Abstract
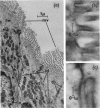
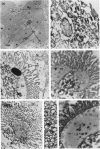
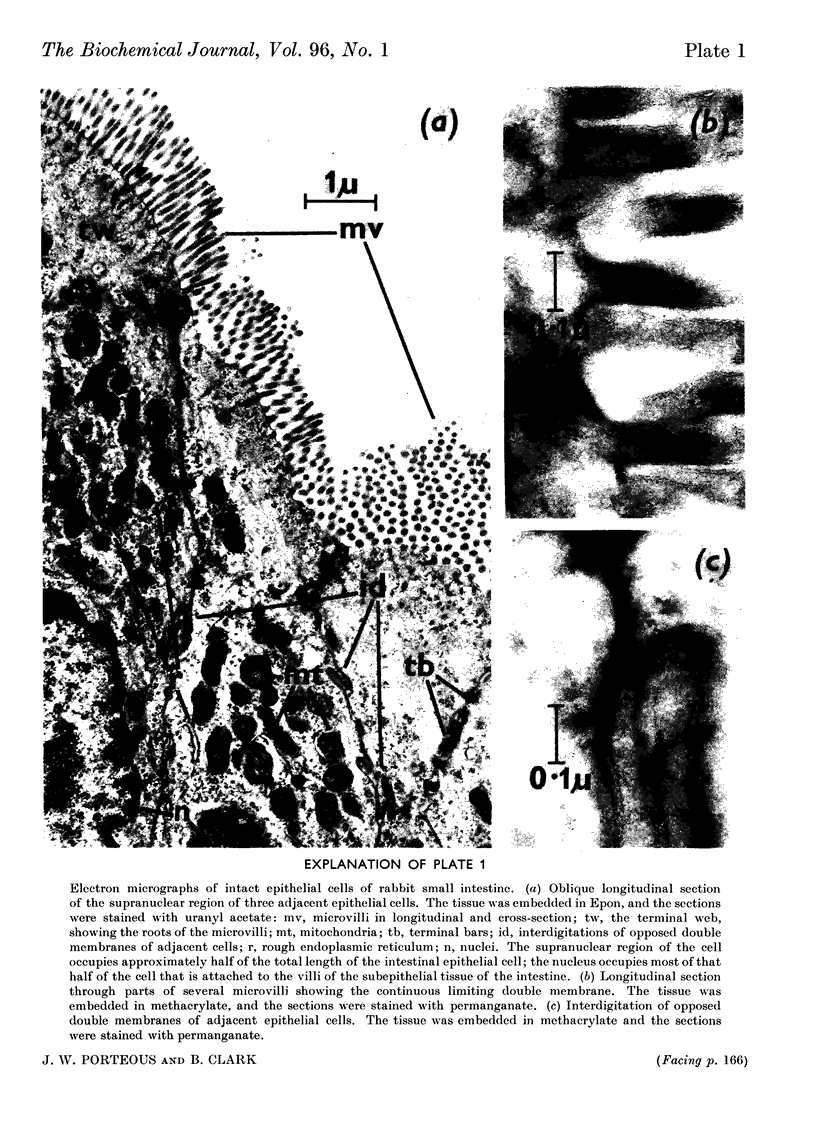
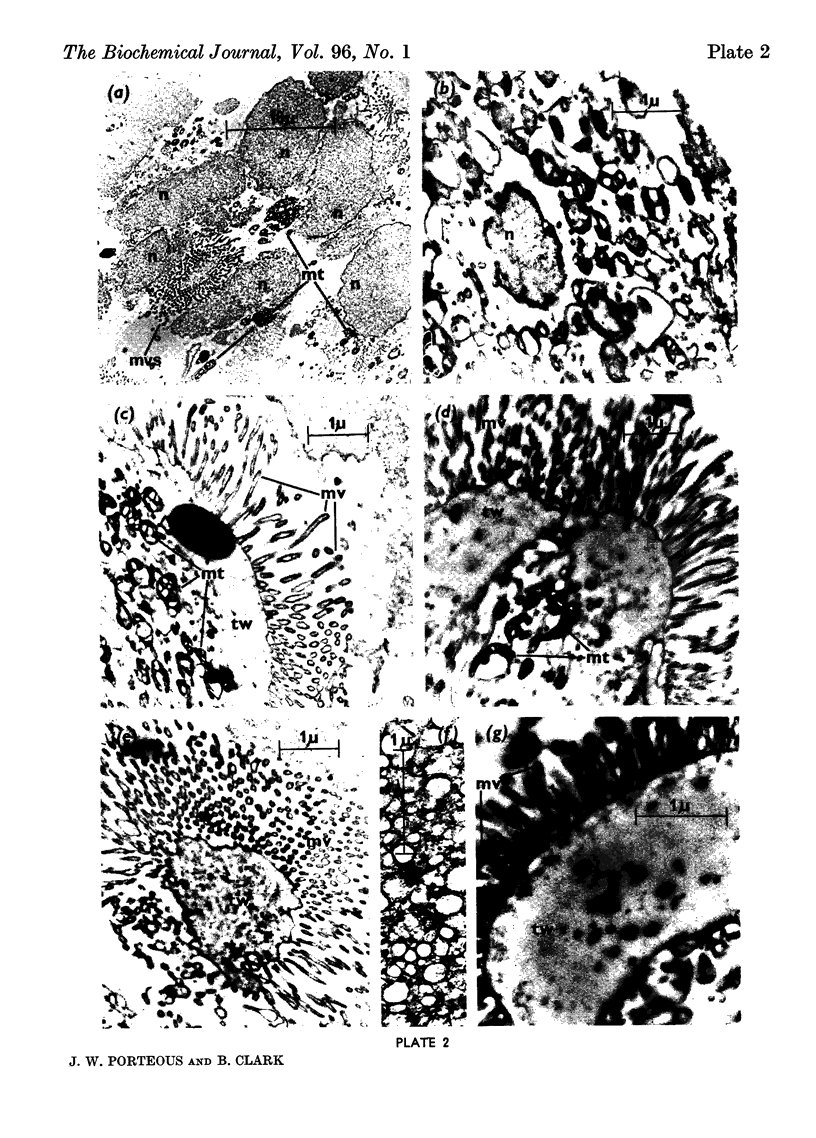
1. Homogenization of the epithelial cells of rabbit small intestine in 0·3m-sucrose–5mm-EDTA, pH7·4, maintains intact the microvillus sheets that form the lumenal surface of the cells, the nuclei, the mitochondria and the vesicles (microsomes) formed from the endoplasmic reticulum. 2. These particulate components of the cell, and the cell-sap fraction, have been isolated by differential centrifuging of cell homogenates. 3. The nuclei and microvillus sheets sediment together and it has been impossible to separate these subcellular components by centrifugal methods. 4. The isolated subcellular fractions have been identified by a combination of light-microscopic examination, electron-microscopic examination, chemical analysis and assay for selected enzyme activities.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AILHAUD G., SAMUEL D., DESNUELLE P. [Subcellular localization of acyl-CoA synthetase from intestinal mucosa]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:150–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91806-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLARD C., DE LAMIRANDE G., CANTERO A. Enzymes and cytological studies in rat hepatoma transplants, primary liver tumors, and in liver following azo dye feeding or partial hepatectomy. Cancer Res. 1957 Oct;17(9):862–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILEY J. M., PENTCHEV P. DISTRIBUTION OF MUTAROTASE IN SUBFRACTIONS OF RAT INTESTINAL MUCOSA AND RAT KIDNEY. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:796–800. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRBECK M. S., REID E. Development of an improved medium for the isolation of liver mitochondria. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Sep 25;2(5):609–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.5.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANDES D., ZETTERQVIST H., SHELDON H. Histochemical techniques for electron microscopy: alkaline phosphatase. Nature. 1956 Feb 25;177(4504):382–383. doi: 10.1038/177382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGOS M. H., DEANE H. W., KARNOVSKY M. L. Histochemical and chemical evidence for more than one alkaline phosphomonoesterase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 Mar;3(2):103–121. doi: 10.1177/3.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARNIE J. A., PORTEOUS J. W. The invertase activity of rabbit small intestine. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:450–456. doi: 10.1042/bj0850450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARNIE J. A., PORTEOUS J. W. The solubilization, thermolability, chromatographic purification and intracellular distribution of some glycosidases of rabbit small intestine. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:620–629. doi: 10.1042/bj0850620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK B., PORTEOUS J. W. THE METAL ION ACTIVATION OF THE ALKALINE BETA-GLYCEROPHOSPHATASE OF RABBIT SMALL INTESTINE. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:475–482. doi: 10.1042/bj0950475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE C. W., NEUBERGER A. The digestion and absorption of protein by normal man. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:313–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0740313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE R. K. Intestinal absorption of sugars. Physiol Rev. 1960 Oct;40:789–825. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.4.