Full text
PDF

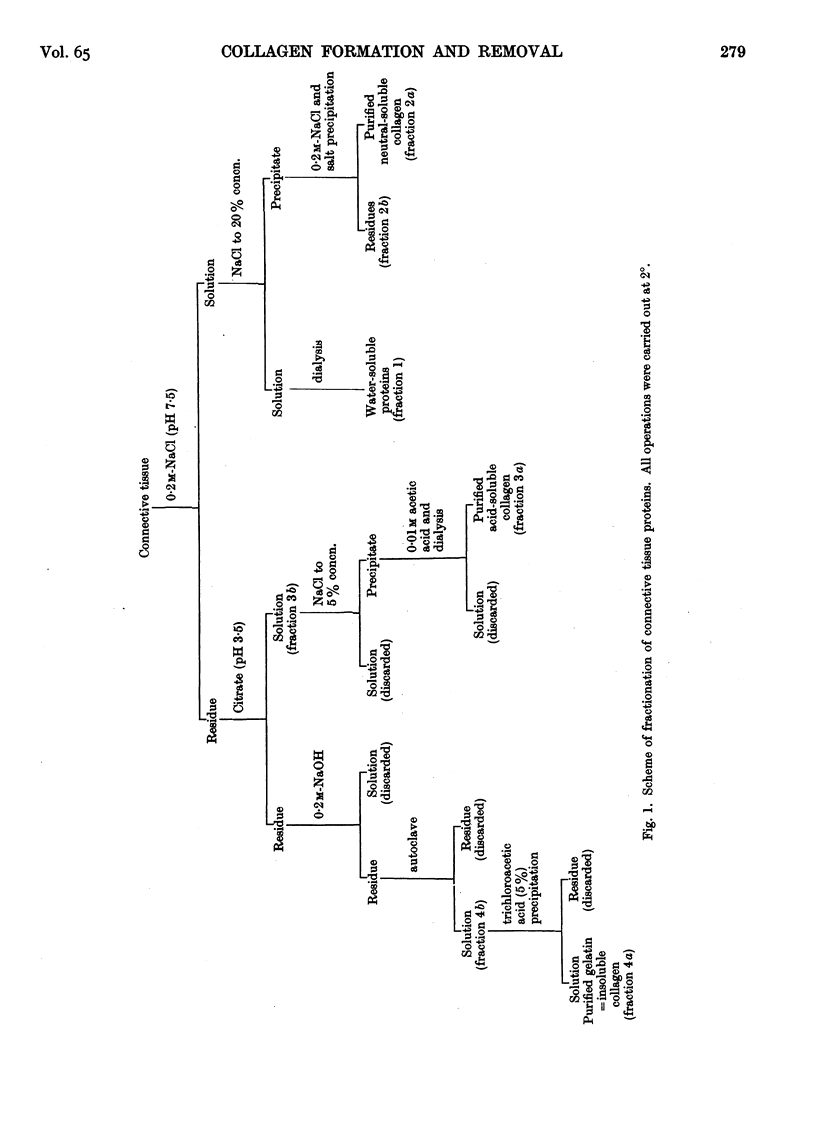
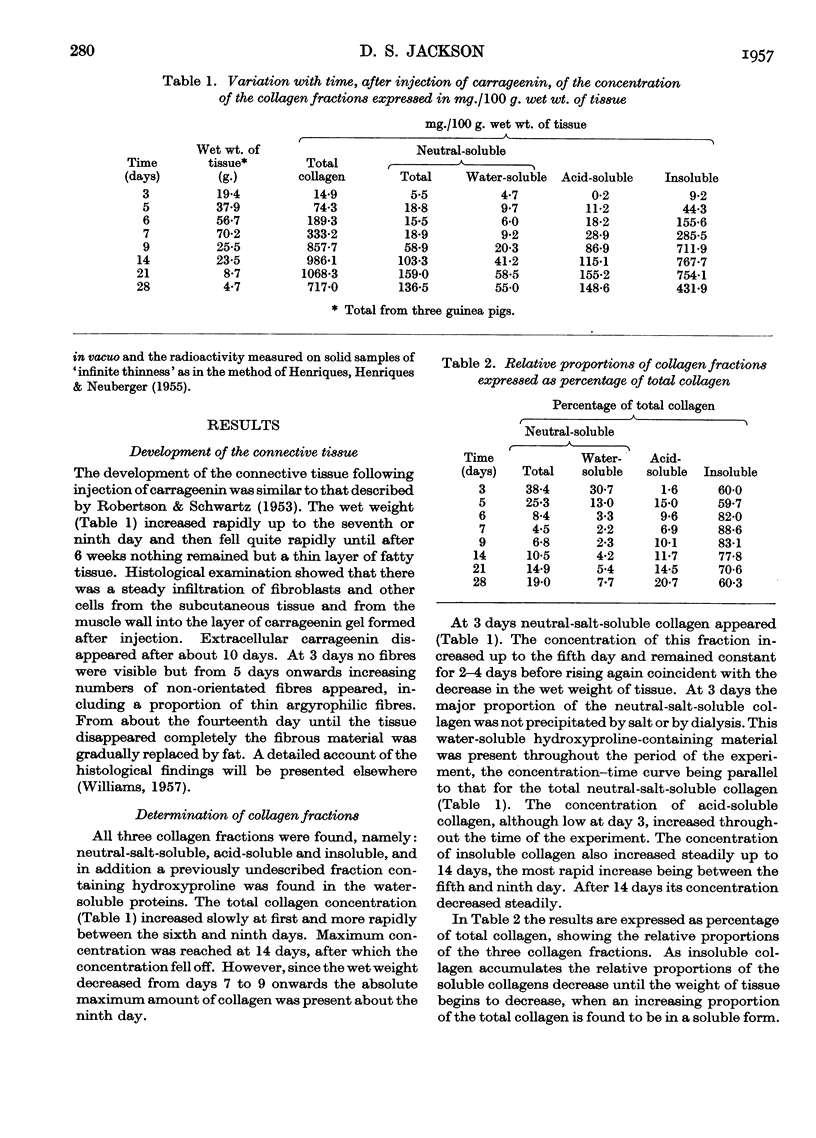

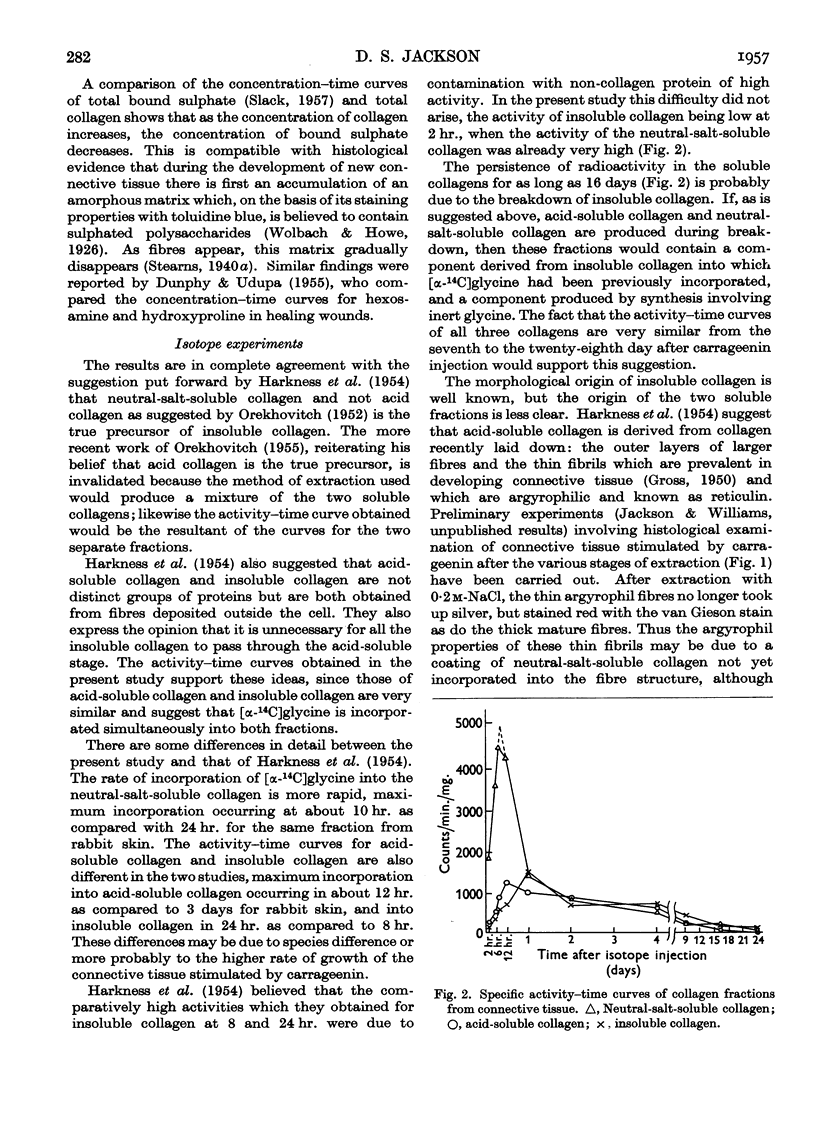


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANFIELD W. G. Width and length of collagen fibrils during the development of human skin, in granulation tissue and in the skin of adult animals. J Gerontol. 1955 Jan;10(1):13–17. doi: 10.1093/geronj/10.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWES J. H., ELLIOTT R. G., MOSS J. A. The composition of collagen and acid-soluble collagen of bovine skin. Biochem J. 1955 Sep;61(1):143–150. doi: 10.1042/bj0610143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNPHY J. E., UDUPA K. N. Chemical and histochemical sequences in the normal healing of wounds. N Engl J Med. 1955 Nov 17;253(20):847–851. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195511172532002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARKNESS R. D., MARKO A. M., MUIR H. M., NEUBERGER A. The metabolism of collagen and other proteins of the skin of rabbits. Biochem J. 1954 Apr;56(4):558–569. doi: 10.1042/bj0560558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIQUES O. B., HENRIQUES S. B., NEUBERGER A. Quantitative aspects of glycine metabolism in the rabbit. Biochem J. 1955 Jul;60(3):409–424. doi: 