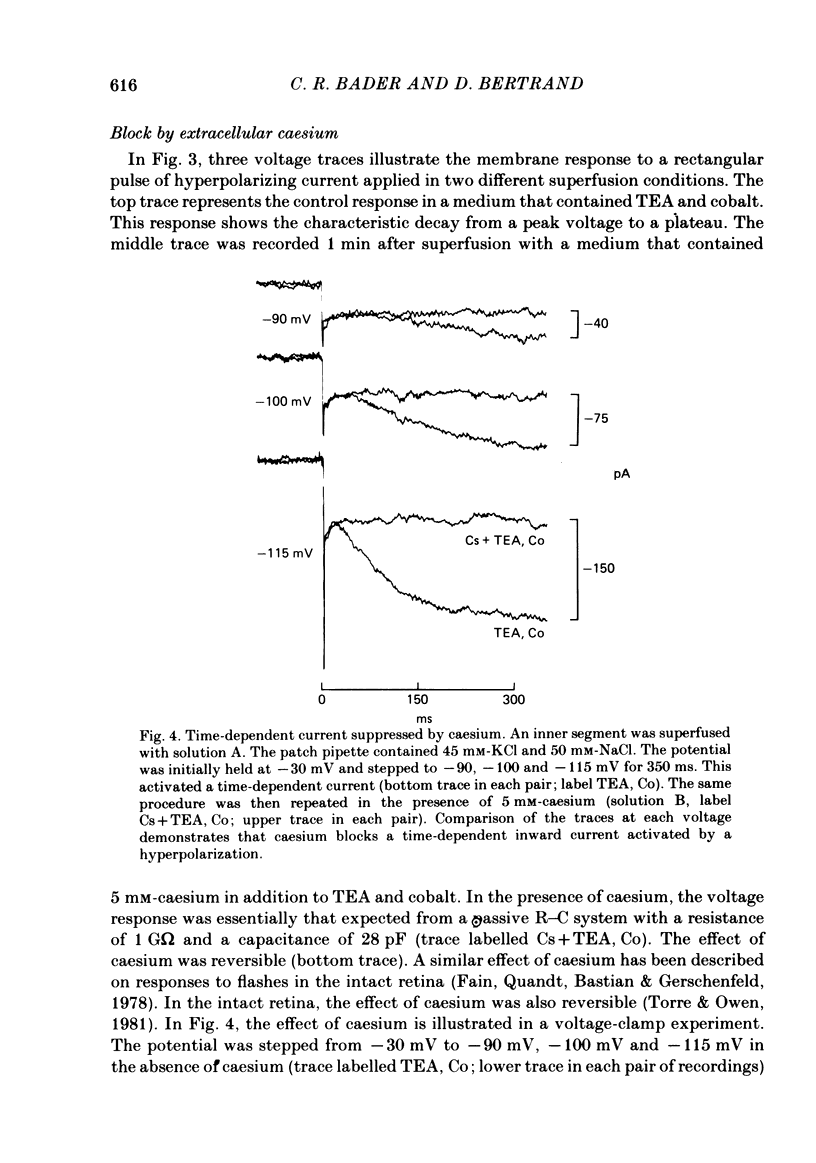
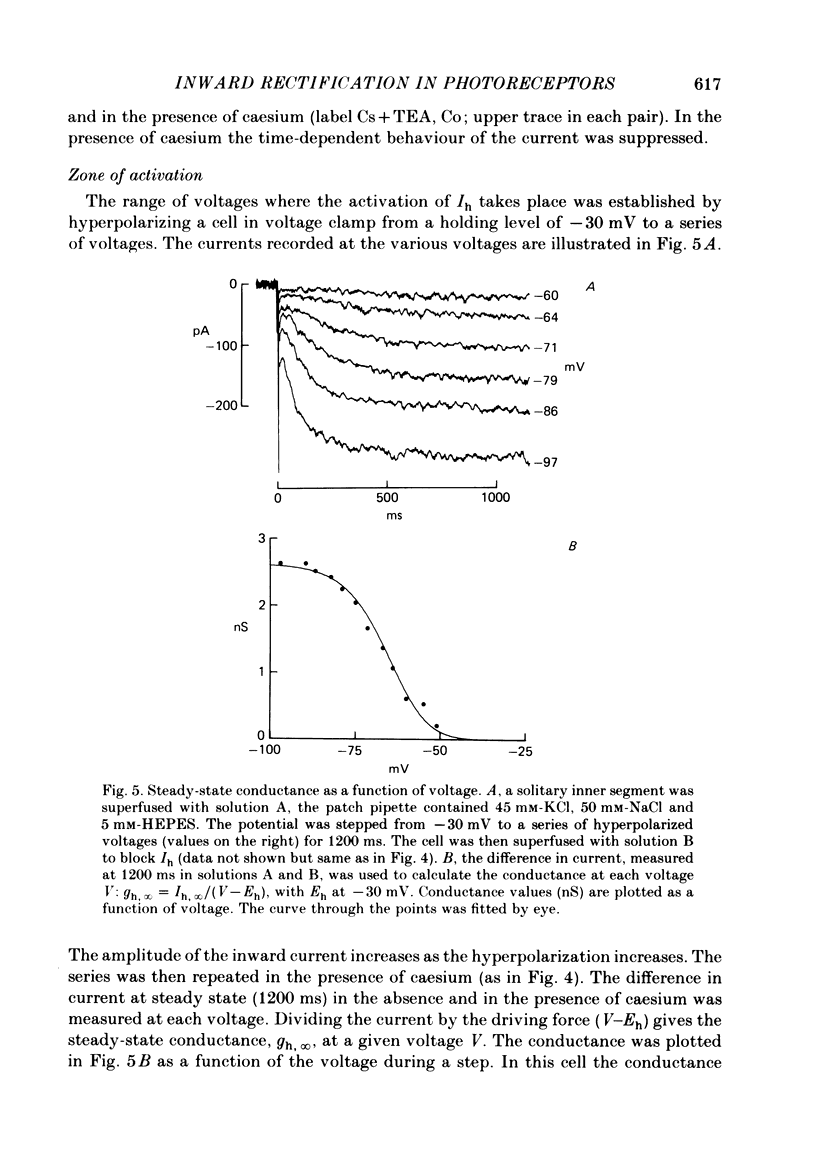
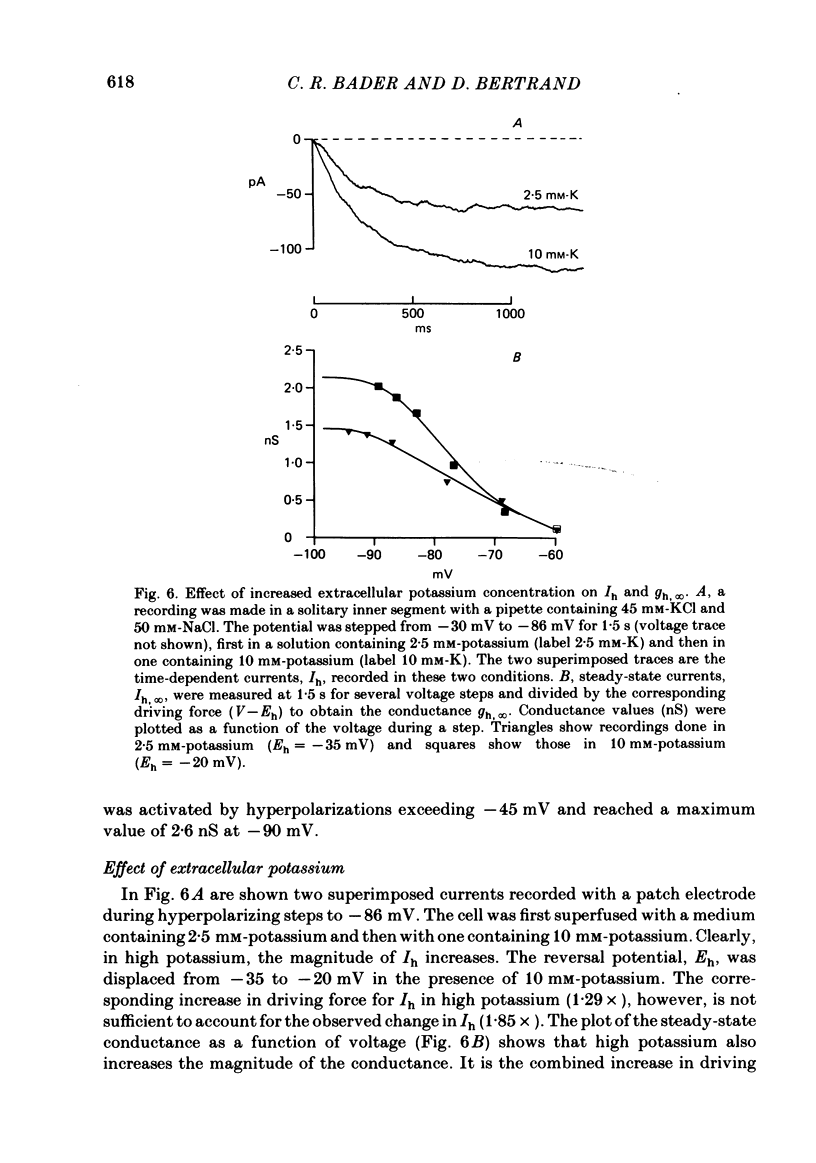
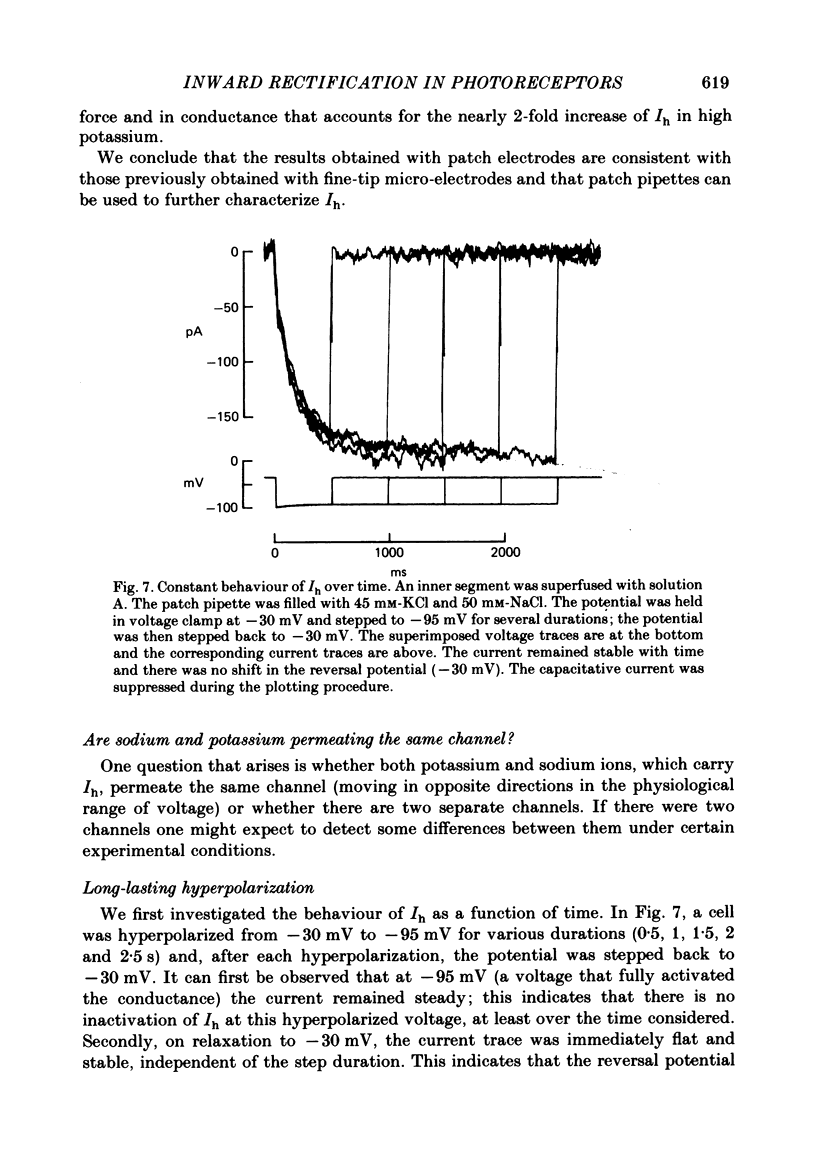
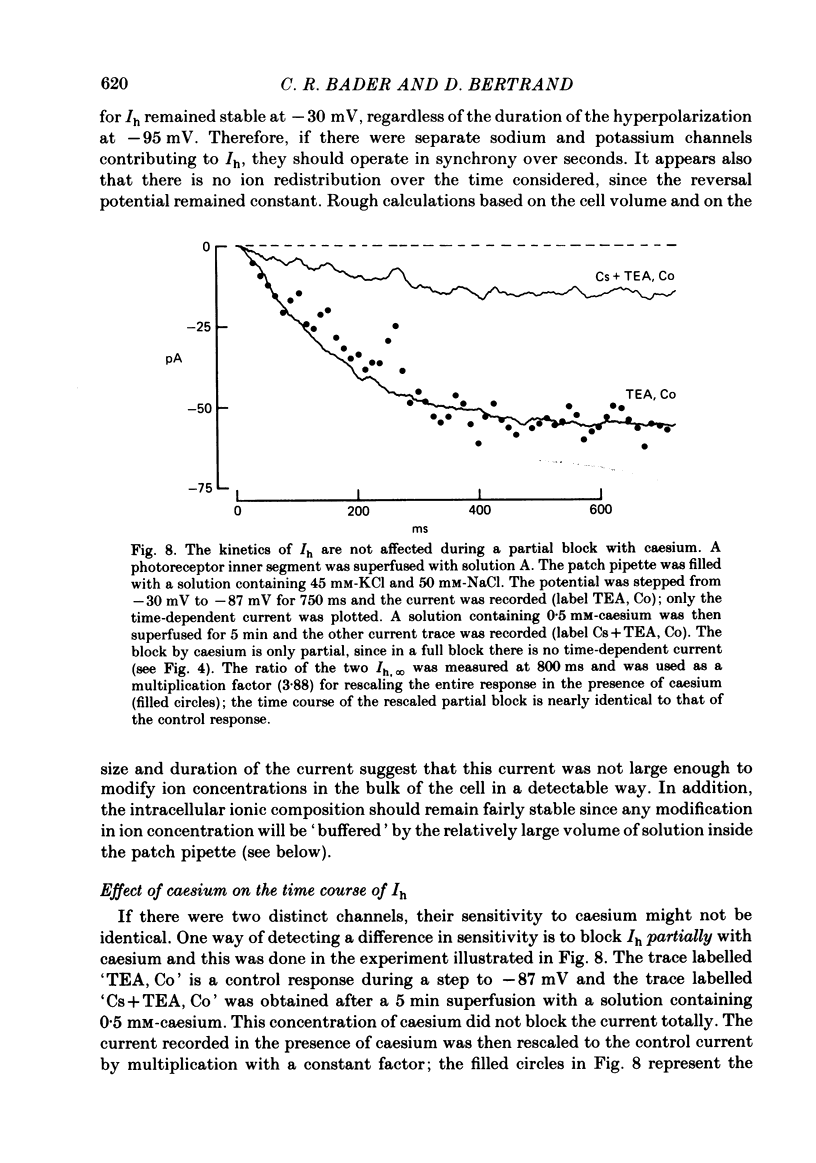
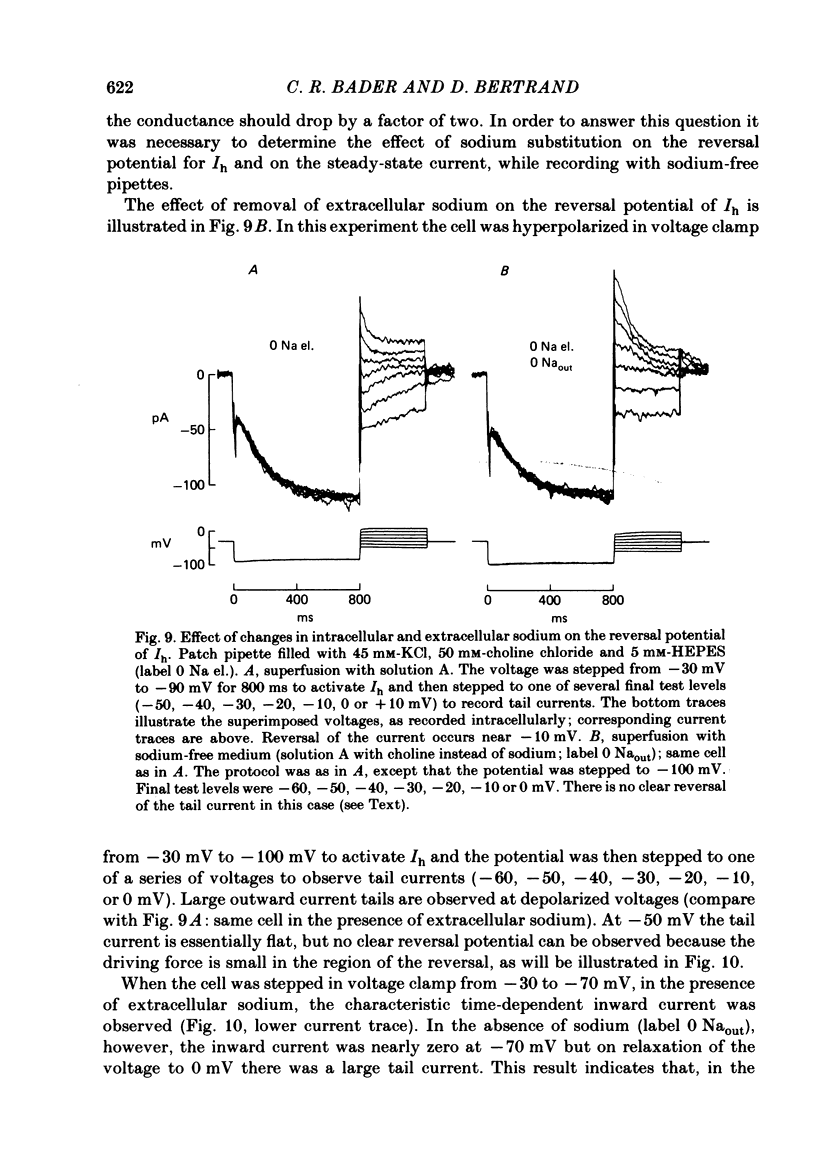
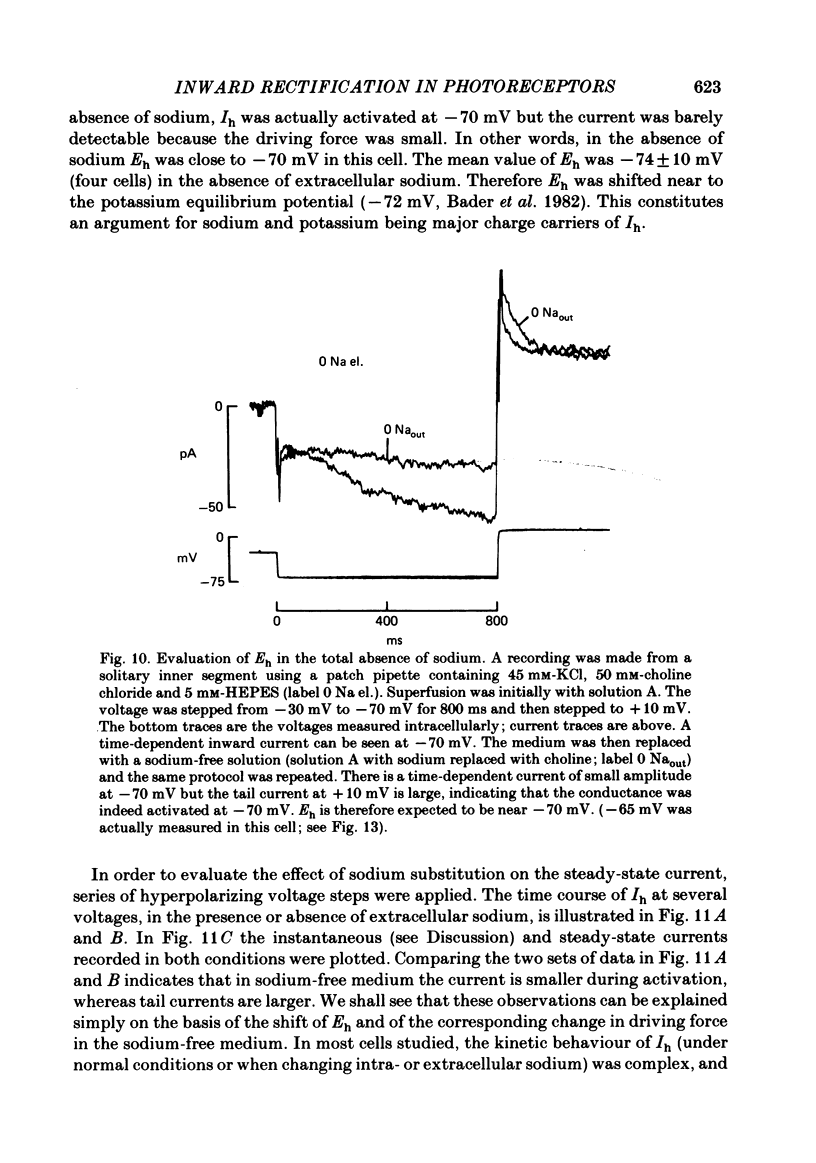
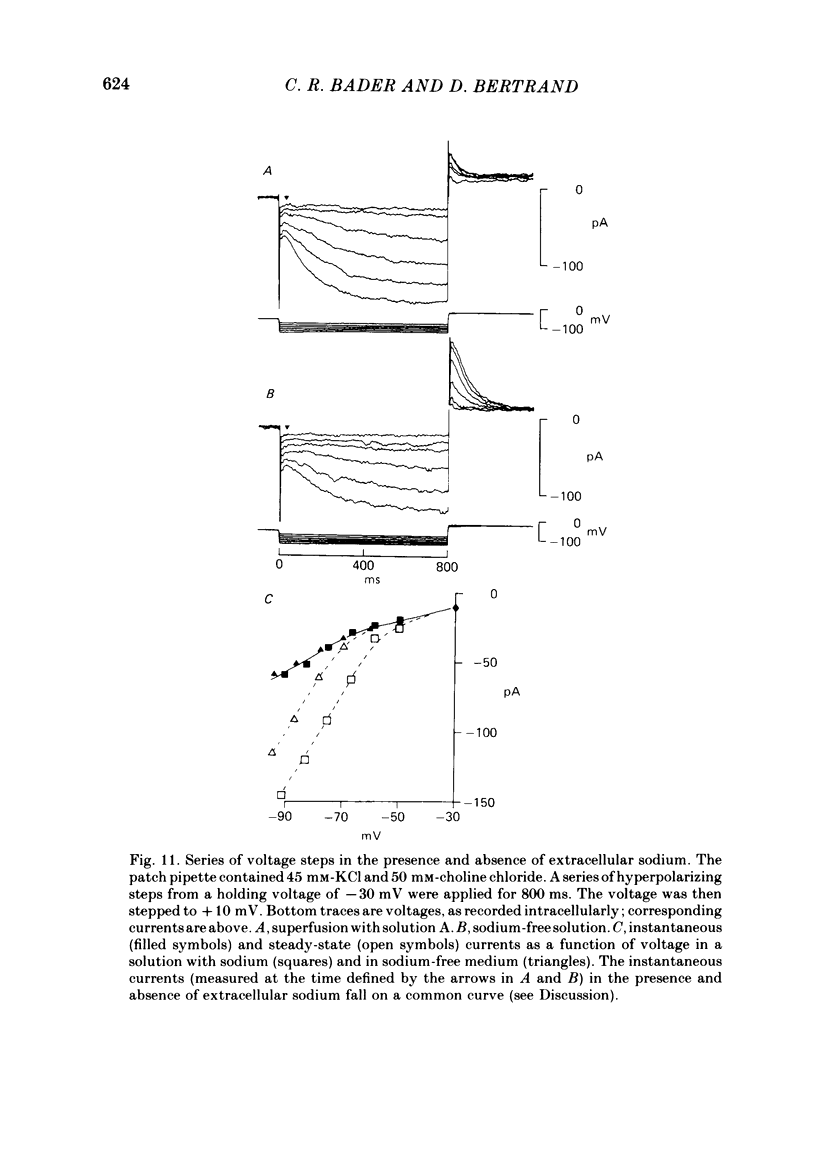
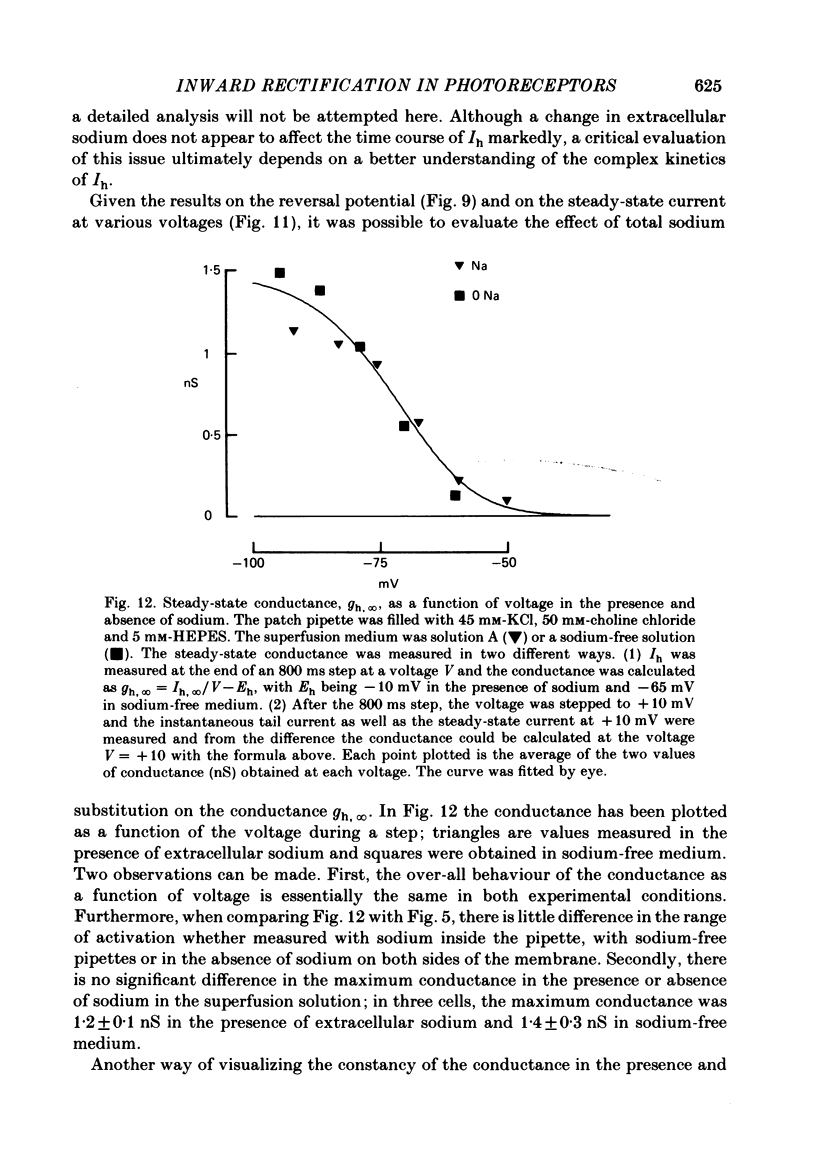
Solitary rod inner segments were obtained by enzymic dissociation of the tiger salamander retina. Ih, an inward current activated by membrane hyperpolarization, was studied using the single-pipette voltage-clamp technique with patch pipettes. In order to investigate Ih in isolation from voltage-dependent potassium and calcium currents, it was necessary to superfuse with a solution containing TEA and cobalt. When the solution in the patch pipette contained 45 mM-KCl and 50 mM-NaCl, the characteristics of Ih were indistinguishable from those previously described with fine-tip micro-electrodes: the reversal potential was near-30 mV and Ih was blocked by extracellular caesium and enhanced by an increase in the extracellular potassium concentration. The increase in Ih observed when the extracellular potassium concentration is raised is due to an increase in conductance and in driving force. Replacement of sodium