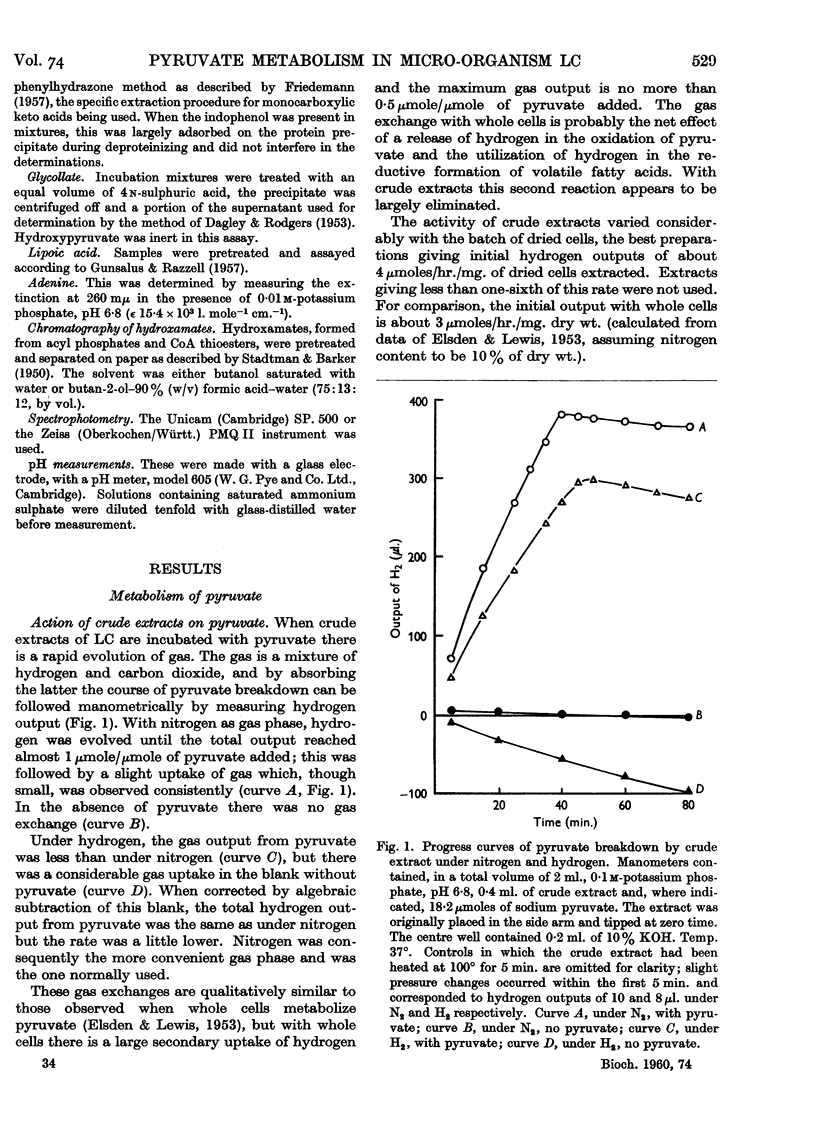
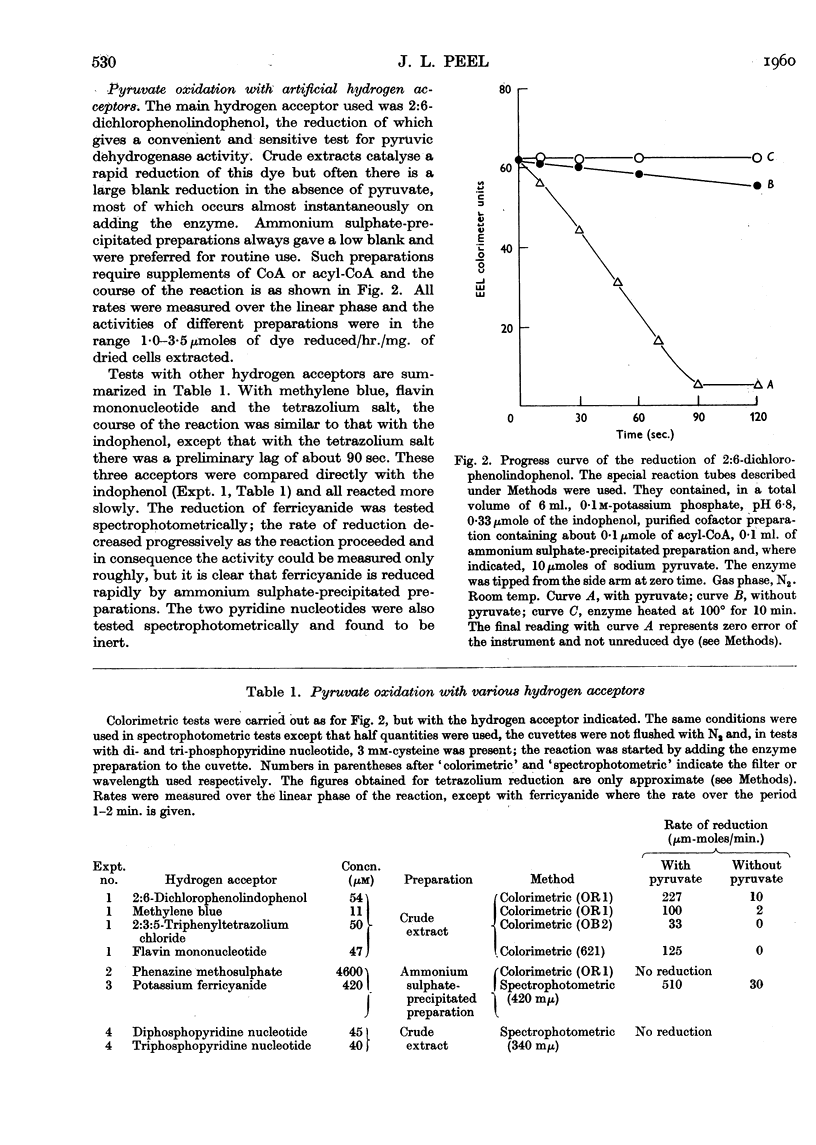
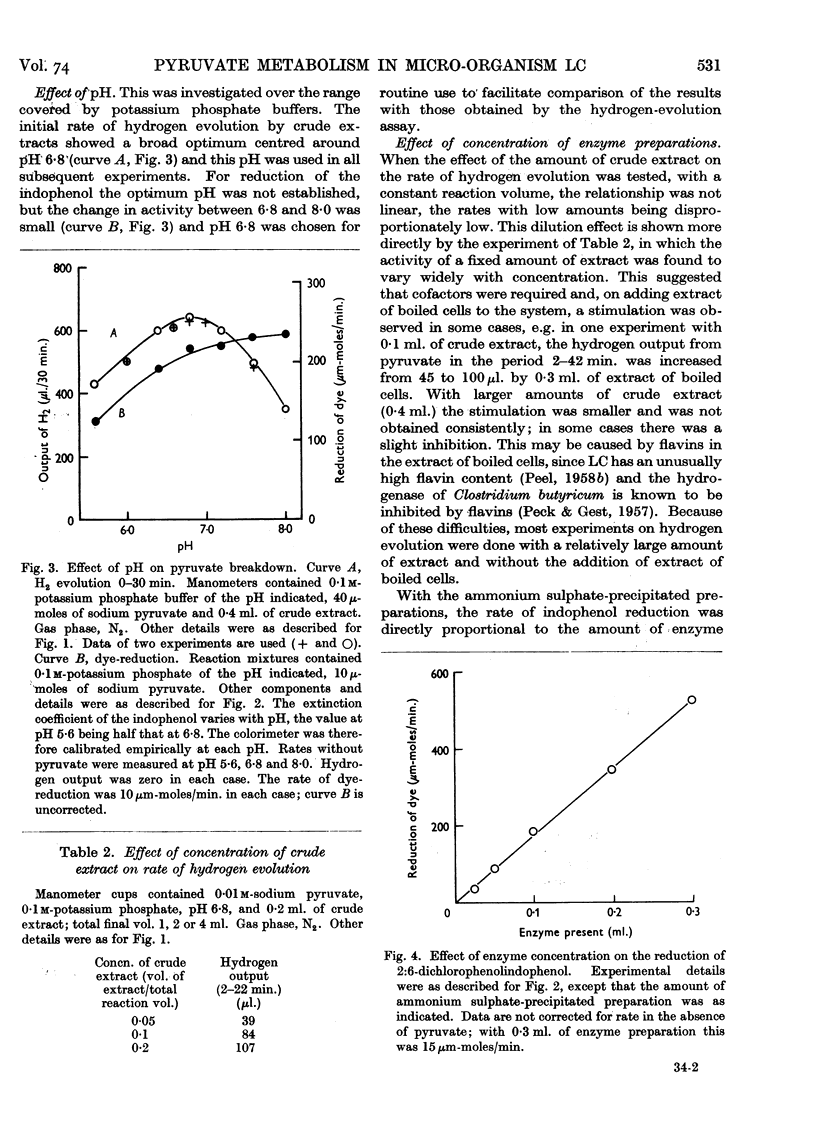
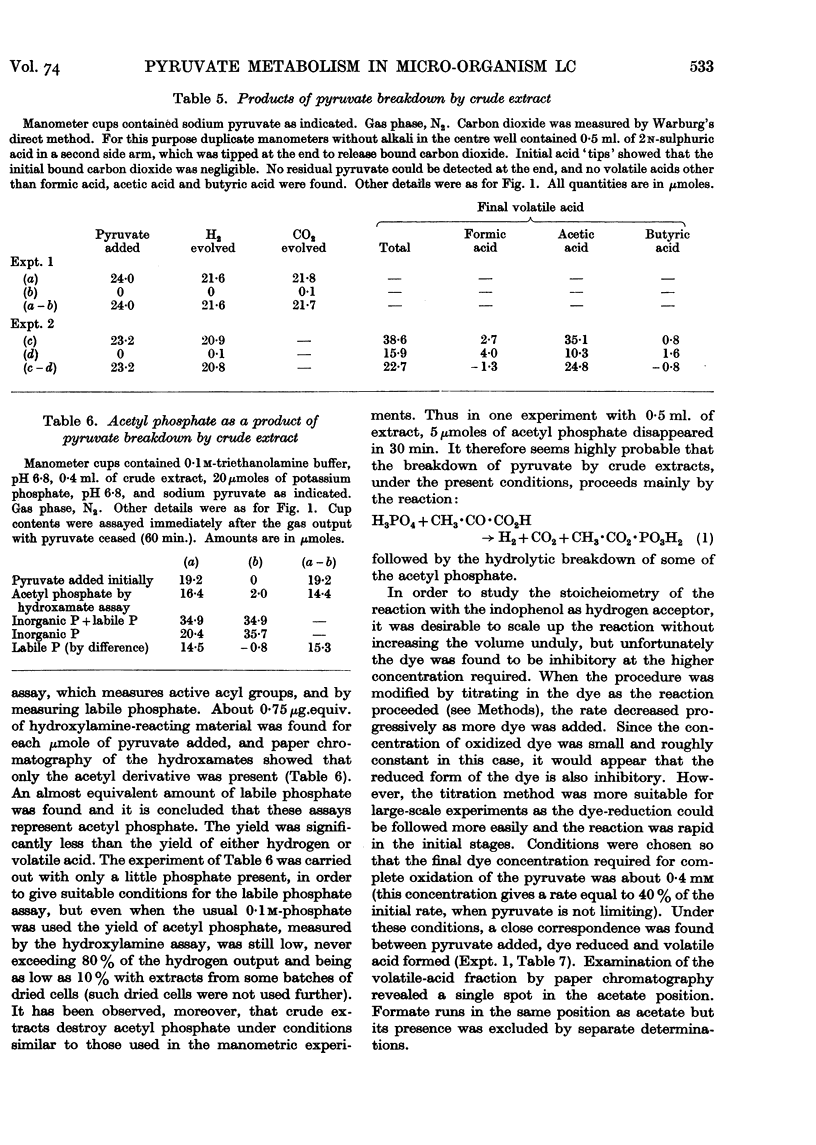
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNISON E. F. Studies on the volatile fatty acids of sheep blood with special reference to formic acid. Biochem J. 1954 Dec;58(4):670–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0580670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenblum I., Chain E. An improved method for the colorimetric determination of phosphate. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):295–298. doi: 10.1042/bj0320295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., RODGERS A. Estimation of glycollic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Dec;12(4):591–591. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSDEN S. R., GILCHRIST F. M., LEWIS D., VOLCANI B. E. Properties of a fatty acid forming organism isolated from the rumen of sheep. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):681–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.681-689.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSDEN S. R., LEWIS D. The production of fatty acids by a gram-negative coccus. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):183–189. doi: 10.1042/bj0550183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEST H. Oxidation and evolution of molecular hydrogen by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1954 Mar;18(1):43–73. doi: 10.1128/br.18.1.43-73.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEST H. Properties of cell-free hydrogenases of Escherichia coli and Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;63(1):111–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.1.111-121.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN D. S. Enzyme systems in the Mycobacteria. IV. The pyruvic oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Mar;27(3):506–512. