Abstract
Nivolumab plus relatlimab demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS), along with a clinically meaningful, but not statistically significant improvement in overall survival (OS) and a numerically higher objective response rate (ORR) compared with nivolumab in the RELATIVITY-047 trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03470922). We report updated descriptive efficacy and safety results from RELATIVITY-047 with a median follow-up of 33.8 months. Median PFS was 10.2 months (95% CI, 6.5 to 15.4) with nivolumab plus relatlimab and 4.6 months (95% CI, 3.5 to 6.5) with nivolumab (hazard ratio [HR], 0.79 [95% CI, 0.66 to 0.95]); median OS was 51.0 months (95% CI, 34.0 to not reached) and 34.1 (95% CI, 25.2 to 44.7) months, respectively (HR, 0.80 [95% CI, 0.66 to 0.99]). ORR was 43.7% (95% CI, 38.4 to 49.0) with nivolumab plus relatlimab and 33.7% (95% CI, 28.8 to 38.9) with nivolumab. Efficacy across the majority of prespecified subgroups favored the combination. No new or unexpected safety signals were identified. Overall, at 3-year follow-up, the benefit observed with nivolumab plus relatlimab compared with nivolumab in patients with advanced melanoma was sustained, with the OS HR 95% CI upper bound now <1. This benefit is accompanied by a safety profile consistent with previous reports.
INTRODUCTION
RELATIVITY-047 is a global phase II/III randomized clinical trial that evaluated nivolumab plus relatlimab fixed-dose combination (FDC) compared with nivolumab alone in patients with previously untreated metastatic or unresectable advanced melanoma. A statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) with the FDC was observed at a median follow-up of 13.2 months, which led to regulatory approval.1 At a median follow-up of 19.3 months, the PFS benefit remained consistent, and a clinically meaningful (but not statistically significant) improvement in overall survival (OS), as well as a numerically higher objective response rate (ORR), was observed.2 Here, we report updated descriptive efficacy and safety results from RELATIVITY-047 at a median follow-up of 33.8 months.
METHODS
Study Design and Patients
The study design of RELATIVITY-047 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03470922) has been described previously.1 Eligible patients were age 12 years and older with previously untreated, histologically confirmed, unresectable advanced stage III or IV melanoma, measurable disease according to RECIST version 1.1,3 and tumor tissue evaluable for expression of lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG-3) and PD-L1. Patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive 480 mg of nivolumab and 160 mg of relatlimab as an FDC or 480 mg of nivolumab alone intravenously once every 4 weeks. Random assignment was stratified according to LAG-3 expression (≥1% or <1%), PD-L1 expression (≥1% or <1%), BRAF V600 mutation status, and metastasis stage (M0 or M1 with normal lactate dehydrogenase [LDH] levels v M1 with elevated LDH levels) as defined in the Cancer Staging Manual of the American Joint Committee on Cancer, eighth edition.4 The protocol and amendments were approved by the appropriate institutional review board and/or ethics committee at each institution. All patients provided written informed consent.
End Points and Statistical Analysis
The primary end point was PFS as assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR). Secondary end points were OS and confirmed ORR by BICR. Exploratory/post hoc analyses in all randomly assigned patients included melanoma-specific survival (MSS), PFS-2 (PFS2), and efficacy on subsequent second-line (2L) therapy. Post hoc analyses were also performed for receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis of PD-L1 association with efficacy. All efficacy analyses in this 3-year update are exploratory and descriptive. Adverse events (AEs) were assessed continuously throughout the trial for at least 100 days after treatment was discontinued.
Kaplan-Meier methods were used to estimate survival rates. ORR and corresponding 95% CIs were generated by using the Clopper-Pearson method for each arm. In responders, duration of response (DOR) per treatment arm was estimated using Kaplan-Meier product-limit methodology. ROC analyses included a probability curve, with the AUC representing the degree of separability.
RESULTS
Patients
A total of 714 patients received nivolumab plus relatlimab (n = 355) or nivolumab (n = 359; Fig 1). Baseline patient characteristics were well balanced (Data Supplement, Table S1 [online only]). Minimum follow-up was 33.0 months and median follow-up was 33.8 months (range, 0.3-64.2 months). Patient disposition can be found in the Data Supplement (Table S2).
FIG 1.
CONSORT diagram.
Efficacy
Median PFS was 10.2 months (95% CI, 6.5 to 15.4) with nivolumab plus relatlimab compared with 4.6 months (95% CI, 3.5 to 6.5) with nivolumab (hazard ratio [HR], 0.79 [95% CI, 0.66 to 0.95]); 3-year PFS rates were 31.8% (95% CI, 26.6 to 37.1) and 26.9% (95% CI, 22.1 to 31.9), respectively (Fig 2A). Median OS was 51.0 months (95% CI, 34.0 to not reached [NR]) with nivolumab plus relatlimab and 34.1 months (95% CI, 25.2 to 44.7) with nivolumab (HR, 0.80 [95% CI, 0.66 to 0.99]); 3-year OS rates were 54.6% (95% CI, 49.2 to 59.6) and 48.0% (95% CI, 42.7 to 53.1), respectively (Fig 2B). BICR-assessed ORR is depicted in Figure 3A and DOR in the Data Supplement (Fig S1). Median MSS was NR (95% CI, NR to NR) with nivolumab plus relatlimab and 46.7 months (95% CI, 34.1 to NR) with nivolumab (HR, 0.75 [95% CI, 0.60 to 0.94]; Fig 3B).
