Abstract
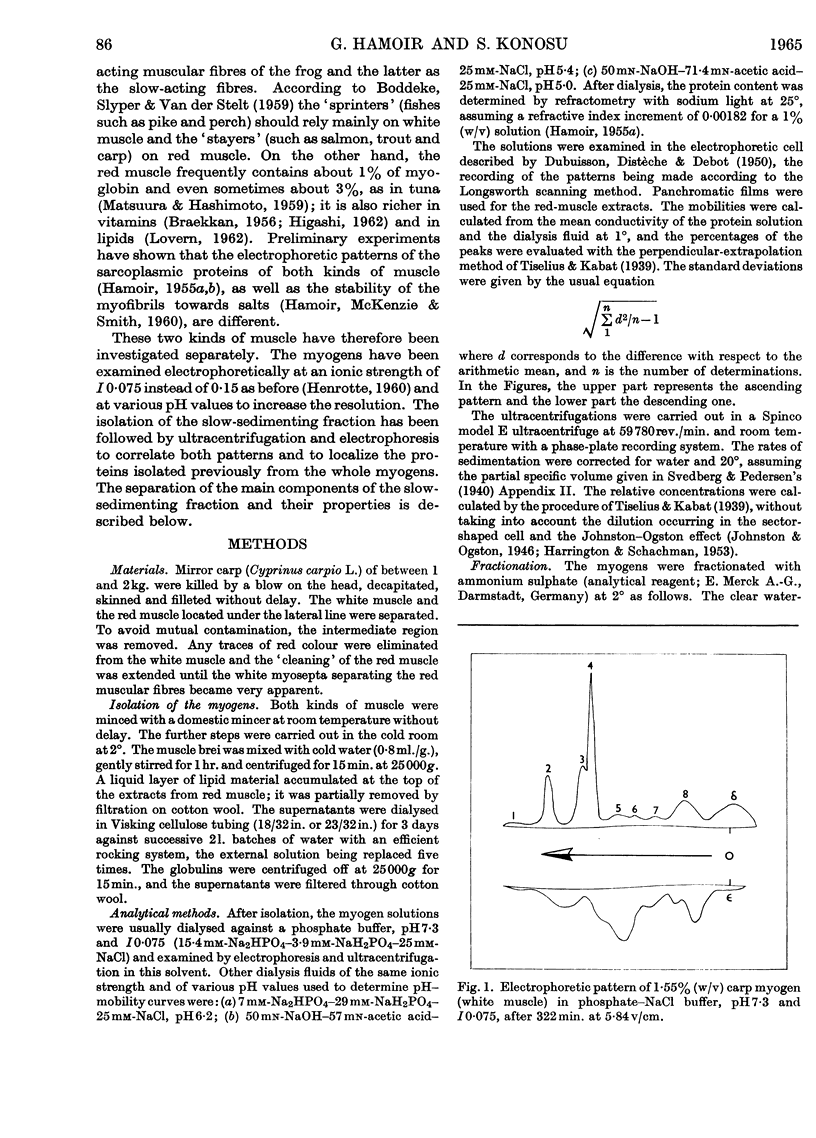
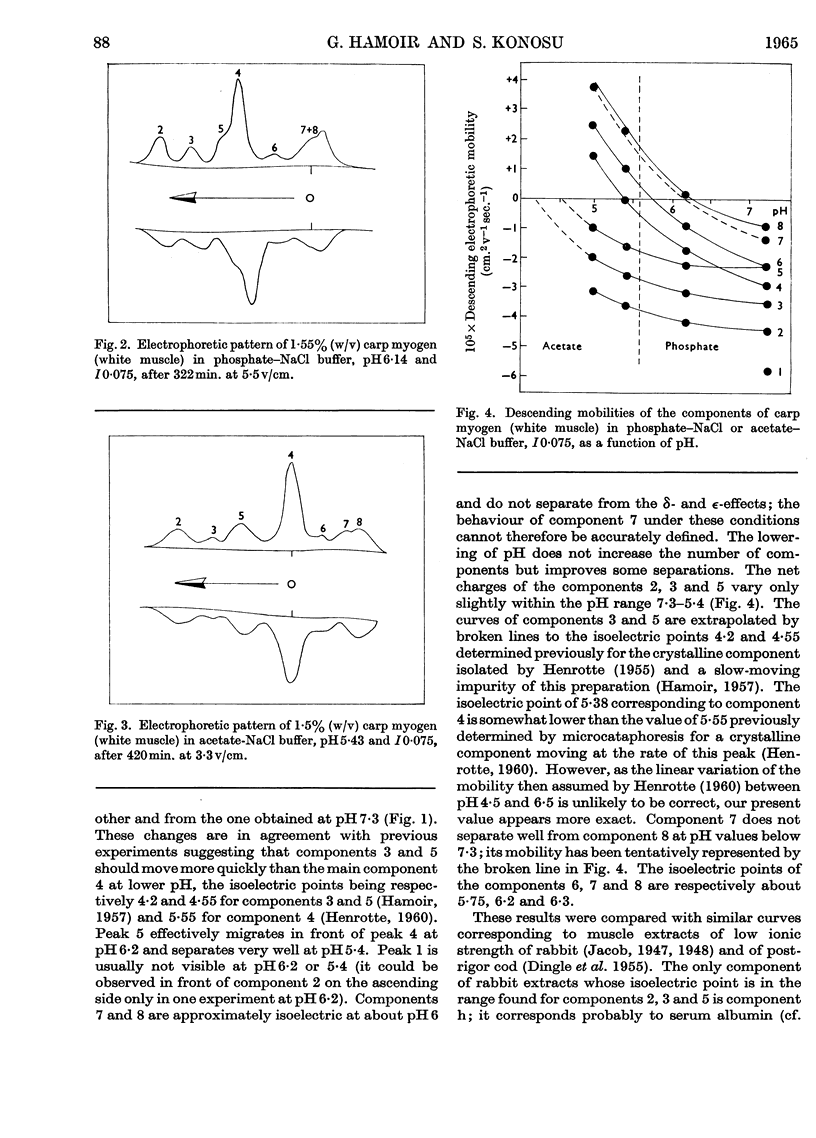
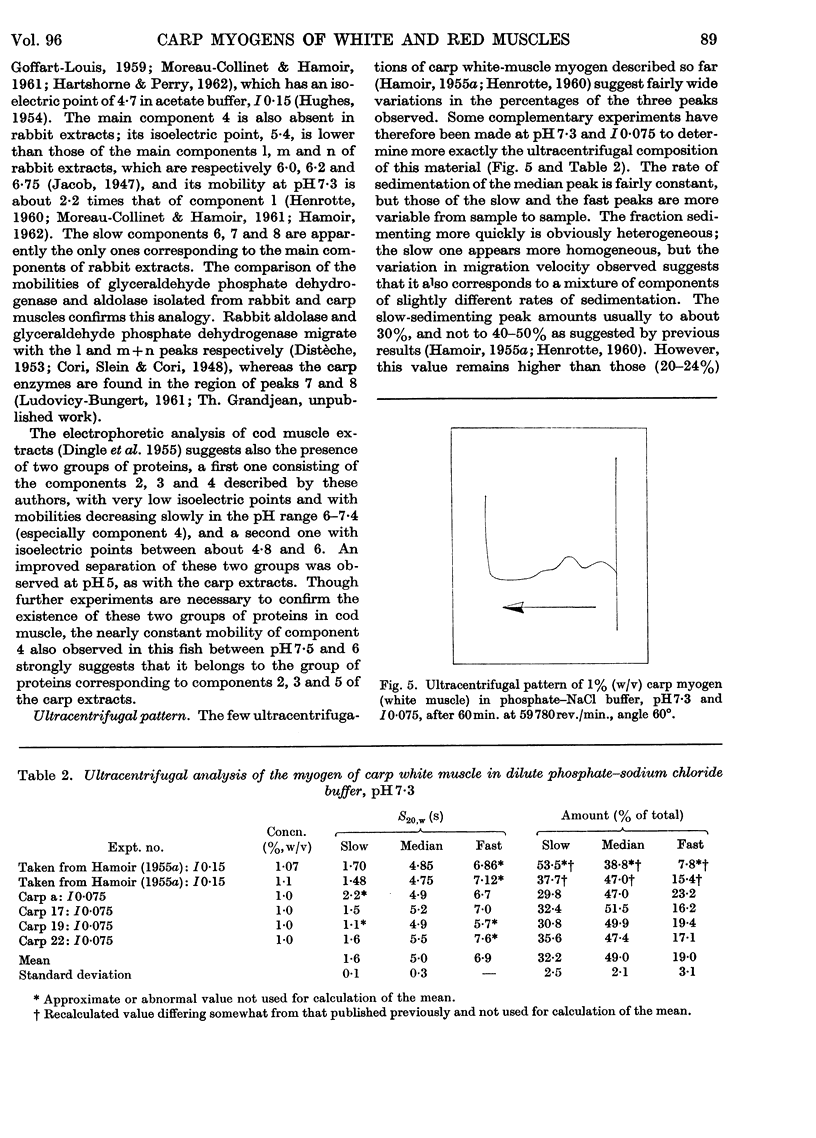
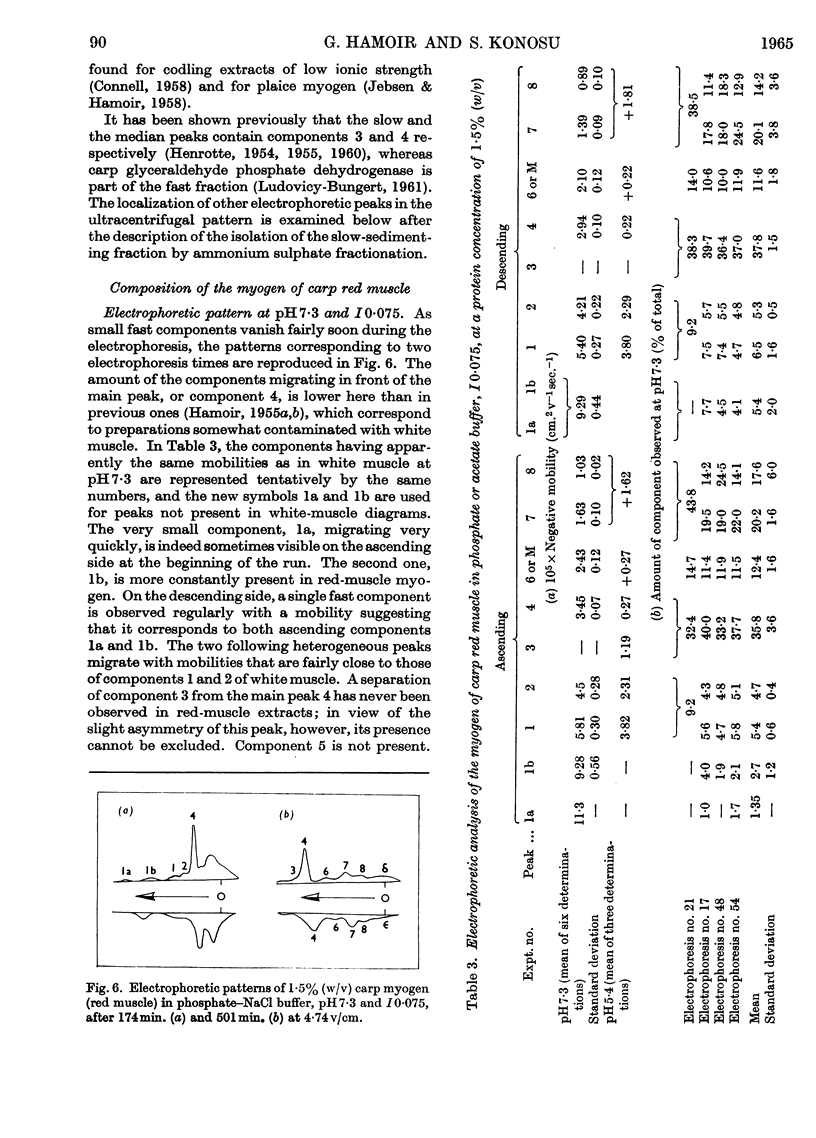
1. The general composition of the carp myogens of white and red muscles was examined by electrophoresis and ultracentrifugation. 2. Eight and nine peaks were found in the electrophoretic analysis at pH7·3 and I0·075 of white and red muscle respectively. Lowering of the pH to 5 or 6 did not increase the number of peaks. The electrophoretic pattern of white-muscle myogen was remarkably different from that of red-muscle myogen, though ultracentrifugal analyses of the both types of myogen gave similar diagrams, in which about one-third of the total myogen sedimented slowly. 3. The pH–mobility curves of the myogen of white muscle indicated that the net charges of the components 2, 3 and 5 vary only slightly within the pH range 7·3–5·4, suggesting that their histidine content is very low. 4. The slow-sedimenting fraction of white-muscle myogen was isolated in fairly good yield by ammonium sulphate fractionation, by taking advantage of their high salting-out range, and the fraction was shown to be composed mainly of components 2, 3 and 5. 5. The same method of fractionation was applied to red-muscle myogen and the absence of the three components was confirmed. These results bring to light a new difference between the two types of fish muscle.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BILINSKI E. Utilizatimn lipids by fish. I. Fatty acid oxidation by tissue slices from dark and white muscle of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdnerii). Can J Biochem Physiol. 