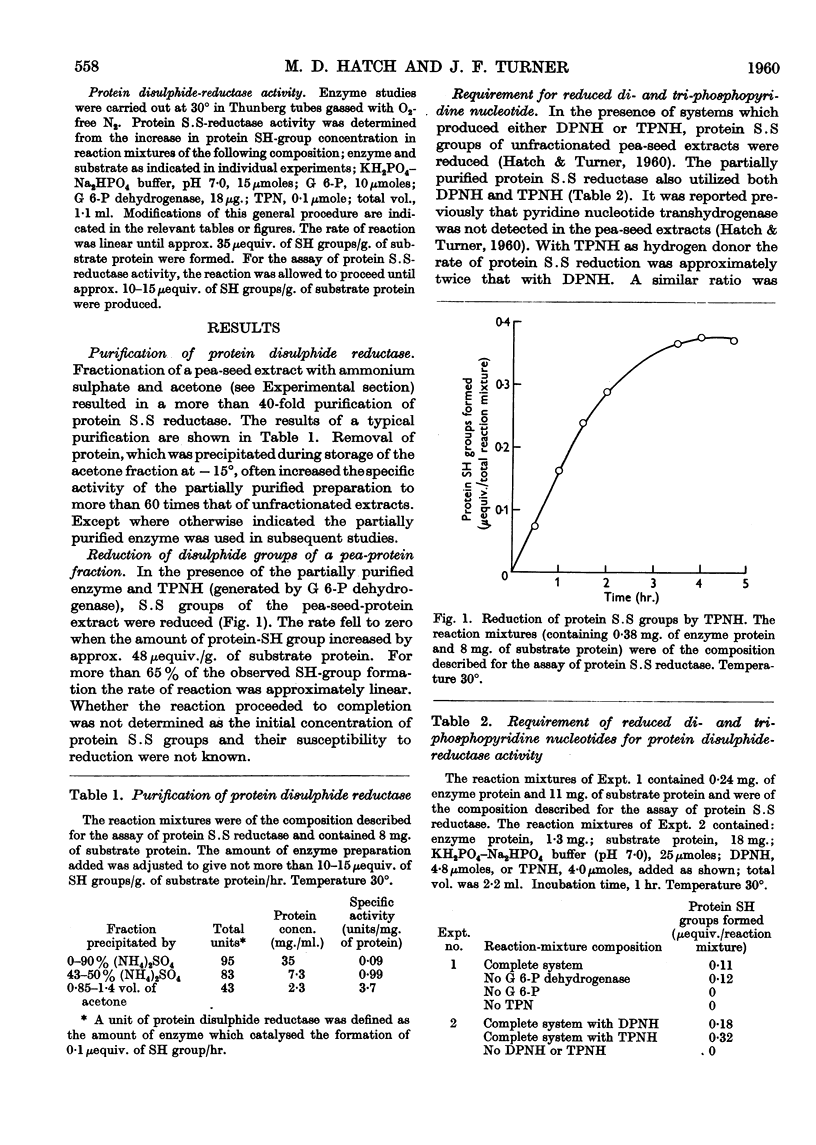
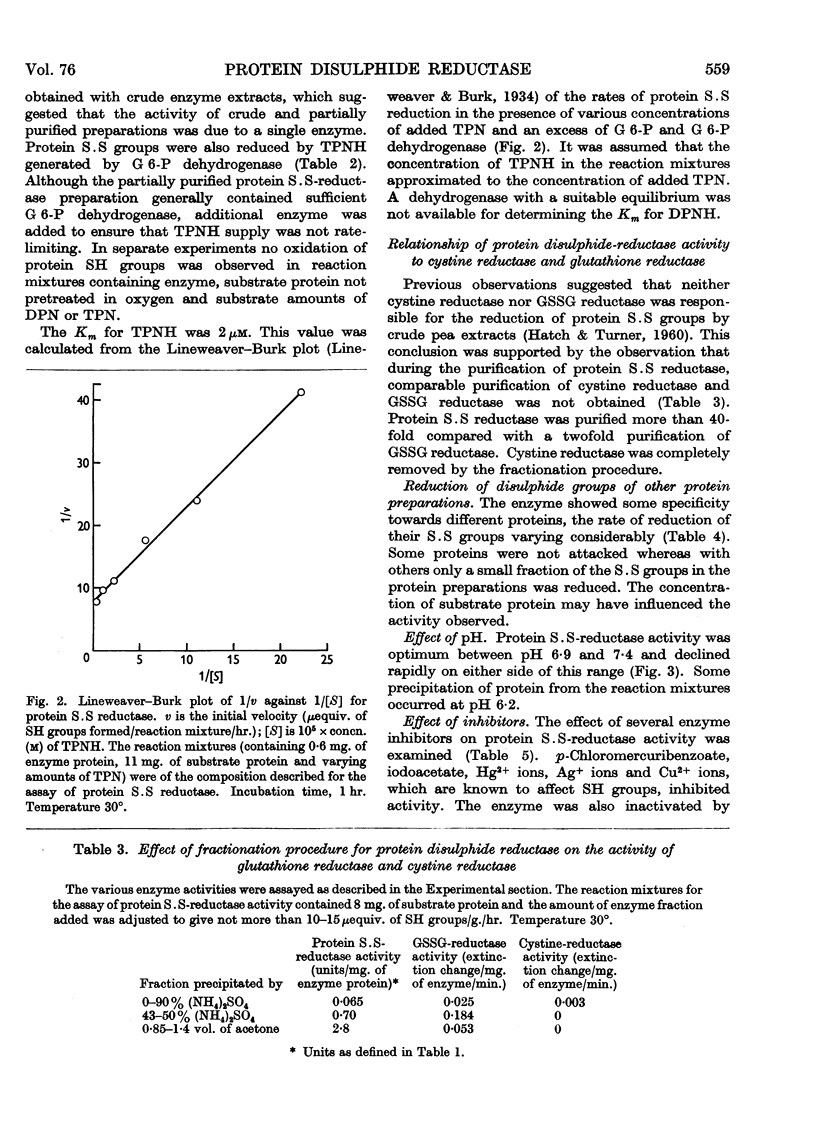
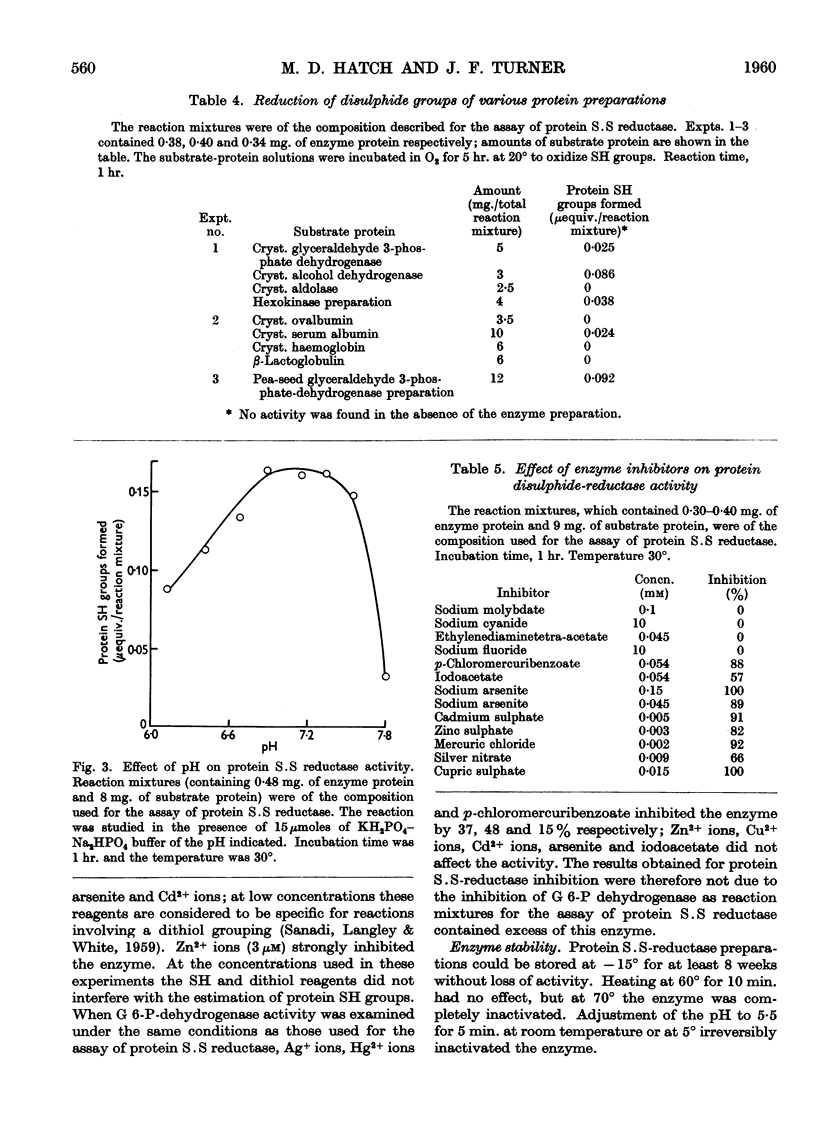
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRON E. S. G., JOHNSON P. Studies on the mechanism of action of ionizing radiations. XI. Inactivation of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase by x-irradiation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jan;48(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONN E. E., VENNESLAND B. Glutathione reductase of wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1951 Sep;192(1):17–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALCONE G., NICKERSON W. J. Identification of protein disulfide reductase as a cellular division enzyme in yeasts. Science. 1956 Oct 19;124(3225):722–723. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3225.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSCHMAN R., GILBERT D. L., NYE S. W., DWYER P., FENN W. O. Oxygen poisoning and x-irradiation: a mechanism in common. Science. 1954 May 7;119(3097):623–626. doi: 10.1126/science.119.3097.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINTSBURG M. B., PANDRE E. M., BINUS N. M. Rol' sul'fgidril'nykh grupp i perekisnykh soedinenii v mekhanizme biologicheskogo deistviia ioniziruiushchego izlucheniia. Biokhimiia. 1957 May-Jun;22(3):467–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGEMAN R. H., ARNON D. I. The isolation of triosephosphate dehydrogenase from pea seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Mar;55(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90554-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATCH M. D., TURNER J. F. The aerobic inhibition of glycolysis in pea-seed extracts and its possible relationship to the Pasteur effect. Biochem J. 1959 Jul;72:524–532. doi: 10.1042/bj0720524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATCH M. D., TURNER J. F. The mechanism of the reversible aerobic inhibition of glycolysis in a pea-seed extract. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:66–72. doi: 10.1042/bj0750066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUGAARD N., HESS M. E., ITSKOVITZ H. The toxic action of oxygen on glucose and pyruvate oxidation in heart homogenates. J Biol Chem. 1957 Aug;227(2):605–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAWAMURA N., DAN K. A cytochemical study of the sulfhydryl groups of sea urchin eggs during the first cleavage. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Sep 25;4(5):615–619. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.5.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LADD J. N. The fermentation of lactic acid by a gram-negative coccus. Biochem J. 1959 Jan;71(1):16–22. doi: 10.1042/bj0710016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDON R. G. Properties and mechanism of action of purified glutathione reductase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Nov;30(2):432–433. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAPSON L. W., GODDARD D. R. The reduction of glutathione by plant tissues. Biochem J. 1951 Oct;49(5):592–601. doi: 10.1042/bj0490592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKERSON W. J., FALCONE G. Enzymatic reduction of disulfide bonds in cell wall protein of baker's yeast. Science. 1956 Aug 17;124(3216):318–319. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3216.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIHL A., ELDJARN L., BREMER J. On the mode of action of x-ray protective agents. III. The enzymatic reduction of disulfides. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jul;227(1):339–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. Glutathione reductase from bakers' yeast and beef liver. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):855–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL T. W., LEHNINGER A. L. Glutathione reductase of animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1952 Jan;194(1):119–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANO A. H., NICKERSON W. J. Cystine reductase of pea seeds and yeasts. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):409–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAI H., DAN K. Studies on sulfhydryl groups during cell division of sea urchin egg. I. Glutatione. Exp Cell Res. 1959 Jan;16(1):24–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(59)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANADI D. R., LANGLEY M., WHITE F. alpha-Ketoglutaric dehydrogenase. VII. The role of thioctic acid. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):183–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER J. F., MAPSON L. W. Aerobic inhibition of glycolysis. Nature. 1958 Jan 24;181(4604):270–270. doi: 10.1038/181270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER J. F. The biosynthesis of sucrose. Biochem J. 1957 Nov;67(3):450–456. doi: 10.1042/bj0670450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMAN N., SCHOENBACH E. B., ARMISTEAD E. B. The determination of sulfhydryl groups in serum. I. Methods and results on normal sera. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):153–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


