Abstract
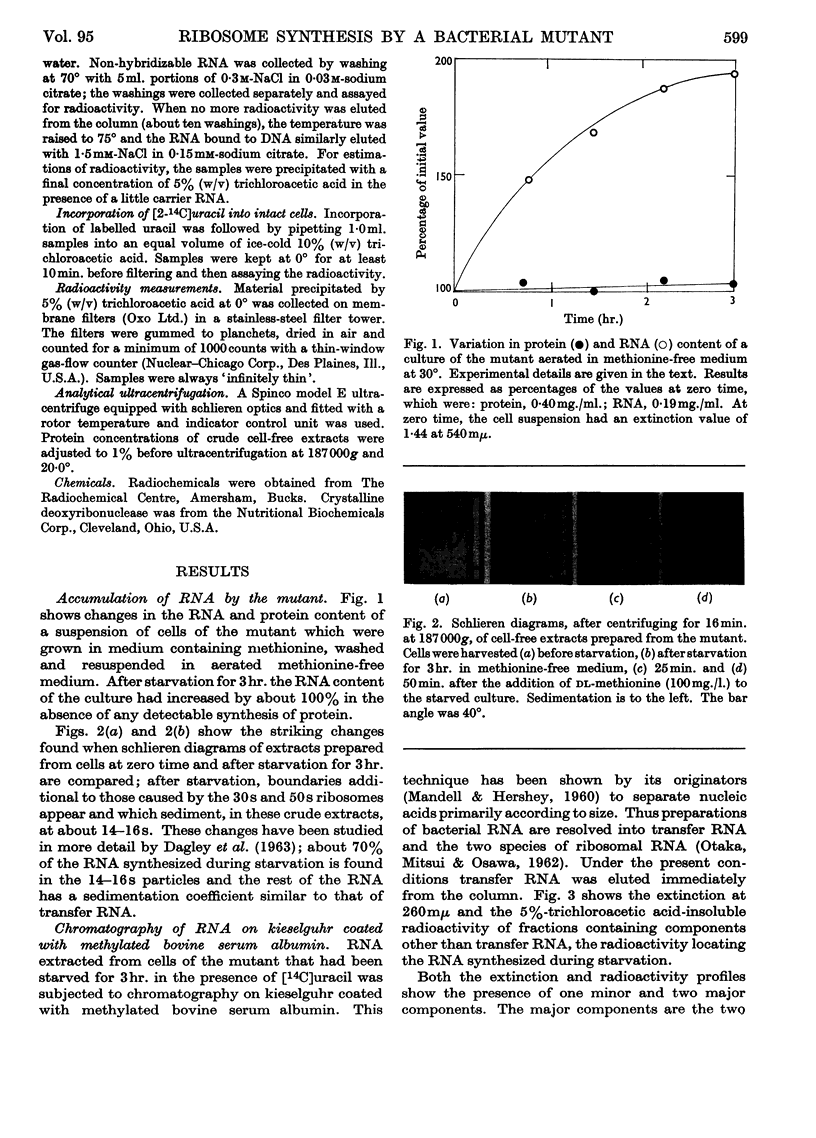
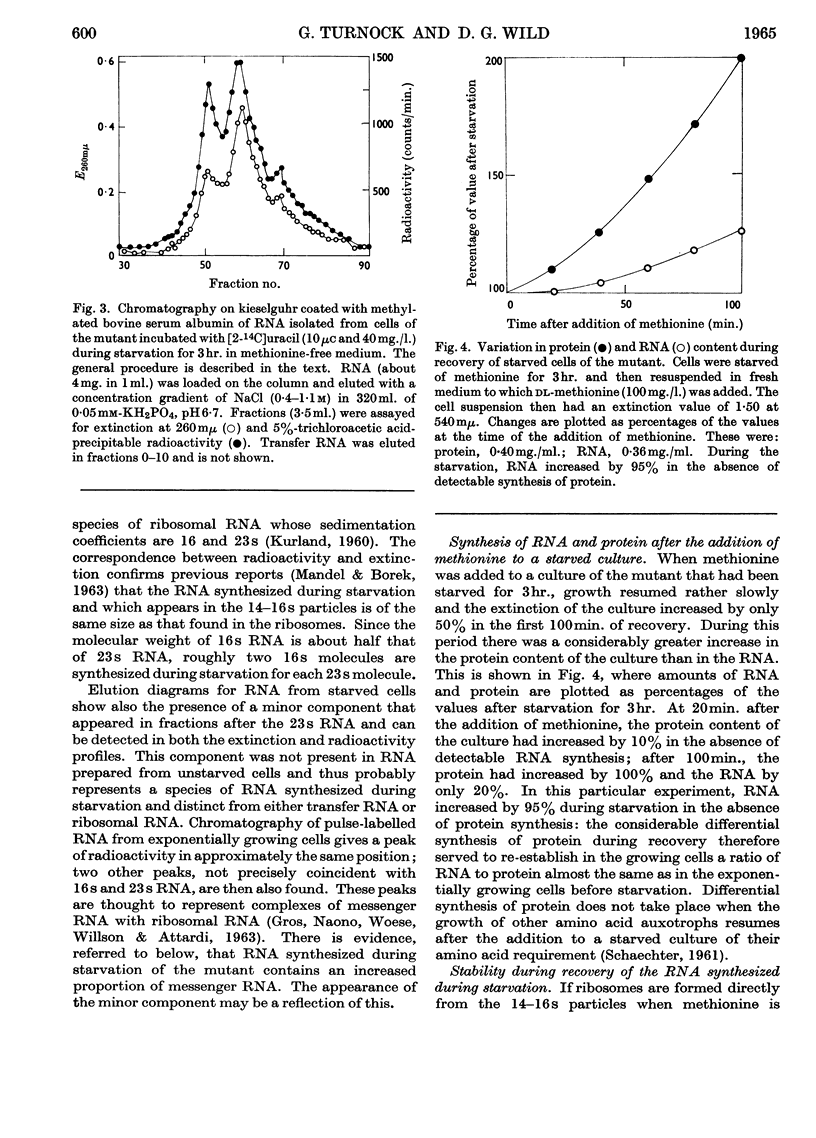
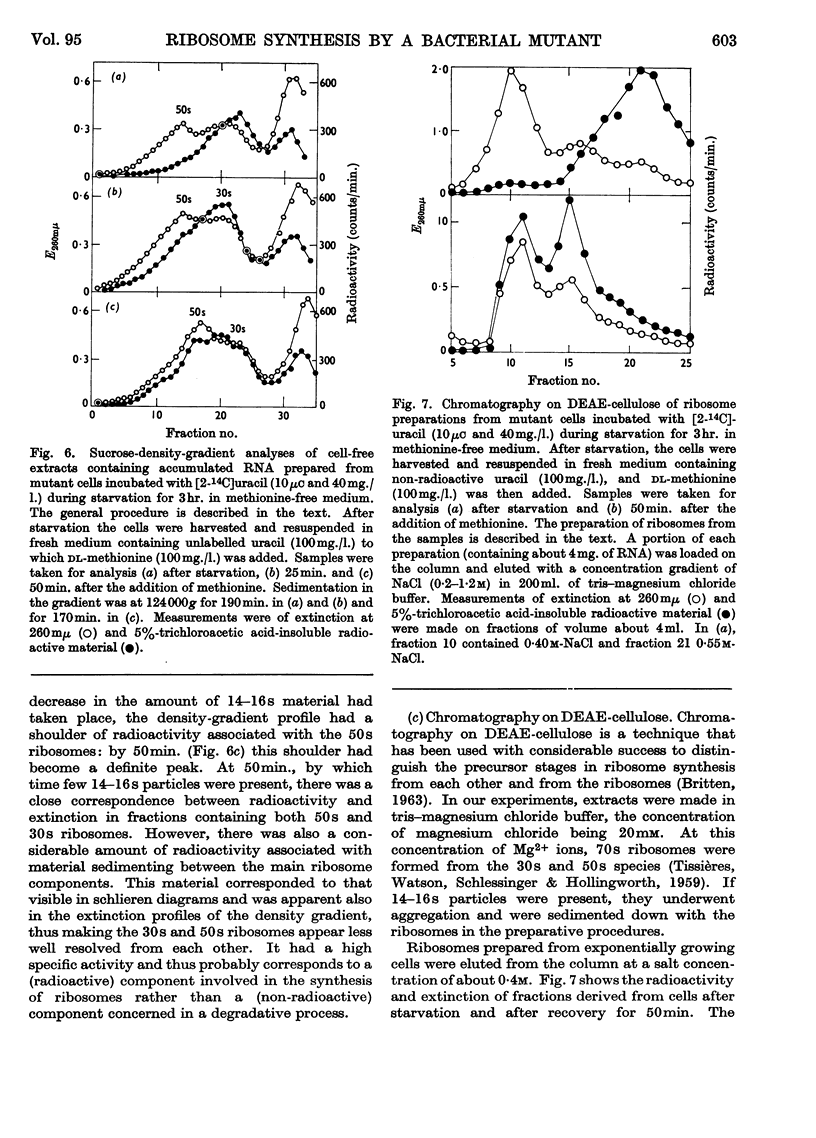
1. When the methionine-requiring mutant 58–161 of Escherichia coli was starved of methionine, ribonucleic acid was made in the absence of protein synthesis. 2. Most of this ribonucleic acid was similar to that found in ribosomes but was contained in particles differing from ribosomes both in sedimentation coefficient and in chromatographic behaviour on diethylaminoethylcellulose. 3. When methionine was added to a starved culture, the ribonucleic acid synthesized during starvation was almost completely undegraded as growth resumed. A transient loss of 5–10% could be largely attributed to breakdown of messenger ribonucleic acid accumulated during starvation. 4. After the addition of methionine, ribosomes were formed from the particles, and during this period preferential synthesis of ribosomal protein took place. 5. It is suggested that under these conditions the direct synthesis of ribosomes from the particles may occur.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOLTON E. T., McCARTHY B. J. A general method for the isolation of RNA complementary to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1390–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOREK E., RYAN A., ROCKENBACH J. Nucleic acid metabolism in relation to the lysogenic phenomenon. J Bacteriol. 1955 Apr;69(4):460–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.4.460-467.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTEN R. The pattern of flow and sequential stages in bacterial nucleic acid synthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 10;108:273–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., SYKES J. Effect of drugs upon components of bacterial cytoplasm. Nature. 