Associated with the fitness movement in the USA is an increased number of participants in water sports. Swimmers wear goggles to allow better vision underwater and to protect their eyes from irritation from chlorine or salt. Goggles come in many sizes and shapes; usually a swimmer finds a particular brand and model most effective and comfortable.
I recently saw a patient who complained of “painful hair.” He had been swimming for 6 years and had recently developed pain and tenderness on the right side of his scalp. Palpating along the tender areas, I outlined the distribution of the right supraorbital nerve. Just prior to the development of the scalp pain, he had developed a leak in his goggles that allowed water to enter the orbital area, causing eye irritation. As he had done before, he tightened the goggle strap to stop the leak. He continued with the swim workout and subsequent workouts 3 to 4 times per week. After approximately 1 week, the scalp pain began.
A Medline search on this topic found 2 letters to the editor in the New England Journal of Medicine in 1983. The first related the experience of a neurologist who developed bitemporal headaches after 1 to 2 hours of swimming. The father of the neurologist, who was a sporting goods retailer, noted that some of his customers complained of headaches associated with the use of ill-fitting swim goggles. The headaches stopped after use of the swim goggles was discontinued and returned when the goggles were worn again. By using goggles that were made of a softer rubber compound and had a looser-fitting strap around the head, the neurologist was able to continue swimming without headaches (1).
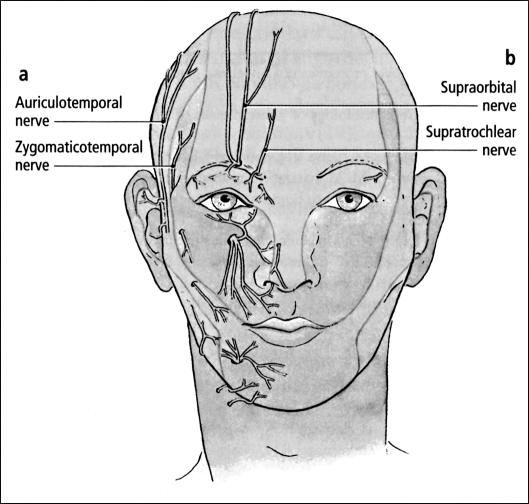
The second letter to the editor, in response to the first, was from another neurologist who developed neuralgia in the distribution of the supraorbital nerve. The headaches and supraorbital-notch pain resolved 3 weeks after he abstained from wearing goggles (2). This neuralgia is similar to that experienced by my patient after he tightened the strap on his goggles. Swimmers with a supraorbital notch (< 100% bony encasement of the nerve) rather than a supraorbital foramen have a greater risk of developing this problem due to the exposed portion of the nerve (3). The affected nerves in these cases of swimmer's headache are illustrated in the Figure.
Figure.
Nerves affected in the 3 described cases of swimmer's headache, (a) Nerves affected in letter 1. (b) Nerves affected in letter 2 and in the author's recent patient. LifeArt image copyright Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. All rights reserved.
Prevention is the best treatment; however, if this condition does occur, the following may help: careful placement of the goggles, use of a different type of goggle with softer rubber and/ or a smaller area of seal around the eyes, and placement of the goggles in different locations to prevent repeated pressure trauma.
A trial block with local anesthesia can confirm the diagnosis so that proper remedial steps can be taken.
Other conditions associated with swimming goggles are eyelid neuromas due to the edge of the goggles (4, 5) and periorbital leukoderma due to contact with the chemical compounds used in goggle manufacture (6). When goggles are worn too tightly, “purpura gogglorum,” or periorbital purpura, can occur (7). Goggles can cause injury to the globe, including rupture (8), and this was the reason the use of goggles was banned by the Royal Life Saving Society during the conduct of its practical examination taken in the water and in initiative tests in competition (9). An excellent review of eye injuries in young athletes has been published in Pediatric Annals (10).