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90379-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN D. S. Enzyme systems in the Mycobacteria. V. The pyruvic dehydrogenase system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Mar;27(3):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTIERREZ J., DAVIS R. E., LINDAHL I. L., WARWICK E. J. Bacterial changes in the rumen during the onset of feed-lot bloat of cattle and characteristics of Peptostreptococcus elsdenii n. sp. Appl Microbiol. 1959 Jan;7(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/am.7.1.16-22.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGER L. P., GELLER D. M., LIPMANN F. Flavoprotein-catalyzed pyruvate oxidation in Lactobacillus delbrueckii. Fed Proc. 1954 Sep;13(3):734–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES A. T., MARTIN A. J. P. Gas-liquid partition chromatography; the separation and micro-estimation of volatile fatty acids from formic acid to dodecanoic acid. Biochem J. 1952 Mar;50(5):679–690. doi: 10.1042/bj0500679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS D., ELSDEN S. R. The fermentation of L-threonine, L-serine, L-cysteine and acrylic acid by a gram-negative coccus. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):683–692. doi: 10.1042/bj0600683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leloir L. F., Muñoz J. M. Fatty acid oxidation in liver. Biochem J. 1939 May;33(5):734–746. doi: 10.1042/bj0330734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYED H. S., O'KANE D. J. Fractionation of the pyruvate oxidase of Proteus vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):375–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYED H. S., O'KANE D. J. The enzymes of the pyruvate oxidase system of Proteus vulgaris. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Aug;39(2):457–458. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham R. A steam distillation apparatus suitable for micro-Kjeldahl analysis. Biochem J. 1942 Dec;36(10-12):790–791. doi: 10.1042/bj0360790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISMAN B. The Stickland reaction. Bacteriol Rev. 1954 Mar;18(1):16–42. doi: 10.1128/br.18.1.16-42.