Abstract
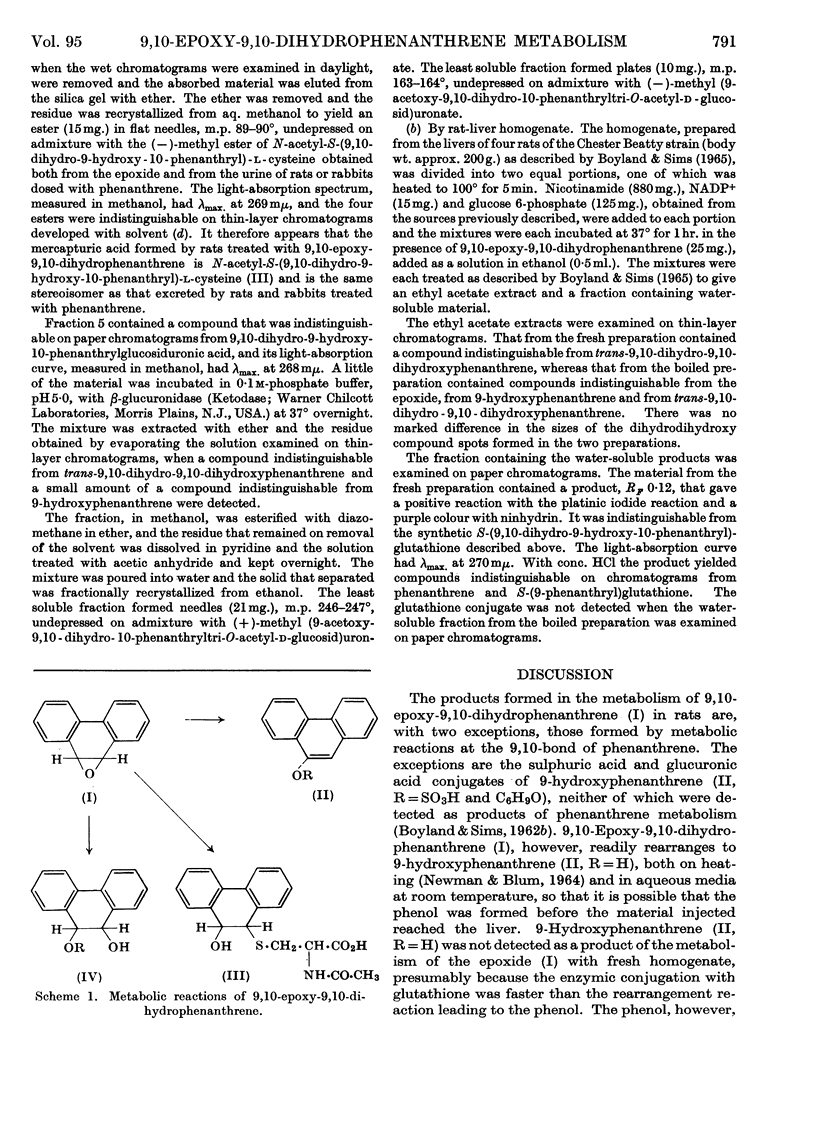
1. 9,10-Epoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene is converted by rats into trans-9,10-dihydro-9,10-dihydroxyphenanthrene and its conjugates and into N-acetyl-S-(9,10-dihydro-9-hydroxy-10-phenanthryl)-l- cysteine. Small amounts of 9-phenanthryl sulphate and glucosiduronate are also formed, together with 9-hydroxy-10-phenanthryl sulphate. 2. The epoxide readily rearranges to 9-hydroxyphenanthrene and reacts with water to give the dihydrodihydroxy compound and with N-acetylcysteine to give the mercapturic acid. One of the diastereoisomeric forms of the methyl ester of the mercapturic acid is identical with the ester of the mercapturic acid excreted by rats dosed with the epoxide or by rats and rabbits dosed with phenanthrene. 3. A rat-liver homogenate converts the epoxide into trans-9,10-dihydrodihydroxyphenanthrene and S-(9,10-dihydro-9-hydroxy-10-phenanthryl)glutathione. The latter compound was not formed when boiled rat-liver homogenate was used, but was formed chemically from the epoxide and glutathione under more vigorous conditions. 4. The results provide further indications that the metabolism of aromatic hydrocarbons involves the intermediary formation of epoxides.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYLAND E., SIMS P. METABOLISM OF POLYCYCLIC COMPOUNDS. THE METABOLISM OF 7,12-DIMETHYLBENZ(ALPHA)ANTHRACENE BY RAT-LIVER HOMOGENATES. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:780–787. doi: 10.1042/bj0950780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYLAND E., SIMS P. Metabolism of polycyclic compounds. 12. An acid-labile precursor of 1-naphthylmercapturic acid and naphthol: an N-acetyl-S-(1:2-dihydrohydroxy-naphthyl)-L-cysteine. Biochem J. 1958 Mar;68(3):440–447. doi: 10.1042/bj0680440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYLAND E., SIMS P. Metabolism of polycyclic compounds. 20. The metabolism of phenanthrene in rabbits and rats: mercapturic acids and related compounds. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:564–570. doi: 10.1042/bj0840564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYLAND E., SIMS P. Metabolism of polycyclic compounds. 21. The metabolism of phenanthrene in rabbits and rats: dihydrodihydroxy compounds and related glucosiduronic acids. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:571–582. doi: 10.1042/bj0840571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYLAND E., SIMS P. Metabolism of polycyclic compounds. 22. The metabolism of trans-9,10-dihydro-9,10-dihydroxyphenanthrene in rats. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:583–586. doi: 10.1042/bj0840583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYLAND E., WILLIAMS K. AN ENZYME CATALYSING THE CONJUGATION OF EPOXIDES WITH GLUTATHIONE. Biochem J. 1965 Jan;94:190–197. doi: 10.1042/bj0940190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyland E., Sims P. Metabolism of polycyclic compounds. 16. The metabolism of 1:2-dihydronaphthalene and 1:2-epoxy-1:2:3:4-tetrahydronaphthalene. Biochem J. 1960 Oct;77(1):175–181. doi: 10.1042/bj0770175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIGHT R. H., YOUNG L. Biochemical studies of toxic agents. 11. The occurrence of premercapturic acids. Biochem J. 1958 Sep;70(1):111–119. doi: 10.1042/bj0700111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMS P. Metabolism of polycyclic compounds. 19. The metabolism of phenanthrene in rabbits and rats: phenols and sulphuric esters. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:558–563. doi: 10.1042/bj0840558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