10.1042/bj0600409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGHBERGER J. H., GROSS J., SCHMITT F. O. The interaction of mucoprotein with soluble collagen; an electron microscope study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 May;37(5):286–291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.5.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON D. S., FESSLER J. H. Isolation and properties of a collagen soluble in salt solution at neutral pH. Nature. 1955 Jul 9;176(4471):69–70. doi: 10.1038/176069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON S. F. Fibrogenesis in connective tissues. Nature. 1954 May 15;173(4411):950–951. doi: 10.1038/173950a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON S. F. The formation of connective and skeletal tissues. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 Sep 27;142(909):536–548. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KODICEK E., LOEWI G. The uptake of (35S) sulphate by mucopolysaccharides of granulation tissue. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1955 Aug 16;144(914):100–115. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1955.0037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROL S. The quantitative estimation of glycine in small samples of proteins. Biochem J. 1952 Oct;52(2):227–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUBERGER A., PERRONE J. C., SLACK H. G. B. The relative metabolic inertia of tendon collagen in the rat. Biochem J. 1951 Jul;49(2):199–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUMAN R. E., LOGAN M. A. The determination of hydroxyproline. J Biol Chem. 1950 May;184(1):299–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRONE J. C. Separation of amino-acids as dinitrophenyl derivatives. Nature. 1951 Mar 31;167(4248):513–515. doi: 10.1038/167513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS W. C., WATSON R. F., PAPPAS G. D., PORTER K. R. Some effects of anti-collagen serum on collagen formation in tissue culture: a preliminary report. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jul 25;1(4):381–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.4.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THE BIOCHEMICAL JOURNAL: fiftieth anniversary. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROBERTSON W. B., SCHWARTZ B. Ascorbic acid and the formation of collagen. J Biol Chem. 1953 Apr;201(2):689–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDRUM G. M., KENT P. W., EASTOE J. E. The constitution of human renal reticulin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Feb;36(1):49–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