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHOA S. Enzymic mechanisms in the citric acid cycle. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1954;15:183–270. doi: 10.1002/9780470122600.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECK H. D., Jr, GEST H. Hydrogenase of Clostridium butylicum. J Bacteriol. 1957 Apr;73(4):569–580. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.4.569-580.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEEL J. L., LOUGHMAN B. C. Some observations on the role of copper ions in the reduction of phosphomolybdate by ascorbic acid and their application in the determination of inorganic orthophosphate. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):709–716. doi: 10.1042/bj0650709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEEL J. L. The separation of flavins by paper electrophoresis and its application to the examination of the flavin contents of micro-organisms. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):403–416. doi: 10.1042/bj0690403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. A., Sinclair H. M., Thompson R. H. An analysis of the inhibition of pyruvate oxidation by arsenicals in relation to the enzyme theory of vesication. Biochem J. 1946;40(4):516–524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson W. V. THE PREPARATION OF SODIUM PYRUVATE. Science. 1942 Jul 24;96(2482):93–94. doi: 10.1126/science.96.2482.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWEET R. S., CHESLOCK K. Pyruvic oxidase of pigeon breast muscle. III. Factors influencing enzymatic activity. J Biol Chem. 1952 Dec;199(2):749–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAMAN G. R. Pyruvate oxidation by extracts of Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Oct;11(2):300–306. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-2-300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAMAN G. R. Role of thioctic acid in the transfer of acyl groups. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Feb;82(2):184–189. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R., BARKER H. A. Fatty acid synthesis by enzyme preparations of Clostridium kluyveri. VI. Reactions of acyl phosphates. J Biol Chem. 1950 Jun;184(2):769–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R., KORNBERG A. The purification of coenzyme A by ion exchange chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jul;203(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R., LIPMANN F. Acetyl phosphate synthesis by reaction of isopropenyl acetate and phosphoric acid. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):549–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R. The coenzyme A transphorase system in Clostridium kluyveri. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jul;203(1):501–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R. The purification and properties of phosphotransacetylase. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(2):527–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER D. J. The purification and properties of the L-threonine deaminase of the rumen micro-organism LC1. Biochem J. 1958 Aug;69(4):524–530. doi: 10.1042/bj0690524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITELEY H. R., ORDAL E. J. Fermentation of alpha keto acids by Micrococcus aerogenes and Micrococcus lactilyticus. J Bacteriol. 1957 Sep;74(3):331–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.3.331-336.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIESENDANGER S. B., NISMAN B. Role de l'ATP et du CoA dans la deshydrogénation du pyruvate par les extraits de Cl. saccharobutyricum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Apr;13(4):480–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90364-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE R. S., O'KANE D. J. Cofactors of the carbon dioxide exchange reaction of Clostridium butyricum. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):637–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE R. S., O'KANE D. J. Cofactors of the phosphoroclastic reaction of Clostridium butyricum. J Biol Chem. 1953 Dec;205(2):755–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


