Abstract
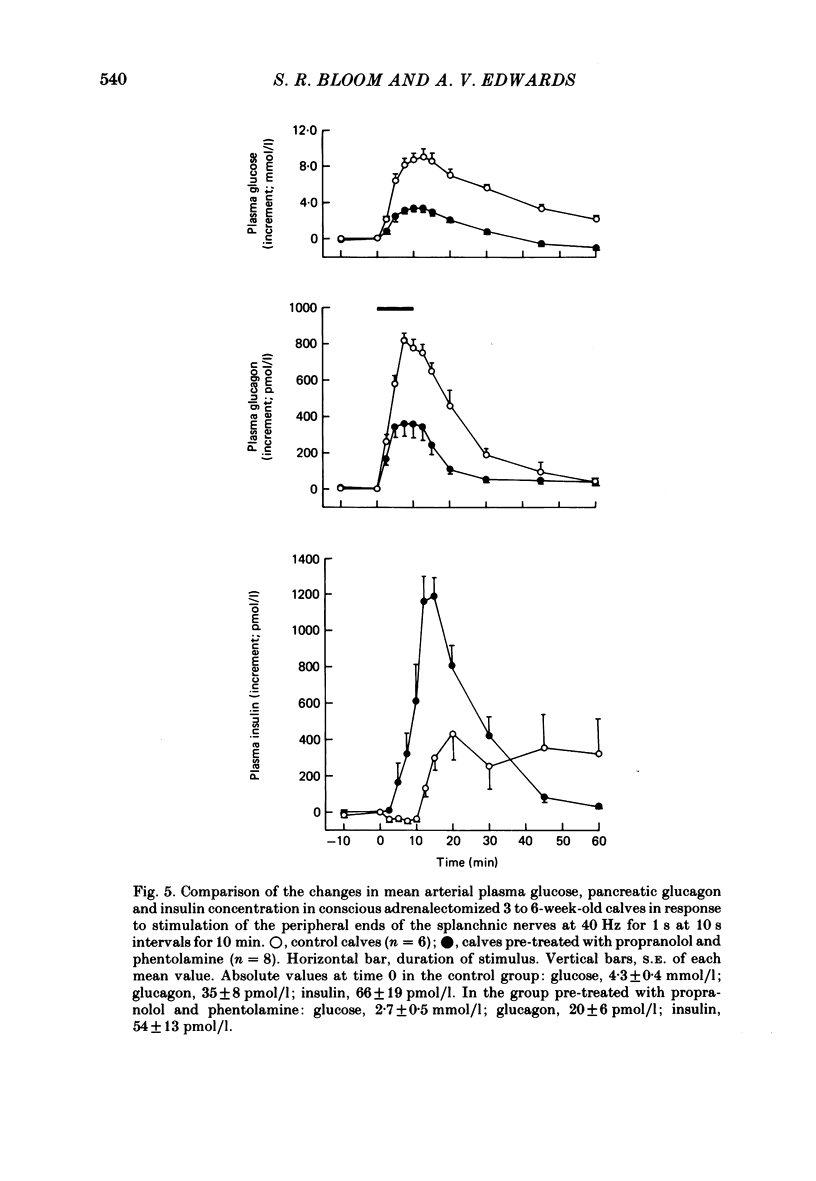
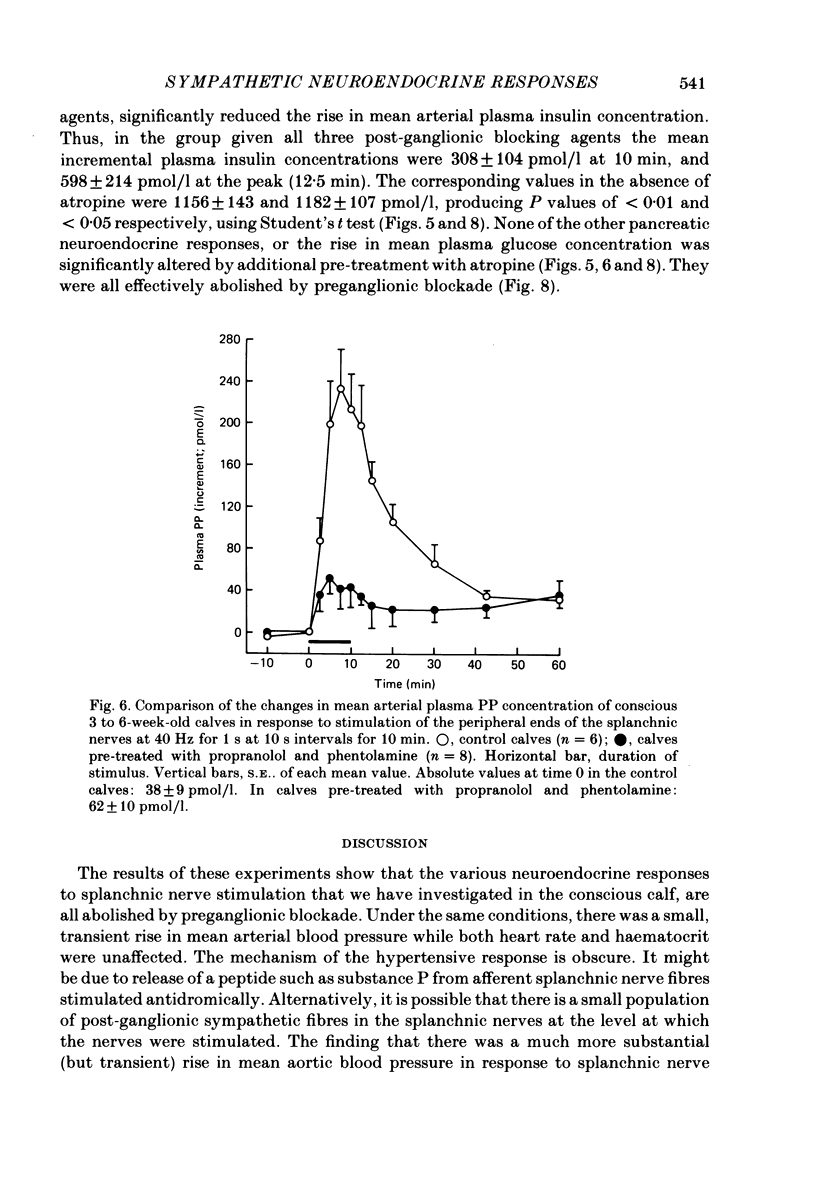
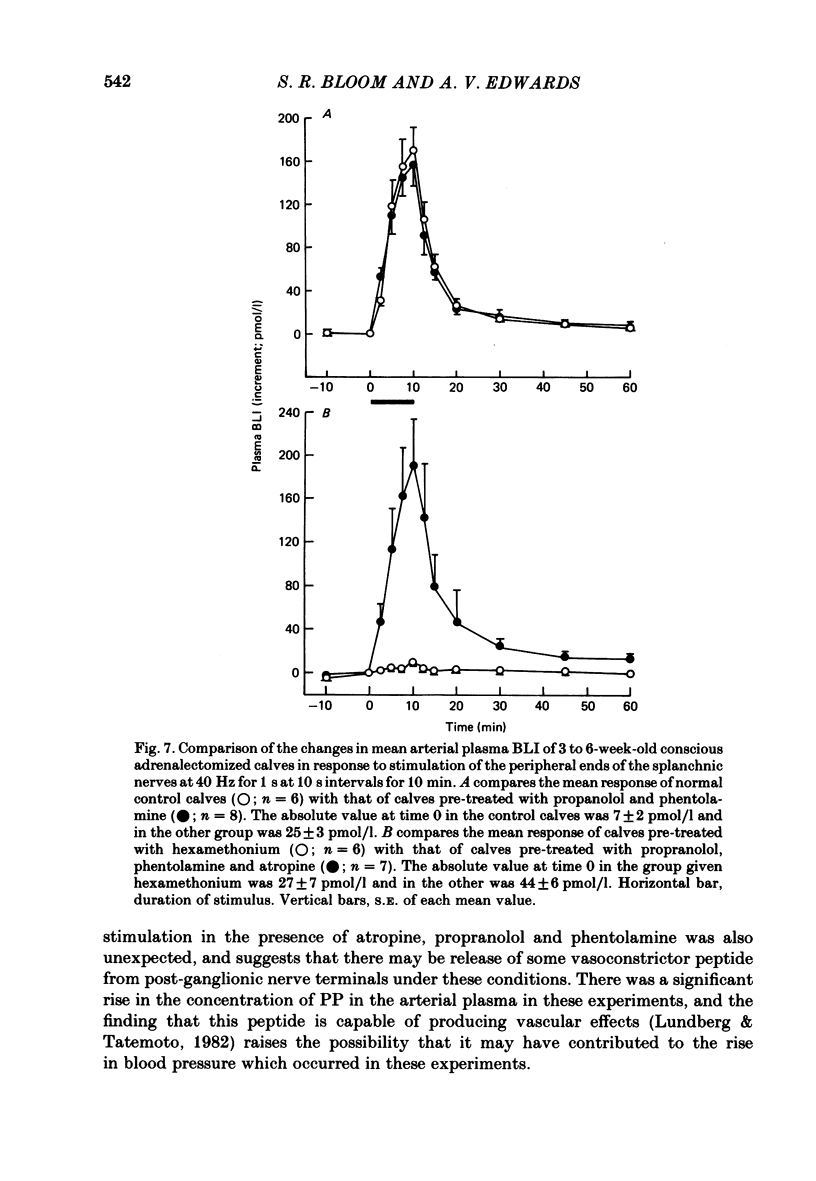
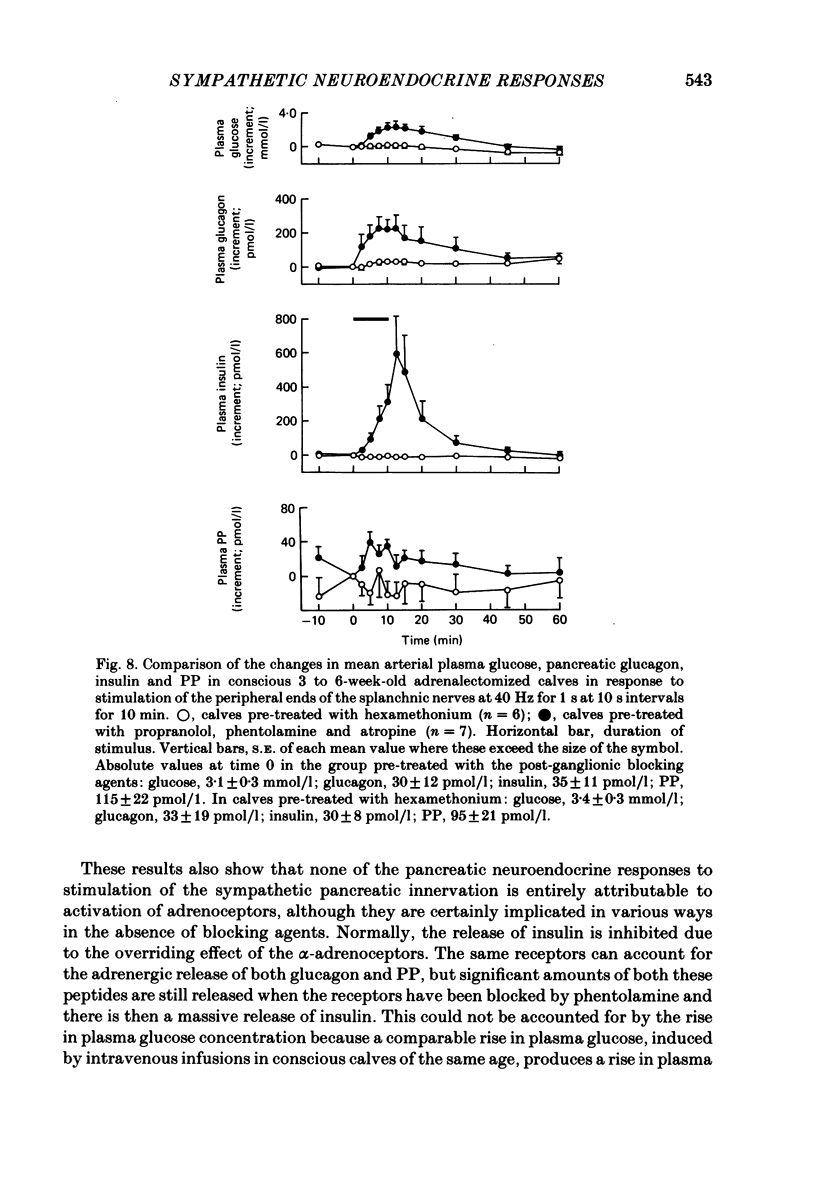
Neuroendocrine responses to splanchnic nerve stimulation in bursts (at 40 Hz for 1 s at 10 s intervals for 10 min) have been investigated in conscious adrenalectomized calves, 3-6 weeks after birth, in the presence of various pharmacological blocking agents. Preganglionic blockade with hexamethonium abolished all the neuroendocrine responses that were monitored. Pre-treatment with phentolamine significantly reduced, but failed to eliminate, the release of both pancreatic glucagon and pancreatic polypeptide. In the presence of phentolamine splanchnic nerve stimulation produced a massive rise in arterial plasma insulin concentration. None of these pancreatic neuroendocrine responses was significantly affected by additional pre-treatment with propranolol. The rise in mean plasma insulin concentration which occurred in calves pre-treated with both phentolamine and propranolol was significantly reduced by atropine. Release of bombesin-like immunoreactivity (BLI) was unaffected by total post-ganglionic adrenergic and cholinergic blockade. The results indicate that pancreatic endocrine responses to splanchnic nerve stimulation may be attributable, at least in part, to release of BLI in this species.