FIG 2.
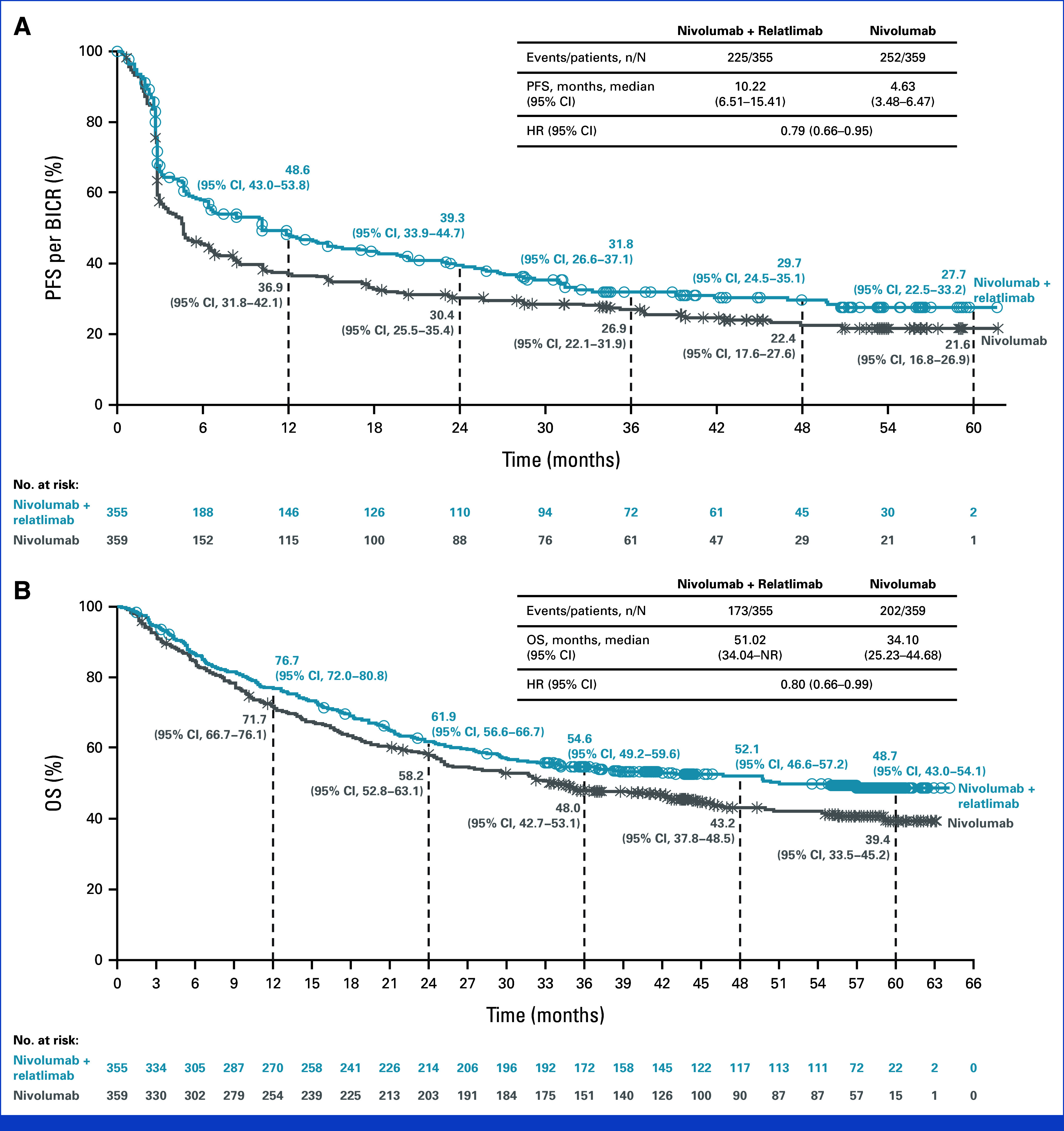
Kaplan–Meier estimates of (A) PFS and (B) OS. BICR, blinded independent central review; HR, hazard ratio; NR, not reached; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival.
FIG 3.