Those of us who see patients with head and neck problems need to be aware of supraorbital neuralgia and include this entity in our differential diagnosis. Various types of headache and pain occur in the craniofacial area. Swimmer's migraine is a sudden, severe headache occurring during swimming (11); it is a form of exertional headache that has an explosive onset with exercise, including sexual activity (12). Frontal sinus infection (13), trigeminal neuralgia (14), cluster headaches, migraines, and other pain syndromes (short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks with conjunctival injection and tearing, or SUNCT [15]) occur. Perineural involvement of the periorbital sensory nerves by skin cancer also is a consideration in patients who have a skin cancer or a history of cutaneous malignancy (16).
Correct diagnosis of supraorbital neuralgia is critical in choosing therapy. A change in the type of goggles may be all that is necessary. For persistent or recurrent pain, acupuncture (17), injection of phenol/glycerol (18) or botulism toxin (19), neurolysis (20), and root section (21) of the trigeminal nerve are methods that have been successfully employed to treat this condition.
References
- 1.Pestronk A, Pestronk S. Goggle migraine. N Engl J Med. 1983;308:226–227. doi: 10.1056/nejm198301273080422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jacobson RI. More “goggle headache”: supraorbital neuralgia. N Engl J Med. 1983;308:1363. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306023082219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Knize DM. A study of the supraorbital nerve. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995;96:564–569. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199509000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wirta DL, Dailey RA, Wobig JL. Eyelid neuroma associated with swim goggle use. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998;116:1537–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jordan DR, Gilberg S, Khouri L. Eyelid masses associated with competitive swimming goggles. Can J Ophthalmol. 2001;36:339–340. doi: 10.1016/s0008-4182(01)80121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goette DK. Raccoon-like periorbital leukoderma from contact with swim goggles. Contact Dermatitis. 1984;10:129–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.1984.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jowett NI, Jowett SG. Ocular purpura in a swimmer. Postgrad Med J. 1997;73:819–820. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.73.866.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jonasson F. Swimming goggles causing severe eye injuries. Br Med J. 1977;1(6065):881. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6065.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Green MF, Cuthbert MF, Stebbing SJ. Swimming goggles and eye injuries. Br Med J. 1977;1(6073):1410–1411. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6073.1410-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Harrison A, Telander DG. Eye injuries in the young athlete: a case-based approach. Pediatr Ann. 2002;31:33–40. doi: 10.3928/0090-4481-20020101-09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Indo T, Takahashi A. Swimmer's migraine. Headache. 1990;30:485–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1990.hed3008485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Green MW. A spectrum of exertional headaches. Med Clin North Am. 2001;85:1085–1092. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(05)70361-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Talmi YP, Finkelstein Y, Wolf M, Ben-Shoshan Y, Kronenberg J. Coincidental supraorbital neuralgia and sinusitis. Am J Rhinol. 1999;13:463–468. doi: 10.2500/105065899781329647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Caminero AB, Pareja JA. Supraorbital neuralgia: a clinical study. Cephalalgia. 2001;21:216–223. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.2001.00190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pareja JA, Caminero AB, Sjaastad O. SUNCT syndrome: diagnosis and treatment. CNS Drugs. 2002;16:373–383. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200216060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Moore CE, Hoyt WF, North JB. Painful ophthalmoplegia following treated squamous carcinoma of the forehead. Orbital apex involvement from centripetal spread via the supraorbital nerve. Med J Austr. 1976;1(18):657–659. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1976.tb140943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xia SZ, Wang WM, Chen ZS, Zheng JZ. Acupuncture treatment of 61 cases of supraorbital neuralgia. J Tradit Chin Med. 1987;7:116–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wilkinson HA. Trigeminal nerve peripheral branch phenol/glycerol injections for tic douloureux. J Neurosurg. 1999;90:828–832. doi: 10.3171/jns.1999.90.5.0828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Argoff CE. A focused review on the use of botulinum toxins for neuropathic pain. Clin J Pain. 2002;18(6 Suppl):S177–S181. doi: 10.1097/00002508-200211001-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Adant JP, Bluth F. Endoscopic supraorbital nerve neurolysis. Acta Chir Belg. 1999;99:182–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Matharu MS, Goadsby PJ. Persistence of attacks of cluster headache after trigeminal nerve root section. Brain. 2002;125:976–984. doi: 10.1093/brain/awf118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]