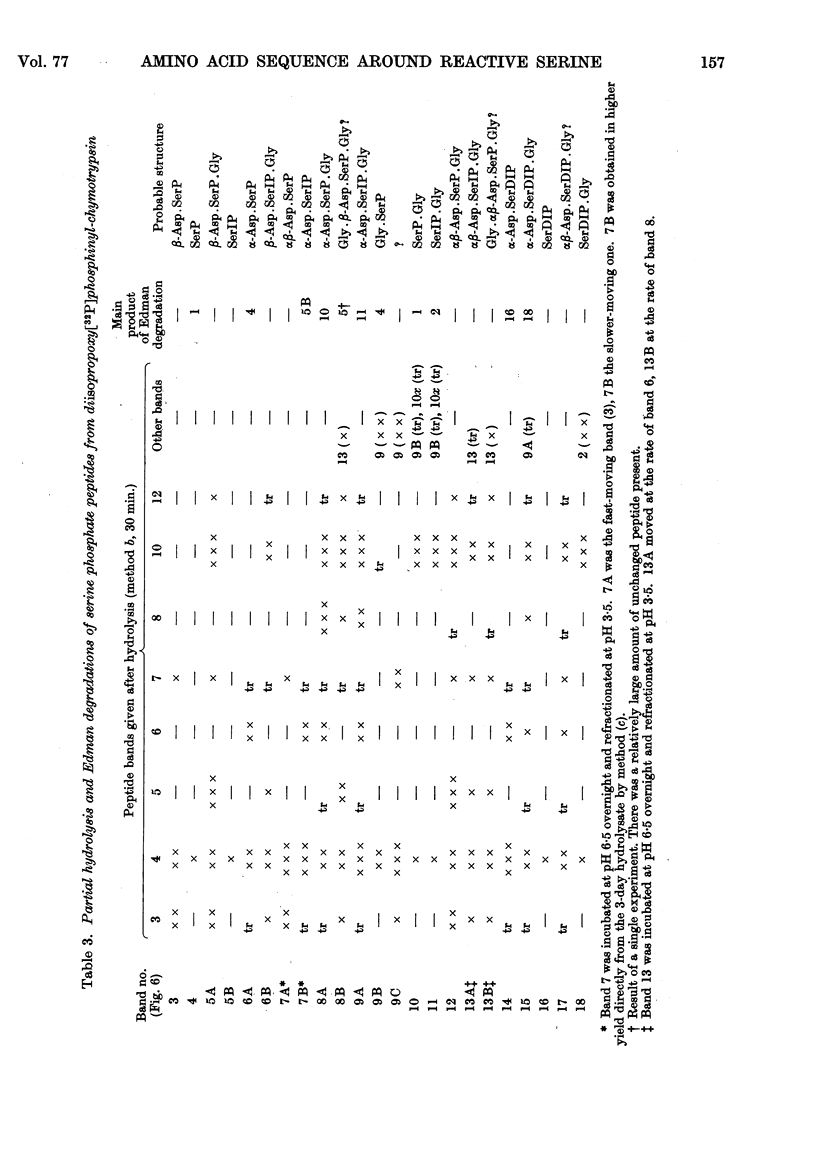
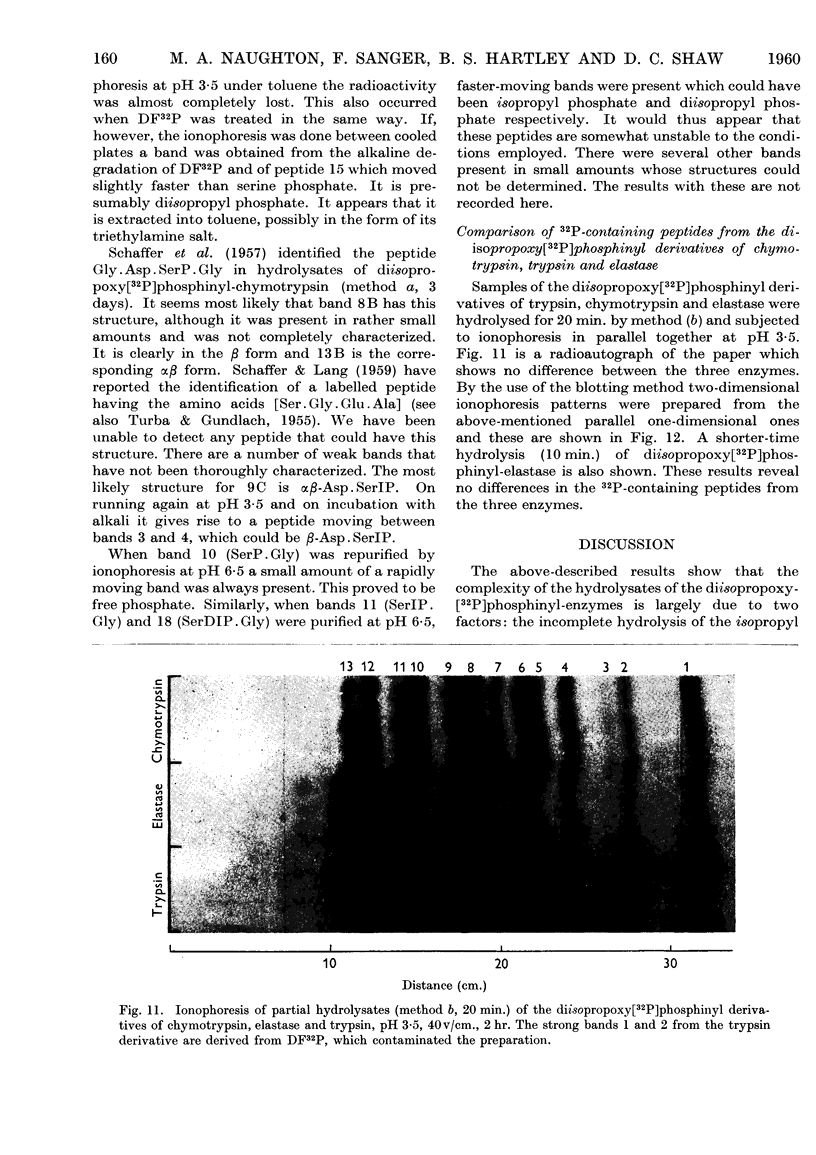
Full text
PDF










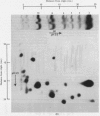
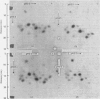
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACKBURN S., LOWTHER A. G. The separation of N-2:4-dinitrophenly amino-acids on paper chromatograms. Biochem J. 1951 Jan;48(1):126–128. doi: 10.1042/bj0480126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAVIN M. The linkage of phosphate to protein in pepsin and ovalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):771–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLSCH G., OSTERBERG R. The apparent acid ionization constants of some O-phosphorylated peptides and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2298–2303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS D. Paper electrophoresis of amino-acids and oligopeptides at very high potential gradients. Nature. 1955 Jul 9;176(4471):72–73. doi: 10.1038/176072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J. I., ROOS P. Amino-acid sequence of a melanophore-stimulating peptide. Nature. 1956 Jul 14;178(4524):90–90. doi: 10.1038/178090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY B. S., NAUGHTON M. A., SANGER F. The amino acid sequence around the reactive serine of elastase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:243–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOHN J. A cellulose acetate supporting medium for zone electrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1957 Aug;2(4):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(57)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OOSTERBAAN R. A., KUNST P., VAN ROTTERDAM J., COHEN J. A. The reaction of chymotrypsin and diisopropylphosphorofluoridate. I. Isolation and analysis of diisopropylphosphoryl-peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Mar;27(3):549–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE S. M., DAVIS H. F. Preferential release of aspartic acid during the hydrolysis of proteins. Nature. 