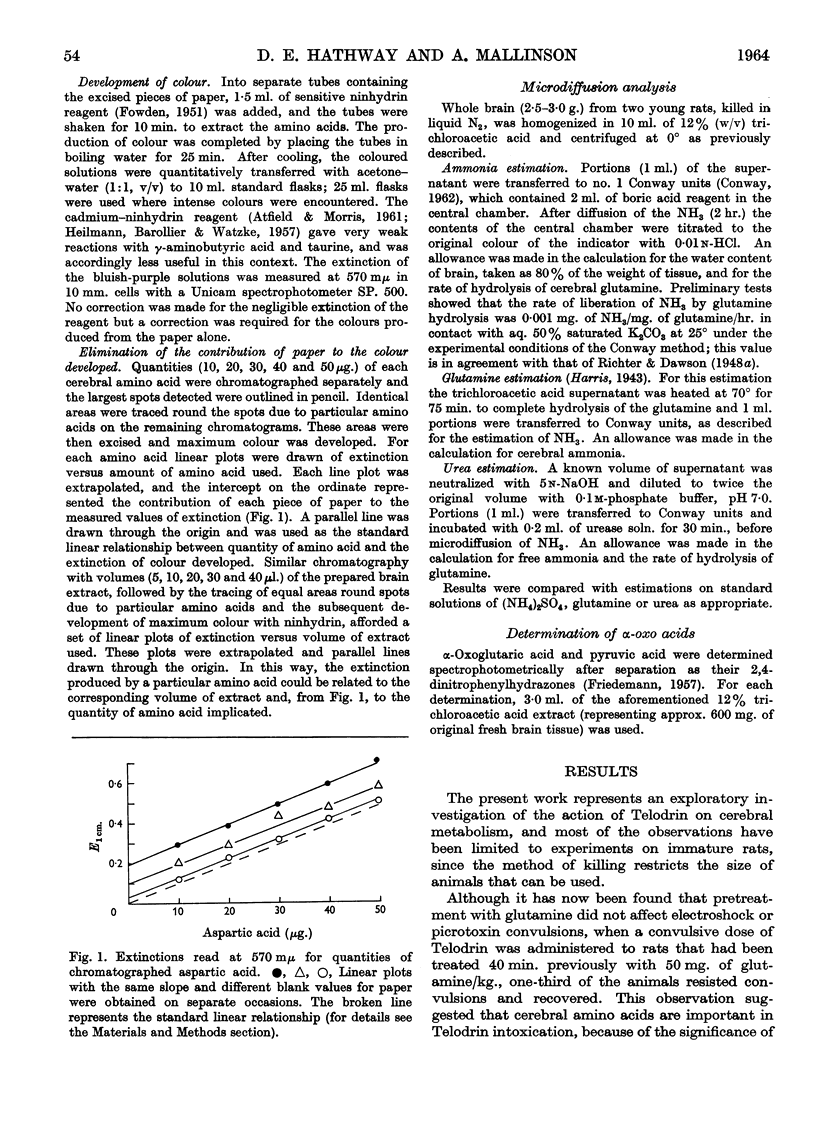
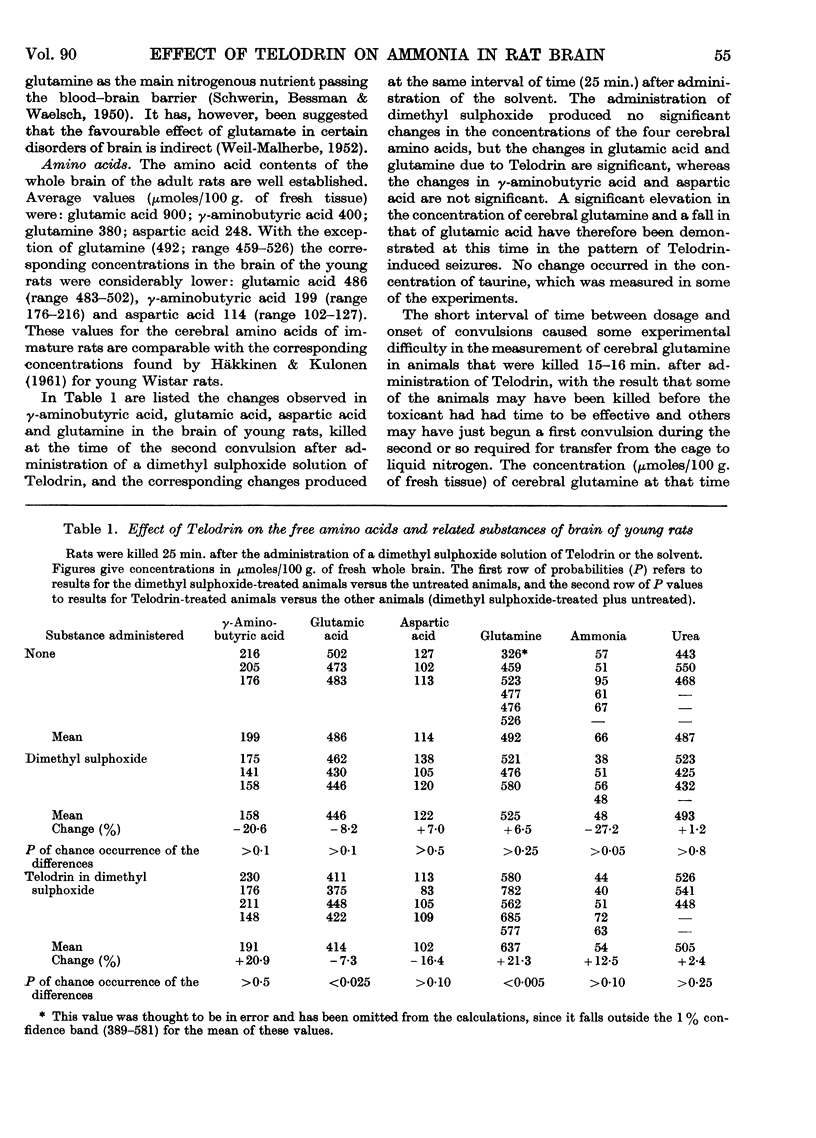
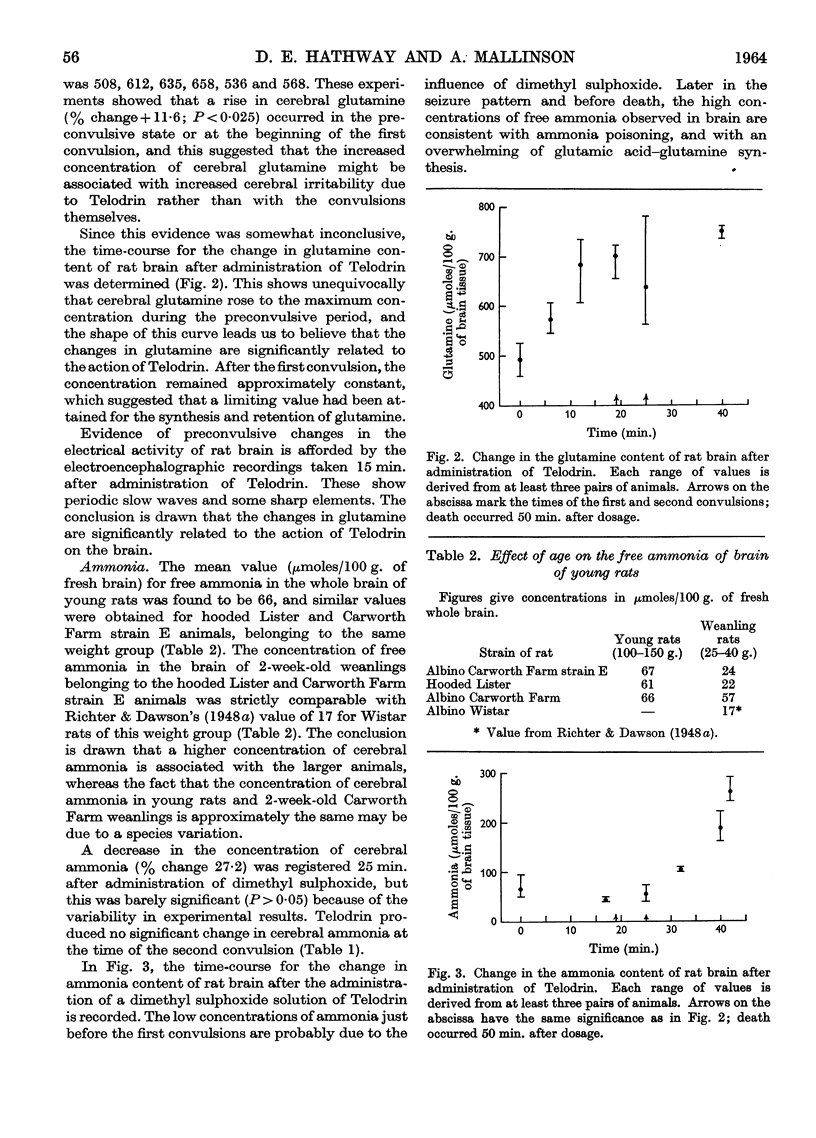
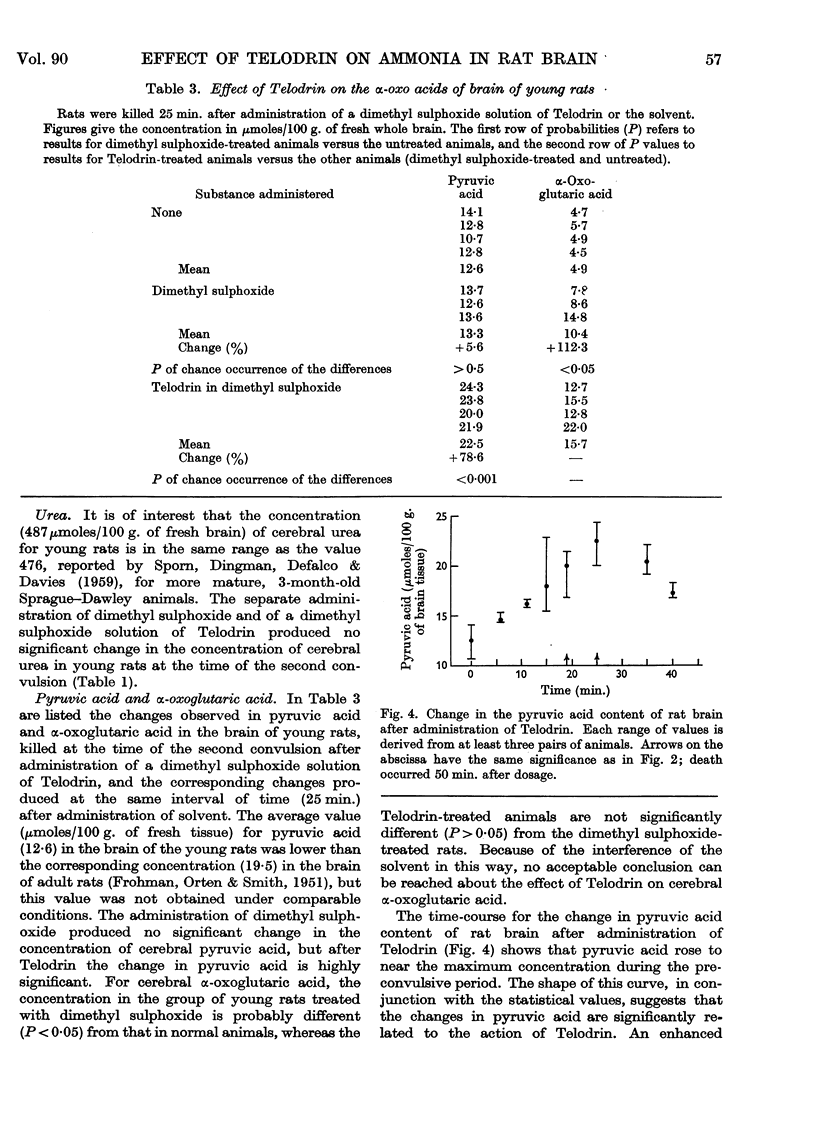
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N., EMERY R. C., STREET B. W. A tissue homogenizer. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:326–327. doi: 10.1042/bj0770326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATFIELD G. N., MORRIS C. J. Analytical separations by highvoltage paper electrophoresis. Amino acids in protein hydrolysates. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:606–614. doi: 10.1042/bj0810606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AWAPARA J., SEALE B. Distribution of transaminases in rat organs. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):497–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALZER H., HOLTZ P., PALM D. On the mechanism of the convulsivant effect of hydrazides in mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 1960 Oct;5:169–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(60)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK G. M., EISEMAN B. Studies in ammonia metabolism. IV. Biochemical changes in brain tissue of dogs during ammoniainduced coma. N Engl J Med. 1958 Jul 24;259(4):178–180. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195807242590406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consden R., Gordon A. H., Martin A. J. The identification of lower peptides in complex mixtures. Biochem J. 1947;41(4):590–596. doi: 10.1042/bj0410590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES R. K., DEFALCO A. J., SHANDER D., KOPELMAN A., KIYASU J. Urea synthesis in the living rat brain. Nature. 1961 Jul 15;191:288–288. doi: 10.1038/191288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOWDEN L. The quantitative recovery and colorimetric estimation of amino-acids separated by paper chromatography. Biochem J. 1951 Mar;48(3):327–333. doi: 10.1042/bj0480327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROHMAN C. E., ORTEN J. M., SMITH A. H. Chromatographic determination of the acids of the citric acid cycle in tissues. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):277–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIGER A. Correlation of brain metabolism and function by the use of a brain perfusion method in situ. Physiol Rev. 1958 Jan;38(1):1–20. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELL C. F., CRANMORE D., CROSBIE R. Rapid freezing of intact living mammals; a method of fixation for physiological evaluation. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Jan;8(4):388–392. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.8.4.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKKINEN H. M., KULONEN E. The effect of ethanol on the amino acids of the rat brain with a reference to the administration of glutamine. Biochem J. 1961 Mar;78:588–593. doi: 10.1042/bj0780588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., HARRIS C. K., MOSCARELLO M. A., TIGANE E. Quantitative chromatographic methods. 4. Stabilized chromatographic systems of high resolving power for amino acids. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Jan;39:163–190. doi: 10.1139/o61-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS C. K., TIGANE E., HANES C. S. Quantitative chromatographic methods. 7. Isolation of amino acids from serum and other fluids. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Feb;39:439–451. doi: 10.1139/o61-042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATHWAY D. E. Amino acids, fruit acids and polyols of myrobalans. Biochem J. 1956 Jul;63(3):380–387. doi: 10.1042/bj0630380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEALD P. J., MCILWAIN H. Techniques in tissue metabolism. 4. Apparatus for maintaining and rapidly transferring tissue sections. Biochem J. 1956 Jun;63(2):231–235. doi: 10.1042/bj0630231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMANN J., BARROLLIER J., WATZKE E. Beitrag zur Aminosäurebestimmung auf Papierchromatogrammen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;309(4-6):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. M., Roth R. T., Harris R. S. STUDIES REGARDING A GLUTAMINE-LIKE SUBSTANCE IN BLOOD AND SPINAL FLUID, INCLUDING A METHOD FOR ITS QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION. J Clin Invest. 1943 Jul;22(4):569–576. doi: 10.1172/JCI101428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNEY E. H., PFEIFFER C. C. The convulsant effect of hydrazides and the antidotal effect of anticonvulsants and metabolites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958 Jan;122(1):110–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON R. I. The isolation of L-pipecolinic acid from Trifolium repens. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):474–478. doi: 10.1042/bj0530474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNTZ J. A. The formation of ammonia in brain extracts. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):221–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORCELLATI G., THOMPSON R. H. The effect of nerve section on the free amino acids of nervous tissue. J Neurochem. 1957;1(4):340–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECKNAGEL R. O., POTTER V. R. Mechanism of the ketogenic effect of ammonium chloride. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jul;191(1):263–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHTER D., CROSSLAND J. Variation in acetylcholine content of the brain with physiological state. Am J Physiol. 1949 Nov;159(2):247–255. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1949.159.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS E., FRANKEL S. gamma-Aminobutyric acid in brain: its formation from glutamic acid. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):55–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERIN P., BESSMAN S. P., WAELSCH H. The uptake of glutamic acid and glutamine by brain and other tissues of the rat and mouse. J Biol Chem. 1950 May;184(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPORN M. B., DINGMAN W., DEFALCO A., DAVIES R. K. The synthesis of urea in the living rat brain. J Neurochem. 1959 Dec;5:62–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1959.tb13333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIGANE E., WADE E. H., WONG J. T., HANES C. S. Quantitative chromatographic methods. 6. Improved procedure for determination of amino compounds on paper chromatograms. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Feb;39:427–437. doi: 10.1139/o61-041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORDA C. Ammonium ion content and electrical activity of the brain during the preconvulsive and convulsive phases induced by various convulsants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1953 Feb;107(2):197–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOWER D. B. Glutamic acid and gamma-aminobutyric acid in seizures. Clin Chim Acta. 1957 Oct;2(5):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(57)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VRBA R., FOLBERGR J., KANTUREK V. Ammonia formation in brain cortex slices. Nature. 1957 Mar 2;179(4557):470–471. doi: 10.1038/179470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE E. H., MATHESON A. T., HANES C. S. Quantitative chromatographic methods. 3. Factors controlling the patterns of separation of the amino acids on paper chromatograms. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Jan;39:141–161. doi: 10.1139/o61-014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE M. The quantitative determination of amino acids by paper chromatography; a solvent to replace phenol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jan;23(1):186–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