Full text
PDF


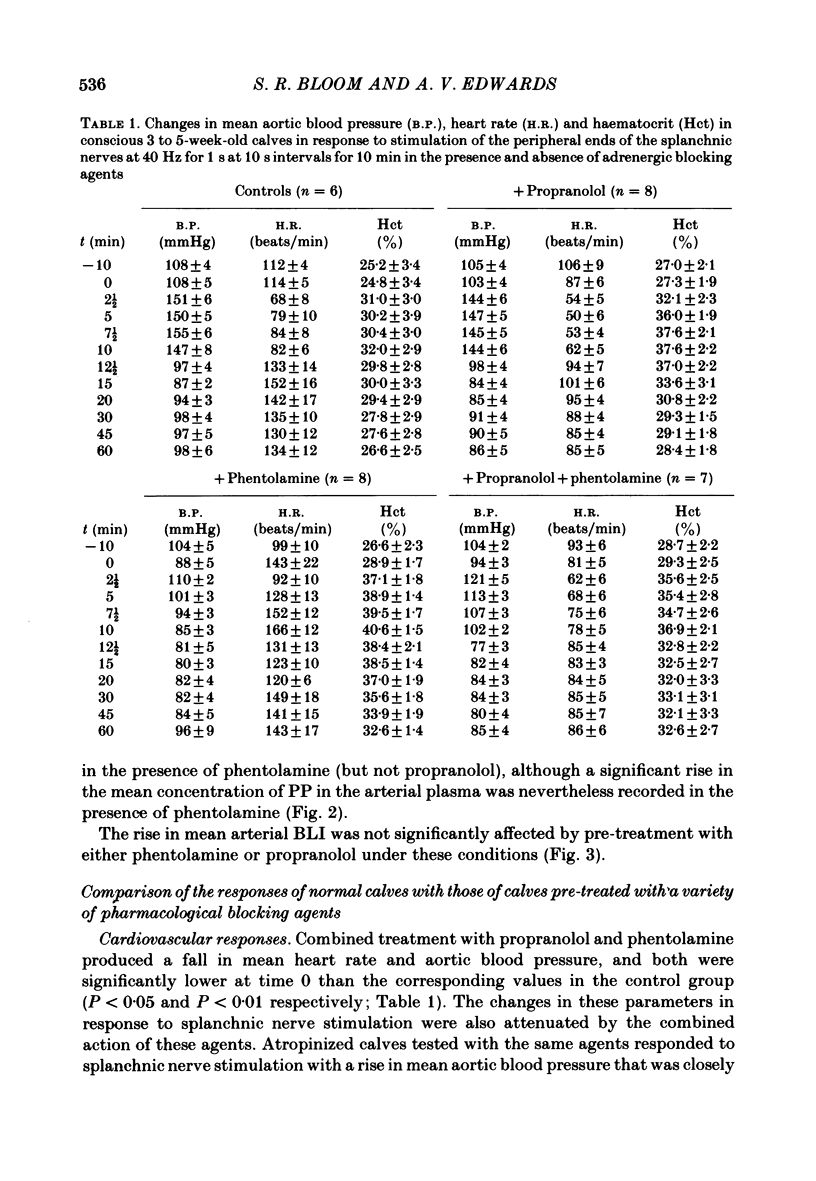
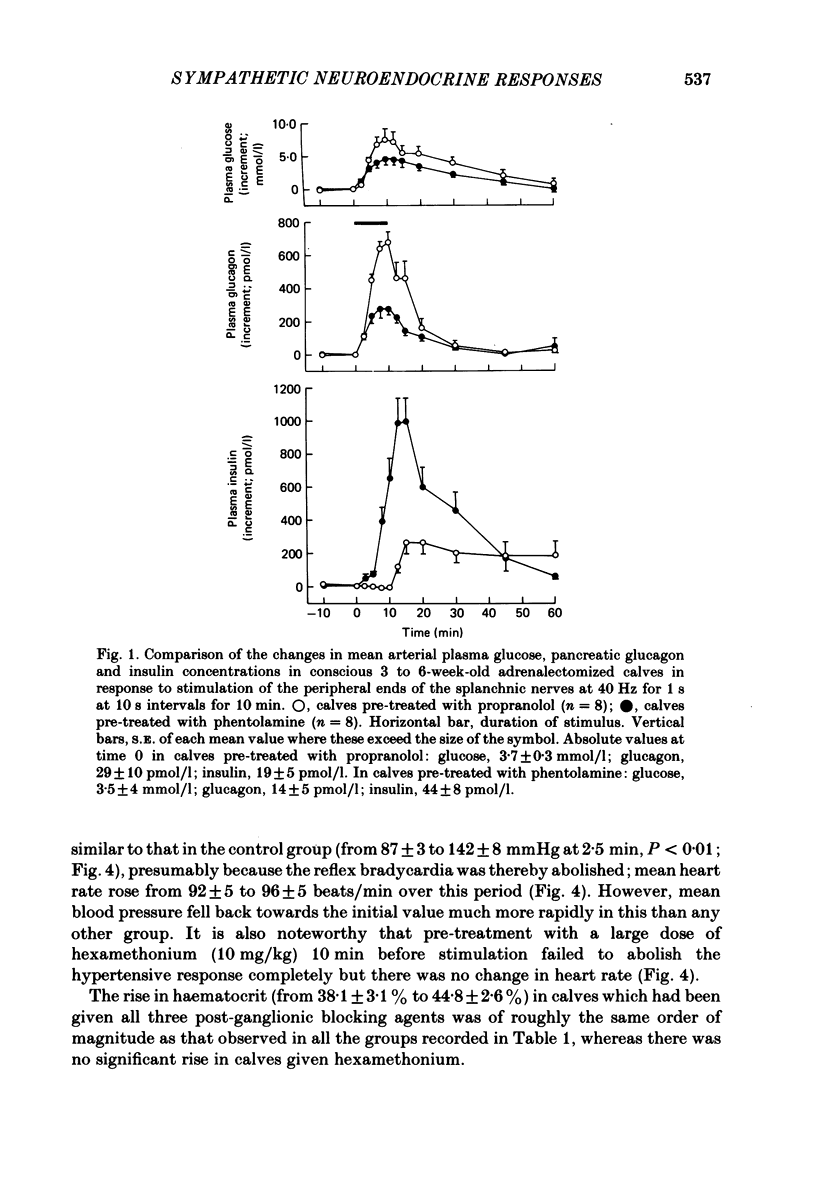
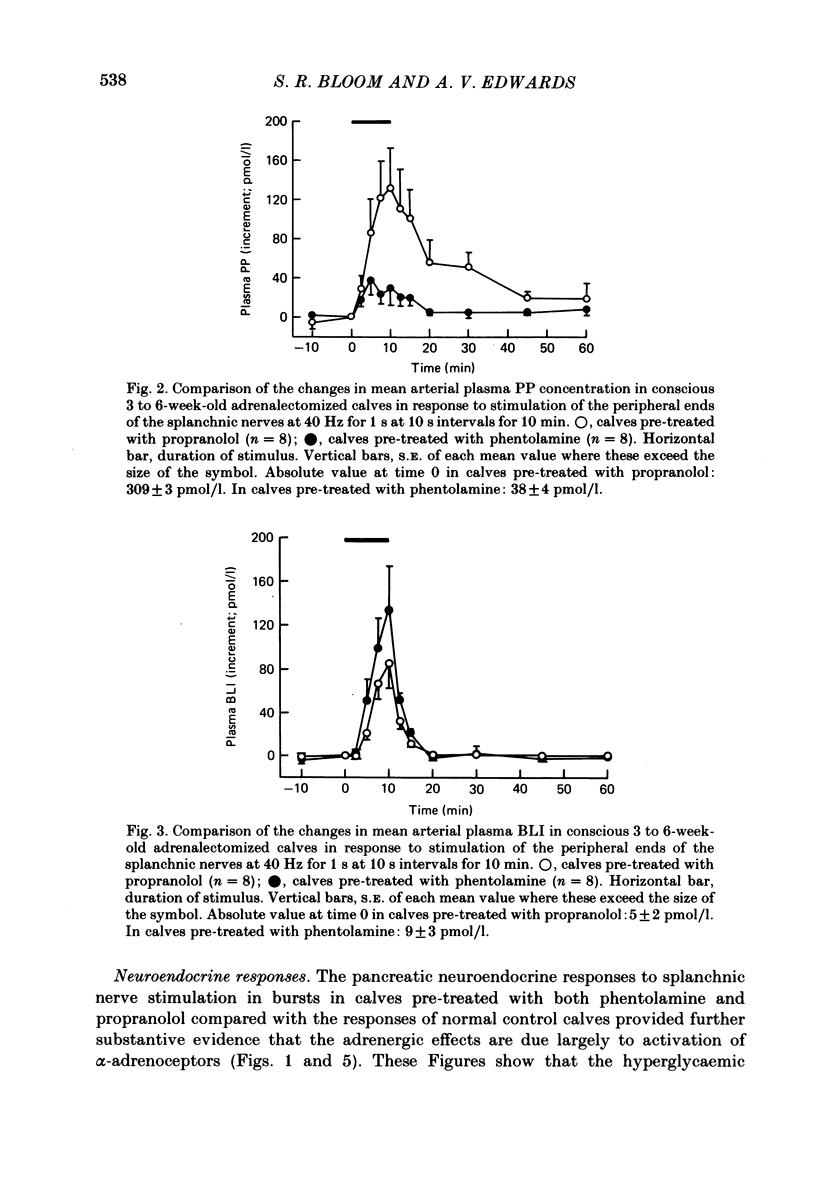
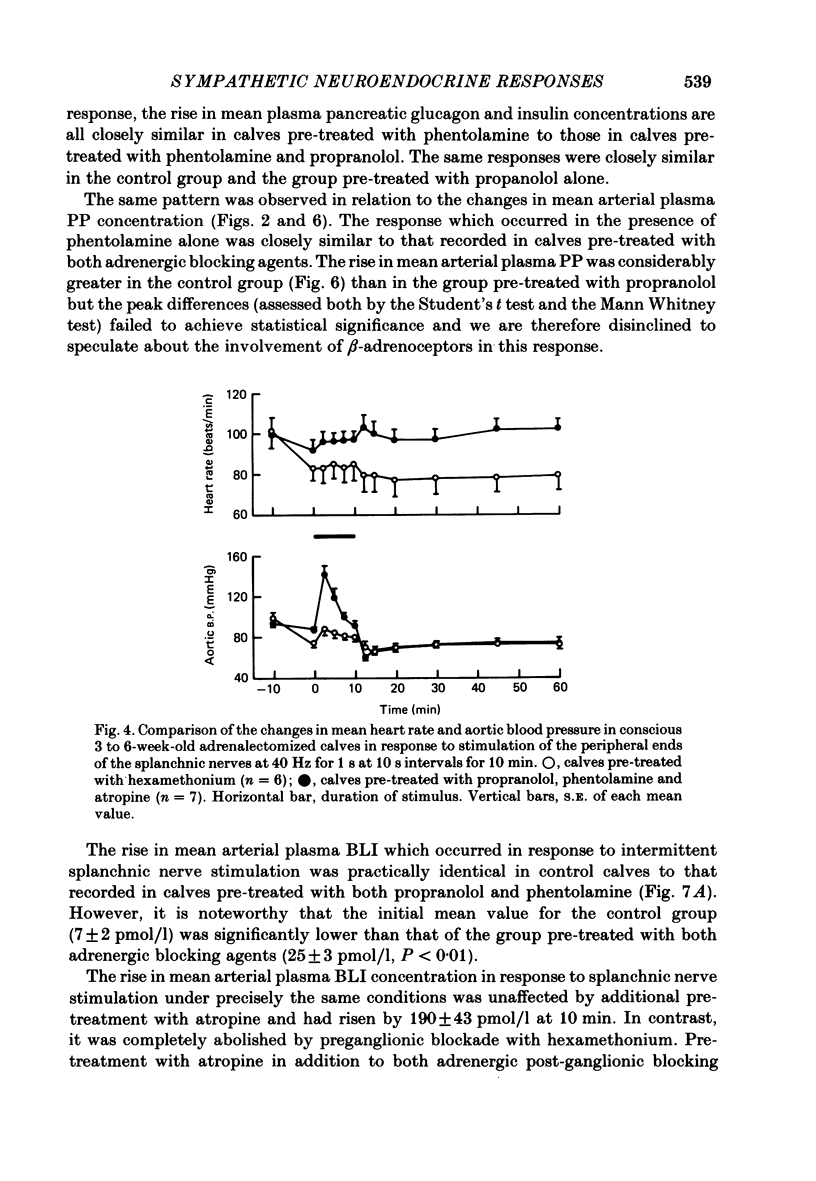


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T. E., Bloom S. R., Bryant M. G., Polak J. M., Heitz P. H., Barnes A. J. Distribution and release of human pancreatic polypeptide. Gut. 1976 Dec;17(12):940–944. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.12.940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T. E., Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. Neuroendocrine responses to stimulation of the vagus nerves in bursts in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:25–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson P. O., Holst J., Järhult J. Effects of adrenergic blockade on the release of insulin, glucagon and somatostatin from the pancreas in response to splanchnic nerve stimulation in cats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assan R., Slusher N. Structure-function and structure-immunoreactivity relationships of the glucagon molecule and related synthetic peptides. Diabetes. 1972 Aug;21(8):843–855. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.8.