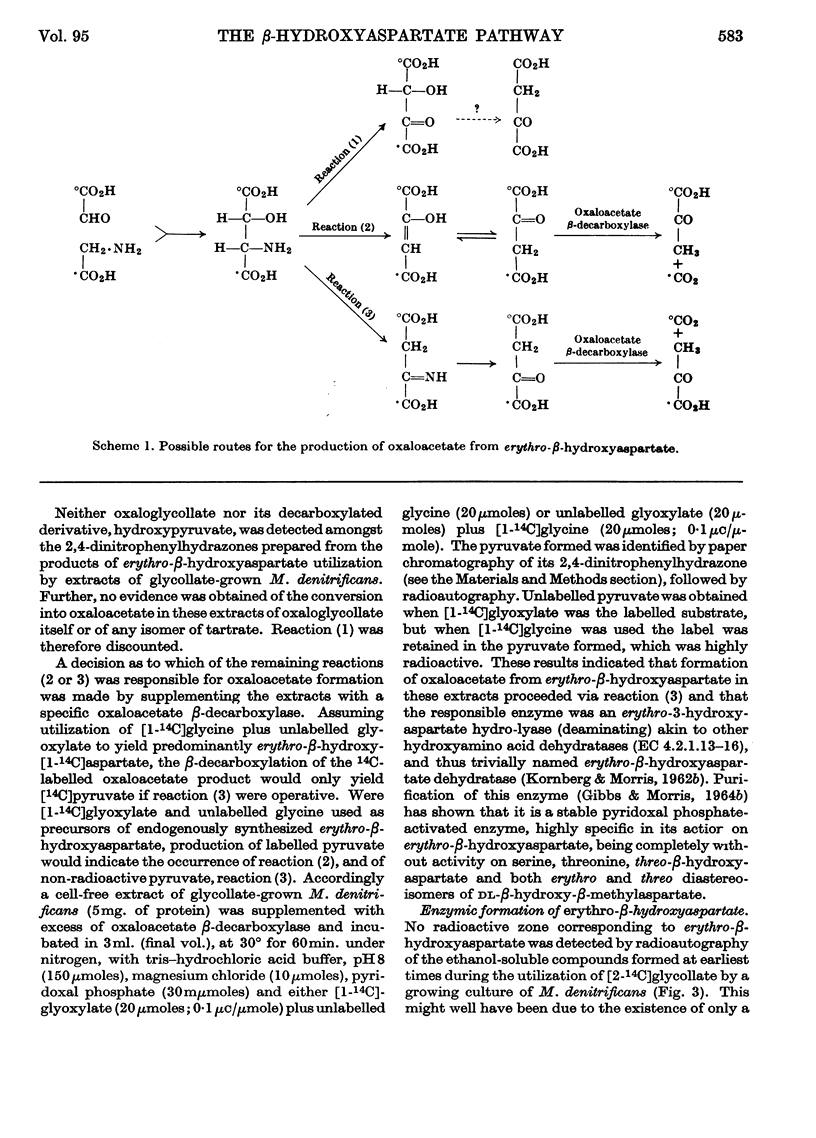
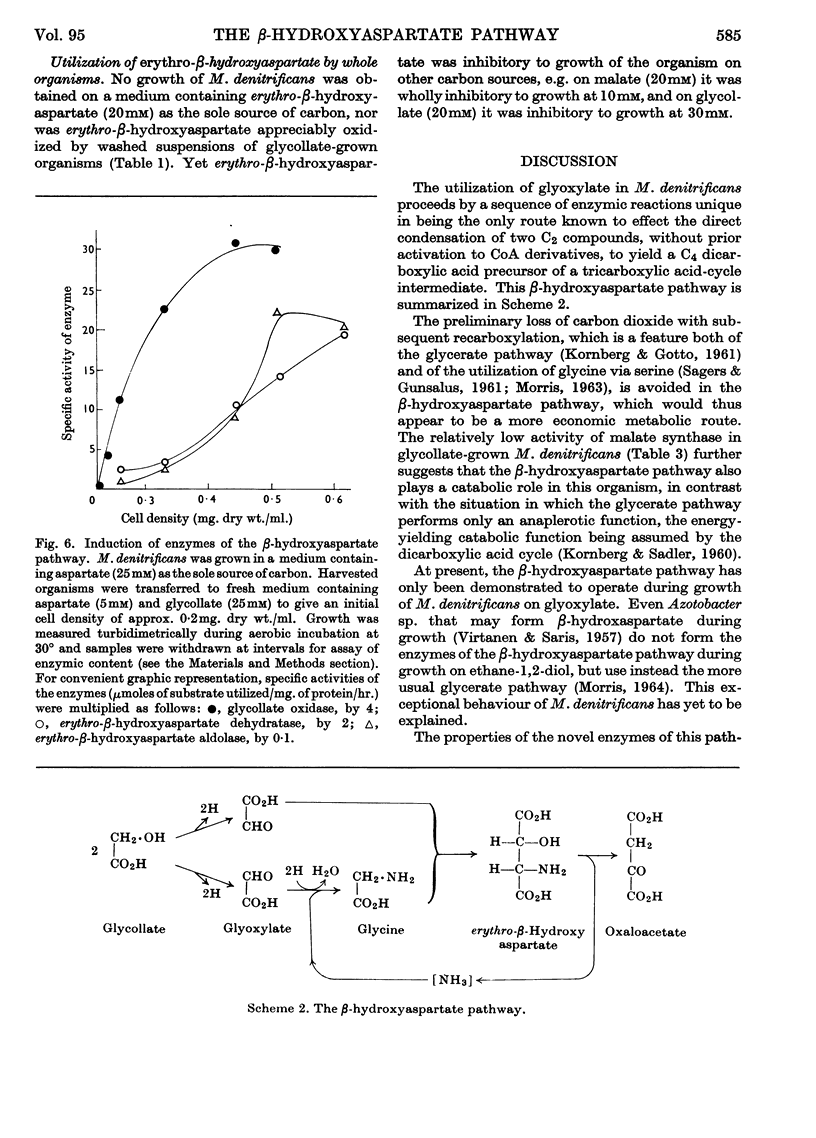
Abstract
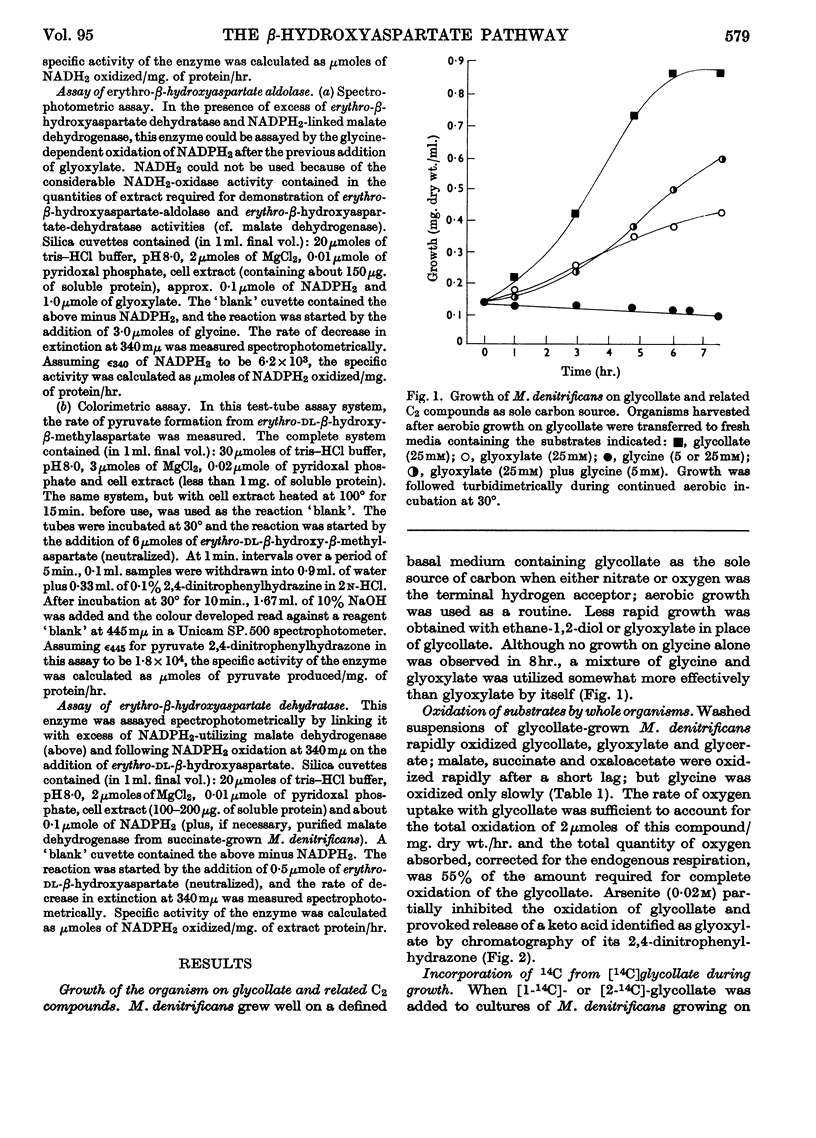
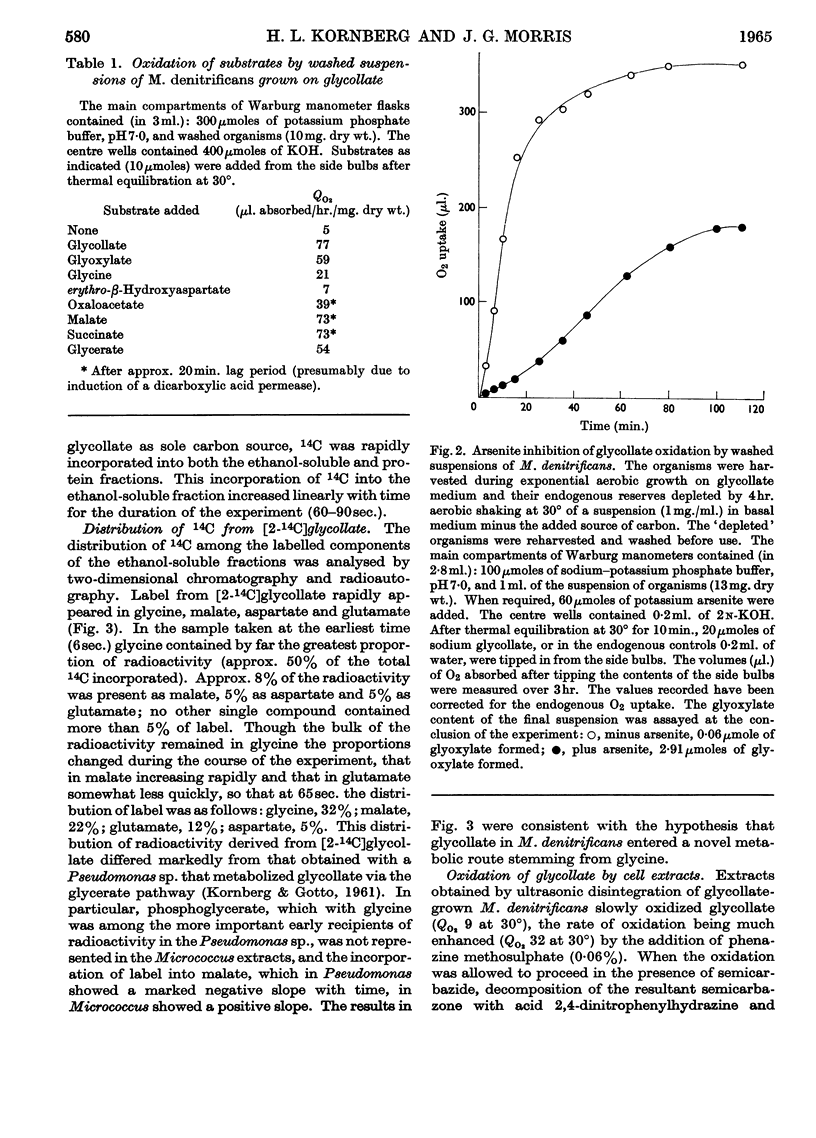
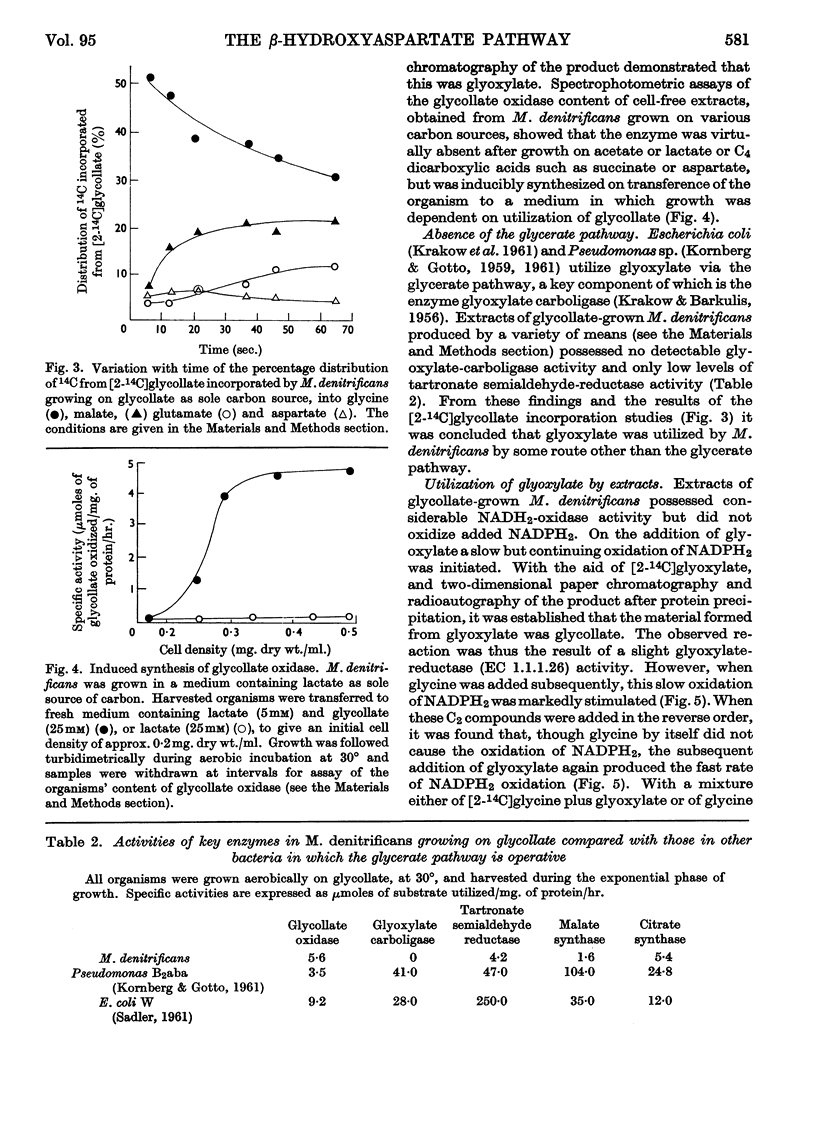
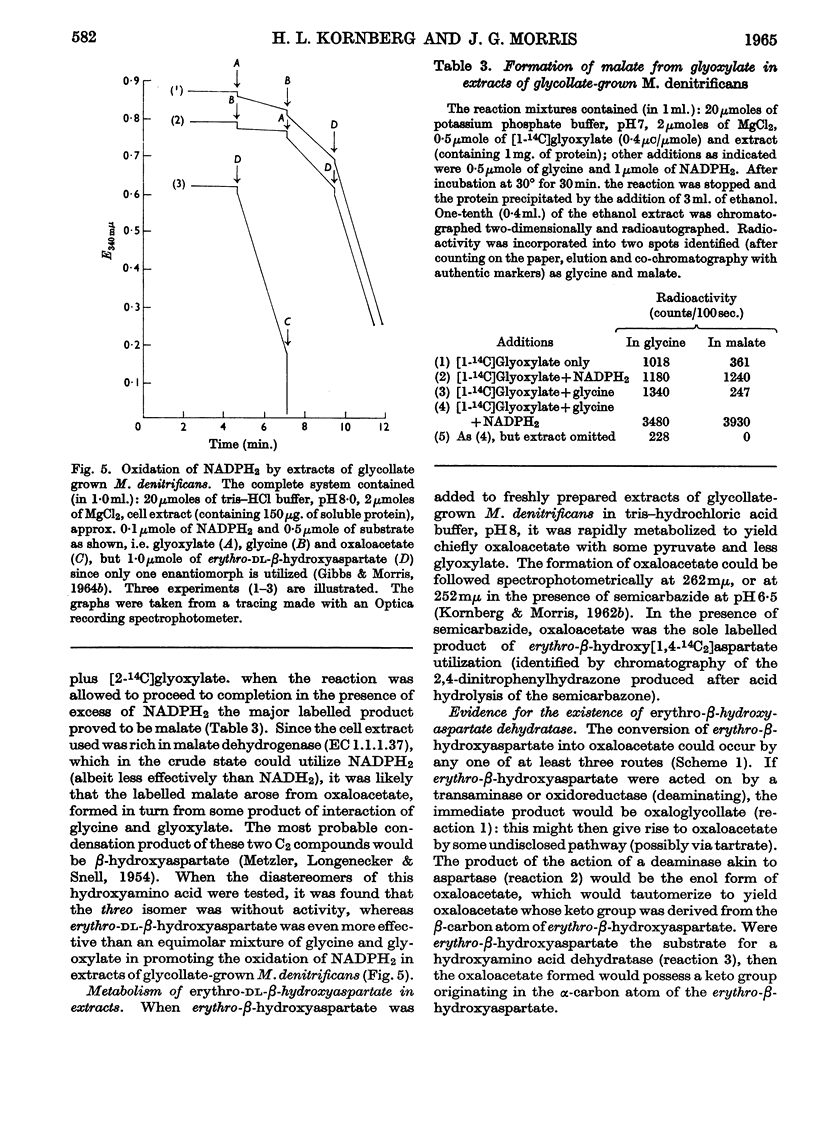
1. Micrococcus denitrificans utilized glycollate as sole carbon source for aerobic growth. Glyoxylate was utilized less well, and though glycine alone did not support growth it enhanced growth on glyoxylate. 2. During growth on glycollate, 14C was incorporated from [2-14C]glycollate into glycine and thence into aspartate, malate and glutamate. No phosphoglycerate was labelled at the earliest times. 3. Glyoxylate was the first product of glycollate utilization, and glycollate oxidase was inducibly formed on transfer of the organism to glycollate-containing media. 4. Extracts of glycollate-grown M. denitrificans contained negligible glyoxylate-carboligase activity and only low tartronate semialdehyde-reductase activity. 5. erythro-β-Hydroxyaspartate is a key intermediate in glyoxylate utilization by this organism. Enzymes catalysing (a) the synthesis of erythro-β-hydroxyaspartate from glyoxylate and glycine, and (b) the conversion