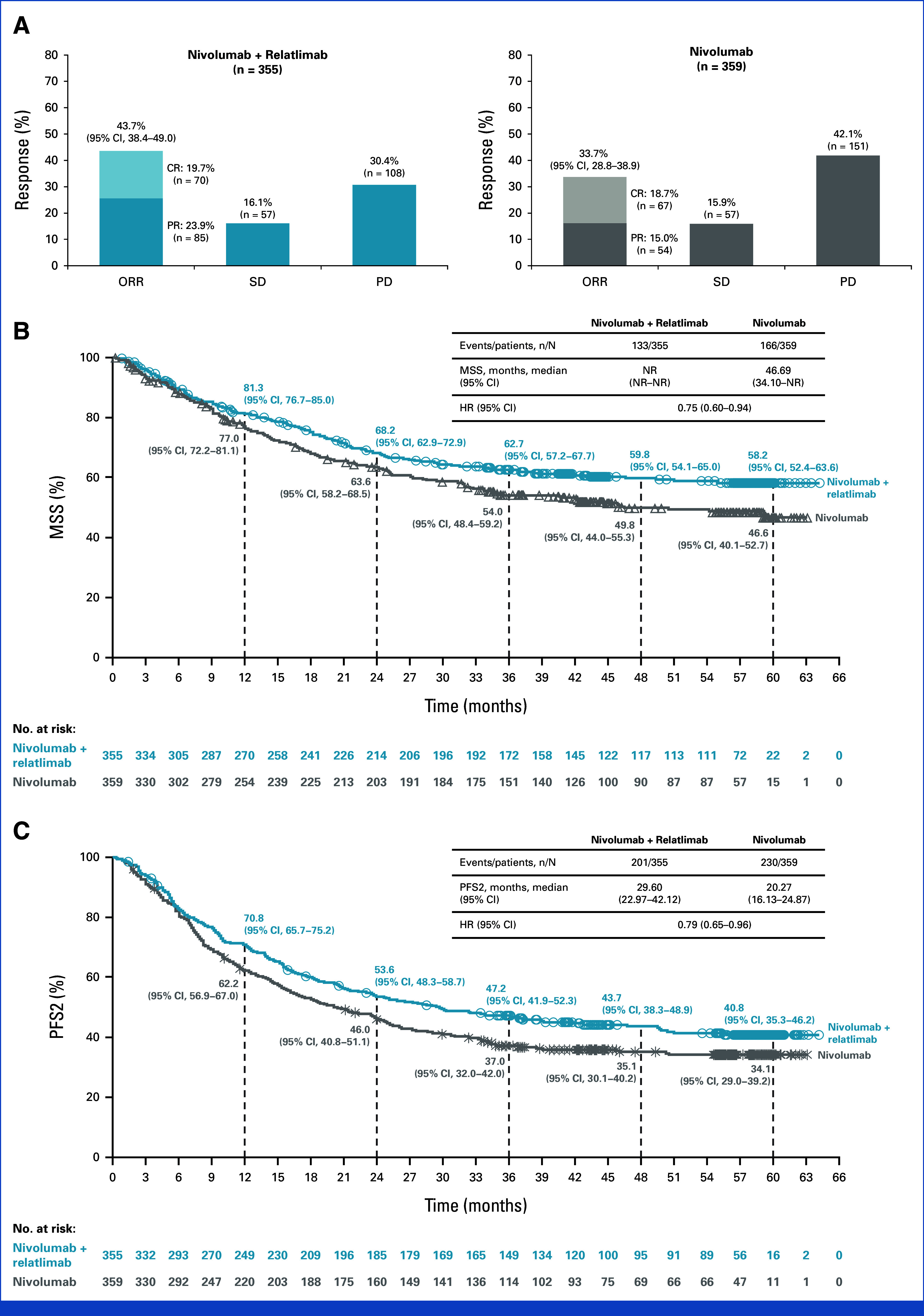
(A) Response to treatment and Kaplan–Meier estimates of (B) MSSa and (C) PFS2. aA total of 375 deaths (52.5%) were reported (173 [48.7%] in the nivolumab plus relatlimab arm and 202 [56.3%] in the nivolumab arm), with 133/355 (37.5%) and 166/359 (46.2%) deaths due to melanoma reported in the nivolumab plus relatlimab arm and nivolumab arm (nonmelanoma deaths occurred in 40 patients [11.3%] and 36 patients [10.0%]), respectively. MSS was defined as the time from random assignment to death due to melanoma per investigator assessment, with deaths for any other reason, including death due to study drug toxicity, being censored. PFS2 was defined as the time from random assignment to progression after the next line of therapy, per investigator assessment, or to death from any cause, whichever occurred first. CR, complete response; HR, hazard ratio; MSS, melanoma-specific survival; NR, not reached; PD, progressive disease; PFS2, progression-free survival-2; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease.
Nivolumab plus relatlimab was favored over nivolumab in the majority of clinically relevant subgroups (Data Supplement, Fig S2). In ROC curve analyses, tumor PD-L1 expression was not predictive for efficacy at any PD-L1 cutoff in either arm (Data Supplement, Fig S3).
