Correction to: Respiratory Research (2024) 25:215
10.1186/s12931-024-02844-9
In the original publication of this article [1], there was an error in Fig. 5. The western blots lines reporting the EGFR and p-Her2 bands for H1299 cell lines were duplicated. The EGFR bands was mistakenly repeated in p-Her2 bands. For completeness and transparency, the old incorrect and correct Fig. 5 are displayed in this correction article.
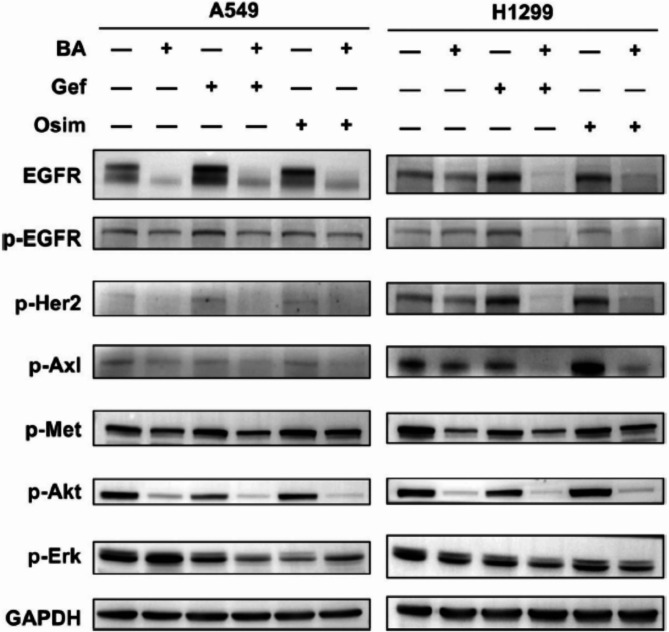
Incorrect Fig. 5:
Fig. 5.
Combination treatment enhanced the suppression of EGFR and its downstream signaling and bypass pathways in wt-EGFR NSCLC cells. A549 and H1299 cells were treated with DMSO, BA, gefitinib, osimertinib or the indicated combination and then harvested for preparation of whole-cell protein lysates and subsequent western blotting to detect the indicated proteins
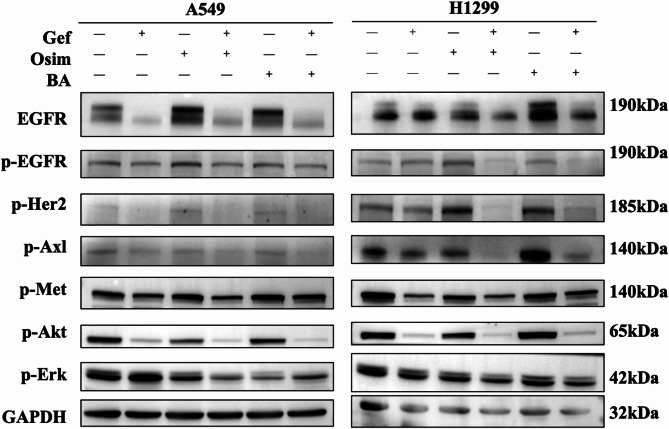
Correct Fig. 5:
Fig. 5.
Combination treatment enhanced the suppression of EGFR and its downstream signaling and bypass pathways in wt-EGFR NSCLC cells. A549 and H1299 cells were treated with DMSO, BA, gefitinib, osimertinib or the indicated combination and then harvested for preparation of whole-cell protein lysates and subsequent western blotting to detect the indicated proteins
Footnotes
The original article can be found online at 10.1186/s12931-024-02844-9.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Han Wang and Xiaohui Du contributed equally to this study.
Contributor Information
Guiru Li, Email: Liguiru_dlmu@126.com.
Qi Wang, Email: wqdlmu@163.com.
References
- 1.Wang H, Du X, Liu W, et al. Combination of betulinic acid and EGFR-TKIs exerts synergistic anti-tumor effects against wild-type EGFR NSCLC by inducing autophagy-related cell death via EGFR signaling pathway. Respir Res. 2024;25:215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]