1963 Jan;41:107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAEKKAN O. R. Function of the red muscle in fish. Nature. 1956 Oct 6;178(4536):747–748. doi: 10.1038/178747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREMMER-HOLZACH O., STAEHELIN M. Nomogramm zur Herstellung von Ammoniumsulfatlösungen von bestimmtem Sättigunsgrad. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1953;11(2):212–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL J. J. Studies on the protein of fish skeletal muscle. 4. Ultracentrifugal analysis of codling extracts. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):5–12. doi: 10.1042/bj0690005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL J. J. Studies on the proteins of fish skeletal muscle. I. Electrophoretic analysis of codling extracts of low ionic strength. Biochem J. 1953 Apr;54(1):119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0540119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL J. J. Studies on the proteins of fish skeletal muscle. II. Electrophoretic analysis of low ionic strength extracts of several species of fish. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):378–388. doi: 10.1042/bj0550378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISTECHE A. Nouvelle contribution à l'étude des conditions de précipitation et de cristallisation des protéines musculaires du groupe du myogène. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Apr;10(4):524–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBUISSON M., DISTECHE A., DEBOT A. Appareillage d'électrophorèse du type Tiselius Longsworth réalisable au laboratoire. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Sep;6(1):97–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMOIR G. Fish proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1955;10:227–288. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMOIR G., McKENZIE H. A., SMITH M. B. The isolation and properties of fish myosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 6;40:141–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTSHORNE D. J., PERRY S. V. A chromatographic and electrophoretic study of sarcoplasm from adult--and foetal-rabbit muscles. Biochem J. 1962 Oct;85:171–177. doi: 10.1042/bj0850171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENROTTE J. G. A crystalline constituent from myogen of carp muscles. Nature. 1952 Jun 7;169(4310):968–969. doi: 10.1038/169968b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENROTTE J. G. [Contribution to the study of myogens of the carp and the plaice]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 25;39:103–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob J. J. The electrophoretic analysis of protein extracts from striated rabbit muscle. Biochem J. 1947;41(1):83–94. doi: 10.1042/bj0410083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob J. J. The electrophoretic analysis of protein extracts from striated rabbit muscle: 2. Denaturation in acetate buffers. Biochem J. 1948;42(1):71–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONOSU S., HAMOIR G., PECHERE J. F. CARP MYOGENS OF WHITE AND RED MUSCLES. PROPERTIES AND AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF THE MAIN LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT COMPONENTS OF WHITE MUSCLE. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:98–112. doi: 10.1042/bj0960098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRIE R. A. The activity of the cytochrome system in muscle and its relation to myoglobin. Biochem J. 1953 Sep;55(2):298–305. doi: 10.1042/bj0550298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUDOVICY-BUNGERT L. [Isolation and properties of D-3-phosphoglyceraldehyde-dehydrogenase of the carp]. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1961 May;69:265–276. doi: 10.3109/13813456109092796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOREAU-COLLINET C., HAMOIR G. [Influence of the nature of the buffer on the electrophoretic patterns of weakly ionic muscle extracts from rabbits]. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1961 Mar;69:121–152. doi: 10.3109/13813456109092784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIKKILA O. E., LINKO R. R. Paper-electrophoretic analysis of protein extracted at low ionic strength from fish skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1955 Jun;60(2):242–247. doi: 10.1042/bj0600242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NODA L., KUBY S. A. Adenosine triphosphate-adenosine monophosphate transphosphorylase (myokinase). II. Homogeneity measurements and physicochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):551–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECHERE J. F., FOCANT B. CARP MYOGENS OF WHITE AND RED MUSCLES. GROSS ISOLATION ON SEPHADEX COLUMNS OF THE LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT COMPONENTS AND EXAMINATION OF THEIR PARTICIPATION IN ANAEROBIC GLYCOGENOLYSIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:113–118. doi: 10.1042/bj0960113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