in the patch pipette with choline caused a 15 mV displacement of the reversal potential for Ih in the depolarized direction. When using sodium-free patch pipettes, replacement of extracellular sodium displaced the reversal potential for Ih to -74 mV, a value in the range of the potassium equilibrium potential in solitary inner segments. Intracellular or intra- and extracellular sodium substitution affected neither the activation range of Ih nor the maximum conductance. From points 3-6 it can be concluded that Ih is carried mainly, if not exclusively, by sodium and potassium and that the channel responsible for Ih is insensitive to modifications of the intra- or extracellular sodium concentration. The results of long-term hyperpolarization, of partial block with caesium and of total sodium substitution are consistent with sodium and potassium permeating the same type of channel.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attwell D., Werblin F. S., Wilson M. The properties of single cones isolated from the tiger salamander retina. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:259–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Wilson M. Behaviour of the rod network in the tiger salamander retina mediated by membrane properties of individual rods. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:287–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Schwartz E. A. Voltage-activated and calcium-activated currents studied in solitary rod inner segments from the salamander retina. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:253–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., MacLeish P. R., Schwartz E. A. Responses to light of solitary rod photoreceptors isolated from tiger salamander retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3507–3511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Macleish P. R., Schwartz E. A. A voltage-clamp study of the light response in solitary rods of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:1–26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastian B. L., Fain G. L. The effects of sodium replacement on the responses of toad rods. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:331–347. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fuortes M. G. Electrical responses of single cones in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):77–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand D., Cand P., Henauer R., Bader C. R. Fabrication of glass microelectrodes with microprocessor control. J Neurosci Methods. 