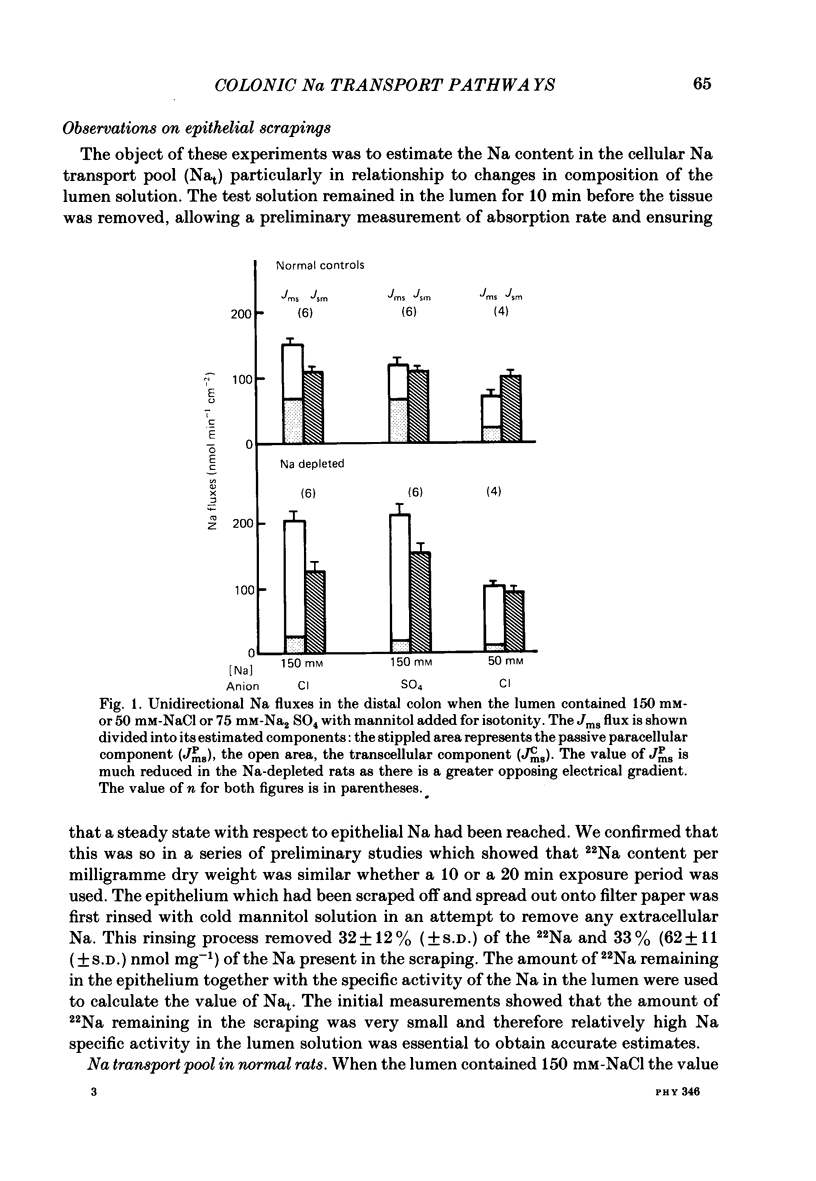
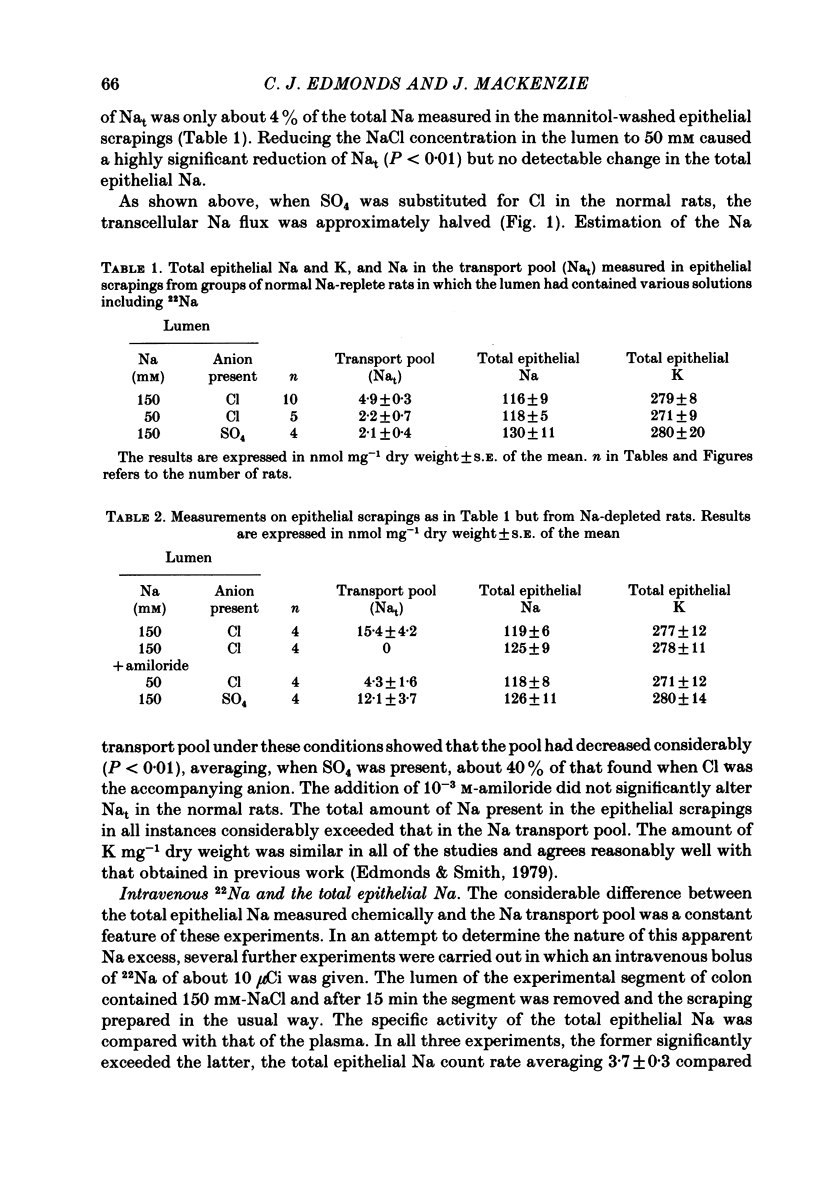
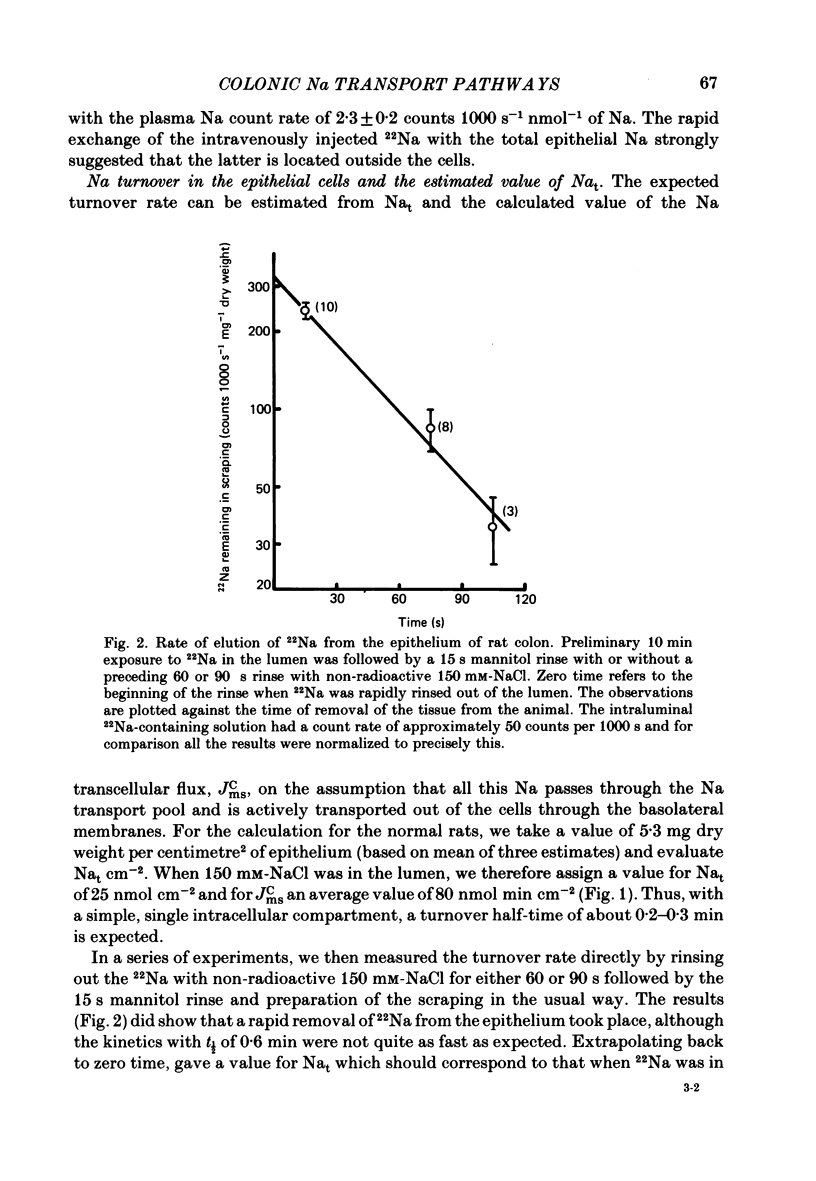
Abstract
Methods for measurement of the epithelial Na transport pool (Nat) using epithelial scrapings and for analysing the transepithelial ionic fluxes of rat distal colon in vivo into transcellular and paracellular components have been used to study the amiloride sensitive (a.s.) and amiloride insensitive (a.i.) transcellular pathways in relation to variations of Nat. In the Na-replete normal rats, substitution of SO4 for Cl in the lumen approximately halved the Na transported by a.i. pathways and reduced Nat by about 60%, but in the Na-depleted rats, substitution of SO4 did not affect either the Na transported by a.s. pathways or Nat. The value of Nat for normal rats, with 150 mM-NaCl in the lumen, was 6-7 nmol Na mg-1 dry weight (corresponding to about 2-3 mmol kg-1 cell water) and fell by about 60% when lumen Na concentration was reduced to 50 mM. Its turnover half-time was 0.6 min. Nat was about threefold greater in the Na-depleted than in the normal rats but became undetectable when amiloride was in the lumen. Amiloride did not affect Nat in normal rats. We conclude that the increased Na absorption in Na depletion depended on substitution of a.s. for a.i. apical membrane pathways allowing increased Na entry into the epithelial cells so expanding Nat and stimulating the basolateral Na pumps.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argenzio R. A., Whipp S. C. Inter-relationship of sodium, chloride, bicarbonate and acetate transport by the colon of the pig. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:365–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Rawlins C. L. Electrolyte transport across isolated large intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1973 Nov;225(5):1232–1239. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.5.