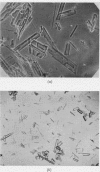
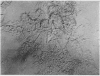
Abstract
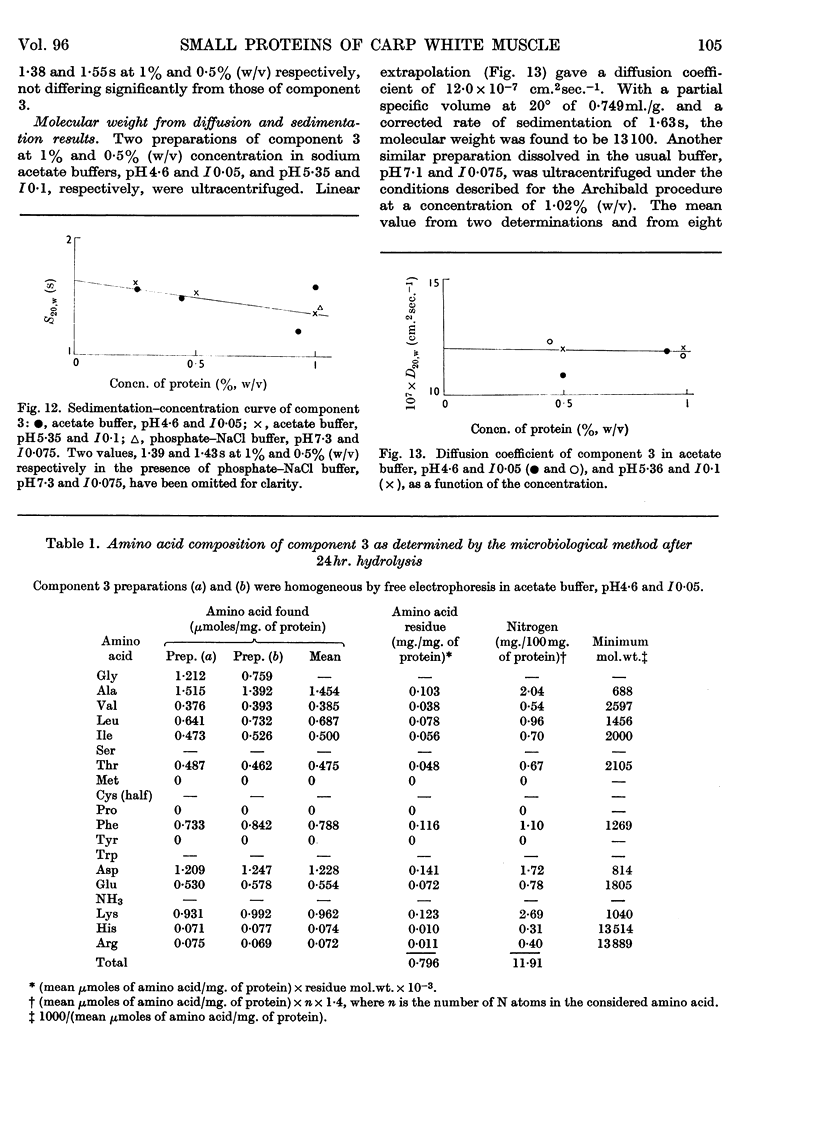
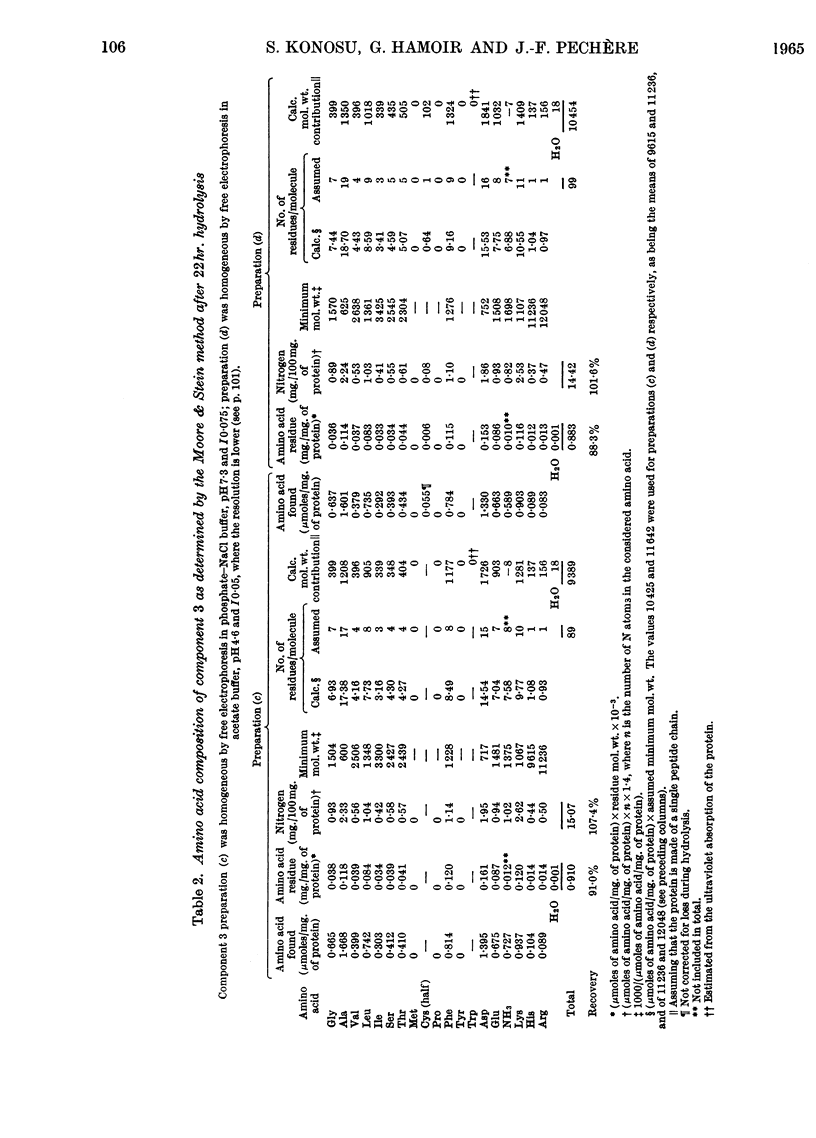
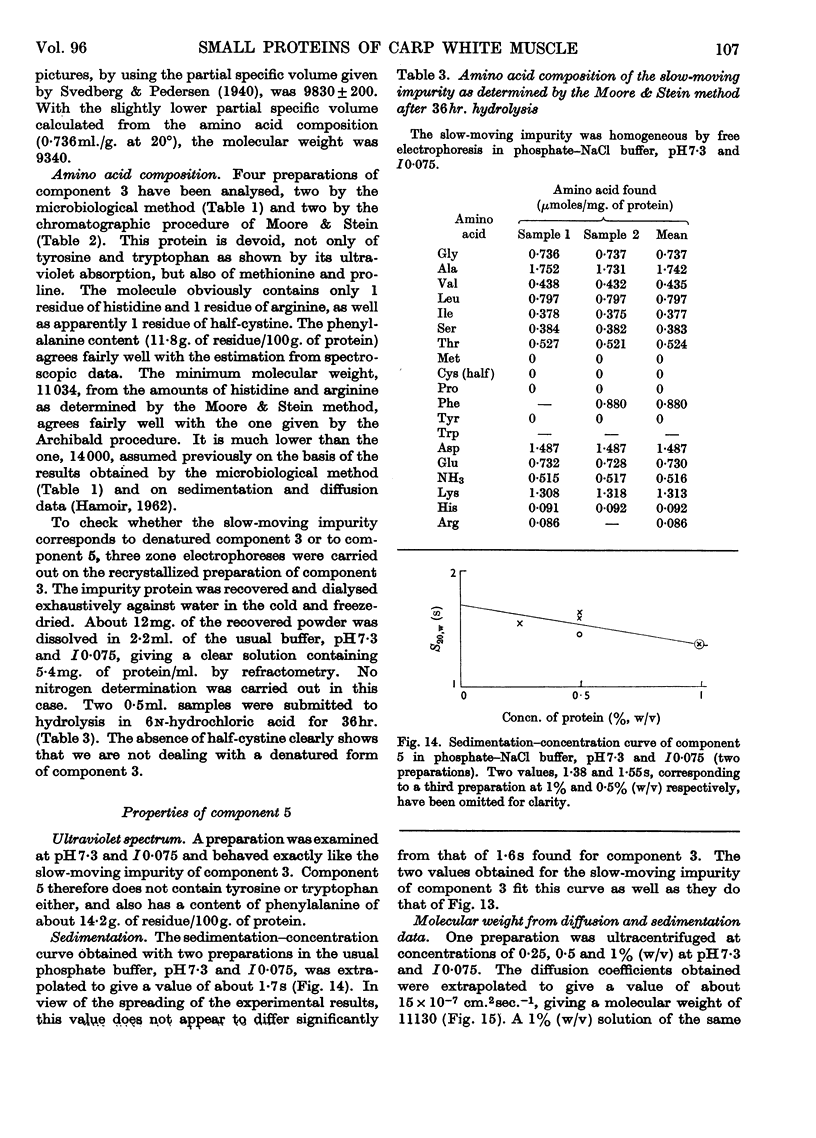
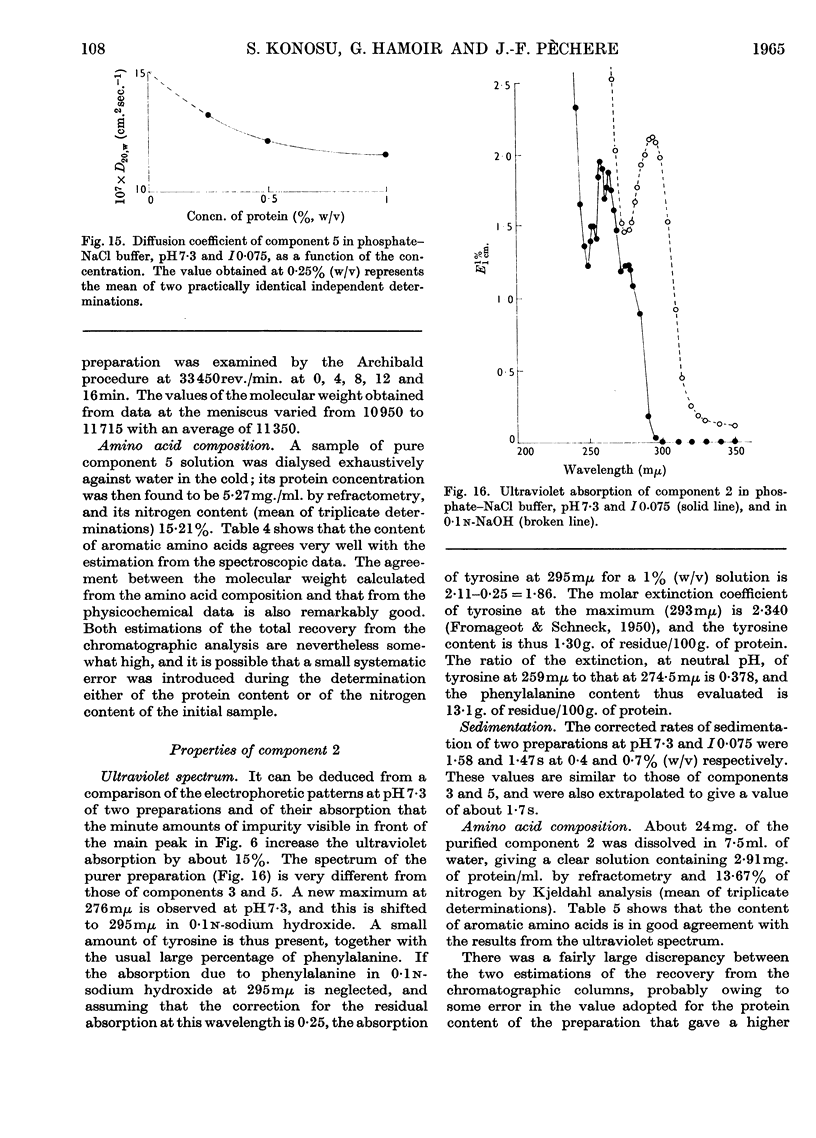
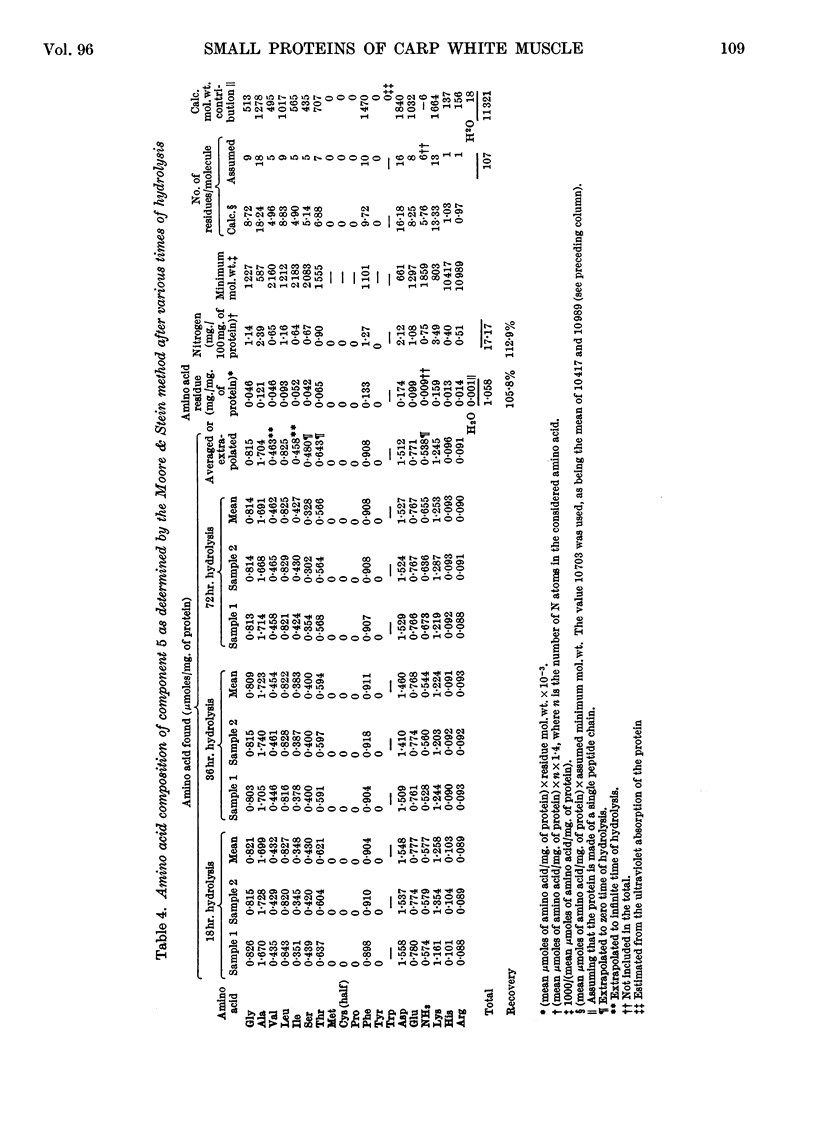
