Abstract
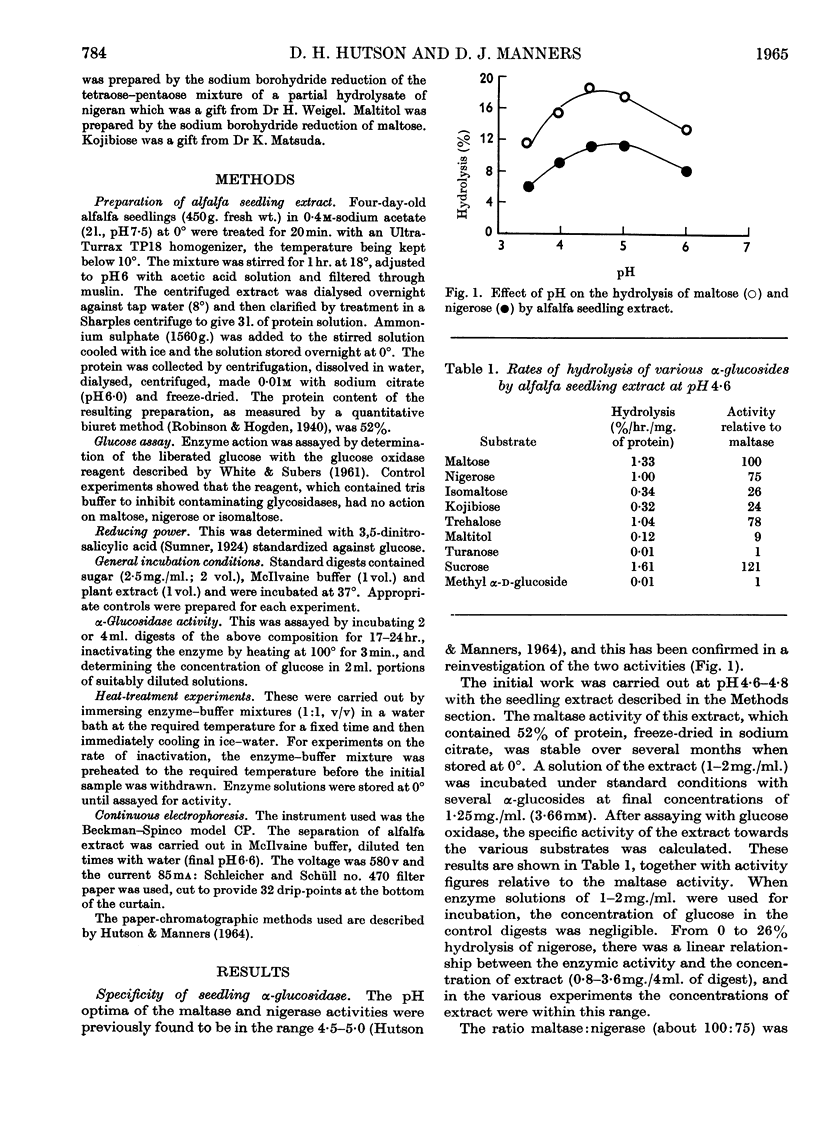
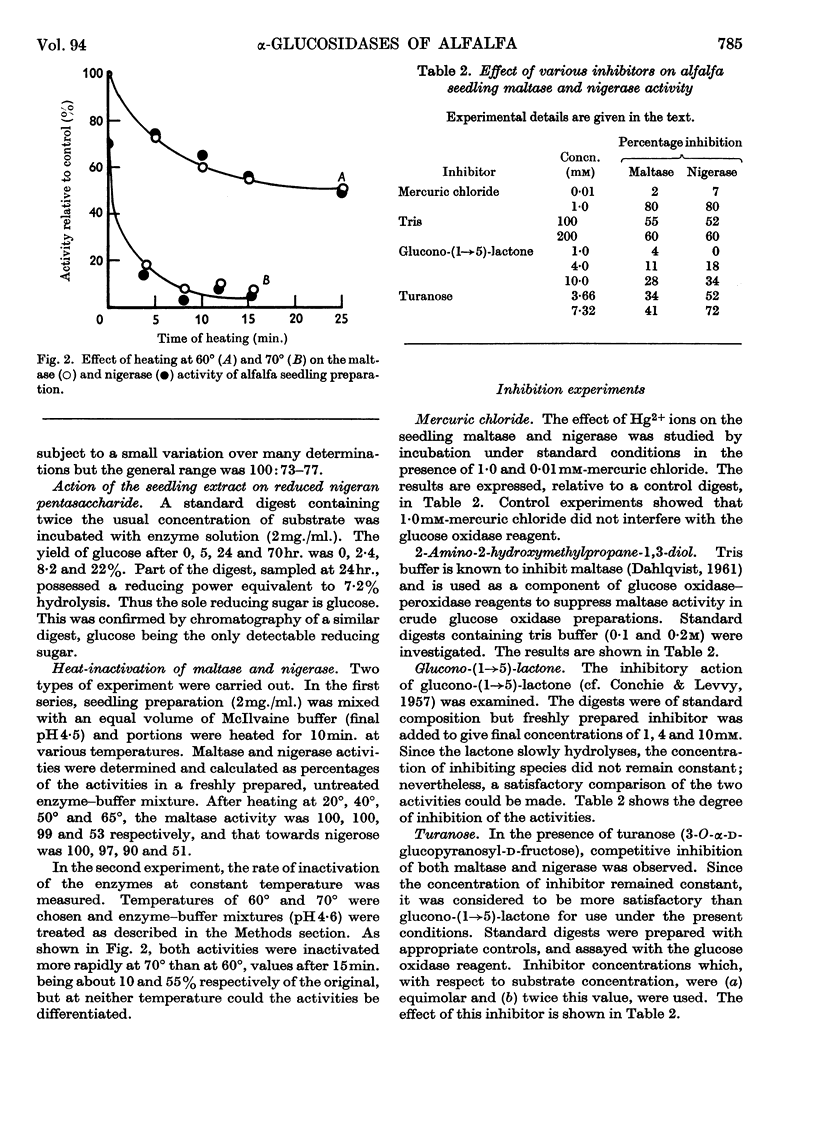
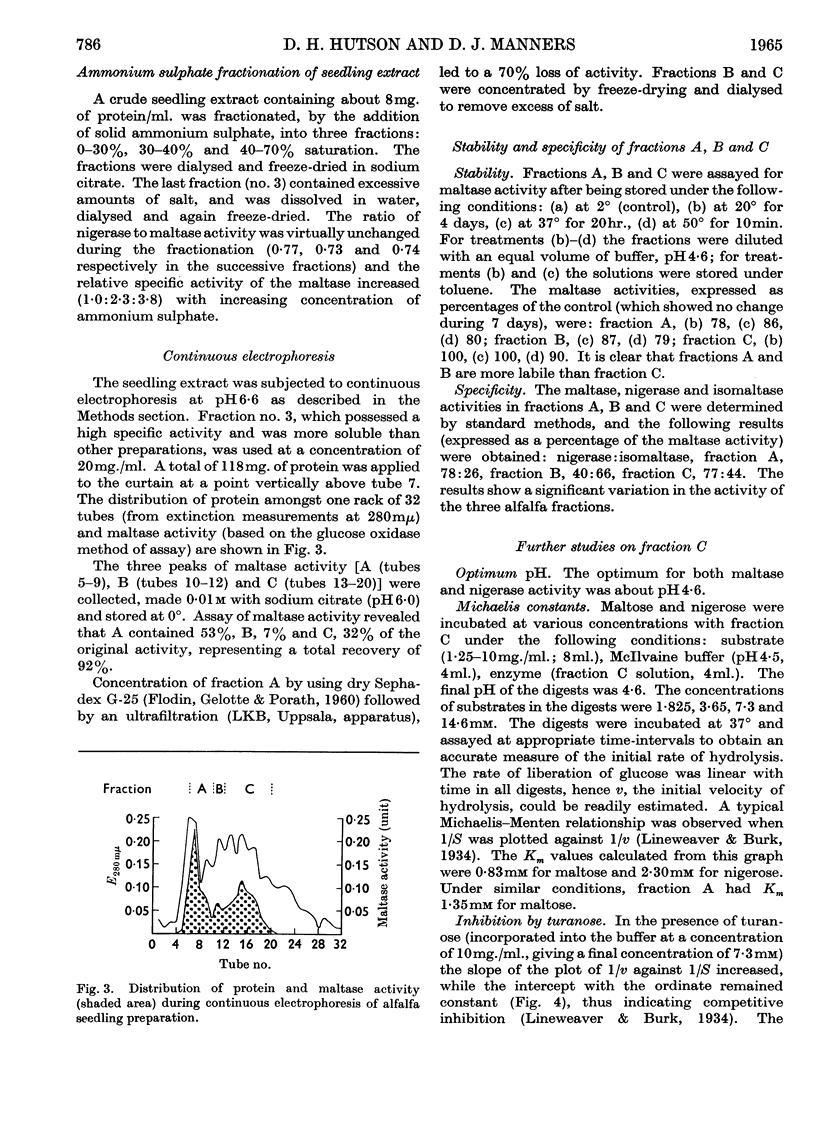
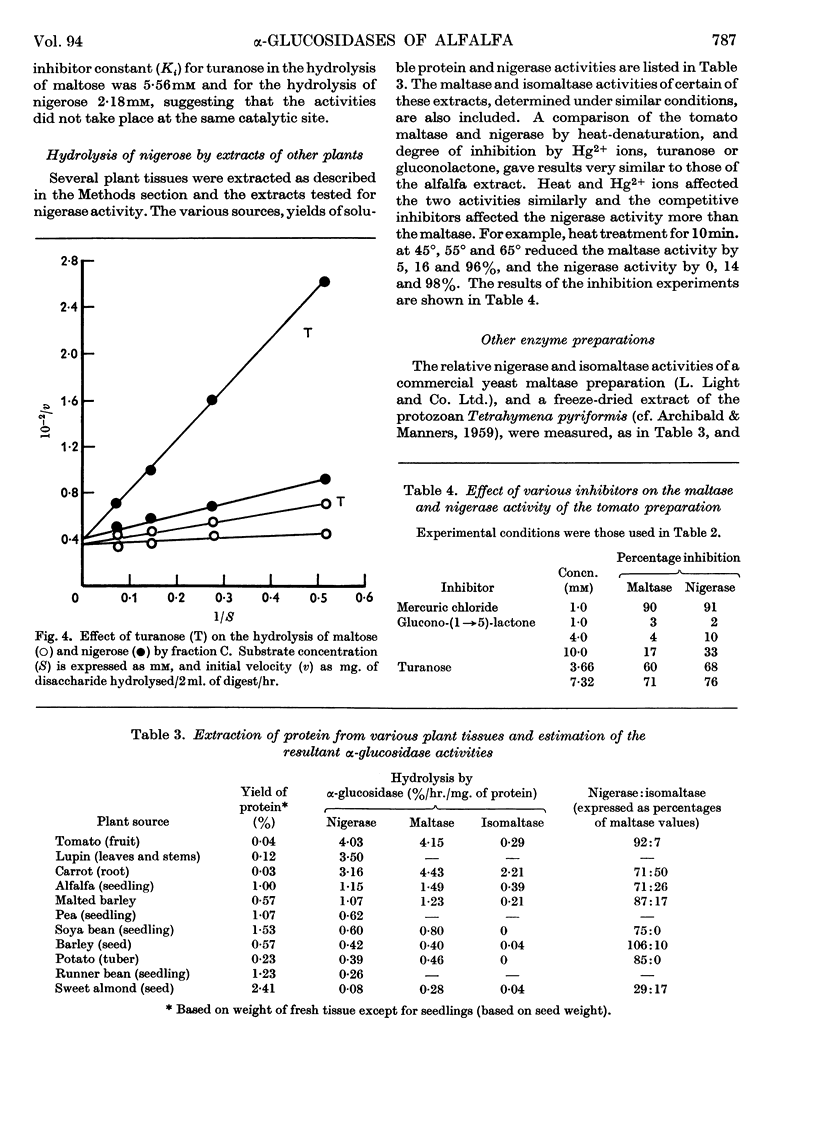
1. Enzyme preparations from 11 plant sources, from yeast and from the protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis show nigerase activity, which, in most preparations, was 70–90% of that towards maltose. 2. These enzyme preparations also hydrolysed isomaltose, but there was a wide variation in relative maltase to isomaltase activity. 3. The maltase and nigerase activities of alfalfa and tomato preparations could not be differentiated by heat inactivation or inhibitor methods. However, with turanose used as a competitive inhibitor, evidence suggesting that maltose and nigerose are hydrolysed at different catalytically active sites in the alfalfa preparation was obtained. 4. It is probable that the alfalfa α-glucosidase exists as a mixture of isoenzymes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHIBALD A. R., MANNERS D. J. Studies on carbohydratemetabolizing enzymes. 2. Trans-alpha-glucosylation by extracts of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Biochem J. 1959 Oct;73:292–295. doi: 10.1042/bj0730292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILEY R. W., BOURNE E. J. Intracellular glycosidases of dextran-producing bacteria. Nature. 