Subsequent systemic therapy was received by 135 patients (38.0%) in the nivolumab plus relatlimab arm and 141 (39.3%) in the nivolumab arm (Data Supplement, Table S3). Efficacy of 2L therapy is presented in the Data Supplement (Table S4). Median PFS2 was 29.6 months (95% CI, 23.0 to 42.1) with nivolumab plus relatlimab and 20.3 months (95% CI, 16.1 to 24.9) with nivolumab (HR, 0.79 [95% CI, 0.65 to 0.96]; Fig 3C).
Safety
Safety summary is shown in Table 1. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related AEs (TRAEs) occurred in 22.0% of patients treated with nivolumab plus relatlimab and 12.0% with nivolumab. No new treatment-related deaths were reported since the last analysis.2 Time to onset of select TRAEs is shown in the Data Supplement (Figs S4 and S5).
TABLE 1.
AE Summary
| Event | Nivolumab Plus Relatlimab (n = 355) | Nivolumab (n = 359) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any grade, No. (%) | Grade 3 or 4, No. (%) | Any grade, No. (%) | Grade 3 or 4, No. (%) | |
| Any AE | 352 (99.2) | 164 (46.2) | 345 (96.1) | 141 (39.3) |
| TRAE | 302 (85.1) | 78 (22.0) | 263 (73.3) | 43 (12.0) |
| Leading to discontinuation | 63 (17.7) | 34 (9.6) | 35 (9.7) | 14 (3.9) |
| TRAEs in ≥5% of patients | ||||
| Pruritus | 93 (26.2) | 0 | 61 (17.0) | 2 (0.6) |
| Fatigue | 84 (23.7) | 5 (1.4) | 47 (13.1) | 1 (0.3) |
| Rash | 61 (17.2) | 3 (0.8) | 54 (15.0) | 2 (0.6) |
| Diarrhea | 60 (16.9) | 5 (1.4) | 39 (10.9) | 2 (0.6) |
| Hypothyroidism | 59 (16.6) | 0 | 47 (13.1) | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 56 (15.8) | 3 (0.8) | 34 (9.5) | 1 (0.3) |
| Vitiligo | 49 (13.8) | 0 | 44 (12.3) | 0 |
| Asthenia | 32 (9.0) | 1 (0.3) | 18 (5.0) | 0 |
| Nausea | 32 (9.0) | 0 | 18 (5.0) | 0 |
| Increased ALT | 31 (8.7) | 5 (1.4) | 17 (4.7) | 2 (0.6) |
| Increased AST | 31 (8.7) | 5 (1.4) | 10 (2.8) | 1 (0.3) |
| Myalgia | 30 (8.5) | 1 (0.3) | 18 (5.0) | 0 |
| Decreased appetite | 28 (7.9) | 0 | 10 (2.8) | 0 |
| Infusion-related reaction | 24 (6.8) | 0 | 13 (3.6) | 1 (0.3) |
| Hyperthyroidism | 23 (6.5) | 0 | 24 (6.7) | 0 |
| IMAEsa | ||||
| Hypothyroidism or thyroiditis | 70 (19.7) | 0 | 54 (15.0) | 0 |
| Rash | 48 (13.5) | 3 (0.8) | 34 (9.5) | 5 (1.4) |
| Diarrhea or colitis | 29 (8.2) | 6 (1.7) | 14 (3.9) | 5 (1.4) |
| Hyperthyroidism | 24 (6.8) | 0 | 26 (7.2) | 0 |
| Hepatitis | 23 (6.5) | 18 (5.1) | 13 (3.6) | 6 (1.7) |
| Adrenal insufficiency | 21 (5.9) | 6 (1.7) | 4 (1.1) | 0 |
| Pneumonitis | 15 (4.2) | 2 (0.6) | 9 (2.5) | 2 (0.6) |
| Hypophysitis | 11 (3.1) | 2 (0.6) | 4 (1.1) | 1 (0.3) |
| Nephritis and renal dysfunction | 7 (2.0) | 4 (1.1) | 5 (1.4) | 4 (1.1) |
| Hypersensitivity | 6 (1.7) | 0 | 5 (1.4) | 0 |
| Treatment-related deathsb | 4 (1.1) | 2 (0.6) | ||
NOTE. Data are No. (%) unless otherwise specified.
Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; IMAE, immune-mediated AE; TRAE, treatment-related AE.
IMAEs included AEs of any grade that occurred in at least 1% of patients in the nivolumab plus relatlimab arm, that were considered by investigators to be potentially immune-mediated, and that met the following criteria: occurred within 100 days after the last dose (regardless of causality) and were treated with immune-modulating medication with no clear alternate cause or had an immune-mediated component.
