Abstract
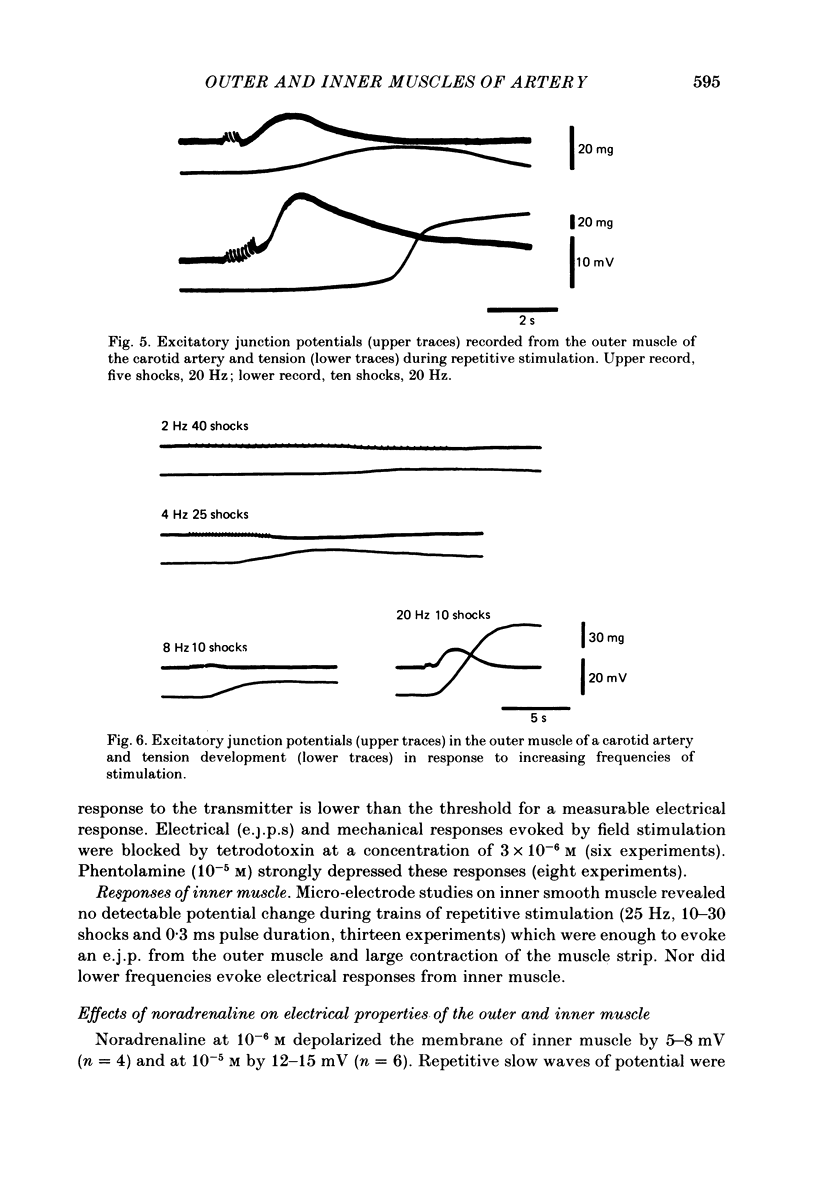
Electrical responses of outer and inner muscle of the rabbit carotid artery to electrical stimulation and noradrenaline were investigated. Mean values of the resting potential and space constant in the direction of the long axis of the cells were -47.3 mV and 1.61 mm for the inner muscle and -45.9 mV and 0.92 mm for the outer muscle. Both muscles showed strong outward-going rectification with no evoked action potential on continuous injection of depolarizing current. Such current spread not only in the direction of the long axis of the smooth muscle cells but also to a lesser degree transverse to this axis (space constant approximately 0.55 mm). There was little or no spread of current from the outer muscle layer to the inner muscle layer. At high frequencies of nerve stimulation (higher than 20 Hz), slow depolarizations representing very slow excitatory junction potentials (e.j.p.s) were recorded from the outer (innervated) muscle. However, e.j.p.s were not evoked from the inner (non-innervated) muscle at any rate of field stimulation. At low frequencies of stimulation (less than 5 Hz) no e.j.p. was observed in either the inner or outer muscle, although the muscle contracted. Noradrenaline (10(-6) M) depolarized inner but not outer muscle. High concentrations of noradrenaline (10(-5) M to 2 X 10(-4) M) caused large depolarization of the inner muscle, and also smaller depolarization of the outer muscle.
