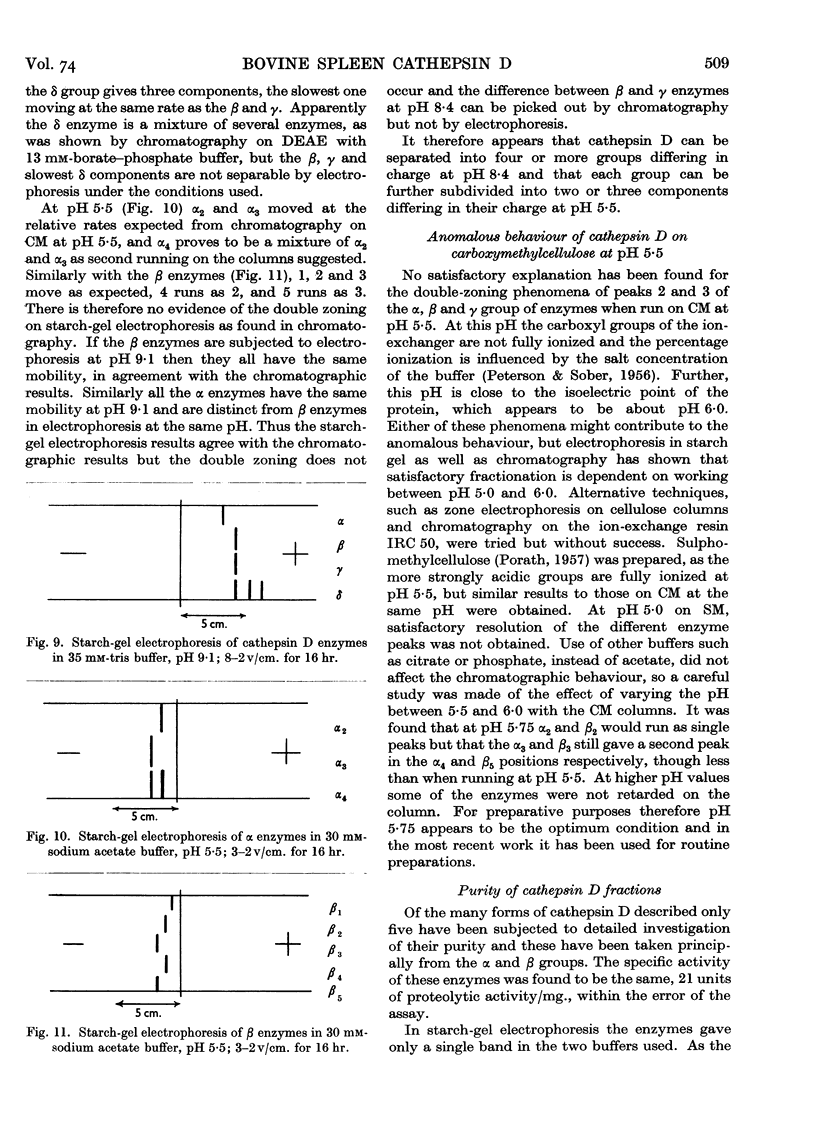
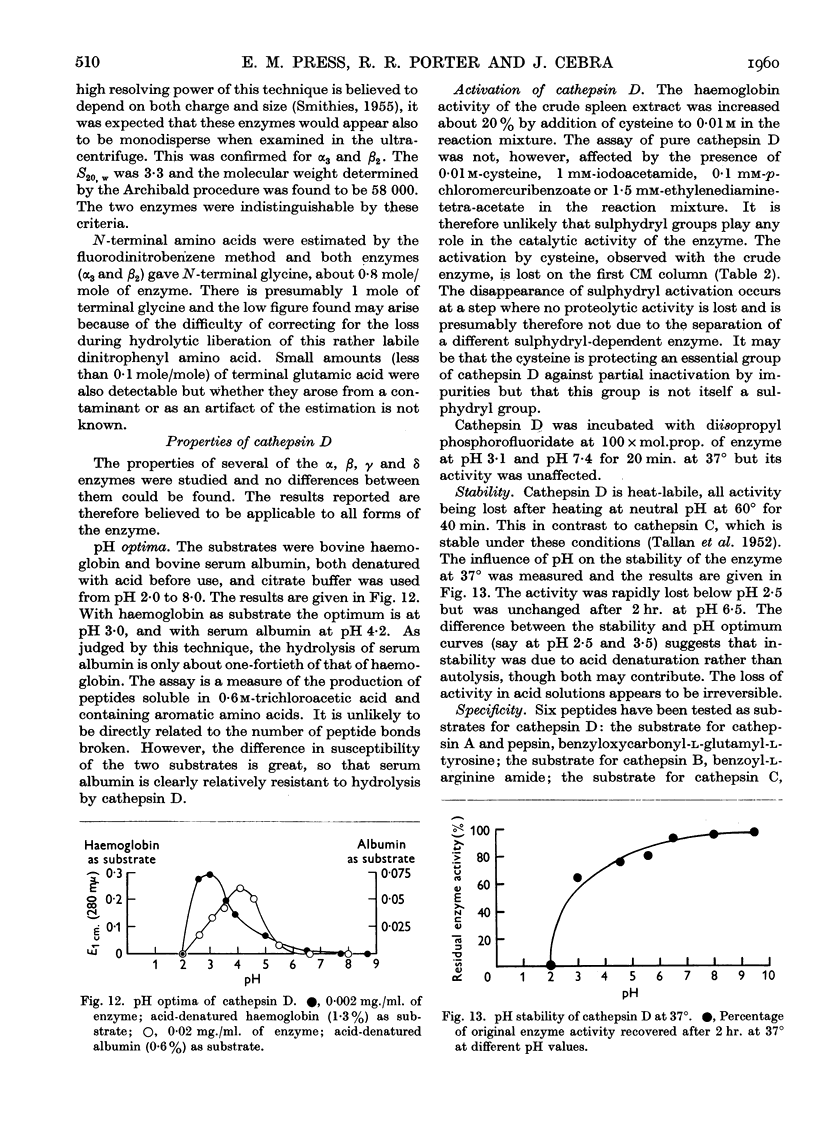
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS E., SMITH E. L. Proteolytic activity of pituitary extracts. J Biol Chem. 1951 Aug;191(2):651–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AQVIST S. E., ANFINSEN C. B. The isolation and characterization of ribonucleases from sheep pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1112–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARONSSON T., GRONWALL A. Electrophoretic separation of serum protein into twelve fractions. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1958;10(3):348–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCKING E. C., YEMM E. W. Estimation of amino acids by ninhydrin. Biochem J. 1954 Jun 19;58(330TH):xii–xii. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBAUM L. M., FRUTON J. S. Purification and properties of beef spleen cathepsin B. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. A chromatographic investigation of chymotrypsinogen alpha. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedin S. G. Investigations on the proteolytic enzymes of the spleen of the ox. J Physiol. 1903 Nov 2;30(2):155–175. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1903.sp000987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOERNER J. F., SINSHEIMER R. L. A deoxyribonuclease from calf spleen. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):1039–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON W. L., NEURATH H. Proteolytic enzymes of the formed elements of human blood. I. Erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jan;200(1):39–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L., Møller F. MULTIPLE FORMS OF ENZYMES: TISSUE, ONTOGENETIC, AND SPECIES SPECIFIC PATTERNS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 May;45(5):753–763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.5.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. J., Synge R. L. A new form of chromatogram employing two liquid phases: A theory of chromatography. 