1959 Jun 6;183(4675):1608–1609. doi: 10.1038/1831608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., TURNOCK G., WILD D. G. THE ACCUMULATION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID BY A MUTANT OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:555–566. doi: 10.1042/bj0880555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISSNER E., BOREK E. A new enzyme of RNA synthesis: RNA methylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1199–1203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. A press for disrupting bacteria and other micro-organisms. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):97–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND C. G., MAALOE O. Regulation of ribosomal and transfer RNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1962 Mar;4:193–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND C. G., NOMURA M., WATSON J. D. The physical properties of the chloromycetin particles. J Mol Biol. 1962 May;4:388–394. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL L. R., BOREK E. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF METHYLATED BASES IN RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1963 May-Jun;2:555–560. doi: 10.1021/bi00903a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDGLEY J. E., McCARTHY B. J. The synthesis and kinetic behavior of deoxyribonucleic acid-like ribonucleic acid in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 26;61:696–717. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDGLEY J. E. The kinetics of transfer ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 26;68:354–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKADA D., ANDERSON I. A., MAGASANIK B. FATE OF THE RIBOSOMAL RNA PRODUCED BY A "RELAXED" MUTANT OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Aug;9:472–488. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80220-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C., GROS F. Metabolic instability of the ribonucleic acid synthesized by Escherichia coli in the presence of chloromycetin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):513–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90521-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C. Properties of a bacterial mutant lacking amino acid control of RNA synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 26;68:365–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTAKA E., MITSUI H., OSAWA S. On the ribonucleic acid synthesized in a cell-free system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Mar 15;48:425–430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARDEE A. B., PRESTIDGE L. S. The dependence of nucleic acid synthesis on the presence of amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jun;71(6):677–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.6.677-683.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M. Patterns of cellular control during unbalanced growth. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:53–62. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLS B. H. RNA SYNTHESIS AND RIBOSOME PRODUCTION IN PUROMYCIN-TREATED CELLS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 17;80:230–241. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S., BRENNER S. A genetic locus for the regulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Dec 15;47:2005–2014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNOCK G., WILD D. G. Accumulation of ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli due to the action of 5-methyl tryptophan. Nature. 1963 Feb 9;197:597–598. doi: 10.1038/197597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