1983 Feb;7(2):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. F., DiFrancesco D., Noble S. J. How does adrenaline accelerate the heart? Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):235–236. doi: 10.1038/280235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H., Difrancesco D. Voltage-clamp investigations of membrane currents underlying pace-maker activity in rabbit sino-atrial node. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:331–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Pinto L. H. Ionic mechanism for the photoreceptor potential of the retina of Bufo marinus. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):575–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capovilla M., Cervetto L., Pasino E., Torre V. The sodium current underlying the responses of toad rods to light. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:223–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervetto L., Piccolino M. Synaptic transmission between photoreceptors and horizontal cells in the turtle retina. Science. 1974 Feb 1;183(4123):417–419. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4123.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoy-Marchais D. A Cl- conductance activated by hyperpolarization in Aplysia neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):359–361. doi: 10.1038/299359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. A new interpretation of the pace-maker current in calf Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:359–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. A study of the ionic nature of the pace-maker current in calf Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:377–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. Block and activation of the pace-maker channel in calf purkinje fibres: effects of potassium, caesium and rubidium. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:485–507. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Ojeda C. Properties of the current if in the sino-atrial node of the rabbit compared with those of the current iK, in Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:353–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Quandt F. N., Bastian B. L., Gerschenfeld H. M. Contribution of a caesium-sensitive conductance increase to the rod photoresponse. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):466–469. doi: 10.1038/272467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Penn R. D., Yoshikami S. Dark current and photocurrent in retinal rods. Biophys J. 1970 