Abstract
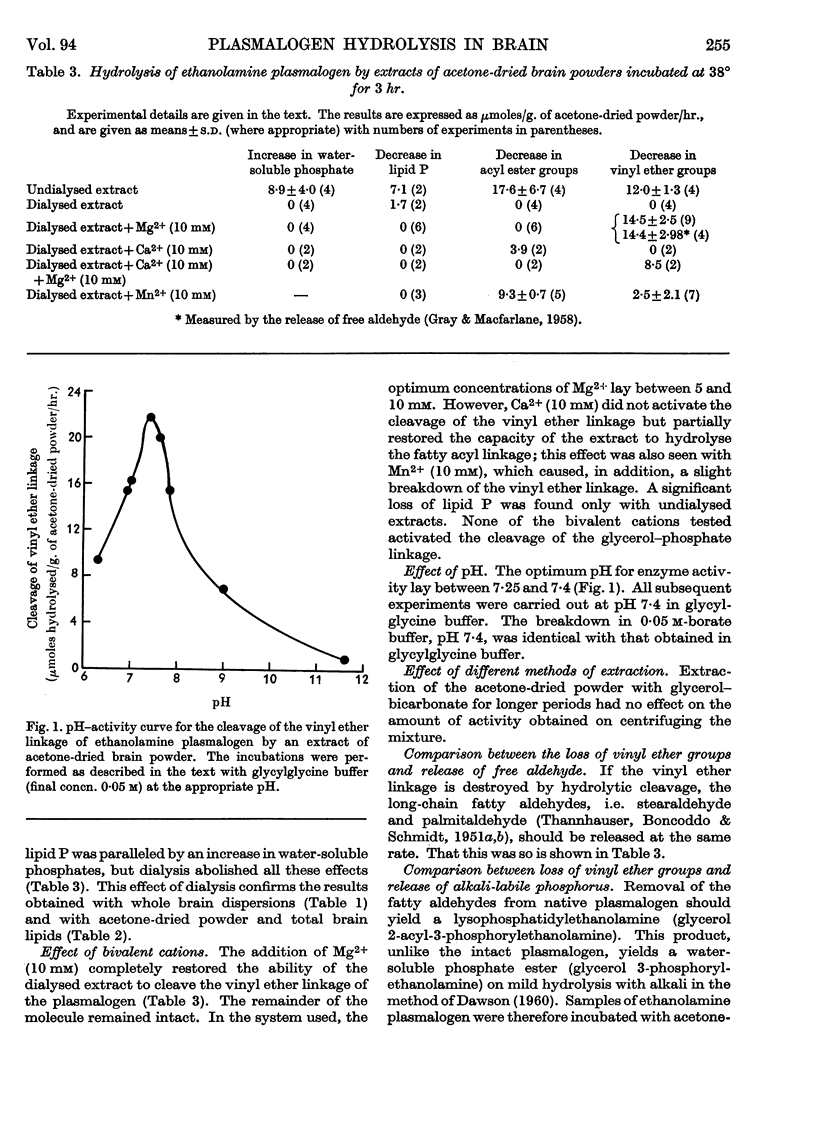
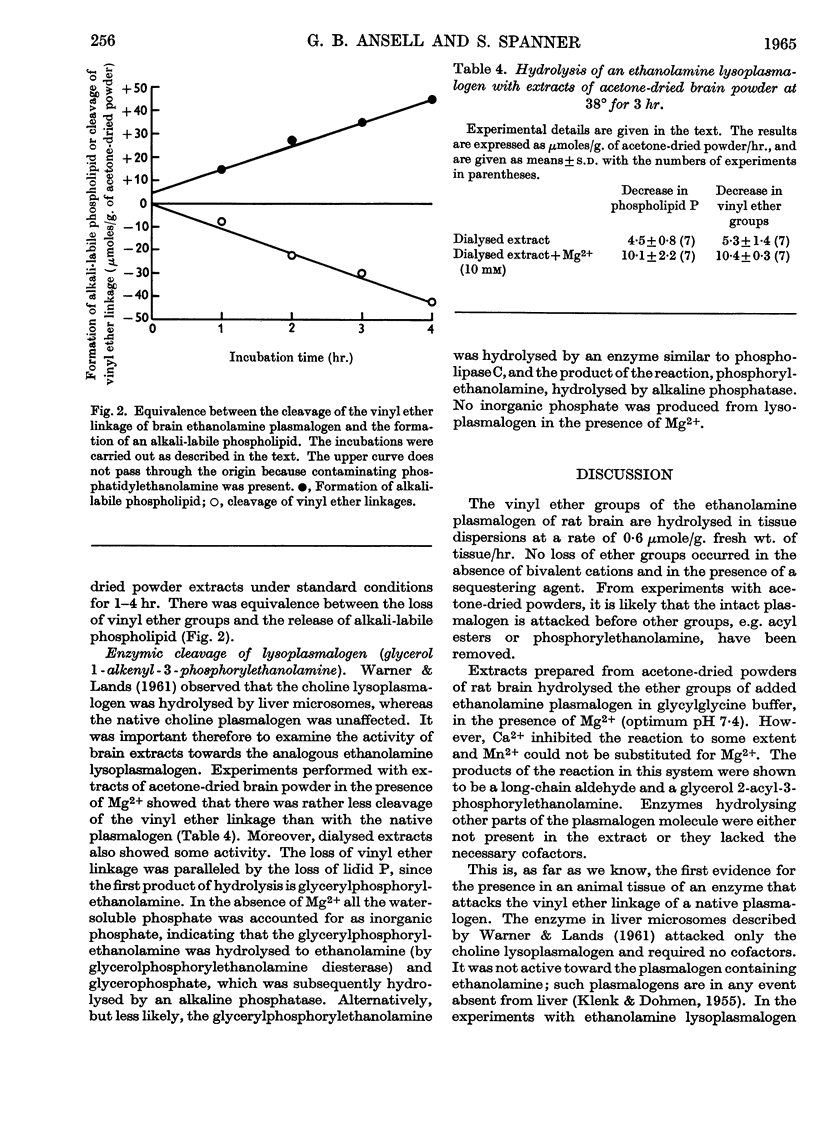
1. There was a significant decrease in the amount of endogenous ethanolamine phospholipids when preparations of whole brain were incubated in bicarbonate–Ringer solutions, leading in particular to the hydrolysis of vinyl ether groups. 2. The hydrolysis of ethanolamine phospholipids in such preparations was abolished in the absence of bivalent cations. 3. An enzyme present in extracts of acetone-dried brain powders that cleaved the vinyl ether linkage in ethanolamine plasmalogen maximally at pH 7·4 required Mg2+ for activity. 4. The cleavage of the vinyl ether linkage of an ethanolamine lysoplasmalogen was enhanced in the presence of Mg2+ but the requirement was not absolute.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANSELL G. B., SPANNER S. THE ALKALINE HYDROLYSIS OF THE ETHANOLAMINE PLASMALOGEN OF BRAIN TISSUE. J Neurochem. 1963 Dec;10:941–945. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb11921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AXELROD J., REICHENTHAL J., BRODIE B. B. The direct determination of phosphatidyl ethanolamine and phosphatidyl serine in plasma and red blood cells. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):903–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLEMAN R., HUEBSCHER G. Metabolism of phospholipids. V. Studies of phosphatidic acid phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:479–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90600-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON A. N., WAJDA M. Analysis of lipids from fresh and preserved adult human brains. Biochem J. 1962 Jan;82:113–117. doi: 10.1042/bj0820113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON A. N., WAJDA M. Metabolism of myelin lipids: estimation and separation of brain lipids in the developing rabbit. J Neurochem. 1959 Oct;4:353–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1959.tb13217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M., HEMINGTON N., DAVENPORT J. B. Improvements in the method of determining individual phospholipids in a complex mixture by successive chemical hydrolyses. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:497–501. doi: 10.1042/bj0840497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. The phospholipase B of liver. Biochem J. 1956 Sep;64(1):192–196. doi: 10.1042/bj0640192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Thompson W. The triphosphoinositide phosphomonoesterase of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):244–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0910244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., ASCOLI I., LEES M., MEATH J. A., LeBARON N. Preparation of lipide extracts from brain tissue. J Biol Chem. 1951 Aug;191(2):833–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLAI-HATCHARD J., MAGEE W. L., THOMPSON R. H., WEBSTER G. R. The formation of lysophosphatides from di-acyl phosphatides by brain preparations. J Neurochem. 1962 Nov-Dec;9:545–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb04209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTFRIED E. L., RAPPORT M. M. The biochemistry of plasmalogens. I. Isolation and characterization of phosphatidal choline, a pure native plasmalogen. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY G. M., MACFARLANE M. G. Separation and composition of the phospholipids of ox heart. Biochem J. 1958 Nov;70(3):409–425. doi: 10.1042/bj0700409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLENK E., DOHMEN H. Die Isolierung von Colaminkephalin aus Rinderleber. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1955;299(5-6):248–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNAUFF H. G., MARX D., MAYER G. [The behavior of proteins and serine- and colamine-containing phosphatides of the central nervous system during insulin hypoglycemia]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1961 Dec 21;326:227–234. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1961.326.1.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARPLES E. A., THOMPSON R. H. The distribution of phospholipase B in mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:123–127. doi: 10.1042/bj0740123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCILWAIN H., BUDDLE H. L. Techniques in tissue metabolism. I. A mechanical chopper. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):412–420. doi: 10.1042/bj0530412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., NORTON W. T. Chemistry of the lipids. Annu Rev Biochem. 1962;31:103–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.31.070162.