Full text
PDF
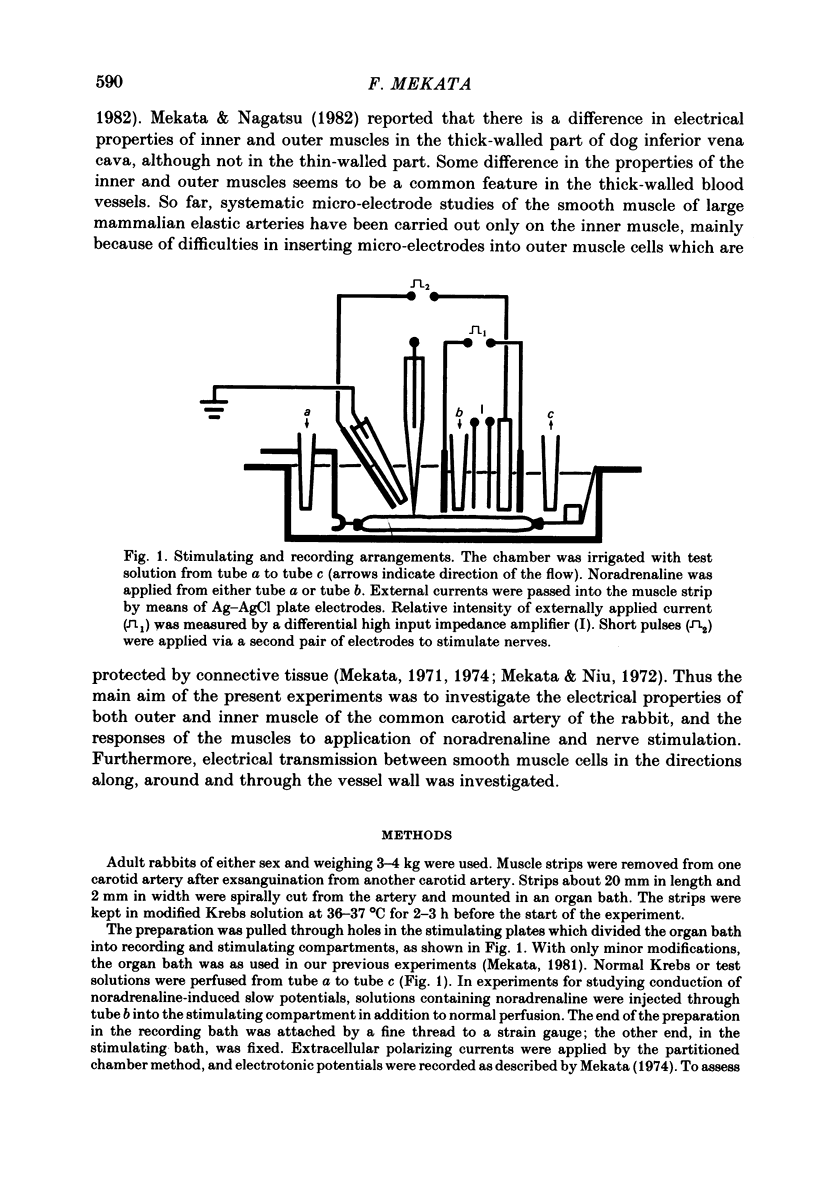
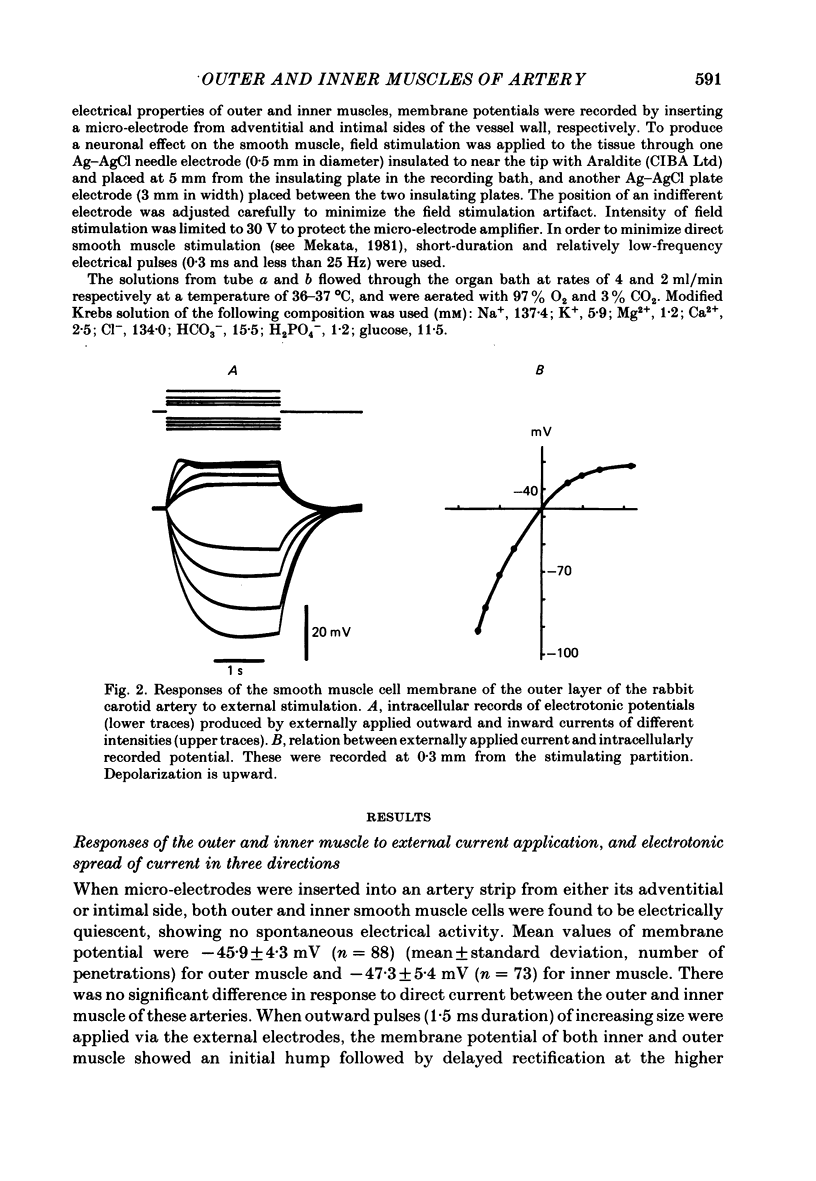
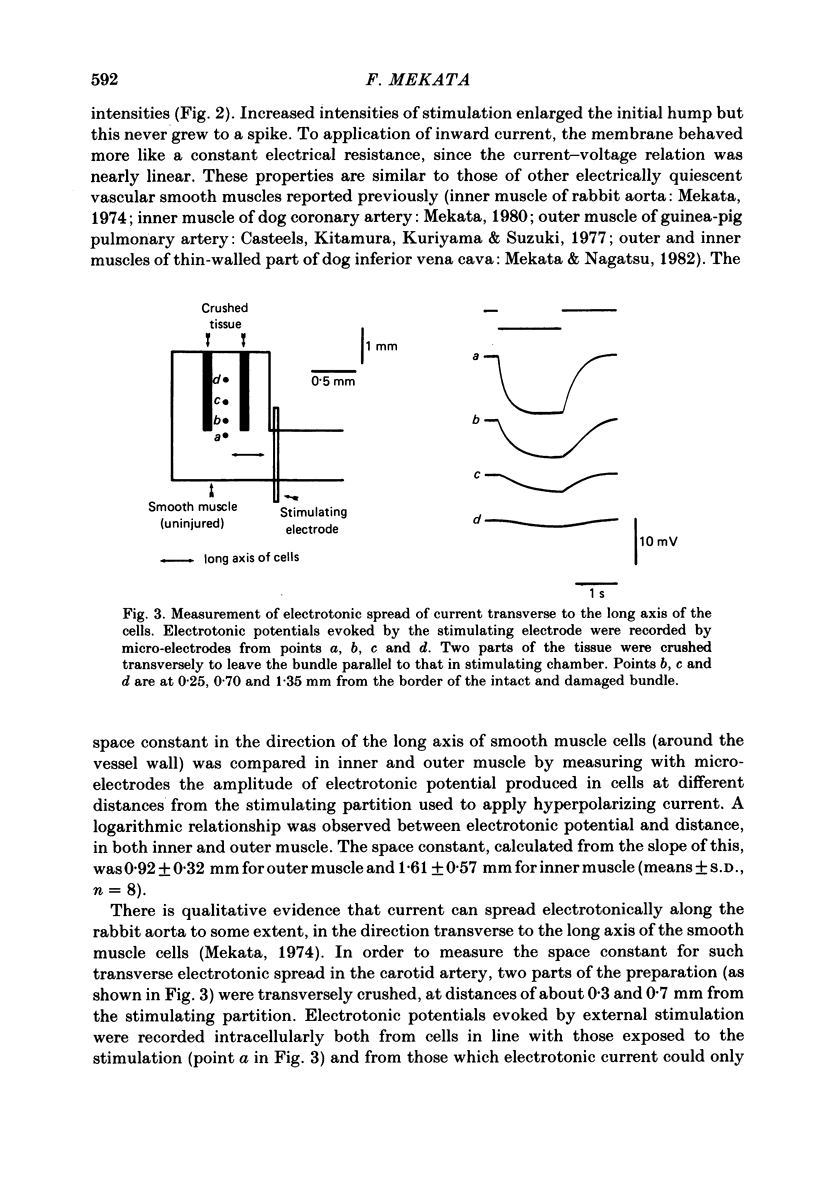
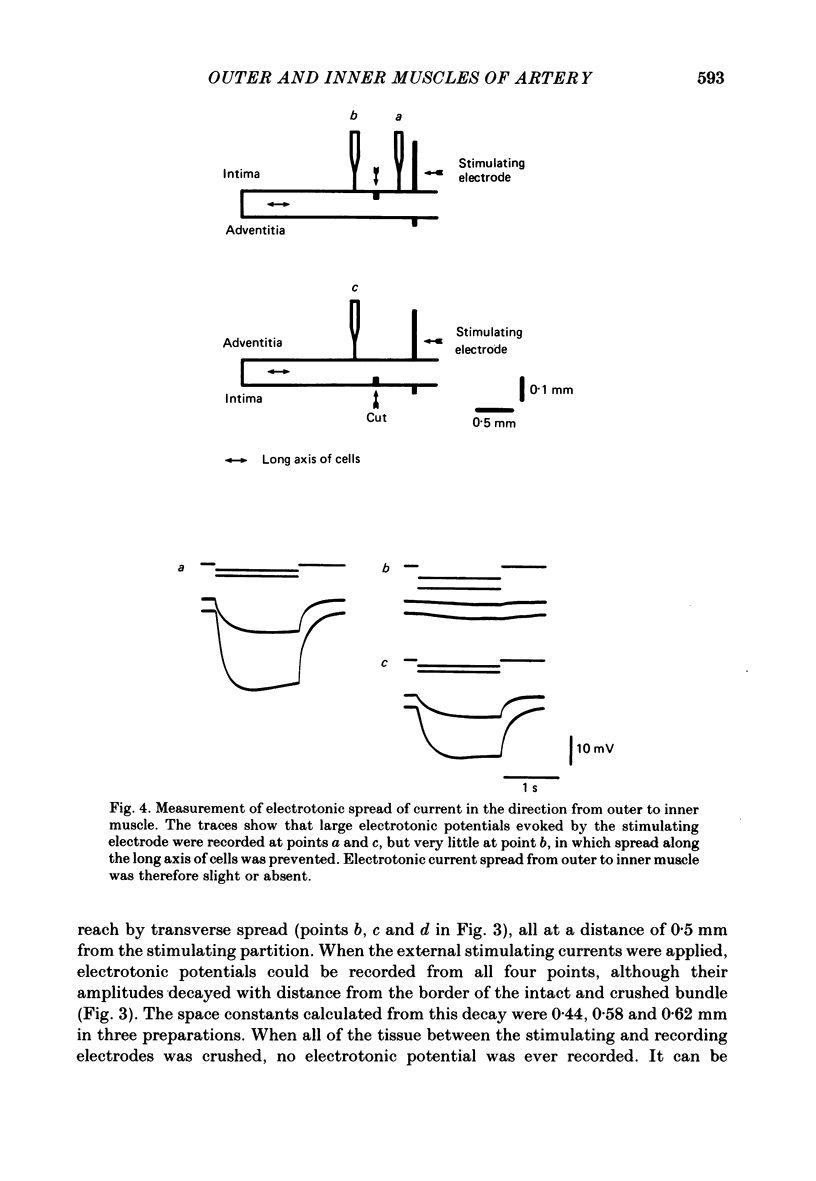




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell C. Transmission from vasoconstrictor and vasodilator nerves to single smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig uterine artery. J Physiol. 1969 Dec;205(3):695–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C., Vogt M. Release of endogenous noradrenaline from an isolated muscular artery. Release of endogenous noradrenaline from an isolated muscular artery. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):509–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan J. A., Osher J. V. Distribution of norepinephrine released from adrenergic motor terminals in arterial wall. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970;13(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biamino G., Kruckenberg P. Synchronization and conduction of excitation in the rat aorta. Am J Physiol. 1969 Aug;217(2):376–382. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Excitation-contraction coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):63–79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung D. W. Spontaneous and evoked excitatory junction potentials in rat tail arteries. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:449–459. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland C. J., Keatinge W. R. Constrictor actions of acetylcholine, 5-hydroxytryptamine and histamine on bovine coronary artery inner and outer muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:363–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. M., Keatinge W. R. Differences in sensitivity to vasoconstrictor drugs within the wall of the sheep carotid artery. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):477–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Localization of specialized noradrenaline receptors at neuromuscular junctions on arterioles of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1981;313:343–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Some properties of spontaneous excitatory junction potentials recorded from arterioles of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:43–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D. Neuromuscular transmission in arterioles of guinea-pig submucosa. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):263–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Surprenant A. M. Some properties of the excitatory junction potentials recorded from saphenous arteries of rabbits. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:337–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keatinge W. R. Electrical and mechanical response of arteries to stimulation of sympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1966 Aug;185(3):701–715. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keatinge W. R., Torrie C. Action of sympathetic nerves of inner and outer muscle of sheep carotid artery, and effect of pressure on nerve distribution. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;257(3):699–712. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Current spread in the smooth muscle of the rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(1):143–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Electrical current-induced contraction in the smooth muscle of the rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:149–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Electrophysiological properties of the smooth muscle cell membrane of the dog coronary artery. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:205–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Electrophysiological studies of the smooth muscle cell membrane of the rabbit common carotid artery. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jun;57(6):738–751. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.6.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F., Nagatsu I. Electrophysiology and innervation of the smooth muscle of dog inferior vena cava. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:201–211. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F., Niu H. Biophysical effects of adrenaline on the smooth muscle of the rabbit common carotid artery. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jan;59(1):92–102. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Rectification in the smooth muscle cell membrane of rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(2):269–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees P. M. The distribution of biogenic amines in the carotid bifurcation region. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):245–253. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SU C., BEVAN J. A., URSILLO R. C. ELECTRICAL QUIESCENCE OF PULMONARY ARTERY SMOOTH MUSCLE DURING SYMPATHOMIMETIC STIMULATION. Circ Res. 1964 Jul;15:26–27. doi: 10.1161/01.res.15.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. A comparative study of neuromuscular transmission in several mammalian muscular arteries. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Jul;386(1):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00584192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoutte P. M., Verbeuren T. J., Webb R. C. Local modulation of adrenergic neuroeffector interaction in the blood vessel well. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jan;61(1):151–247. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