1961 Jul 15;191:277–278. doi: 10.1038/191277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILEY R. W., ROBERTON A. M. Carbohydrases of a rumen strain of Lactobacillus bifidus. 2. The intracellular alpha-1-6-glucosidase (isomaltodextrinase). Biochem J. 1962 Feb;82:272–277. doi: 10.1042/bj0820272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONCHIE J., LEVVY G. A. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. Biochem J. 1957 Feb;65(2):389–395. doi: 10.1042/bj0650389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. Determination of maltase and isomaltase activities with a glucose-oxidase reagent. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:547–551. doi: 10.1042/bj0800547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLODIN P., GELOTTE B., PORATH J. A method for concentrating solutes of high molecular weight. Nature. 1960 Nov 5;188:493–494. doi: 10.1038/188493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESTRIN S., LINDEGREN C. C. Carbohydrases in Saccharomyces haploid stocks of defined genotype. II. Gene-controlled induction of glucosidases by alpha-glucosides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Jul;38:317–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson D. H., Manners D. J. Studies on carbohydrate-metabolizing enzymes. 12. A survey of the carbohydrases of alfalfa. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):545–550. doi: 10.1042/bj0930545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUKOMSKAIA I. S. [Degradation of trehalose, kojibiose, nigerose, maltose and isomaltose by liver enzymes]. Biokhimiia. 1962 Sep-Oct;27:875–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L., Møller F. MULTIPLE FORMS OF ENZYMES: TISSUE, ONTOGENETIC, AND SPECIES SPECIFIC PATTERNS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 May;45(5):753–763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.5.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAZUR J. H., KLEPPE K. The hydrolysis of alpha-D-glucosides by amyloglucosidase from Aspergillus niger. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1002–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. J., HALVORSON H. O. The components of maltozymase in yeast, and their behavior during deadaptation. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):186–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.186-198.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE J. W., Jr, SUBERS M. H. A glucose oxidase reagent for maltase assay. Anal Biochem. 1961 Aug;2:380–384. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(61)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