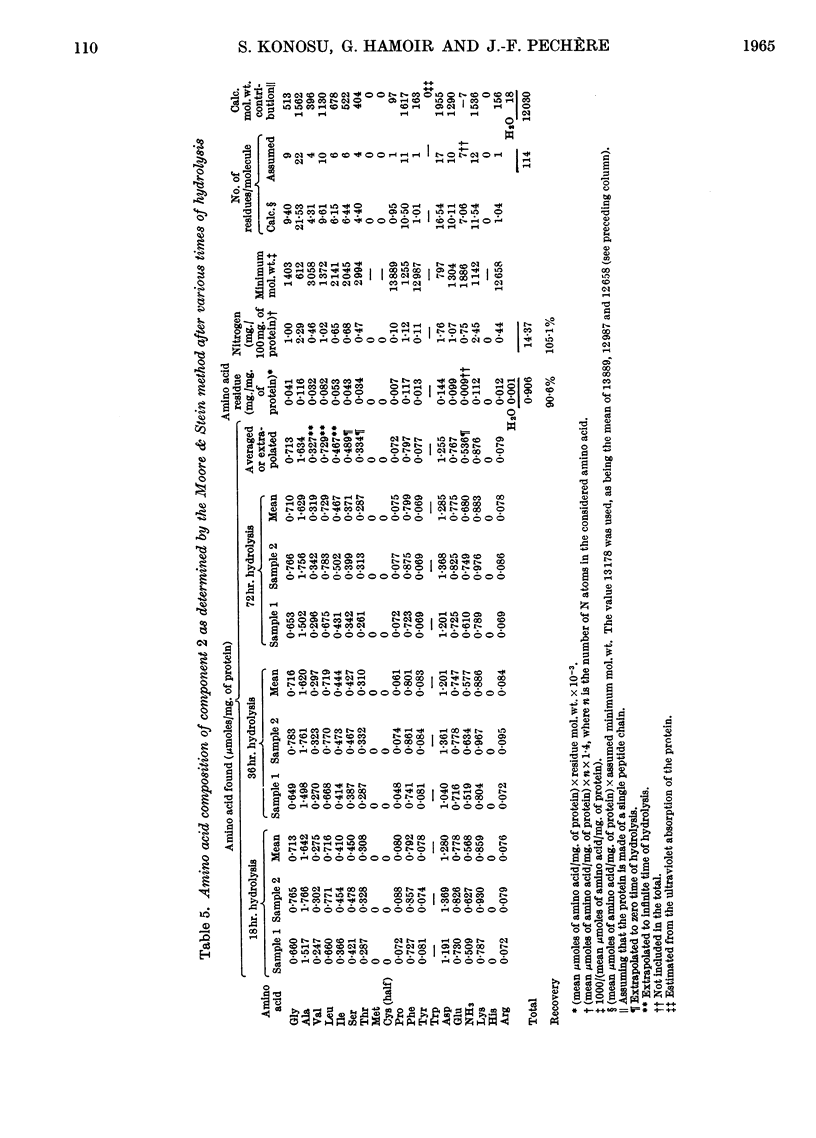
1. The three main components of the 1·5–2s ultracentrifugal peak of carp myogen (white muscle) have been isolated by ammonium sulphate fractionation and zone electrophoresis, and crystallized. 2. The molecular weights of these three proteins were determined by sedimentation and diffusion, by the Archibald method and by amino acid analysis, and found to lie between 9000 and 13000. 3. Their complete amino acid compositions were determined by column chromatography and by their ultraviolet spectra. Both methods revealed abnormal compositions, including the absence of tryptophan and methionine and the presence of large amounts of phenylalanine. At most 1 residue each of tyrosine, cysteine, proline, arginine and histidine was found/molecule. 4. The specific viscosity of component 3 was lower than that of other small globular proteins described so far, a fact that suggests that these proteins approximate more closely to the ideal case of the spherical protein molecule. Also, the presence of a single residue of several amino acids, the absence of disulphide bonds, and the apparent reversibility of denaturation by urea of component 3 suggest that the study of these molecules could provide new information on the structure of proteins.