of erythro-β-hydroxyaspartate into oxaloacetate, were inducibly formed during growth on glycollate and on other substrates yielding glyoxylate. Methods for the assay of these enzymes were developed. 6. It is concluded that in M. denitrificans the biosynthesis of cell materials from glycollate is accomplished by the `β-hydroxyaspartate pathway', a novel metabolic route that may also perform a catabolic role in glyoxylate oxidation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKULIS S. S., KRAKOW G. Conversion of glyoxylate to hydroxypyruvate by extracts of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Sep;21(3):593–594. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS R. G., MORRIS J. G. ASSAY AND PROPERTIES OF BETA-HYDROXYASPARTATE ALDOLASE FROM MICROCOCCUS DENITRIFICANS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 1;85:501–503. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTO A. M., KORNBERG H. L. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. 7. Preparation and properties of crystalline tartronic semialdehyde reductase. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:273–284. doi: 10.1042/bj0810273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORTON A. A., KORNBERG H. L. OXALOACETATE 4-CARBOXY-LYASE FROM PSEUDOMONAS OVALIS CHESTER. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 26;89:381–383. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. A press for disrupting bacteria and other micro-organisms. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):97–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS W. T. Glutamic-aspartic transaminase. VI. The reaction with certain beta-substituted aspartic acid analogues. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1121–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., GOTTO A. M. Formation of malate from glycollate by Pseudomonas ovalis Chester. Nature. 1959 Jun 27;183:1791–1793. doi: 10.1038/1831791a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., GOTTO A. M. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. 6. Synthesis of cell constituents from glycollate by Pseudomonas sp. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:69–82. doi: 10.1042/bj0780069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., MORRIS J. G. Beta-Hydroxyaspartate pathway: a new route for biosyntheses from glyoxylate. Nature. 