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODNIGHT R. Cerebral diphosphoinositide breakdown: activation, complexity and distribution in animal (mainly nervous) tissues. Biochem J. 1956 Jun;63(2):223–231. doi: 10.1042/bj0630223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLOANE-STANLEY G. H. Anaerobic reactions of phospholipins in brain suspensions. Biochem J. 1953 Mar;53(4):613–619. doi: 10.1042/bj0530613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH S. W., WEISS S. B., KENNEDY E. P. The enzymatic dephosphorylation of phosphatidic acids. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):915–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN I., SHAPIRO B. A rapid and simple method for the determination of esterified fatty acids and for total fatty acids in blood. J Clin Pathol. 1953 May;6(2):158–160. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.2.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THANNAHAUSER S. J., BONCODDO N. F., SCHMIDT G. Studies of acetal phospholipides of brain. III. The fatty aldehydes present in crystalline acetal alpha-phospholipide of brain. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jan;188(1):427–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THANNHAUSER S. J., BONCODDO N. F., SCHMIDT G. Studies of acetal phospholipides of brain. I. Procedure of isolation of crystallized acetal phospholipide from brain. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jan;188(1):417–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYRRELL L. W. A cephalinase in nervous tissue. Nature. 1950 Aug 19;166(4216):310–310. doi: 10.1038/166310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W., Dawson R. M. The hydrolysis of triphosphoinositide by extracts of ox brain. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):233–236. doi: 10.1042/bj0910233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W., Dawson R. M. The triphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj0910237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER H. R., LANDS W. E. The metabolism of plasmalogen: enzymatic hydrolysis of the vinyl ether. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2404–2409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER G. R. On the acylation of lysolecithin by rat-liver and brain mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 5;64:573–575. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL-MALHERBE H., GREEN R. H. Ammonia formation in brain. I. Studies on slices and suspensions. Biochem J. 1955 Oct;61(2):210–218. doi: 10.1042/bj0610210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