Treatment-related deaths: nivolumab plus relatlimab (n = 4): hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, acute edema of the lung, pneumonitis, and multiorgan failure; nivolumab (n = 2): sepsis and myocarditis, and worsening pneumonia. No new treatment-related deaths were reported since the last database lock.12
DISCUSSION
The updated 3-year descriptive results presented here confirm the sustained efficacy benefit of nivolumab plus relatlimab versus nivolumab. Of note, the HR 95% CI upper bound for the descriptive analysis of OS is now <1. Efficacy results continued to favor nivolumab plus relatlimab across the majority of prespecified subgroups, including in BRAF-mutant and BRAF-wildtype patients. Nivolumab plus relatlimab maintained benefit over time versus nivolumab in low-risk subgroups, where anti–PD-1 monotherapy may have otherwise been considered to balance efficacy with toxicity (low LDH and low tumor burden).5-7 Additionally, a sustained benefit was observed with nivolumab plus relatlimab in patients with high LDH, high tumor burden, stage M1C disease, and mucosal and acral melanoma subtypes, where combination immunotherapy may be considered.5-7 The ROC analysis indicated that tumor PD-L1 was not useful in predicting efficacy, indicating that the level of tumor PD-L1 expression alone is a poor predictive biomarker of efficacy.
PFS2 results further support the long-term benefits of nivolumab plus relatlimab, with a median PFS2 of 29.6 months for nivolumab plus relatlimab and 20.3 months for nivolumab. The therapeutic benefit of 2L therapies in this study appears consistent with that of other studies in this setting.8-12 Moreover, in patients whose disease did not respond to or progressed on first-line therapy, the therapeutic benefit of 2L therapy did not appear to be negatively affected by previous treatment with nivolumab plus relatlimab versus nivolumab. The use of subsequent therapy was not prespecified in the protocol and was based on local standards of care per the investigator's decision. Given the small sample size, and because the use of subsequent therapy was not prespecified in the protocol and was based on local standards of care per the investigator's decision, additional data on patients whose disease is resistant to or progresses on first-line immunotherapy are required.
Although targeting two immune checkpoints in patients with advanced melanoma is a well-established treatment strategy, to our knowledge, RELATIVITY-047 is the first study to test and show a statistically significant improvement in PFS for an immunotherapy combination versus PD-1 monotherapy. Furthermore, to our knowledge, this analysis is the first to demonstrate an OS HR 95% CI upper bound ≤1 for a combination immunotherapy over anti–PD-1 monotherapy. Overall, these descriptive analyses continued to show a benefit for nivolumab plus relatlimab in patients with previously untreated metastatic or unresectable advanced melanoma.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank the patients and investigators who participated in the RELATIVITY-047 trial. The authors thank personnel at Dako, an Agilent Technologies company, for collaborative development of the PD-L1 IHC 28-8 pharmDx assay as well as personnel at LabCorp for collaborative development of the LAG-3 IHC assay, including analytic and clinical assay validations. Professional medical writing and editorial assistance were provided by Jessica R. Augello, PhD, Melissa Kirk, PhD, and Michele Salernitano of Ashfield MedComms, an Inizio company, and funded by Bristol Myers Squibb.
Hussein A. Tawbi
Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche, Merck, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Boxer Capital, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Medicenna, Regeneron, IO Biotech
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Merck (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline (Inst), Genentech/Roche (Inst), Dragonfly Therapeutics (Inst), RAPT Therapeutics (Inst), Regeneron (Inst)
F. Stephen Hodi
Employment: Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Leadership: Bicara Therapeutics
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Apricity Health, Torque, Pionyr, Bicara Therapeutics
Consulting or Advisory Role: Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Genentech/Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Compass Therapeutics, Rheos Medicines, Checkpoint THerapeutics, Bioentre, Gossamer Bio, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Catalym, Immunocore, Kairos Therapeutics, Zumutor Biologics, Corner Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Curis, Pliant, Solu Therapeutics, Vir biotechnology, 92Bio
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck Sharp & Dohme (Inst), Genentech/Roche (Inst), Novartis (Inst)
Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: patent pending as per institutional policy, patent pending royalties received on MICA related disorders application to institution per institutional IP policy, Angiopoietin-2 Biomarkers Predictive of Anti-immune checkpoint response (Inst), Compositions and Methods for Identification, Assessment, Prevention, and Treatment of Melanoma using PD-L1 Isoforms, Methods of Using Pembrolizumab and Trebananib (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb
Other Relationship: Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche
Evan J. Lipson
Honoraria: Bristol Myers Squibb