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE R. K., MANDELSTAM P. The active transport of sugars by various preparations of hamster intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 18;45:460–476. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE R. K., WILSON T. H. In vitro method for the study of the rate of intestinal absorption of sugars. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Jan;12(1):145–146. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.12.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A., BORGSTROM B. Digestion and absorption of disaccharides in man. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:411–418. doi: 10.1042/bj0810411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. Determination of maltase and isomaltase activities with a glucose-oxidase reagent. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:547–551. doi: 10.1042/bj0800547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:375–412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER R. B., PARSONS D. S. Glucose absorption from surviving rat small intestine. J Physiol. 1949 Dec;110(3-4):281–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG V., HERS H. G. On the conversion of fructose to glucose by guinea pig intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:427–434. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBARG J. A., RUTENBURG A. M. The colorimetric determination of leucine aminopeptidase in urine and serum of normal subjects and patients with cancer and other diseases. Cancer. 1958 Mar-Apr;11(2):283–291. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195803/04)11:2<283::aid-cncr2820110209>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKIM A., LESTER R. G., LIFSON N. Absorption by an in vitro preparation of dog intestinal mucosa. J Appl Physiol. 1963 Mar;18:409–413. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1963.18.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King E. J. The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1932;26(2):292–297. doi: 10.1042/bj0260292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond C. P., Stevens C. E., Bogoroch R. Histological Localization of Newly-formed Desoxyribonucleic Acid. Science. 1948 Nov 12;108(2811):531–533. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2811.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDOUGAL D. B., Jr, LITTLE K. D., CRANE R. K. Studies on the me hanism of intestinal absorption of sugars. IV. Localization of galactose concenhrations within the intestinal wall during active transport, in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 18;45:483–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91484-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D., CRANE R. K. The digestive function of the epithelium of the small intestine. I. An intracellular locus of disaccharide and sugar phosphate ester hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:281–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90677-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON R. K. The purification of aklaline phosphatases of animal tissues. Biochem J. 1954 Aug;57(4):595–603. doi: 10.1042/bj0570595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISSIM J. A. MECHANISM OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTION: THE CONCEPT OF A SPECTRUM OF INTRACELLULAR PLASMA. Nature. 1964 Oct 10;204:148–151. doi: 10.1038/204148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1952 Mar;95(3):285–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.95.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E., SIEKEVITZ P. Liver microsomes; an integrated morphological and biochemical study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Mar 25;2(2):171–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E., SIEKEVITZ P. Pancreatic microsomes; an integrated morphological and biochemical study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Nov 25;2(6):671–690. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALAY S. L., KARLIN L. J. An electron microscopic study of the intestinal villus. I. The fasting animal. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):363–372. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALAY S. L., KARLIN L. J. An electron microscopic study of the intestinal villus. II. The pathway of fat absorption. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):373–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENNINGTON R. J. Biochemistry of dystrophic muscle. Mitochondrial succinate-tetrazolium reductase and adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:649–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0800649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON G. B. The distribution of peptidases in subcellular fractions from the mucosa of the small intestine of the rat. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:162–168. doi: 10.1042/bj0880162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALOMON L. L., JOHNSON J. E. Transfer of fructose and glucose across surviving guinea pig intestine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEKEVITZ P. Protoplasm: endoplasmic reticulum and microsomes and their properties. Annu Rev Physiol. 1963;25:15–40. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.25.030163.000311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMYTH D. H. Intestinal absorption. Proc R Soc Med. 1961 Sep;54:769–773. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR C. B. The effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and some related compounds on transport and metabolism in the intestine of the rat in vitro. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:199–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRIANTAPHYLLOPOULOS E., TUBA J. Studies on the distribution and kinetics of the alkaline phosphatase of rat small intestine. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 May;37(5):699–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRIER J. S. STUDIES ON SMALL INTESTINAL CRYPT EPITHELIUM. I. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE CRYPT EPITHELIUM OF THE PROXIMAL SMALL INTESTINE OF FASTING HUMANS. J Cell Biol. 1963 Sep;18:599–620. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UGOLEV A. M., IESUITOVA N. N., TIMOFEEVA N. M., FEDIUSHINA I. N. LOCATION OF HYDROLYSIS OF CERTAIN DISACCHARIDES AND PEPTIDES IN THE SMALL INTESTINE. Nature. 1964 May 23;202:807–809. doi: 10.1038/202807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB J. M. A sensitive method for the determination of ribonucleic acid in tissues and microorganisms. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):635–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. H., WISEMAN G. Metabolic activity of the small intestine of the rat and golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus). J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):126–130. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. H., WISEMAN G. The use of sacs of everted small intestine for the study of the transference of substances from the mucosal to the serosal surface. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):116–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOERNLEY D. L., CARRUTHERS C. A versatile method of isolating cell nuclei based on the employment of a high-viscosity suspending medium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Apr;67(2):493–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90305-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]