1963 Feb 2;197:456–457. doi: 10.1038/197456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., MORRIS J. G. Enzymic formation of oxaloacetate from erythro beta-hydroxyaspartate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:537–540. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., MORRIS J. G. The influence of growth substrates on oxaloacetate formation from beta-hydroxyasparate by Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 4;65:378–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., PHIZACKERLEY P. J., SADLER J. R. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. 5. Biosynthesis of cell materials from acetate in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1960 Dec;77:438–445. doi: 10.1042/bj0770438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., SADLER J. R. Microbial oxidation of glycollate via a dicarboxylic acid cycle. Nature. 1960 Jan 16;185:153–155. doi: 10.1038/185153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L. Selective utilization of metabolic routes by Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:257–260. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. I. The incorporation of [2-14C] acetate by Pseudomonas fluorescens, and by a Corynebacterium, grown on ammonium acetate. Biochem J. 1958 Mar;68(3):535–542. doi: 10.1042/bj0680535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOW G., BARKULIS S. S., HAYASHI J. A. Glyoxylic acid carboligase: an enzyme present in glycolate-grown Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:509–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.509-518.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS J. G. THE ASSIMILATION OF 2-C COMPOUNDS OTHER THAN ACETATE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Aug;32:167–170. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGERS R. D., GUNSALUS I. C. Intermediatry metabolism of Diplococcus glycinophilus. I. Glycine cleavage and one-carbon interconversions. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:541–549. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.541-549.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELITCH I., OCHOA S. Oxidation and reduction of glycolic and glyoxylic acids in plants. I. Glycolic and oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1953 Apr;201(2):707–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