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Merck, Instil Bio, Nektar, OncoSec, Pfizer, Rain Therapeutics, Regeneron, CareDX, Immunocore, Replimune, HUYA Bioscience International
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck (Inst), Regeneron (Inst), Sanofi (Inst)
Dirk Schadendorf
Honoraria: Roche/Genentech, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Immunocore, Merck Serono, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Philogen, Regeneron, 4SC, Sanofi/Regeneron, NeraCare GmbH, Sun Pharma, InflarxGmbH, Ultimovacs, Daiichi Sankyo Japan, LabCorp, Replimune, Agenus, AstraZeneca, Erasca, Inc, immatics, Novigenix, Pamgene, Seagen
Consulting or Advisory Role: Roche/Genentech, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron, Agenus, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Erasca, Inc, immatics, Immunocore, NeraCare GmbH, Replimune
Speakers' Bureau: Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron, Merck KGaA
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Roche (Inst), MSD Oncology (Inst), Array BioPharma/Pfizer (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Regeneron (Inst), Agenus (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Roche/Genentech, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Serono, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron
Paolo A. Ascierto
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche/Genentech, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Merck Serono, Pierre Fabre, AstraZeneca, Sun Pharma, Sanofi, Idera, Ultimovacs, Sandoz, Immunocore, 4SC, Italfarmaco, Nektar, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eisai, Regeneron, Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, OncoSec, Nouscom, Lunaphore Technologies, Seagen, ITeos Therapeutics, Medicenna, Bio-AI Health, ValoTx, Replimune, Bayer, Erasca, Inc, Philogen, BioNTech SE, Anaveon
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Roche/Genentech (Inst), Sanofi (Inst), Pfizer (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Pfizer, Bio-AI Health, Replimune, MSD Oncology, Pierre Fabre
Piotr Rutkowski
Honoraria: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Merck
Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Blueprint Medicines, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, MSD, Amgen, Philogen, AstraZeneca
Speakers' Bureau: Pfizer, Novartis, Pierre Fabre
Research Funding: Novartis (Inst), Roche (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Pierre Fabre (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Orphan Europe, Pierre Fabre
Helen Gogas
Honoraria: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD Oncology, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD Oncology, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Roche (Inst), MSD Oncology (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Iovance Biotherapeutics (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi
Christopher D. Lao
Employment: Bristol Myers Squibb
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Oncosec
Juliana Janoski De Menezes
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb/Medarex
Stéphane Dalle
Employment: Sanofi Pasteur (I)
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Sanofi (I)
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), MSD (Inst)
Speakers' Bureau: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), MSD (Inst)
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck Sharp & Dohme (Inst), Roche (Inst), Pierre Fabre (Inst)
Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: TRIM24 regulation pending patent (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD
Ana Maria Arance
Consulting or Advisory Role: BMS, Roche, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, MSD, BioNTech SE, Almirall
Speakers' Bureau: Novartis, MSD, BMS, Pierre Fabre
Research Funding: Novartis (Inst), Roche (Inst), BMS (Inst), MSD (Inst), BioNTech SE (Inst), Replimune (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: BMS, MSD, Pierre Fabre, Novartis
Jean-Jacques Grob
Consulting or Advisory Role: BMS, MSD Oncology, Roche/Genentech, Novartis, Amgen, Pierre fabre, Sun Pharma, Merck KGaA, Sanofi, Roche, Philogen, Ultimovacs
Speakers' Bureau: Novartis, Pierre Fabre
Barbara Ratto
Employment: Novartis (I), Bristol Myers Squibb, Arcus Biosciences
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Arcus Biosciense
Saima Rodriguez
Employment: Bristol Myers Squibb
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Bristol Myers Squibb
Antonella Mazzei
Employment: Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Bristol Myers Squib
Sonia Dolfi
Employment: Bristol Myers Squibb
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Bristol Myers Squibb
Georgina V. Long
This author is a member of the Journal of Clinical Oncology Editorial Board. Journal policy recused the author from having any role in the peer review of this manuscript.
Honoraria: BMS, Pierre Fabre
Consulting or Advisory Role: Agenus, Amgen, Array BioPharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Evaxion Biotech, Hexal, Highlight Therapeutics, Innovent Biologics, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, OncoSec, PHMR, Pierre Fabre, Regeneron, AstraZeneca, IO Biotech, Immunocore Ireland Limited, Bayer, Scancell LImited, Skyline Diagnostics, GI Innovation Inc
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: BMS, MSD Oncology, Novartis, Pierre Fabre
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
PRIOR PRESENTATION
Presented at the 2024 ASCO annual meeting, Chicago, IL, May 31-June 4, 2024.
SUPPORT
Supported by Bristol Myers Squibb.