May;10(5):380–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86308-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Yoshikami S. Ionic mechanisms in excitation of photoreceptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:314–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Yoshii M. Effects of internal potassium and sodium on the anomalous rectification of the starfish egg as examined by internal perfusion. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:251–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell J. V., Adams P. R. Voltage-clamp analysis of muscarinic excitation in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 28;250(1):71–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90954-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Shimazaki H. Synaptic transmission from photoreceptors to bipolar and horizontal cells in the carp retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:537–546. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. A voltage-clamp analysis of inward (anomalous) rectification in mouse spinal sensory ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:19–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Torre V. High-pass filtering of small signals by retinal rods. Ionic studies. Biophys J. 1983 Mar;41(3):325–339. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84444-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozeki M., Freeman A. R., Grundfest H. The membrane components of crustacean neuromuscular systems. II. Analysis of interactions among the electrogenic components. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):1335–1349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.0491335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer S. F., Raviola E. Membrane recycling in the cone cell endings of the turtle retina. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):802–825. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Responses of single rods in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;232(3):503–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillman A. J., Ito H., Tomita T. Studies on the mass receptor potential of the isolated frog retina. II. On the basis of the ionic mechanism. Vision Res. 1969 Dec;9(12):1443–1451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(69)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T. Electrophysiological study of the mechanisms subserving color coding in the fish retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:559–566. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torre V. The contribution of the electrogenic sodium-potassium pump to the electrical activity of toad rods. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:315–341. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda J., Hashimoto H., Anno H., Tomita T. The rod response in the frog and studies by intracellular recording. Vision Res. 1970 Nov;10(11):1093–1100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(70)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. E. Kinetic properties of the chloride conductance of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):291–312. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S. Time- and voltage-dependent ionic components of the rod response. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:613–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. M., Miller C. A voltage-gated anion channel from the electric organ of Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10161–10166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., McNaughton P. A., Hodgkin A. L. Effect of ions on the light-sensitive current in retinal rods. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):502–505. doi: 10.1038/292502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