Full text
PDF
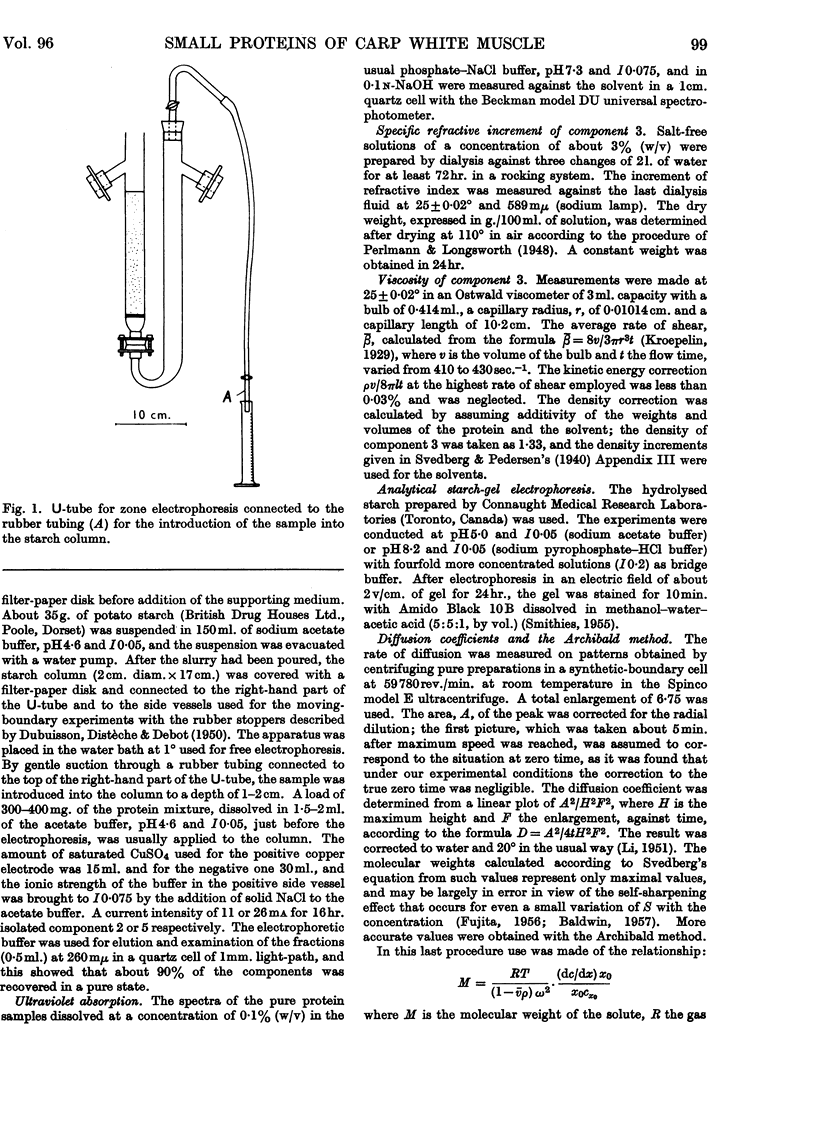
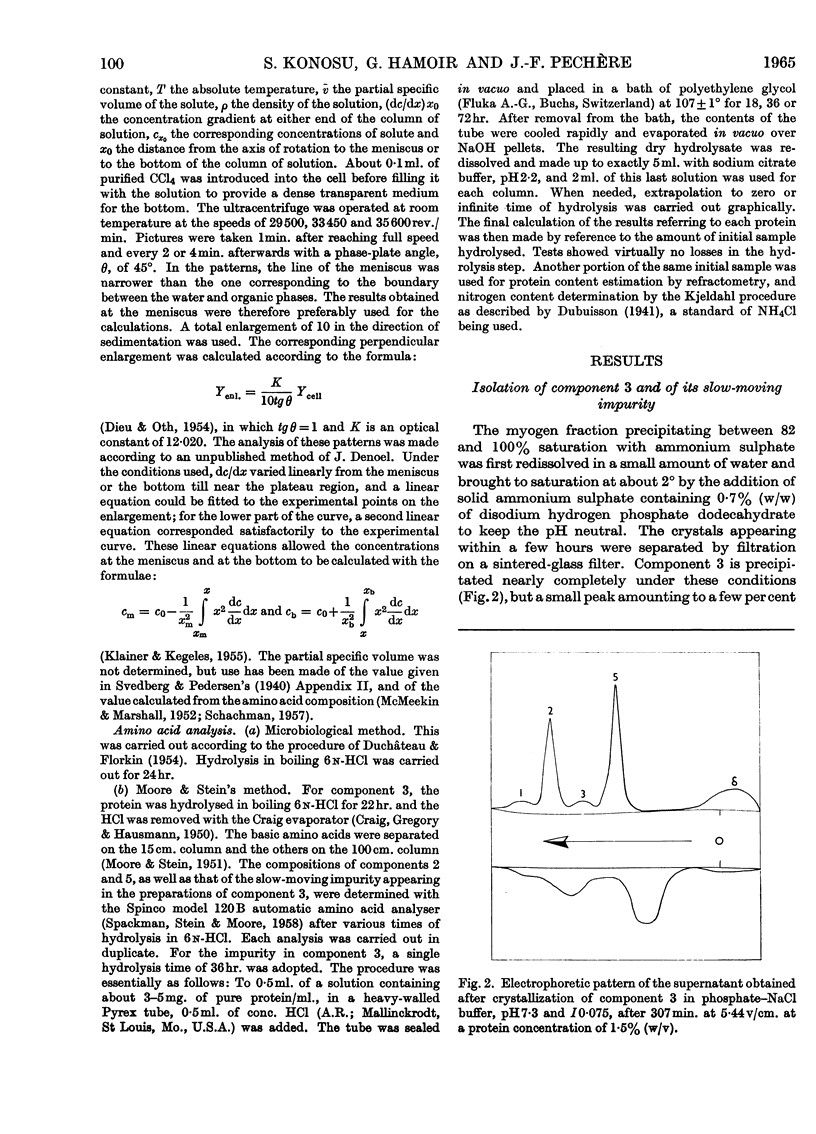


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALDWIN R. L. Boundary spreading in sedimentation-velocity experiments. V. Measurement of the diffusion coefficient of bovine albumin by Fujita's equation. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):503–512. doi: 10.1042/bj0650503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL J. J., HOWGATE P. F. Studies on the proteins of fish skeletal muscle. 6. Amino acid composition of cod fibrillar proteins. Biochem J. 1959 Jan;71(1):83–86. doi: 10.1042/bj0710083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL J. J. Studies on the protein of fish skeletal muscle. 4. Ultracentrifugal analysis of codling extracts. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):5–12. doi: 10.1042/bj0690005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUCHATEAU G., FLORKIN M. Types de composition du pool des acides aminés non protéiques des muscles. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1954 Dec;62(4):487–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROMAGEOT C., SCHNEK G. Le spectre ultra-violet du lysozyme; avec des considérations sur le spectre ultra-violet de divers acides aminés et de quelquesuns de leurs peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Sep;6(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMOIR G., KONOSU S. CARP MYOGENS OF WHITE AND RED MUSCLES. GENERAL COMPOSITION AND ISOLATION OF LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT COMPONENTS OF ABNORMAL AMINO ACID COMPOSITION. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:85–97. doi: 10.1042/bj0960085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Chromatography of amino acids on sulfonated polystyrene resins. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):663–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMEEKIN T. L., MARSHALL K. Specific volumes of proteins and the relationship to their amino acid contents. Science. 1952 Aug 8;116(3006):142–143. doi: 10.1126/science.116.3006.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECHERE J. F., FOCANT B. CARP MYOGENS OF WHITE AND RED MUSCLES. GROSS ISOLATION ON SEPHADEX COLUMNS OF THE LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT COMPONENTS AND EXAMINATION OF THEIR PARTICIPATION IN ANAEROBIC GLYCOGENOLYSIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:113–118. doi: 10.1042/bj0960113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R., RICHMOND M. H. Low cyst(e)ine content of bacterial extracellular proteins: its possible physiological significance. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:446–449. doi: 10.1038/194446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]