CLINICAL TRIAL INFORMATION
DATA SHARING STATEMENT
Bristol Myers Squibb's policy on data sharing may be found at https://www.bms.com/researchers-and-partners/independent-research/data-sharing-request-process.html.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception and design: Hussein A. Tawbi, F. Stephen Hodi, Evan J. Lipson, Dirk Schadendorf, Paolo A. Ascierto, Luis Matamala, Erika Castillo Gutiérrez, Piotr Rutkowski
Administrative support: Jean-Jacques Grob, Barbara Ratto
Provision of study materials or patients: Hussein A. Tawbi, F. Stephen Hodi, Evan J. Lipson, Dirk Schadendorf, Paolo A. Ascierto, Luis Matamala, Erika Castillo Gutiérrez, Piotr Rutkowski, Helen Gogas, Christopher D. Lao, Juliana Janoski De Menezes, Stéphane Dalle, Ana Maria Arance, Saima Rodriguez, Antonella Mazzei, Sonia Dolfi, Georgina V. Long
Collection and assembly of data: Hussein A. Tawbi, F. Stephen Hodi, Evan J. Lipson, Dirk Schadendorf, Paolo A. Ascierto, Luis Matamala, Erika Castillo Gutiérrez, Piotr Rutkowski, Helen Gogas, Christopher D. Lao, Juliana Janoski De Menezes, Stéphane Dalle, Jean-Jacques Grob, Barbara Ratto
Data analysis and interpretation: Hussein A. Tawbi, F. Stephen Hodi, Evan J. Lipson, Dirk Schadendorf, Paolo A. Ascierto, Luis Matamala, Erika Castillo Gutiérrez, Piotr Rutkowski, Helen Gogas, Christopher D. Lao, Juliana Janoski De Menezes, Stéphane Dalle, Ana Maria Arance, Jean-Jacques Grob, Barbara Ratto, Saima Rodriguez, Antonella Mazzei, Sonia Dolfi, Georgina V. Long
Manuscript writing: All authors
Final approval of manuscript: All authors
Accountable for all aspects of the work: All authors
AUTHORS' DISCLOSURES OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Three-Year Overall Survival With Nivolumab Plus Relatlimab in Advanced Melanoma From RELATIVITY-047
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/jco/authors/author-center.
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (Open Payments).
Hussein A. Tawbi
Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche, Merck, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Boxer Capital, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Medicenna, Regeneron, IO Biotech
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Merck (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline (Inst), Genentech/Roche (Inst), Dragonfly Therapeutics (Inst), RAPT Therapeutics (Inst), Regeneron (Inst)
F. Stephen Hodi
Employment: Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Leadership: Bicara Therapeutics
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Apricity Health, Torque, Pionyr, Bicara Therapeutics
Consulting or Advisory Role: Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Genentech/Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Compass Therapeutics, Rheos Medicines, Checkpoint THerapeutics, Bioentre, Gossamer Bio, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Catalym, Immunocore, Kairos Therapeutics, Zumutor Biologics, Corner Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Curis, Pliant, Solu Therapeutics, Vir biotechnology, 92Bio
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck Sharp & Dohme (Inst), Genentech/Roche (Inst), Novartis (Inst)
Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: patent pending as per institutional policy, patent pending royalties received on MICA related disorders application to institution per institutional IP policy, Angiopoietin-2 Biomarkers Predictive of Anti-immune checkpoint response (Inst), Compositions and Methods for Identification, Assessment, Prevention, and Treatment of Melanoma using PD-L1 Isoforms, Methods of Using Pembrolizumab and Trebananib (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb
Other Relationship: Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche
Evan J. Lipson
Honoraria: Bristol Myers Squibb
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Merck, Instil Bio, Nektar, OncoSec, Pfizer, Rain Therapeutics, Regeneron, CareDX, Immunocore, Replimune, HUYA Bioscience International
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck (Inst), Regeneron (Inst), Sanofi (Inst)
Dirk Schadendorf
Honoraria: Roche/Genentech, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Immunocore, Merck Serono, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Philogen, Regeneron, 4SC, Sanofi/Regeneron, NeraCare GmbH, Sun Pharma, InflarxGmbH, Ultimovacs, Daiichi Sankyo Japan, LabCorp, Replimune, Agenus, AstraZeneca, Erasca, Inc, immatics, Novigenix, Pamgene, Seagen
Consulting or Advisory Role: Roche/Genentech, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron, Agenus, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Erasca, Inc, immatics, Immunocore, NeraCare GmbH, Replimune
Speakers' Bureau: Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron, Merck KGaA
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Roche (Inst), MSD Oncology (Inst), Array BioPharma/Pfizer (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Regeneron (Inst), Agenus (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Roche/Genentech, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Serono, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron
Paolo A. Ascierto
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche/Genentech, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Merck Serono, Pierre Fabre, AstraZeneca, Sun Pharma, Sanofi, Idera, Ultimovacs, Sandoz, Immunocore, 4SC, Italfarmaco, Nektar, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eisai, Regeneron, Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, OncoSec, Nouscom, Lunaphore Technologies, Seagen, ITeos Therapeutics, Medicenna, Bio-AI Health, ValoTx, Replimune, Bayer, Erasca, Inc, Philogen, BioNTech SE, Anaveon
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Roche/Genentech (Inst), Sanofi (Inst), Pfizer (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Pfizer, Bio-AI Health, Replimune, MSD Oncology, Pierre Fabre
Piotr Rutkowski
Honoraria: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Merck
Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Blueprint Medicines, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, MSD, Amgen, Philogen, AstraZeneca