1950 Jan 14;165(4185):62–62. doi: 10.1038/165062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYDON H. N. A possible mechanism of action of esterases inhibitable by organophosphorus compounds. Nature. 1958 Oct 4;182(4640):928–929. doi: 10.1038/182928a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYLE A. P., SANGER F., SMITH L. F., KITAI R. The disulphide bonds of insulin. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):541–556. doi: 10.1042/bj0600541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGER F., THOMPSON E. O. P. The amino-acid sequence in the glycyl chain of insulin. I. The identification of lower peptides from partial hydrolysates. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):353–366. doi: 10.1042/bj0530353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFER N. K., HARSHMAN S., ENGLE R. R. Phosphoserylglycine from diisopropylphosphoryl chymotrypsin and inversion of its peptide sequence by acid. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jun;214(2):799–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFER N. K., SIMET L., HARSHMAN S., ENGLE R. R., DRISKO R. W. Phosphopeptides from acid-hydrolyzed P32-labeled diisopropylphosphoryl chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):197–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWALLOW D. L., ABRAHAM E. P. Formation of epsilon-(aminosuccinyl)-lysine from epsilon-aspartyl-lysine from bacitracin A, and from the cell of lactobacilli. Biochem J. 1958 Nov;70(3):364–373. doi: 10.1042/bj0700364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON E. O. Modification of tyrosine during performic acid oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Nov;15(3):440–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURBA F., GUNDLACH G. Aminosäure-Sequenz in der Umgebung des reaktiven Serinrestes im Chymotrypsin-Molekül. Biochem Z. 1955;327(3):186–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]