2. Application to the micro-determination of the higher monoamino-acids in proteins. Biochem J. 1941 Dec;35(12):1358–1368. doi: 10.1042/bj0351358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martland M., Robison R. Possible Significance of Hexosephosphoric Esters in Ossification: Part VI. Phosphoric Esters in Blood-Plasma. Biochem J. 1926;20(4):847–855. doi: 10.1042/bj0200847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORATH J. Methodological studies of zone-electrophoresis in vertical columns. I. Fractionation in cellulose powder columns of substances of low molecular weight exemplified by amino acids and related compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Oct;22(1):151–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90234-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. Partition chromatography of insulin and other proteins. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(2):320–328. doi: 10.1042/bj0530320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D., SMITHIES O. Comparison and combination of the starch-gel and filter-paper electrophoretic methods applied to human sera: two-dimensional electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):636–643. doi: 10.1042/bj0680636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYLE A. P., SANGER F., SMITH L. F., KITAI R. The disulphide bonds of insulin. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):541–556. doi: 10.1042/bj0600541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGER F., TUPPY H. The amino-acid sequence in the phenylalanyl chain of insulin. I. The identification of lower peptides from partial hydrolysates. Biochem J. 1951 Sep;49(4):463–481. doi: 10.1042/bj0490463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O., WALKER N. F. Genetic control of some serum proteins in normal humans. Nature. 1955 Dec 31;176(4496):1265–1266. doi: 10.1038/1761265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRICK M. G. Phagocytosis of M. tuberculosis and M. smegmatis stained with indicator dyes. Am Rev Tuberc. 1956 Oct;74(4):552–565. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1956.74.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. Fractionation of oxidized insulin. Biochem J. 1949;44(1):126–128. doi: 10.1042/bj0440126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. The free amino groups of insulin. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):507–515. doi: 10.1042/bj0390507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALLAN H. H., JONES M. E., FRUTON J. S. On the proteolytic enzymes of animal tissues. X. Beef spleen cathepsin C. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):793–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