Speakers' Bureau: Pfizer, Novartis, Pierre Fabre
Research Funding: Novartis (Inst), Roche (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Pierre Fabre (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Orphan Europe, Pierre Fabre
Helen Gogas
Honoraria: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD Oncology, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD Oncology, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi/Regeneron
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Roche (Inst), MSD Oncology (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Iovance Biotherapeutics (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi
Christopher D. Lao
Employment: Bristol Myers Squibb
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Oncosec
Juliana Janoski De Menezes
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb/Medarex
Stéphane Dalle
Employment: Sanofi Pasteur (I)
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Sanofi (I)
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), MSD (Inst)
Speakers' Bureau: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), MSD (Inst)
Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck Sharp & Dohme (Inst), Roche (Inst), Pierre Fabre (Inst)
Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: TRIM24 regulation pending patent (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD
Ana Maria Arance
Consulting or Advisory Role: BMS, Roche, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, MSD, BioNTech SE, Almirall
Speakers' Bureau: Novartis, MSD, BMS, Pierre Fabre
Research Funding: Novartis (Inst), Roche (Inst), BMS (Inst), MSD (Inst), BioNTech SE (Inst), Replimune (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: BMS, MSD, Pierre Fabre, Novartis
Jean-Jacques Grob
Consulting or Advisory Role: BMS, MSD Oncology, Roche/Genentech, Novartis, Amgen, Pierre fabre, Sun Pharma, Merck KGaA, Sanofi, Roche, Philogen, Ultimovacs
Speakers' Bureau: Novartis, Pierre Fabre
Barbara Ratto
Employment: Novartis (I), Bristol Myers Squibb, Arcus Biosciences
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Arcus Biosciense
Saima Rodriguez
Employment: Bristol Myers Squibb
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Bristol Myers Squibb
Antonella Mazzei
Employment: Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Bristol Myers Squib
Sonia Dolfi
Employment: Bristol Myers Squibb
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Bristol Myers Squibb
Georgina V. Long
This author is a member of the Journal of Clinical Oncology Editorial Board. Journal policy recused the author from having any role in the peer review of this manuscript.
Honoraria: BMS, Pierre Fabre
Consulting or Advisory Role: Agenus, Amgen, Array BioPharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Evaxion Biotech, Hexal, Highlight Therapeutics, Innovent Biologics, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, OncoSec, PHMR, Pierre Fabre, Regeneron, AstraZeneca, IO Biotech, Immunocore Ireland Limited, Bayer, Scancell LImited, Skyline Diagnostics, GI Innovation Inc
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: BMS, MSD Oncology, Novartis, Pierre Fabre
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
REFERENCES
- 1.Tawbi HA, Schadendorf D, Lipson EJ, et al. : Relatlimab and nivolumab versus nivolumab in untreated advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 386:24-34, 2022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Long GV, Stephen Hodi F, Lipson EJ, et al. : Overall survival and response with nivolumab and relatlimab in advanced melanoma. NEJM Evid 2:EVIDoa2200239, 2023. [Erratum: NEJM Evid 2:EVIDx2300104, 2023] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. : New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228-247, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.American Joint Committee on Cancer : AJCC Cancer Staging Manual (ed 8). Chicago, IL, American College of Surgeons, 2018 [Google Scholar]
- 5.National Comprehensive Cancer Network : (NCCN Guidelines): For melanoma cutaneous V.2.2024. 2924. https://www.nccn.org/
- 6.Steininger J, Gellrich FF, Schulz A, et al. : Systemic therapy of metastatic melanoma: On the road to cure. Cancers (Basel) 13:1430, 2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Krattinger R, Ramelyte E, Dornbierer J, et al. : Is single versus combination therapy problematic in the treatment of cutaneous melanoma? Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 14:9-23, 2021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.VanderWalde A, Bellasea SL, Kendra KL, et al. : Ipilimumab with or without nivolumab in PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade refractory metastatic melanoma: A randomized phase 2 trial. Nat Med 29:2278-2285, 2023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boutros A, Tanda ET, Croce E, et al. : Activity and safety of first-line treatments for advanced melanoma: A network meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer 188:64-79, 2023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Thosar M, Khankhel Z, McDonald L, et al. : Network meta-analysis (NMA) of immuno-oncology (IO) treatments for first-line (1L) advanced or metastatic melanoma. Presented at ISPOR Europe 2023, Copenhagen, Denmark, November 12-15, 2023 (Poster CO62)
- 11.Schadendorf D, Tawbi H, Lipson E, et al. : Efficacy and safety of first-line nivolumab plus relatlimab versus nivolumab in advanced melanoma: An indirect treatment comparison using patient-level data for RELATIVITY-047 and CHEKMATE 067. Presented at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, June 2-6, 2023 (9552)
- 12.Zhao B-W, Zhang F-Y, Wang Y, et al. : LAG3-PD1 or CTLA4-PD1 inhibition in advanced melanoma: Indirect cross comparisons of the CheckMate-067 and RELATIVITY-047 trials. Cancers 14:4975, 2022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Bristol Myers Squibb's policy on data sharing may be found at https://www.bms.com/researchers-and-partners/independent-research/data-sharing-request-process.html.



