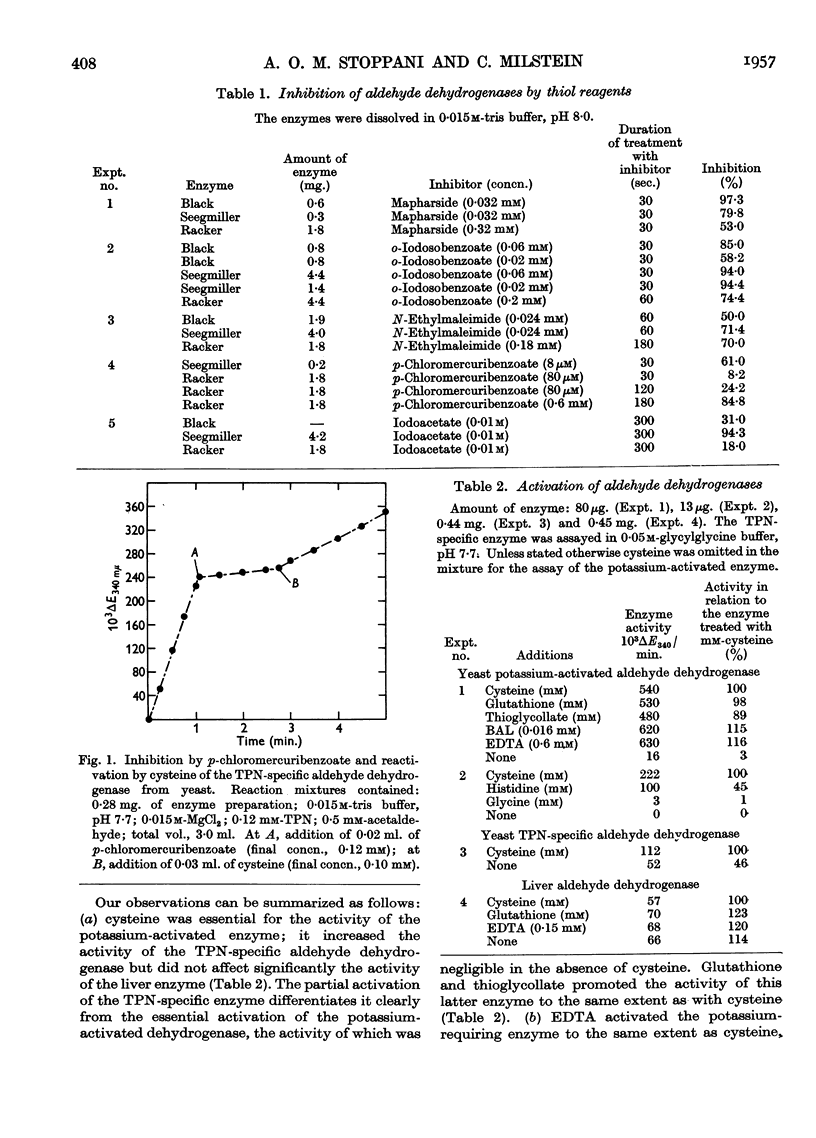
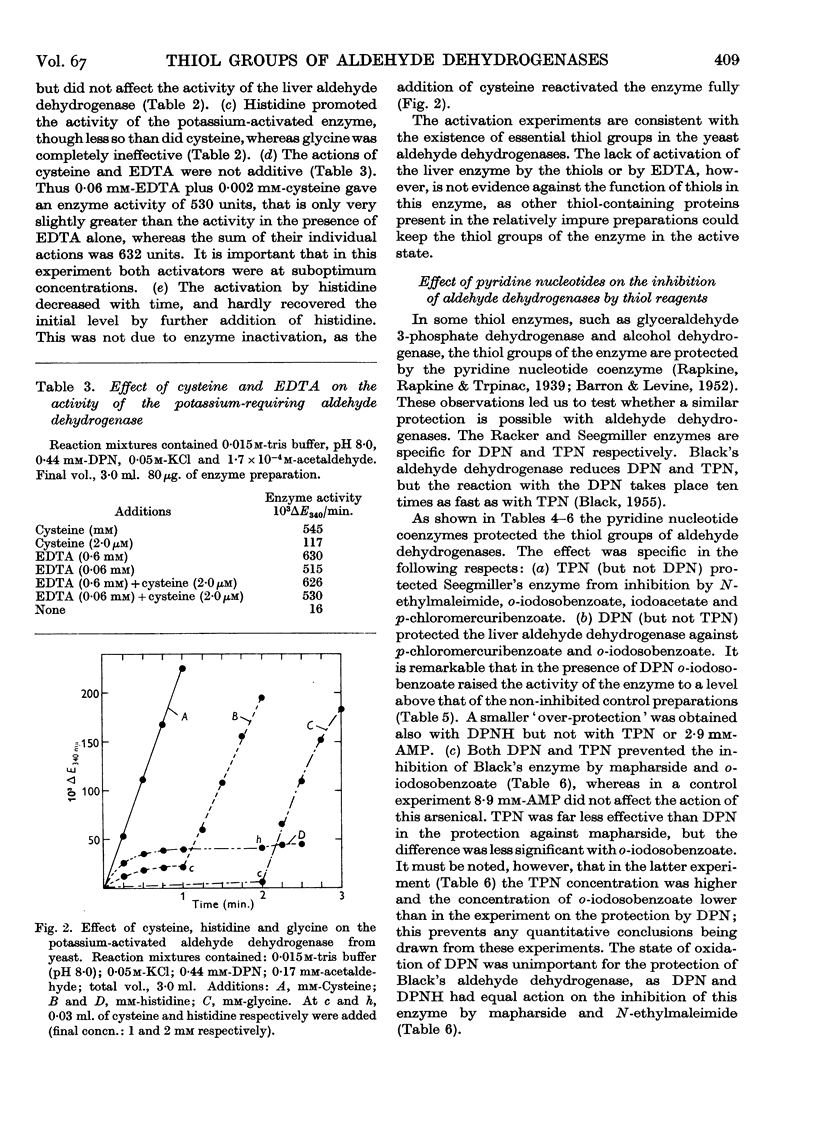
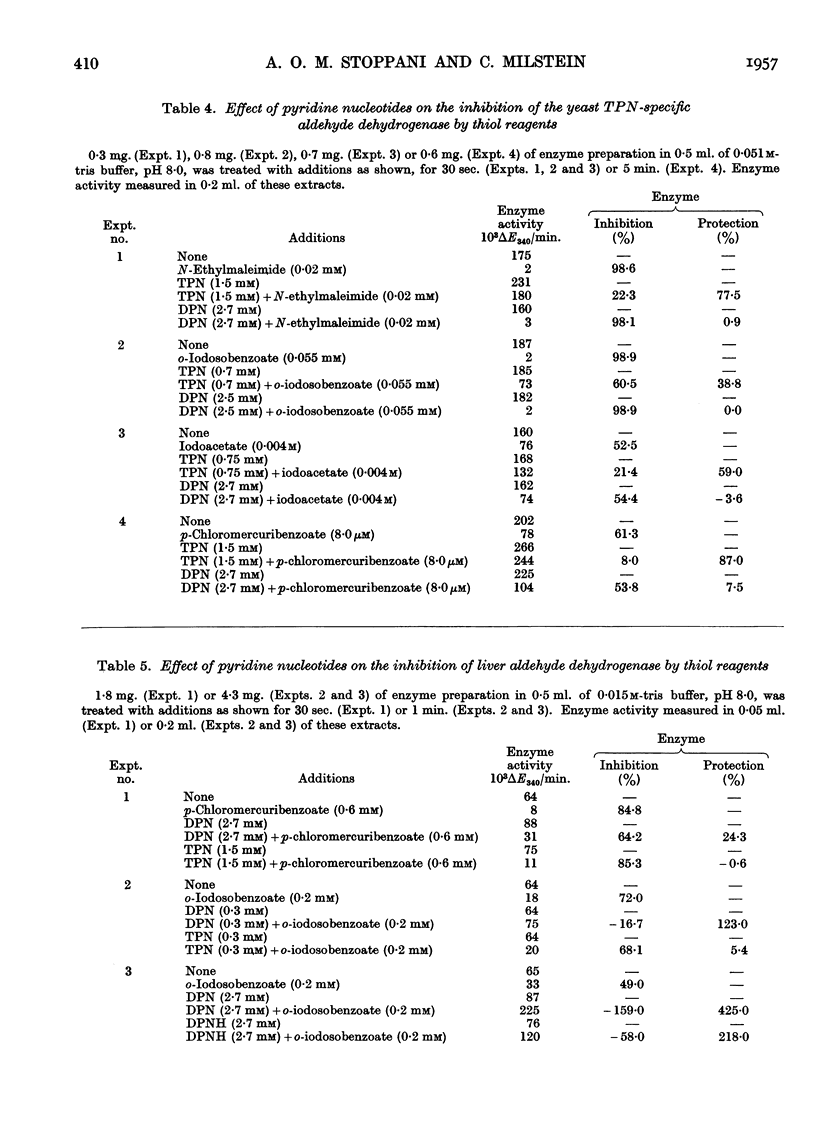
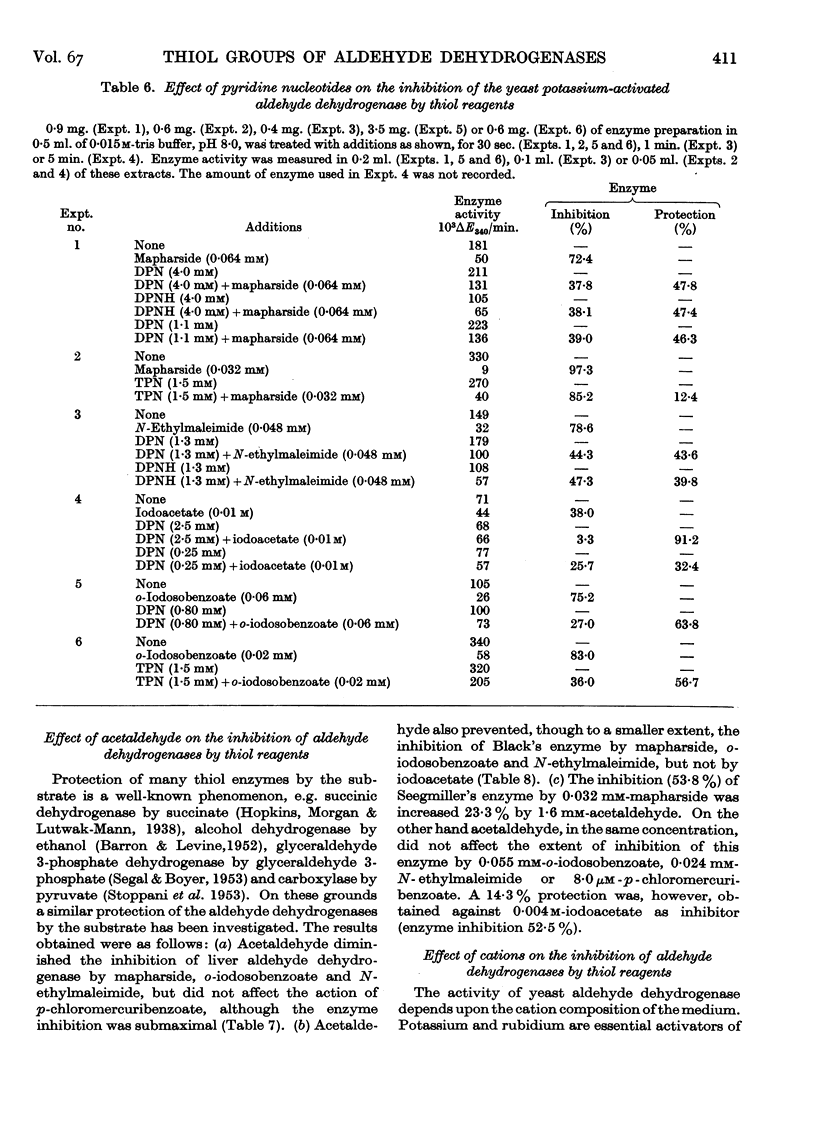
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A. Quantitative studies of the avidity of naturally occurring substances for trace metals. II. Amino-acids having three ionizing groups. Biochem J. 1952 Mar;50(5):690–697. doi: 10.1042/bj0500690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRON E. S. G., LEVINE S. Oxidation of alcohols by yeast alcohol dehydrogenase and by the living cell; the thiol groups of the enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Nov;41(1):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90518-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONNER W. D. Activation of the succinic dehydrogenase-cytochrome system. Biochem J. 1954 Feb;56(2):274–285. doi: 10.1042/bj0560274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURD F. R., WILCOX P. E. Complex formation between metallic cations and proteins, peptides and amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1956;11:311–427. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60424-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins F. G., Morgan E. J., Lutwak-Mann C. The influence of thiol groups in the activity of dehydrogenases. II: With an addendum on the location of dehydrogenases in muscle. Biochem J. 1938 Oct;32(10):1829–1848. doi: 10.1042/bj0321829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KACHMAR J. F., BOYER P. D. Kinetic analysis of enzyme reactions. II. The potassium activation and calcium inhibition of pyruvic phosphoferase. J Biol Chem. 1953 Feb;200(2):669–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN N. O., CIOTTI M. M. Direct evidence for a diphosphopyridine nucleotide-hydroxylamine complex with horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Nov;211(1):431–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEPPE O. J., BOYER P. D., STULBERG M. P. On the occurrence, equilibria, and site of acyl-enzyme formation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):569–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEEGMILLER J. E. Triphosphopyridine nucleotide-linked aldehyde dehydrogenase from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1953 Apr;201(2):629–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGAL H. L., BOYER P. D. The role of sulfhydryl groups in the activity of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):265–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R., NOVELLI G. D., LIPMANN F. Coenzyme A function in and acetyl transfer by the phosphotransacetylase system. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jul;191(1):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOPPANI A. O., ACTIS A. S., DEFERRARI J. O., GONZALEZ E. L. The role of sulphydryl groups of yeast carboxylase. Biochem J. 1953 Jun;54(3):378–390. doi: 10.1042/bj0540378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOPPANI A. O., MILSTEIN C. Specific protection of the thiol groups of aldehyde dehydrogenases by pyridine-nucleotide coenzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):655–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERAYAMA H., VESTLING C. S. Sodium sulfide inhibition of liver lactic dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Jun;20(3):586–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90371-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN EYS J., KAPLAN N. O. Yeasl alcohol dehydrogenase. I. The effect of pyridine derivatives on the reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Mar;23(3):574–581. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