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremaschi D., Ferguson D. R., Hénin S., James P. S., Meyer G., Smith M. W. Post-natal development of amiloride sensitive sodium transport in pig distal colon. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:481–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Channels in epithelial cell membranes and junctions. Fed Proc. 1978 Oct;37(12):2639–2643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C. Intracellular sodium ion activity and sodium transport in rabbit urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:527–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J. Amiloride sensitivity of the transepithelial electrical potential and of sodium and potassium transport in rat distal colon in vivo. J Physiol. 1981;313:547–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J. Anion transport in the colon. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):575–584. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J., Nielsen O. E. Transmembrane electrical potential differences and ionic composition of mucosal cells of rat colon. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Mar;72(3):338–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb03856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J., Smith T. Epithelial transport pathways of rat colon determined in vivo by impulse response analysis. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:471–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldrup E., Frederiksen O., Møllgård K., Rostgaard J. Effects of a small serosal hydrostatic pressure on sodium and water transport and morphology in rabbit gall-bladder. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:67–85. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Koch M. J., Schultz S. G. Ion transport by rabbit colon. I. Active and passive components. J Membr Biol. 1976;27(3):297–316. doi: 10.1007/BF01869142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann B., Van Driessche W. Sodium-specific membrane channels of frog skin are pores: current fluctuations reveal high turnover. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):292–294. doi: 10.1126/science.299785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D., Leaf A. The sodium transport pool. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):F1–F9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D., Mason D. R., Rose R. C., Sherman B. Ions and water in the epithelial cells of rabbit descending colon. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:111–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møllgård K., Rostgaard J. Morphological aspects of some sodium transporting epithelia suggesting a transcellular pathway via elements of endoplasmic reticulum. J Membr Biol. 1978;40(Spec No):71–89. doi: 10.1007/BF02025999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson B. D., Edmonds C. J. Aldosterone, sodium depletion and hypothyroidism on the ATPase activity of rat colonic epithelium. J Endocrinol. 1974 Sep;62(3):489–496. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0620489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will P. C., Lebowitz J. L., Hopfer U. Induction of amiloride-sensitive sodium transport in the rat colon by mineralocorticoids. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):F261–F268. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.4.F261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills N. K., Lewis S. A., Eaton D. C. Active and passive properties of rabbit descending colon: a microelectrode and nystatin study. J Membr Biol. 1979 Mar 28;45(1-2):81–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01869296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiske W., Wills N. K., Van Driessche W. Na+ channels and amiloride-induced noise in the mammalian colon epithelium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90595-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