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. Certain pharmacological characteristics of the release of pancreatic glucagon in response to stimulation of the splanchnic nerves. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:25–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Ghatei M. A. Endocrine responses to exogenous bombesin and gastrin releasing peptide in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:37–48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. Pancreatic endocrine responses to stimulation of the peripheral ends of the splanchnic nerves in the conscious adrenalectomized calf. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:39–48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. The release of pancreatic glucagon and inhibition of insulin in response to stimulation of the sympathetic innervation. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):157–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. The role of the parasympathetic system in the control of insulin release in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:37–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Vaughan N. J. The role of the sympathetic innervation in the control of plasma glucagon concentration in the calf. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(2):457–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J., Vaillant C., Walsh J. H. The neuronal origin of bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Neuroscience. 1979;4(11):1561–1568. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterhuizen A. C., Howell S. L. Ultrastructure of the A-cells of cat islets of Langerhans following sympathetic stimulation of glucagon secretion. J Cell Biol. 1970 Sep;46(3):593–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghatei M. A., Jung R. T., Stevenson J. C., Hillyard C. J., Adrian T. E., Lee Y. C., Christofides N. D., Sarson D. L., Mashiter K., MacIntyre I. Bombesin: action on gut hormones and calcium in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 May;54(5):980–985. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-5-980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J., Grønholt R., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. B., Fahrenkrug J. Nervous control of pancreatic endocrine secretion in pigs. V. Influence of the sympathetic nervous system on the pancreatic secretion of insulin and glucagon, and on the insulin and glucagon response to vagal stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981;113(3):279–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järhult J., Andersson P. O., Holst J., Moghimzadeh E., Nobin A. On the sympathetic innervation to the cat's liver and its role for hepatic glucose release. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Sep;110(1):5–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kajinuma H., Kosaka K. Effect of splanchnic nerve stimulation on glucagon and insulin output in the dog. Endocrinology. 1975 Jan;96(1):143–150. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Girardier L., Seydoux J., Wollheim C. B., Kanazawa Y., Orci L., Renold A. E., Porte D., Jr Glucagon release induced by pancreatic nerve stimulation in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1246–1259. doi: 10.1172/JCI107292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E. Neural inhibition of insulin secretion from the isolated canine pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jul;229(1):144–149. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.1.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


